Abstract
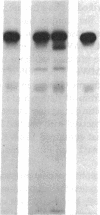
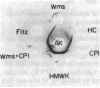
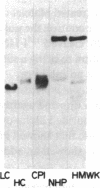
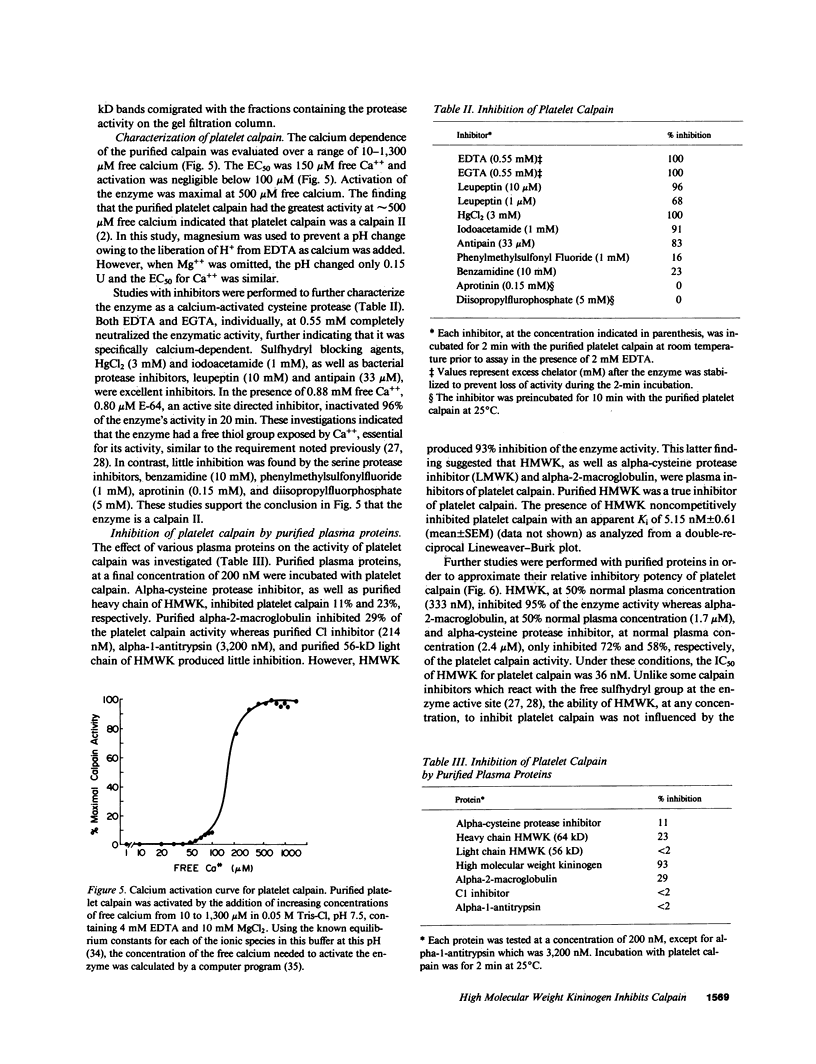
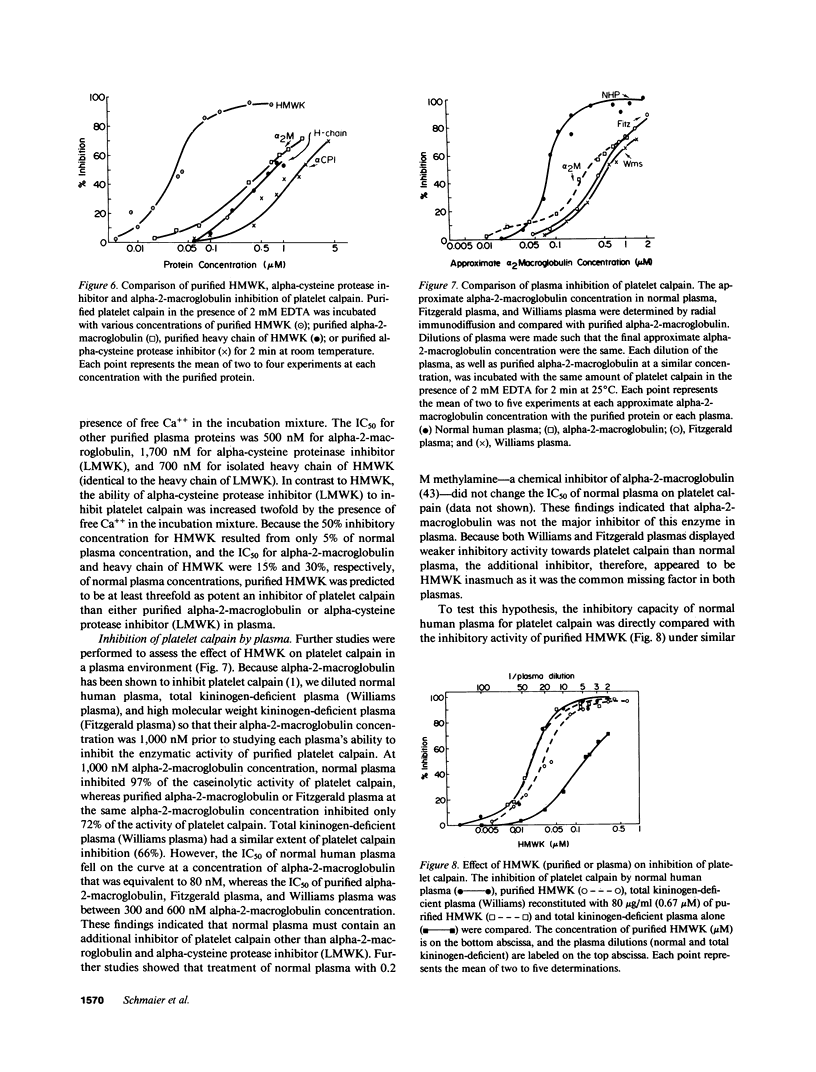
Recent studies from our laboratory indicate that a high concentration of platelet-derived calcium-activated cysteine protease (calpain) can cleave high molecular weight kininogen (HMWK). On immunodiffusion and immunoblot, antiserum directed to the heavy chain of HMWK showed immunochemical identity with alpha-cysteine protease inhibitor--a major plasma inhibitor of tissue calpains. Studies were then initiated to determine whether purified or plasma HMWK was also an inhibitor of platelet calpain. Purified alpha-cysteine protease inhibitor, alpha-2-macroglobulin, as well as purified heavy chain of HMWK or HMWK itself inhibited purified platelet calpain. Kinetic analysis revealed that HMWK inhibited platelet calpain noncompetitively (Ki approximately equal to 5 nM). Incubation of platelet calpain with HMWK, alpha-2-macroglobulin, purified heavy chain of HMWK, or purified alpha-cysteine protease inhibitor under similar conditions resulted in an IC50 of 36, 500, 700, and 1,700 nM, respectively. The contribution of these proteins in plasma towards the inhibition of platelet calpain was investigated next. Normal plasma contained a protein that conferred a five to sixfold greater IC50 of purified platelet calpain than plasma deficient in either HMWK or total kininogen. Reconstitution of total kininogen deficient plasma with purified HMWK to normal levels (0.67 microM) completely corrected the subnormal inhibitory activity. However, reconstitution of HMWK deficient plasma to normal levels of low molecular weight kininogen (2.4 microM) did not fully correct the subnormal calpain inhibitory capacity of this plasma. These studies indicate that HMWK is a potent inhibitor as well as a substrate of platelet calpain and that the plasma and cellular kininogens may function as regulators of cytosolic, calcium-activated cysteine proteases.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(76)90527-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DAVIS B. J. DISC ELECTROPHORESIS. II. METHOD AND APPLICATION TO HUMAN SERUM PROTEINS. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1964 Dec 28;121:404–427. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1964.tb14213.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeMartino G. N., Blumenthal D. K. Identification and partial purification of a factor that stimulates calcium-dependent proteases. Biochemistry. 1982 Aug 31;21(18):4297–4303. doi: 10.1021/bi00261a019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glaser C. B., Karic L., Fallat R. Isolation and characterization of alpha-1-antitrypsin from the Cohn fraction IV-I of human plasma. Prep Biochem. 1975;5(4):333–348. doi: 10.1080/00327487508061581. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gounaris A. D., Brown M. A., Barrett A. J. Human plasma alpha-cysteine proteinase inhibitor. Purification by affinity chromatography, characterization and isolation of an active fragment. Biochem J. 1984 Jul 15;221(2):445–452. doi: 10.1042/bj2210445. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kerbiriou D. M., Griffin J. H. Human high molecular weight kininogen. Studies of structure-function relationships and of proteolysis of the molecule occurring during contact activation of plasma. J Biol Chem. 1979 Dec 10;254(23):12020–12027. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kitahara A., Sasaki T., Kikuchi T., Yumoto N., Yoshimura N., Hatanaka M., Murachi T. Large-scale purification of porcine calpain I and calpain II and comparison of proteolytic fragments of their subunits. J Biochem. 1984 Jun;95(6):1759–1766. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kitamura N., Takagaki Y., Furuto S., Tanaka T., Nawa H., Nakanishi S. A single gene for bovine high molecular weight and low molecular weight kininogens. Nature. 1983 Oct 6;305(5934):545–549. doi: 10.1038/305545a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kunicki T. J., Montgomery R. R., Schullek J. Cleavage of human von Willebrand factor by platelet calcium-activated protease. Blood. 1985 Feb;65(2):352–356. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kunicki T. J., Mosesson M. W., Pidard D. Cleavage of fibrinogen by human platelet calcium-activated protease. Thromb Res. 1984 Jul 15;35(2):169–182. doi: 10.1016/0049-3848(84)90212-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MOLNAR J., LORAND L. Studies on apyrases. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1961 May;93:353–363. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(61)90278-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murachi T., Tanaka K., Hatanaka M., Murakami T. Intracellular Ca2+-dependent protease (calpain) and its high-molecular-weight endogenous inhibitor (calpastatin). Adv Enzyme Regul. 1980;19:407–424. doi: 10.1016/0065-2571(81)90026-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mustard J. F., Perry D. W., Ardlie N. G., Packham M. A. Preparation of suspensions of washed platelets from humans. Br J Haematol. 1972 Feb;22(2):193–204. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1972.tb08800.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Müller-Esterl W., Fritz H., Machleidt W., Ritonja A., Brzin J., Kotnik M., Turk V., Kellermann J., Lottspeich F. Human plasma kininogens are identical with alpha-cysteine proteinase inhibitors. Evidence from immunological, enzymological and sequence data. FEBS Lett. 1985 Mar 25;182(2):310–314. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(85)80322-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Müller-Esterl W., Vohle-Timmermann M., Boos B., Dittman B. Purification and properties of human low molecular weight kininogen. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1982 Sep 7;706(2):145–152. doi: 10.1016/0167-4838(82)90480-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nawa H., Kitamura N., Hirose T., Asai M., Inayama S., Nakanishi S. Primary structures of bovine liver low molecular weight kininogen precursors and their two mRNAs. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jan;80(1):90–94. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.1.90. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Phillips D. R., Jakábová M. Ca2+-dependent protease in human platelets. Specific cleavage of platelet polypeptides in the presence of added Ca2+. J Biol Chem. 1977 Aug 25;252(16):5602–5605. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pixley R. A., Schapira M., Colman R. W. The regulation of human factor XIIa by plasma proteinase inhibitors. J Biol Chem. 1985 Feb 10;260(3):1723–1729. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Proud D., Pierce J. V., Pisano J. J. Radioimmunoassay of human high molecular weight kininogen in normal and deficient plasmas. J Lab Clin Med. 1980 Apr;95(4):563–574. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ross E., Schatz G. Assay of protein in the presence of high concentrations of sulfhydryl compounds. Anal Biochem. 1973 Jul;54(1):304–306. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(73)90280-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sakon M., Kambayashi J., Ohno H., Kosaki G. Two forms of Ca++-activated neutral protease in platelets. Thromb Res. 1981 Nov 1;24(3):207–214. doi: 10.1016/0049-3848(81)90090-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schapira M., Silver L. D., Scott C. F., Colman R. W. New and rapid functional assay for C1 inhibitor in human plasma. Blood. 1982 Apr;59(4):719–724. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmaier A. H., Claypool W., Colman R. W. Crotalocytin: recognition and purification of a timber rattlesnake platelet aggregating protein. Blood. 1980 Dec;56(6):1013–1019. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmaier A. H., Gustafson E., Idell S., Colman R. W. Plasma prekallikrein assay: reversible inhibition of C-1 inhibitor by chloroform and its use in measuring prekallikrein in different mammalian species. J Lab Clin Med. 1984 Dec;104(6):882–892. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmaier A. H., Silver L., Adams A. L., Fischer G. C., Munoz P. C., Vroman L., Colman R. W. The effect of high molecular weight kininogen on surface-adsorbed fibrinogen. Thromb Res. 1984 Jan 1;33(1):51–67. doi: 10.1016/0049-3848(84)90154-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmaier A. H., Smith P. M., Colman R. W. Platelet C1- inhibitor. A secreted alpha-granule protein. J Clin Invest. 1985 Jan;75(1):242–250. doi: 10.1172/JCI111680. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmaier A. H., Smith P. M., Purdon A. D., White J. G., Colman R. W. High molecular weight kininogen: localization in the unstimulated and activated platelet and activation by a platelet calpain(s). Blood. 1986 Jan;67(1):119–130. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmaier A. H., Zuckerberg A., Silverman C., Kuchibhotla J., Tuszynski G. P., Colman R. W. High-molecular weight kininogen. A secreted platelet protein. J Clin Invest. 1983 May;71(5):1477–1489. doi: 10.1172/JCI110901. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sueyoshi T., Enjyoji K., Shimada T., Kato H., Iwanaga S., Bando Y., Kominami E., Katunuma N. A new function of kininogens as thiol-proteinase inhibitors: inhibition of papain and cathepsins B, H and L by bovine, rat and human plasma kininogens. FEBS Lett. 1985 Mar 11;182(1):193–195. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(85)81182-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suzuki K. Reaction of calcium-activated neutral protease (CANP) with an epoxysuccinyl derivative (E64c) and iodoacetic acid. J Biochem. 1983 May;93(5):1305–1312. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a134264. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suzuki K., Tsuji S., Ishiura S. Effect of Ca2+ on the inhibition of calcium-activated neutral protease by leupeptin, antipain and epoxysuccinate derivatives. FEBS Lett. 1981 Dec 21;136(1):119–122. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(81)81227-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson R. E., Mandle R., Jr, Kaplan A. P. Characterization of human high molecular weight kininogen. Procoagulant activity associated with the light chain of kinin-free high molecular weight kininogen. J Exp Med. 1978 Feb 1;147(2):488–499. doi: 10.1084/jem.147.2.488. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Timmons S., Hawiger J. Separation of human platelets from plasma proteins including factor VIII VWF by a combined albumin gradient-gel filtration method using HEPES buffer. Thromb Res. 1978 Feb;12(2):297–306. doi: 10.1016/0049-3848(78)90300-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tracy P. B., Nesheim M. E., Mann K. G. Proteolytic alterations of factor Va bound to platelets. J Biol Chem. 1983 Jan 10;258(1):662–669. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Truglia J. A., Stracher A. Purification and characterization of a calcium dependent sulfhydryl protease from human platelets. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1981 May 29;100(2):814–822. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(81)80247-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waxman L. Calcium-activated proteases in mammalian tissues. Methods Enzymol. 1981;80(Pt 100):664–680. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(81)80051-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waxman L., Krebs E. G. Identification of two protease inhibitors from bovine cardiac muscle. J Biol Chem. 1978 Sep 10;253(17):5888–5891. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoshida N., Weksler B., Nachman R. Purification of human platelet calcium-activated protease. Effect on platelet and endothelial function. J Biol Chem. 1983 Jun 10;258(11):7168–7174. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoshimura N., Kikuchi T., Sasaki T., Kitahara A., Hatanaka M., Murachi T. Two distinct Ca2+ proteases (calpain I and calpain II) purified concurrently by the same method from rat kidney. J Biol Chem. 1983 Jul 25;258(14):8883–8889. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]