Abstract
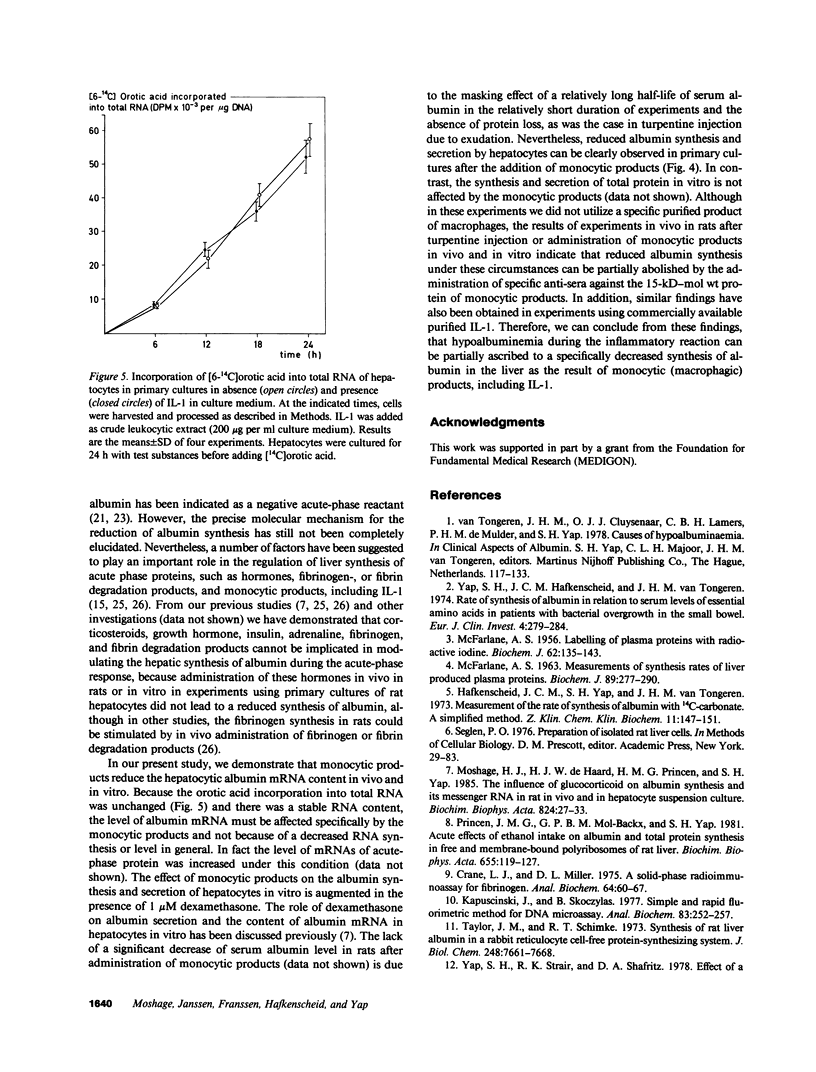
Hypoalbuminemia in inflammatory disorders is not an infrequent finding. However, little is known about albumin synthesis in these patients. In the present study we have measured the albumin synthesis in four patients with inflammatory diseases using the [14C]carbonate technique. Because inflammation causes a decreased albumin synthesis and this decreased synthesis could not be related to a reduced amino acid supply, we have also examined the possible molecular mechanisms of reduced albumin synthesis during inflammation using in vivo and in vitro experiments in rats. In rats with turpentine-induced inflammation, serum albumin concentration and liver albumin mRNa level were markedly decreased. These changes could not be reproduced by administration of fibrinogen-, or fibrin-degradation products, or several hormones, such as corticosteroids, growth hormone, and adrenaline. However, monocytic products, especially interleukin 1, postulated to be important mediators of the inflammatory response, reduced albumin synthesis and liver albumin messenger RNA content but not total protein synthesis in rats in vivo and in primary cultures of rat hepatocytes. These findings suggest that monocytic products play an important role in reduced albumin synthesis during inflammation.
Full text
PDF


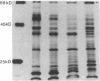
Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aviv H., Leder P. Purification of biologically active globin messenger RNA by chromatography on oligothymidylic acid-cellulose. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Jun;69(6):1408–1412. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.6.1408. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bornstein D. L. Leukocytic pyrogen: a major mediator of the acute phase reaction. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1982;389:323–337. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1982.tb22147.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crane L. J., Miller D. L. A solid-phase radioimmunoassay for fibrinogen. Anal Biochem. 1975 Mar;64(1):60–67. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(75)90404-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dinarello C. A. Interleukin-1. Rev Infect Dis. 1984 Jan-Feb;6(1):51–95. doi: 10.1093/clinids/6.1.51. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dinarello C. A., Renfer L., Wolff S. M. Human leukocytic pyrogen: purification and development of a radioimmunoassay. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Oct;74(10):4624–4627. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.10.4624. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gery I., Gershon R. K., Waksman B. H. Potentiation of the T-lymphocyte response to mitogens. I. The responding cell. J Exp Med. 1972 Jul 1;136(1):128–142. doi: 10.1084/jem.136.1.128. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hafkenscheid J. C., Yap S. H., van Tongeren J. H. Measurement of the rate of synthesis of albumin with 14C-carbonate: a simplified method. Z Klin Chem Klin Biochem. 1973 Apr;11(4):147–151. doi: 10.1515/cclm.1973.11.4.147. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kapuściński J., Skoczylas B. Simple and rapid fluorimetric method for DNA microassay. Anal Biochem. 1977 Nov;83(1):252–257. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(77)90533-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MCFARLANE A. S. Labelling of plasma proteins with radioactive iodine. Biochem J. 1956 Jan;62(1):135–143. doi: 10.1042/bj0620135. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MCFARLANE A. S. MEASUREMENT OF SYNTHESIS RATES OF LIVER-PRODUCED PLASMA PROTEINS. Biochem J. 1963 Nov;89:277–290. doi: 10.1042/bj0890277. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moshage H. J., de Haard H. J., Princen H. M., Yap S. H. The influence of glucocorticoid on albumin synthesis and its messenger RNA in rat in vivo and in hepatocyte suspension culture. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1985 Jan 29;824(1):27–33. doi: 10.1016/0167-4781(85)90025-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Princen H. M., Moshage H. J., Emeis J. J., de Haard H. J., Nieuwenhuizen W., Yap S. H. Fibrinogen fragments X, Y, D and E increase levels of plasma fibrinogen and liver mRNAs coding for fibrinogen polypeptides in rats. Thromb Haemost. 1985 Apr 22;53(2):212–215. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Princen H. M., Moshage H. J., de Haard H. J., van Gemert P. J., Yap S. H. The influence of glucocorticoid on the fibrinogen messenger RNA content of rat liver in vivo and in hepatocyte suspension culture. Biochem J. 1984 Jun 15;220(3):631–637. doi: 10.1042/bj2200631. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Princen H. M., Selten G. C., Selten-Versteegen A. M., Mol-Backx G. P., Nieuwenhuizen W., Yap S. H. Distribution of mRNAS of fibrinogen polypeptides and albumin in free and membrane-bound polyribosomes and induction of alpha-fetoprotein mRNA synthesis during liver regeneration after partial hepatectomy. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1982 Nov 30;699(2):121–130. doi: 10.1016/0167-4781(82)90145-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Princen J. M., Mol-Backx G. P., Yap S. H. Acute effects of ethanol intake on albumin and total protein synthesis in free and membrane-bound polyribosomes of rat liver. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1981 Sep 28;655(2):119–127. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(81)90001-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Princen J. M., Nieuwenhuizen W., Mol-Backx G. P., Yap S. H. Direct evidence of transcriptional control of fibrinogen and albumin synthesis in rat liver during the acute phase response. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1981 Sep 30;102(2):717–723. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(81)80191-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ritchie D. G., Fuller G. M. An in vitro bioassay for leukocytic endogenous mediator(s) using cultured rat hepatocytes. Inflammation. 1981 Dec;5(4):275–287. doi: 10.1007/BF00911093. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seglen P. O. Preparation of isolated rat liver cells. Methods Cell Biol. 1976;13:29–83. doi: 10.1016/s0091-679x(08)61797-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Selten G. C., Princen H. M., Selten-Versteegen A. M., Mol-Backx G. P., Yap S. H. Sequence content of alpha-fetoprotein, albumin and fibrinogen polypeptide mRNAs in different organs, developing tissues and in liver during carcinogenesis in rats. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1982 Nov 30;699(2):131–137. doi: 10.1016/0167-4781(82)90146-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor J. M., Schimke R. T. Synthesis of rat liver albumin in a rabbit reticulocyte cell-free protein-synthesizing system. J Biol Chem. 1973 Nov 25;248(22):7661–7668. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yap S. H., Hafkenscheid J. C., Goossens C. M., Buys W. C., Binkhorst R. A., van Tongeren J. H. Estimation of radiation dosage and transmutation effect of 14-C involved in measuring rate of albumin synthesis with 14-C-carbonate. J Nucl Med. 1975 Jul;16(7):642–648. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yap S. H., Hafkenscheid J. C., van Tongeren J. H., Trijbels J. M. Rate of synthesis of albumin in relation to serum levels of essential amino acids in patients with bacterial overgrowth in the small bowel. Eur J Clin Invest. 1974 Aug;4(4):279–284. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2362.1974.tb00404.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yap S. H., Strair R. K., Shafritz D. A. Effect of a short term fast on the distribution of cytoplasmic albumin messenger ribonucleic acid in rat liver. Evidence for formation of free albumin messenger ribonucleoprotein particles. J Biol Chem. 1978 Jul 25;253(14):4944–4950. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]