Abstract
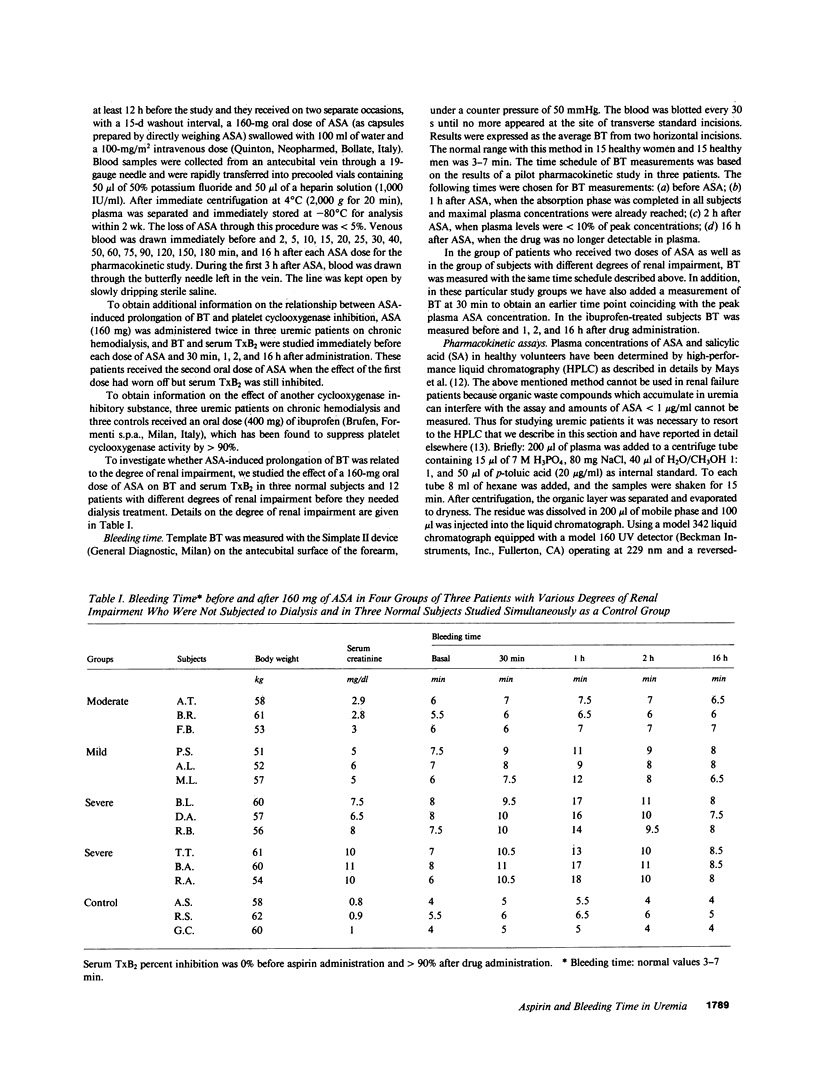
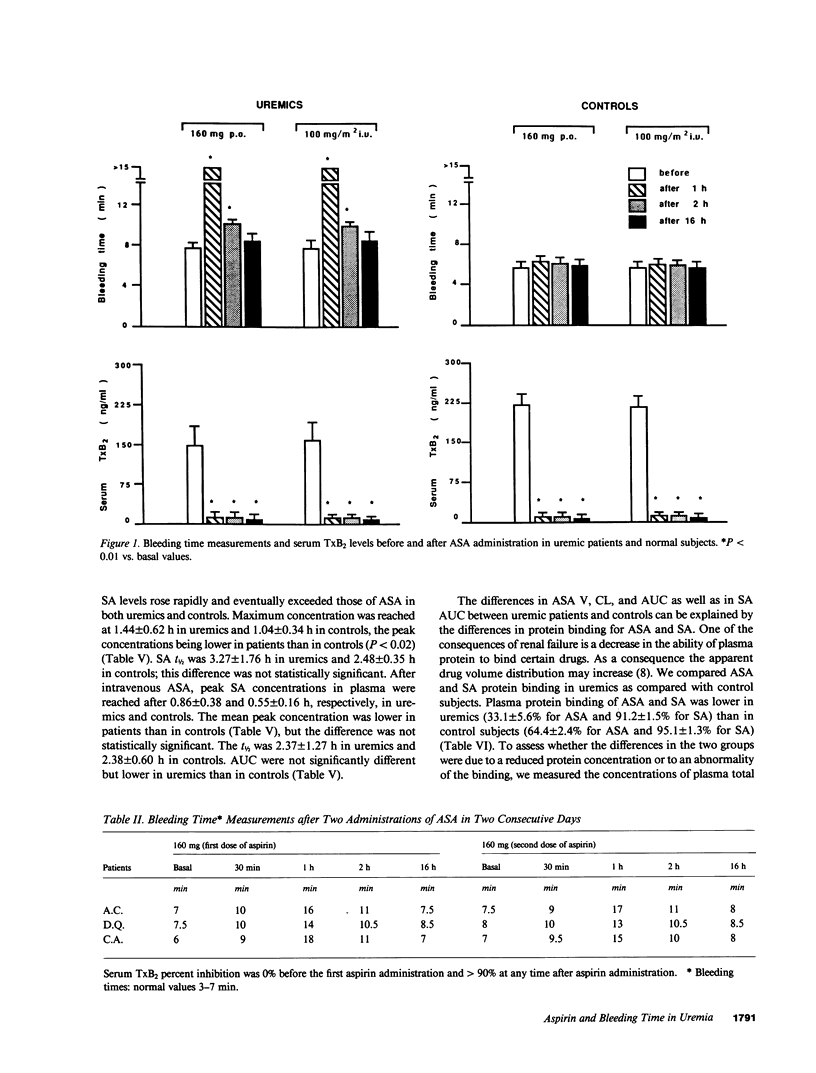
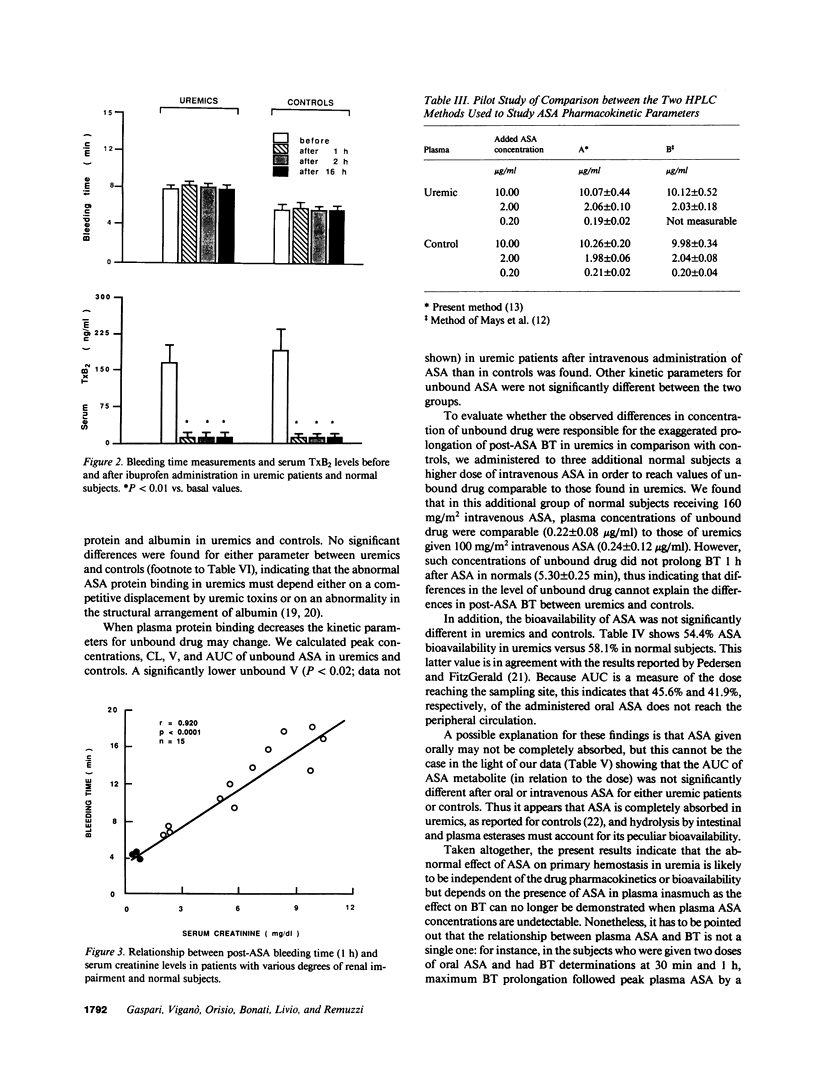
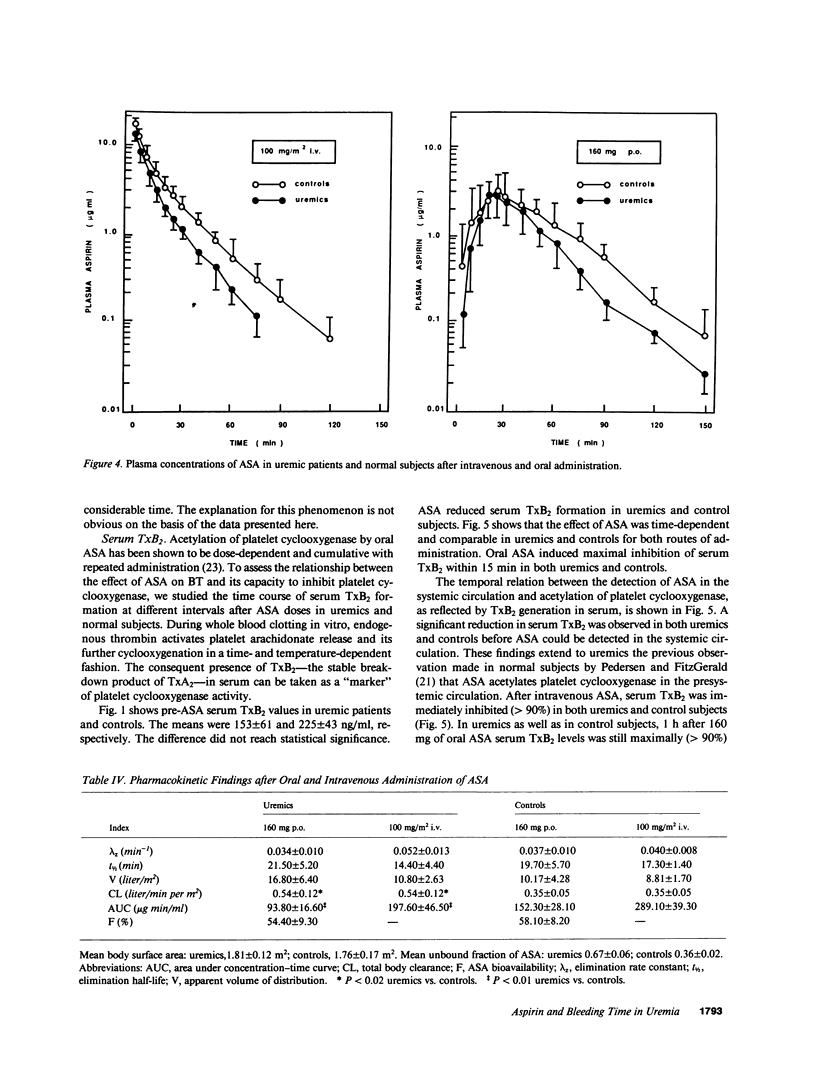
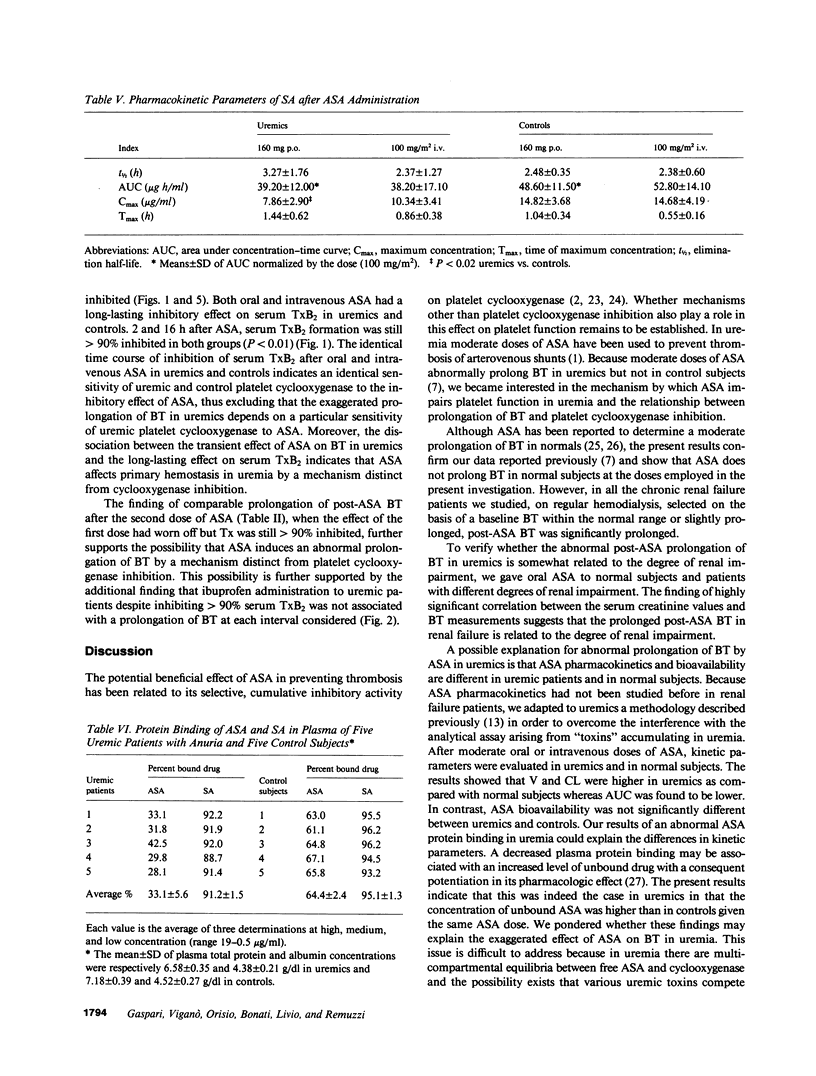
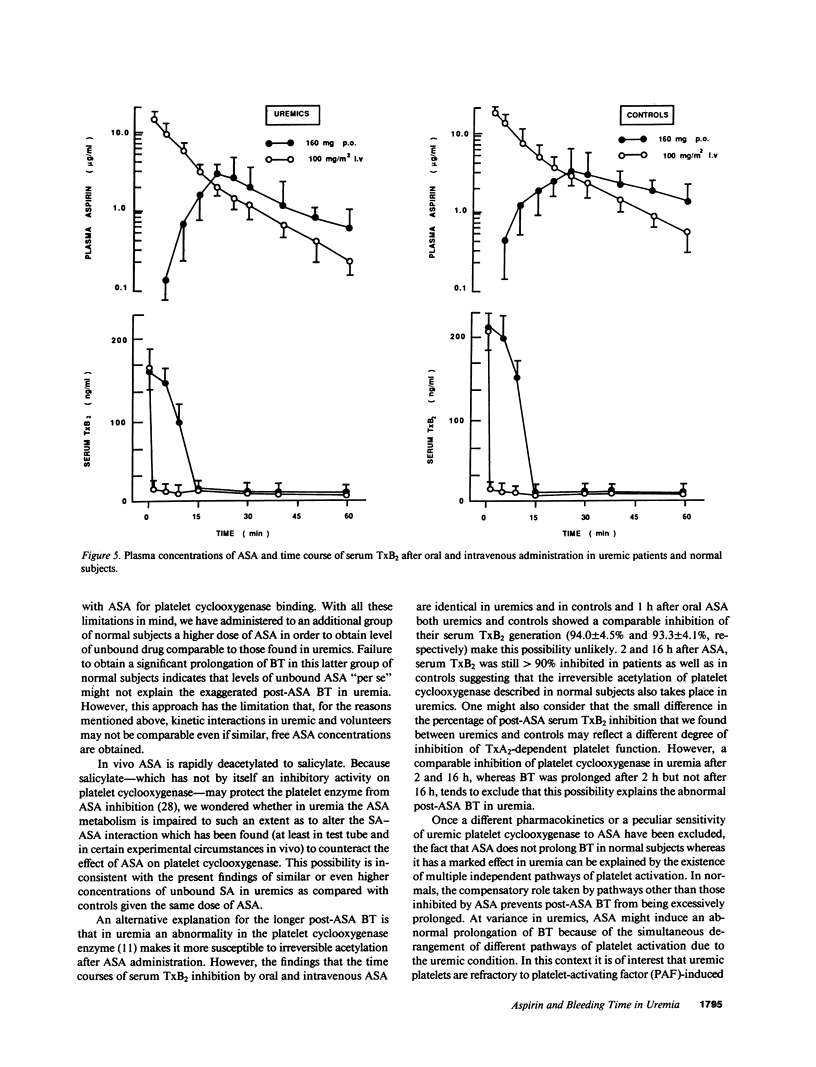
We reported that aspirin (ASA) abnormally prolongs bleeding time (BT) in uremia. The present study was designed to investigate whether the abnormally prolonged post-ASA BT in uremia is due to different ASA pharmacokinetics and bioavailability that might be a consequence of uremic condition, platelet cyclooxygenase is peculiarly sensitive to ASA in uremia, and ASA affects primary hemostasis in uremia by a mechanism independent of cyclooxygenase inhibition. Our results showed that in patients with uremia, but not in normal subjects, ASA markedly prolongs the BT. This effect is transient and depends on the presence of ASA in the blood. The observed differences in ASA kinetic parameters are not an explanation of the exaggerated effect of ASA on primary hemostasis in uremia. The sensitivity of platelet cyclooxygenase to ASA inhibition is comparable in uremics and in normal subjects. The temporal dissociation between ASA-induced prolongation of BT and the effect on platelet thromboxane A2 generation suggests that ASA inhibits platelet function in uremia by a mechanism distinct from cyclooxygenase blocking. This possibility is strengthened by the observation that ibuprofen at a dose that fully inhibits platelet cyclooxygenase activity does not significantly prolong BT.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Andreasen F. Protein binding of drugs in plasma from patients with acute renal failure. Acta Pharmacol Toxicol (Copenh) 1973;32(6):417–429. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0773.1973.tb01488.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deykin D., Janson P., McMahon L. Ethanol potentiation of aspirin-induced prolongation of the bleeding time. N Engl J Med. 1982 Apr 8;306(14):852–854. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198204083061406. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deykin D. Uremic bleeding. Kidney Int. 1983 Nov;24(5):698–705. doi: 10.1038/ki.1983.214. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eknoyan G., Brown C. H., 3rd Biochemical abnormalities of platelets in renal failure. Evidence for decreased platelet serotonin, adenosine diphosphate and Mg-dependent adenosine triphosphatase. Am J Nephrol. 1981;1(1):17–23. doi: 10.1159/000166482. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harter H. R., Burch J. W., Majerus P. W., Stanford N., Delmez J. A., Anderson C. B., Weerts C. A. Prevention of thrombosis in patients on hemodialysis by low-dose aspirin. N Engl J Med. 1979 Sep 13;301(11):577–579. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197909133011103. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hawkins D., Pinckard R. N., Crawford I. P., Farr R. S. Structural changes in human serum albumin induced by ingestion of acetylsalicylic acid. J Clin Invest. 1969 Mar;48(3):536–542. doi: 10.1172/JCI106011. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Livio M., Benigni A., Remuzzi G. Coagulation abnormalities in uremia. Semin Nephrol. 1985 Jun;5(2):82–90. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Livio M., Benigni A., Viganò G., Mecca G., Remuzzi G. Moderate doses of aspirin and risk of bleeding in renal failure. Lancet. 1986 Feb 22;1(8478):414–416. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(86)92372-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Livio M., Mannucci P. M., Viganò G., Mingardi G., Lombardi R., Mecca G., Remuzzi G. Conjugated estrogens for the management of bleeding associated with renal failure. N Engl J Med. 1986 Sep 18;315(12):731–735. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198609183151204. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Majerus P. W. Arachidonate metabolism in vascular disorders. J Clin Invest. 1983 Nov;72(5):1521–1525. doi: 10.1172/JCI111110. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mannucci P. M., Remuzzi G., Pusineri F., Lombardi R., Valsecchi C., Mecca G., Zimmerman T. S. Deamino-8-D-arginine vasopressin shortens the bleeding time in uremia. N Engl J Med. 1983 Jan 6;308(1):8–12. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198301063080102. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marcus A. J. Aspirin as an antithrombotic medication. N Engl J Med. 1983 Dec 15;309(24):1515–1517. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198312153092410. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mays D. C., Sharp D. E., Beach C. A., Kershaw R. A., Bianchine J. R., Gerber N. Improved method for the determination of aspirin and its metabolites in biological fluids by high-performance liquid chromatography: applications to human and animal studies. J Chromatogr. 1984 Nov 28;311(2):301–309. doi: 10.1016/s0378-4347(00)84723-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Grady J., Moncada S. Aspirin: A paradoxical effect on bleeding-time. Lancet. 1978 Oct 7;2(8093):780–780. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(78)92661-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Odar-Cederlöf I., Borgå O. Kinetics of diphenylhydantoin in uraemic patients: consequences of decreased plasma protein binding. Eur J Clin Pharmacol. 1974;7(1):31–37. doi: 10.1007/BF00614387. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patrignani P., Filabozzi P., Patrono C. Selective cumulative inhibition of platelet thromboxane production by low-dose aspirin in healthy subjects. J Clin Invest. 1982 Jun;69(6):1366–1372. doi: 10.1172/JCI110576. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pedersen A. K., FitzGerald G. A. Dose-related kinetics of aspirin. Presystemic acetylation of platelet cyclooxygenase. N Engl J Med. 1984 Nov 8;311(19):1206–1211. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198411083111902. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Remuzzi G., Benigni A., Dodesini P., Schieppati A., Livio M., De Gaetano G., Day S. S., Smith W. L., Pinca E., Patrignani P. Reduced platelet thromboxane formation in uremia. Evidence for a functional cyclooxygenase defect. J Clin Invest. 1983 Mar;71(3):762–768. doi: 10.1172/JCI110824. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roth G. J., Majerus P. W. The mechanism of the effect of aspirin on human platelets. I. Acetylation of a particulate fraction protein. J Clin Invest. 1975 Sep;56(3):624–632. doi: 10.1172/JCI108132. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roth G. J., Stanford N., Majerus P. W. Acetylation of prostaglandin synthase by aspirin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Aug;72(8):3073–3076. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.8.3073. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rowland M., Riegelman S., Harris P. A., Sholkoff S. D. Absorption kinetics of aspirin in man following oral administration of an aqueous solution. J Pharm Sci. 1972 Mar;61(3):379–385. doi: 10.1002/jps.2600610312. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salzman E. W., Neri L. L. Adhesiveness of blood platelets in uremia. Thromb Diath Haemorrh. 1966 Jan 31;15(1):84–92. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steiner R. W., Coggins C., Carvalho A. C. Bleeding time in uremia: a useful test to assess clinical bleeding. Am J Hematol. 1979;7(2):107–117. doi: 10.1002/ajh.2830070203. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Uraemic platelets. Lancet. 1986 Apr 19;1(8486):913–914. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Gaetano G., Cerletti C., Dejana E., Latini R. Pharmacology of platelet inhibition in humans: implications of the salicylate-aspirin interaction. Circulation. 1985 Dec;72(6):1185–1193. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.72.6.1185. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]




