Abstract
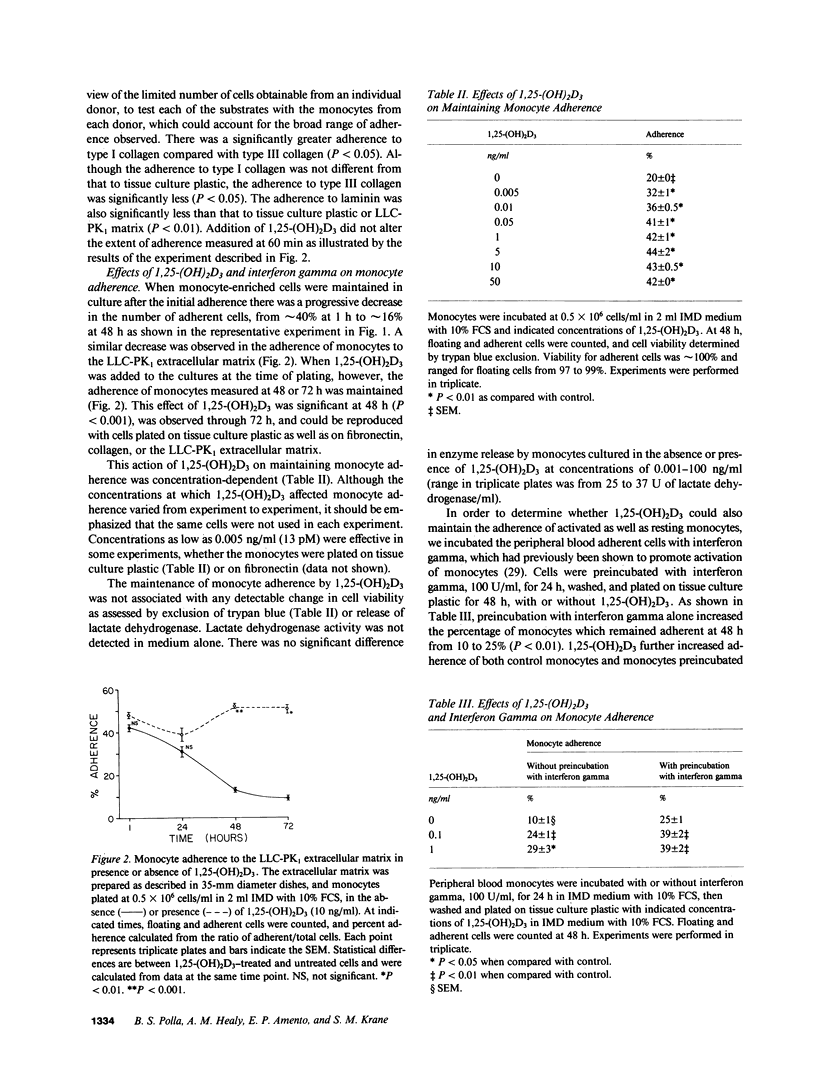
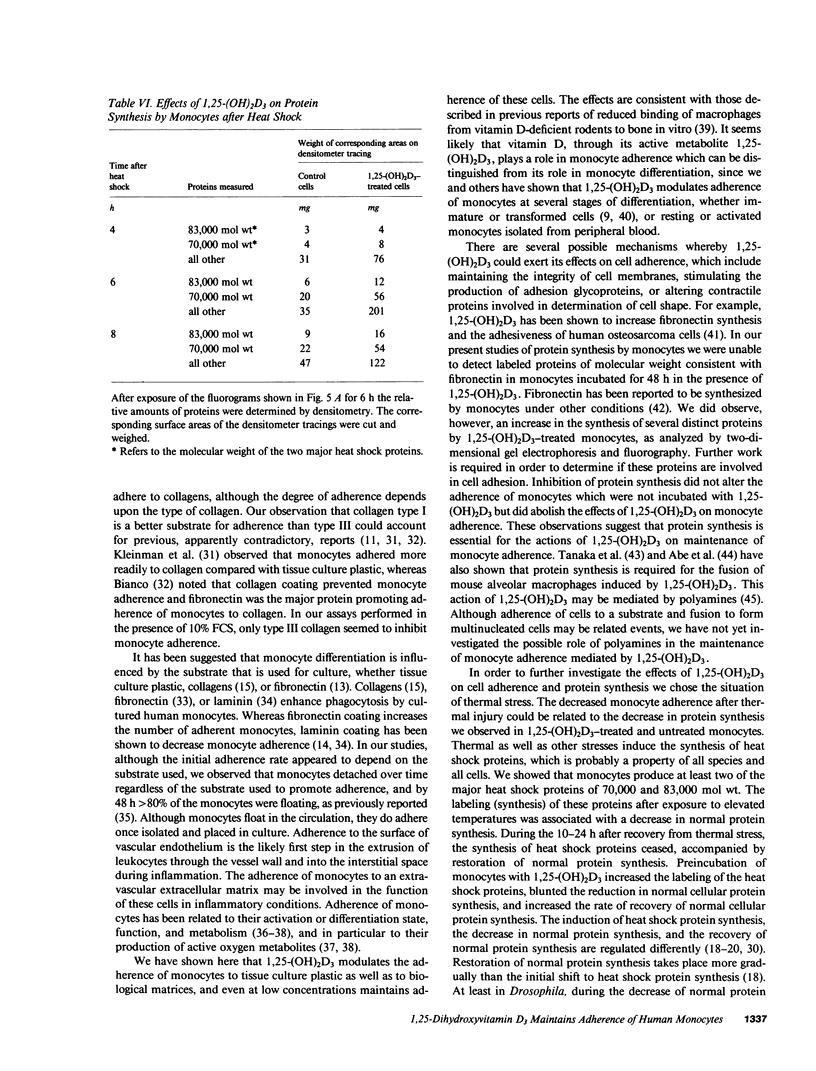
Adherence to a substratum is a characteristic feature of monocyte-macrophages which may be required for several effector functions. Human peripheral blood monocytes selected by adherence were found to readhere preferentially at 1 h to fibronectin or to a biological matrix. There was then a progressive decrease in the number of adherent cells, and by 48 h only 8-20% of monocytes remained adherent. This loss of adherence occurred while monocytes remained viable by criteria such as exclusion of trypan blue or release of lactate dehydrogenase. 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3 (1,25-(OH)2D3) maintained the adherence of cultured monocytes to tissue culture plastic as well as to the biological matrix. This effect was concentration- and time-dependent, and suppressed by inhibitors of protein synthesis. Cellular proteins were labeled after incubation with [35S]methionine. Analysis by two-dimensional gel electrophoresis revealed increased labeling of several distinct proteins in 1,25-(OH)2D3-treated monocytes compared with control monocytes. The increased loss of adherence and decreased overall protein synthesis observed in monocytes incubated at 45 degrees C was partially prevented by preincubation of the cells with 1,25-(OH)2D3. We further evaluated the effects of thermal stress and 1,25-(OH)2D3 on protein synthesis by monocytes, and found that 1,25-(OH)2D3 increased the synthesis of heat shock proteins, protected normal protein synthesis, and increased the rate of recovery of normal protein synthesis after the thermal stress. These observations suggest that 1,25-(OH)2D3 influences monocytes by preserving the synthesis of proteins, including those critical for the maintenance of cell adherence.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abe E., Miyaura C., Tanaka H., Shiina Y., Kuribayashi T., Suda S., Nishii Y., DeLuca H. F., Suda T. 1 alpha,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3 promotes fusion of mouse alveolar macrophages both by a direct mechanism and by a spleen cell-mediated indirect mechanism. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Sep;80(18):5583–5587. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.18.5583. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alitalo K., Hovi T., Vaheri A. Fibronectin is produced by human macrophages. J Exp Med. 1980 Mar 1;151(3):602–613. doi: 10.1084/jem.151.3.602. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Amento E. P., Bhalla A. K., Kurnick J. T., Kradin R. L., Clemens T. L., Holick S. A., Holick M. F., Krane S. M. 1 alpha,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3 induces maturation of the human monocyte cell line U937, and, in association with a factor from human T lymphocytes, augments production of the monokine, mononuclear cell factor. J Clin Invest. 1984 Mar;73(3):731–739. doi: 10.1172/JCI111266. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arenzana-Seisdedos F., Virelizier J. L., Fiers W. Interferons as macrophage-activating factors. III. Preferential effects of interferon-gamma on the interleukin 1 secretory potential of fresh or aged human monocytes. J Immunol. 1985 Apr;134(4):2444–2448. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bar-Shavit Z., Kahn A. J., Teitelbaum S. L. Defective binding of macrophages to bone in rodent osteomalacia and vitamin D deficiency. In vitro evidence for a cellular defect and altered saccharides in the bone matrix. J Clin Invest. 1983 Aug;72(2):526–534. doi: 10.1172/JCI111000. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bar-Shavit Z., Noff D., Edelstein S., Meyer M., Shibolet S., Goldman R. 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3 and the regulation of macrophage function. Calcif Tissue Int. 1981;33(6):673–676. doi: 10.1007/BF02409507. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bell N. H. Vitamin D-endocrine system. J Clin Invest. 1985 Jul;76(1):1–6. doi: 10.1172/JCI111930. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bhalla A. K., Amento E. P., Clemens T. L., Holick M. F., Krane S. M. Specific high-affinity receptors for 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3 in human peripheral blood mononuclear cells: presence in monocytes and induction in T lymphocytes following activation. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1983 Dec;57(6):1308–1310. doi: 10.1210/jcem-57-6-1308. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bhalla A. K., Amento E. P., Serog B., Glimcher L. H. 1,25-Dihydroxyvitamin D3 inhibits antigen-induced T cell activation. J Immunol. 1984 Oct;133(4):1748–1754. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bianco C. Fibrin, fibronectin, and macrophages. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1983 Jun 27;408:602–609. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1983.tb23277.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bohnsack J. F., Kleinman H. K., Takahashi T., O'Shea J. J., Brown E. J. Connective tissue proteins and phagocytic cell function. Laminin enhances complement and Fc-mediated phagocytosis by cultured human macrophages. J Exp Med. 1985 May 1;161(5):912–923. doi: 10.1084/jem.161.5.912. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown A. F. Neutrophil and monocyte behaviour in three-dimensional collagen matrices. Scan Electron Microsc. 1984;(Pt 2):747–754. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Christman M. F., Morgan R. W., Jacobson F. S., Ames B. N. Positive control of a regulon for defenses against oxidative stress and some heat-shock proteins in Salmonella typhimurium. Cell. 1985 Jul;41(3):753–762. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(85)80056-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen M. S., Ryan J. L., Root R. K. The oxidative metabolism of thioglycollate-elicited mouse peritoneal macrophages: the relationship between oxygen, superoxide and hydrogen peroxide and the effect of monolayer formation. J Immunol. 1981 Sep;127(3):1007–1011. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dayer J. M., Trentham D. E., Krane S. M. Collagens act as ligands to stimulate human monocytes to produce mononuclear cell factor (MCF) and prostaglandins (PGE2). Coll Relat Res. 1982 Nov;2(6):523–540. doi: 10.1016/s0174-173x(82)80007-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dinarello C. A., Kent E. F., Jr Chemical characterization of an interleukin-1-inducing substance derived from human mixed leukocyte reactions: IL-1-inducing substance is not gamma interferon. Yale J Biol Med. 1985 Mar-Apr;58(2):101–113. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Engvall E., Ruoslahti E., Miller E. J. Affinity of fibronectin to collagens of different genetic types and to fibrinogen. J Exp Med. 1978 Jun 1;147(6):1584–1595. doi: 10.1084/jem.147.6.1584. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fridovich I. The biology of oxygen radicals. Science. 1978 Sep 8;201(4359):875–880. doi: 10.1126/science.210504. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giavazzi R., Hart I. R. Mononuclear phagocyte adherence in the presence of laminin. A possible marker of cellular differentiation. Exp Cell Res. 1983 Jul;146(2):391–399. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(83)90141-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gospodarowicz D. J. Extracellular matrices and the control of cell proliferation and differentiation in vitro. Prog Clin Biol Res. 1984;145:103–128. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gospodarowicz D., Delgado D., Vlodavsky I. Permissive effect of the extracellular matrix on cell proliferation in vitro. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Jul;77(7):4094–4098. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.7.4094. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hull R. N., Cherry W. R., Weaver G. W. The origin and characteristics of a pig kidney cell strain, LLC-PK. In Vitro. 1976 Oct;12(10):670–677. doi: 10.1007/BF02797469. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaplan G., Gaudernack G. In vitro differentiation of human monocytes. Differences in monocyte phenotypes induced by cultivation on glass or on collagen. J Exp Med. 1982 Oct 1;156(4):1101–1114. doi: 10.1084/jem.156.4.1101. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karin M. Metallothioneins: proteins in search of function. Cell. 1985 May;41(1):9–10. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90051-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kleinman H. K., Klebe R. J., Martin G. R. Role of collagenous matrices in the adhesion and growth of cells. J Cell Biol. 1981 Mar;88(3):473–485. doi: 10.1083/jcb.88.3.473. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kleinman H. K., McGarvey M. L., Liotta L. A., Robey P. G., Tryggvason K., Martin G. R. Isolation and characterization of type IV procollagen, laminin, and heparan sulfate proteoglycan from the EHS sarcoma. Biochemistry. 1982 Nov 23;21(24):6188–6193. doi: 10.1021/bi00267a025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kleinman H. K., Murray J. C., McGoodwin E. B., Martin G. R. Connective tissue structure: cell binding to collagen. J Invest Dermatol. 1978 Jul;71(1):9–11. doi: 10.1111/1523-1747.ep12543641. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kolset S. O., Seljelid R., Lindahl U. Modulation of the morphology and glycosaminoglycan biosynthesis of human monocytes, induced by culture substrates. Biochem J. 1984 May 1;219(3):793–799. doi: 10.1042/bj2190793. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kunkel S. L., Duque R. E. The macrophage adherence phenomenon: its relationship to prostaglandin E2 and superoxide anion production and changes in transmembrane potential. Prostaglandins. 1983 Dec;26(6):893–904. doi: 10.1016/0090-6980(83)90152-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li G. C. Induction of thermotolerance and enhanced heat shock protein synthesis in Chinese hamster fibroblasts by sodium arsenite and by ethanol. J Cell Physiol. 1983 May;115(2):116–122. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041150203. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCarthy D. M., San Miguel J. F., Freake H. C., Green P. M., Zola H., Catovsky D., Goldman J. M. 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3 inhibits proliferation of human promyelocytic leukaemia (HL60) cells and induces monocyte-macrophage differentiation in HL60 and normal human bone marrow cells. Leuk Res. 1983;7(1):51–55. doi: 10.1016/0145-2126(83)90057-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nathan C. F., Prendergast T. J., Wiebe M. E., Stanley E. R., Platzer E., Remold H. G., Welte K., Rubin B. Y., Murray H. W. Activation of human macrophages. Comparison of other cytokines with interferon-gamma. J Exp Med. 1984 Aug 1;160(2):600–605. doi: 10.1084/jem.160.2.600. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nathan C. F., Root R. K. Hydrogen peroxide release from mouse peritoneal macrophages: dependence on sequential activation and triggering. J Exp Med. 1977 Dec 1;146(6):1648–1662. doi: 10.1084/jem.146.6.1648. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neidhardt F. C., VanBogelen R. A., Vaughn V. The genetics and regulation of heat-shock proteins. Annu Rev Genet. 1984;18:295–329. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.18.120184.001455. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Norman A. W., Roth J., Orci L. The vitamin D endocrine system: steroid metabolism, hormone receptors, and biological response (calcium binding proteins). Endocr Rev. 1982 Fall;3(4):331–366. doi: 10.1210/edrv-3-4-331. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Farrell P. H. High resolution two-dimensional electrophoresis of proteins. J Biol Chem. 1975 May 25;250(10):4007–4021. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Farrell P. H., O'Farrell P. Z. Two-dimensional polyacrylamide gel electrophoretic fractionation. Methods Cell Biol. 1977;16:407–420. doi: 10.1016/s0091-679x(08)60116-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perussia B., Dayton E. T., Fanning V., Thiagarajan P., Hoxie J., Trinchieri G. Immune interferon and leukocyte-conditioned medium induce normal and leukemic myeloid cells to differentiate along the monocytic pathway. J Exp Med. 1983 Dec 1;158(6):2058–2080. doi: 10.1084/jem.158.6.2058. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Provvedini D. M., Tsoukas C. D., Deftos L. J., Manolagas S. C. 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3 receptors in human leukocytes. Science. 1983 Sep 16;221(4616):1181–1183. doi: 10.1126/science.6310748. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanaka H., Hayashi T., Shiina Y., Miyaura C., Abe E., Suda T. 1 alpha, 25-Dihydroxyvitamin D3 directly induces fusion of alveolar macrophages by a mechanism involving RNA and protein synthesis, but not DNA synthesis. FEBS Lett. 1984 Aug 20;174(1):61–65. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(84)81078-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanguay R. M. Genetic regulation during heat shock and function of heat-shock proteins: a review. Can J Biochem Cell Biol. 1983 Jun;61(6):387–394. doi: 10.1139/o83-053. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsoukas C. D., Provvedini D. M., Manolagas S. C. 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3: a novel immunoregulatory hormone. Science. 1984 Jun 29;224(4656):1438–1440. doi: 10.1126/science.6427926. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tumarkin L., Damewood G. P., 4th, Sreevalsan T. Potentiation of thermal injury in mouse cells by interferon. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1985 Apr 16;128(1):179–184. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(85)91661-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ULMER D. D., VALLEE B. L., WACKER W. E. Metalloenzymes and myocardial infarction. II. Malic and lactic dehydrogenase activities and zinc concentrations in serum. N Engl J Med. 1956 Sep 6;255(10):450–456. doi: 10.1056/NEJM195609062551001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wright S. D., Craigmyle L. S., Silverstein S. C. Fibronectin and serum amyloid P component stimulate C3b- and C3bi-mediated phagocytosis in cultured human monocytes. J Exp Med. 1983 Oct 1;158(4):1338–1343. doi: 10.1084/jem.158.4.1338. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamada K. M. Cell surface interactions with extracellular materials. Annu Rev Biochem. 1983;52:761–799. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.52.070183.003553. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]