Abstract
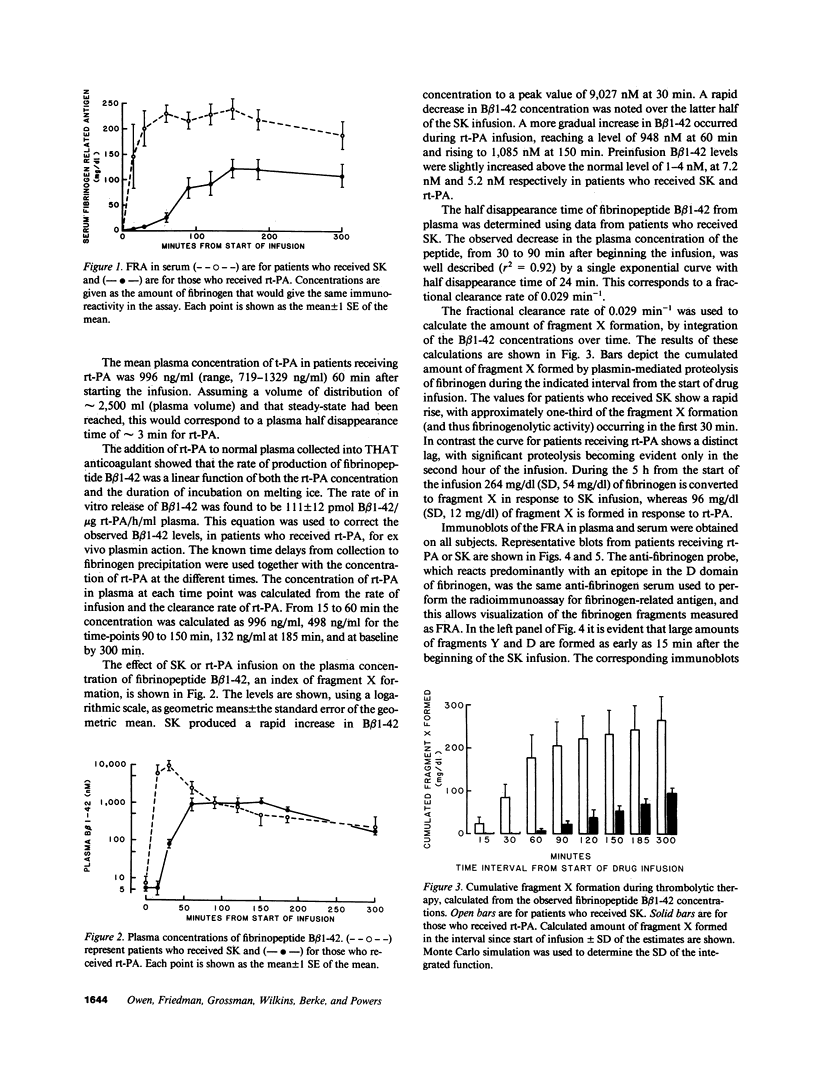
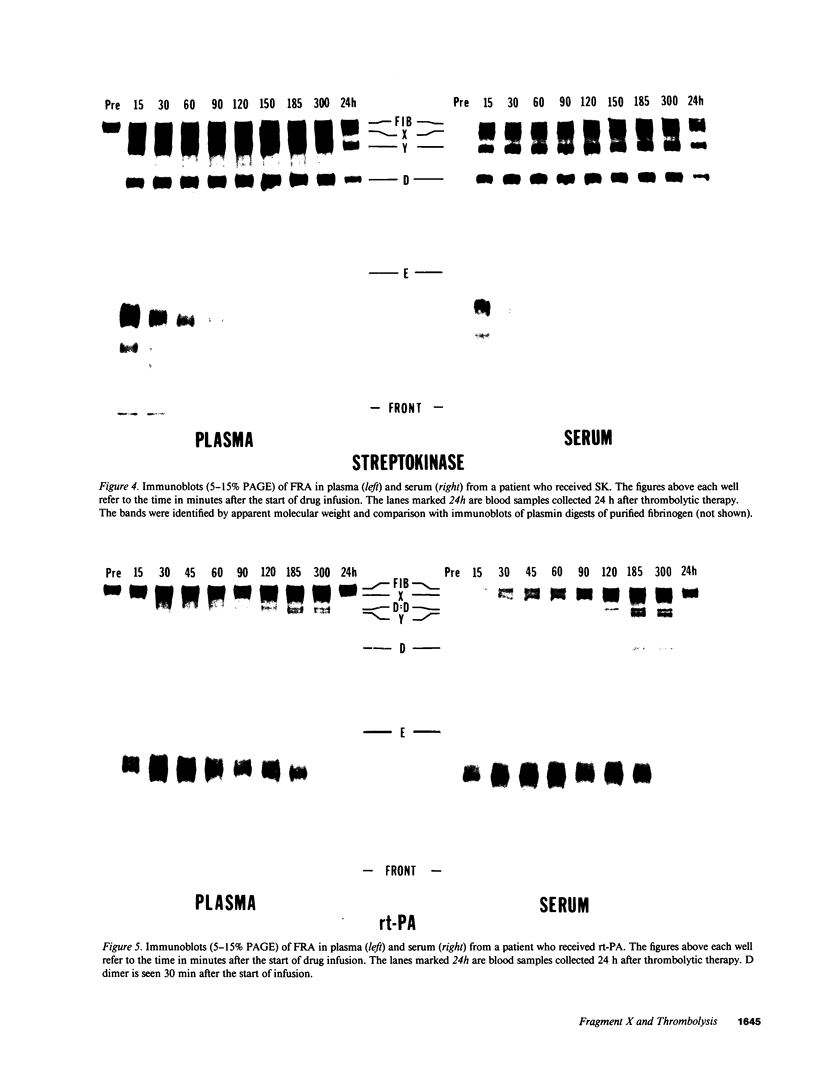
We have determined the extent of fragment X formation during thrombolytic therapy by integration over time of the plasma fibrinopeptide B beta 1-42 concentration. This peptide is quantitatively released when fragment X is formed by plasmin action on fibrinogen or fibrin I. In response to streptokinase (SK) and rt-PA, 264 +/- 54 and 95 +/- 12 mg/dl respectively of fibrinogen was converted to fragment X. By immunoblotting, fragment X was demonstrated as early as 5 min after SK and 30 min after rt-PA, and was still evident 24 h after treatment. Patients treated with SK showed extensive further plasmin degradation of fragment X to fragments Y and D. Thus fragment X concentrations tend to be more similar in the two groups than would be expected from the extent of fibrinogen breakdown. Fragment X forms clots, but these have lower tensile strength and are more susceptible to further plasmin lysis than clots of fibrin. Thus the similar bleeding observed in the two treatment groups might be a reflection of their similar plasma fragment X concentrations.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bergmann S. R., Fox K. A., Ter-Pogossian M. M., Sobel B. E., Collen D. Clot-selective coronary thrombolysis with tissue-type plasminogen activator. Science. 1983 Jun 10;220(4602):1181–1183. doi: 10.1126/science.6602378. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeWood M. A., Spores J., Notske R., Mouser L. T., Burroughs R., Golden M. S., Lang H. T. Prevalence of total coronary occlusion during the early hours of transmural myocardial infarction. N Engl J Med. 1980 Oct 16;303(16):897–902. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198010163031601. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GREENWOOD F. C., HUNTER W. M., GLOVER J. S. THE PREPARATION OF I-131-LABELLED HUMAN GROWTH HORMONE OF HIGH SPECIFIC RADIOACTIVITY. Biochem J. 1963 Oct;89:114–123. doi: 10.1042/bj0890114. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ganz W., Buchbinder N., Marcus H., Mondkar A., Maddahi J., Charuzi Y., O'Connor L., Shell W., Fishbein M. C., Kass R. Intracoronary thrombolysis in evolving myocardial infarction. Am Heart J. 1981 Jan;101(1):4–13. doi: 10.1016/0002-8703(81)90376-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ganz W., Geft I., Shah P. K., Lew A. S., Rodriguez L., Weiss T., Maddahi J., Berman D. S., Charuzi Y., Swan H. J. Intravenous streptokinase in evolving acute myocardial infarction. Am J Cardiol. 1984 May 1;53(9):1209–1216. doi: 10.1016/0002-9149(84)90066-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holvoet P., Lijnen H. R., Collen D. A monoclonal antibody preventing binding of tissue-type plasminogen activator to fibrin: useful to monitor fibrinogen breakdown during t-PA infusion. Blood. 1986 May;67(5):1482–1487. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoylaerts M., Rijken D. C., Lijnen H. R., Collen D. Kinetics of the activation of plasminogen by human tissue plasminogen activator. Role of fibrin. J Biol Chem. 1982 Mar 25;257(6):2912–2919. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaplan K. L., Owen J. Radioimmunoassay of platelet factor 4. Methods Enzymol. 1982;84:83–92. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(82)84008-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lane D. A., Robbins A., Rampling M. W., Kakkar V. V. SDS polyacrylamide gel characterization of serum FDP produced in response to ancrod and streptokinase/plasminogen infusion in man. Br J Haematol. 1977 May;36(1):137–148. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1977.tb05763.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lipinski B., Wegrzynowicz Z., Budzynski A. Z., Kopeć M., Latallo Z. S., Kowalski E. Soluble unclottable complexes formed in the presence of fibrinogen degradation products (FDP) during the fibrinogen-fibrin conversion and their potential significance in pathology. Thromb Diath Haemorrh. 1967 Feb 28;17(1-2):65–77. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu C. Y., Sobel J. H., Weitz J. I., Kaplan K. L., Nossel H. L. Immunologic identification of the cleavage products from the A alpha- and B beta-chains in the early stages of plasmin digestion of fibrinogen. Thromb Haemost. 1986 Aug 20;56(1):100–106. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marder V. J., Shulman N. R., Carroll W. R. High molecular weight derivatives of human fibrinogen produced by plasmin. I. Physicochemical and immunological characterization. J Biol Chem. 1969 Apr 25;244(8):2111–2119. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marder V. J., Shulman N. R., Carroll W. R. The importance of intermediate degradation products of fibrinogen in fibrinolytic hemorrhage. Trans Assoc Am Physicians. 1967;80:156–167. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marder V. J. The use of thrombolytic agents: choice of patient, drug administration, laboratory monitoring. Ann Intern Med. 1979 May;90(5):802–808. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-90-5-802. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mathey D. G., Sheehan F. H., Schofer J., Dodge H. T. Time from onset of symptoms to thrombolytic therapy: a major determinant of myocardial salvage in patients with acute transmural infarction. J Am Coll Cardiol. 1985 Sep;6(3):518–525. doi: 10.1016/s0735-1097(85)80107-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McDonagh R. P., Jr, McDonagh J., Duckert F. The influence of fibrin crosslinking on the kinetics of urokinase-induced clot lysis. Br J Haematol. 1971 Sep;21(3):323–332. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1971.tb03444.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mentzer R. L., Budzynski A. Z., Sherry S. High-dose, brief-duration intravenous infusion of streptokinase in acute myocardial infarction: description of effects in the circulation. Am J Cardiol. 1986 Jun 1;57(15):1220–1226. doi: 10.1016/0002-9149(86)90192-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NILSSON I. M., KROOK H., STERNBY N. H., SODERBERG E., SODERSTROM N. Severe thrombotic disease in a young man with bone marrow and skeletal changes and with a high content of an inhibitor in the fibrinolytic system. Acta Med Scand. 1961 Mar;169:323–337. doi: 10.1111/j.0954-6820.1961.tb07838.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nossel H. L., Wasser J., Kaplan K. L., LaGamma K. S., Yudelman I., Canfield R. E. Sequence of fibrinogen proteolysis and platelet release after intrauterine infusion of hypertonic saline. J Clin Invest. 1979 Nov;64(5):1371–1378. doi: 10.1172/JCI109594. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pennica D., Holmes W. E., Kohr W. J., Harkins R. N., Vehar G. A., Ward C. A., Bennett W. F., Yelverton E., Seeburg P. H., Heyneker H. L. Cloning and expression of human tissue-type plasminogen activator cDNA in E. coli. Nature. 1983 Jan 20;301(5897):214–221. doi: 10.1038/301214a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pizzo S. V., Schwartz M. L., Hill R. L., McKee P. A. The effect of plasmin on the subunit structure of human fibrinogen. J Biol Chem. 1972 Feb 10;247(3):636–645. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reduto L. A., Smalling R. W., Freund G. C., Gould K. L. Intracoronary infusion of streptokinase in patients with acute myocardial infarction: effects of reperfusion on left ventricular performance. Am J Cardiol. 1981 Sep;48(3):403–409. doi: 10.1016/0002-9149(81)90066-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reimer K. A., Lowe J. E., Rasmussen M. M., Jennings R. B. The wavefront phenomenon of ischemic cell death. 1. Myocardial infarct size vs duration of coronary occlusion in dogs. Circulation. 1977 Nov;56(5):786–794. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.56.5.786. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rentrop P., Blanke H., Karsch K. R., Kaiser H., Köstering H., Leitz K. Selective intracoronary thrombolysis in acute myocardial infarction and unstable angina pectoris. Circulation. 1981 Feb;63(2):307–317. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.63.2.307. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rentrop P., Blanke H., Karsch K. R., Rutsch W., Schartl M., Merx W., Dörr R., Mathey D., Kuck K. Changes in left ventricular function after intracoronary streptokinase infusion in clinically evolving myocardial infarction. Am Heart J. 1981 Dec;102(6 Pt 2):1188–1193. doi: 10.1016/0002-8703(81)90651-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sheehan F. H., Mathey D. G., Schofer J., Krebber H. J., Dodge H. T. Effect of interventions in salvaging left ventricular function in acute myocardial infarction: a study of intracoronary streptokinase. Am J Cardiol. 1983 Sep 1;52(5):431–438. doi: 10.1016/0002-9149(83)90002-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shen L. L., McDonagh R. P., McDonagh J., Hermans J. Early events in the plasmin digestion of fibrinogen and fibrin. Effects of plasmin on fibrin polymerization. J Biol Chem. 1977 Sep 10;252(17):6184–6189. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sobel B. E., Gross R. W., Robison A. K. Thrombolysis, clot selectivity, and kinetics. Circulation. 1984 Aug;70(2):160–164. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.70.2.160. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van de Werf F., Ludbrook P. A., Bergmann S. R., Tiefenbrunn A. J., Fox K. A., de Geest H., Verstraete M., Collen D., Sobel B. E. Coronary thrombolysis with tissue-type plasminogen activator in patients with evolving myocardial infarction. N Engl J Med. 1984 Mar 8;310(10):609–613. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198403083101001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weitz J. I., Koehn J. A., Canfield R. E., Landman S. L., Friedman R. Development of a radioimmunoassay for the fibrinogen-derived peptide B beta 1-42. Blood. 1986 Apr;67(4):1014–1022. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]





