Abstract
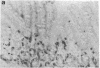
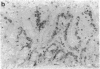
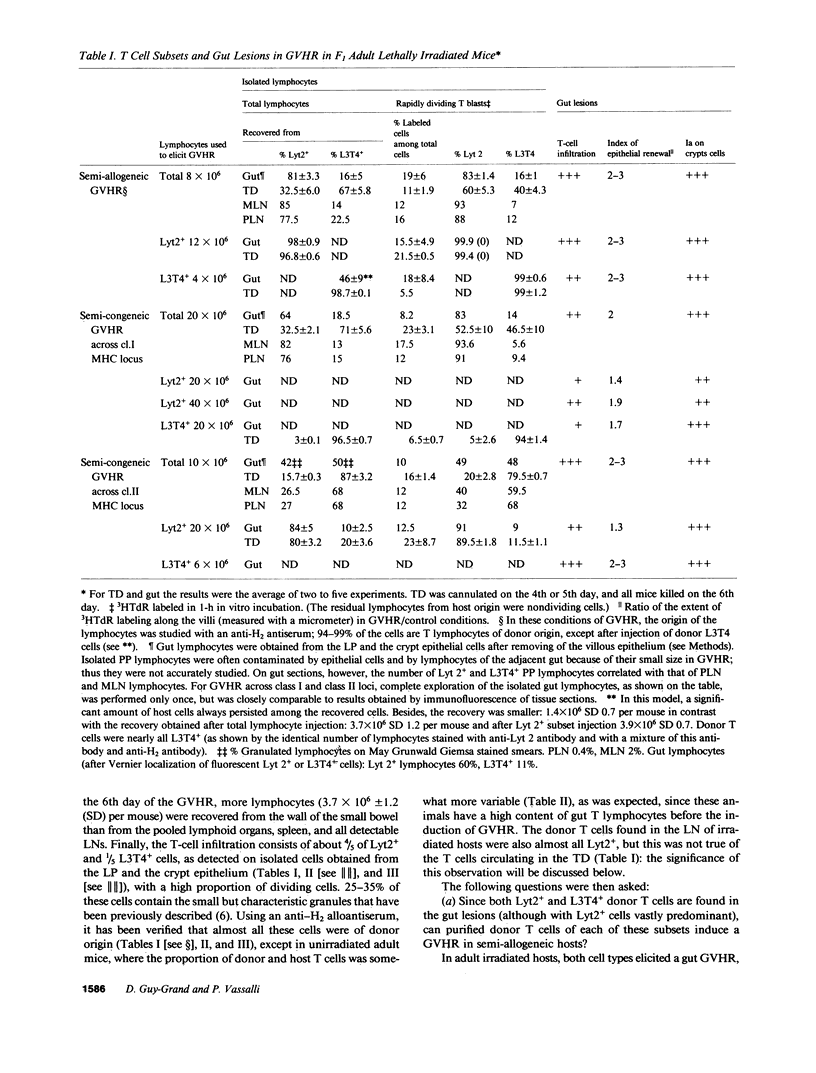
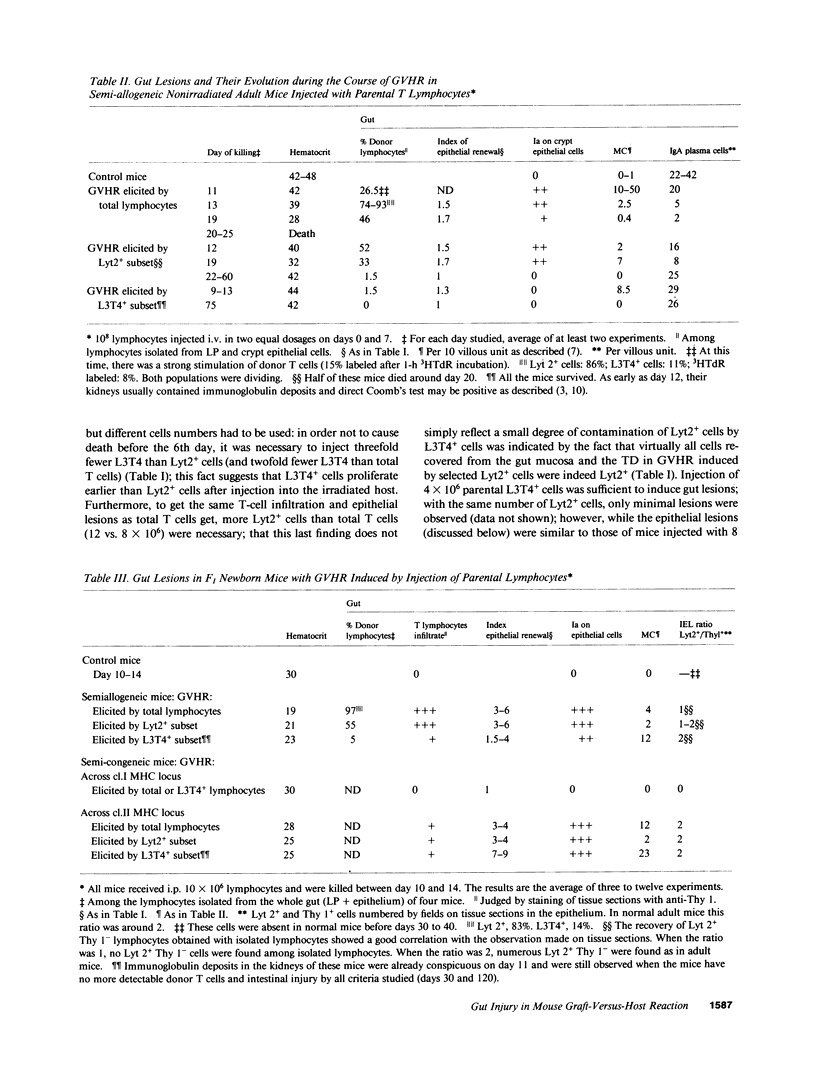
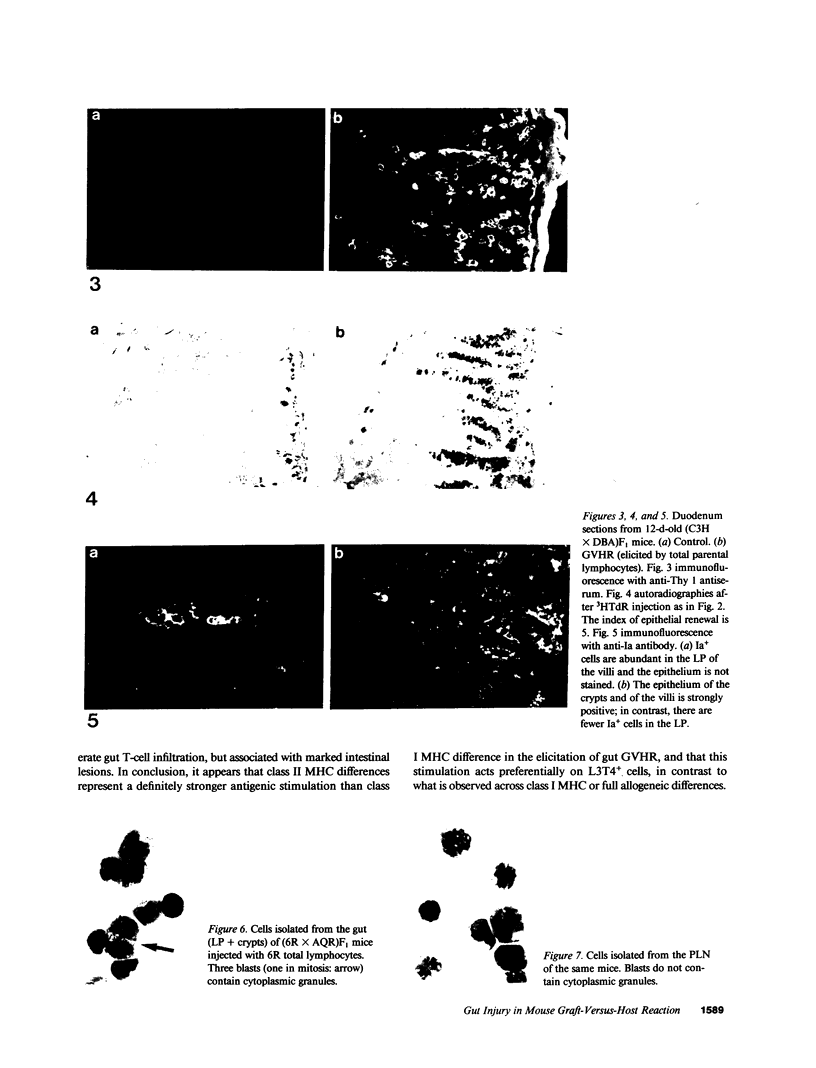
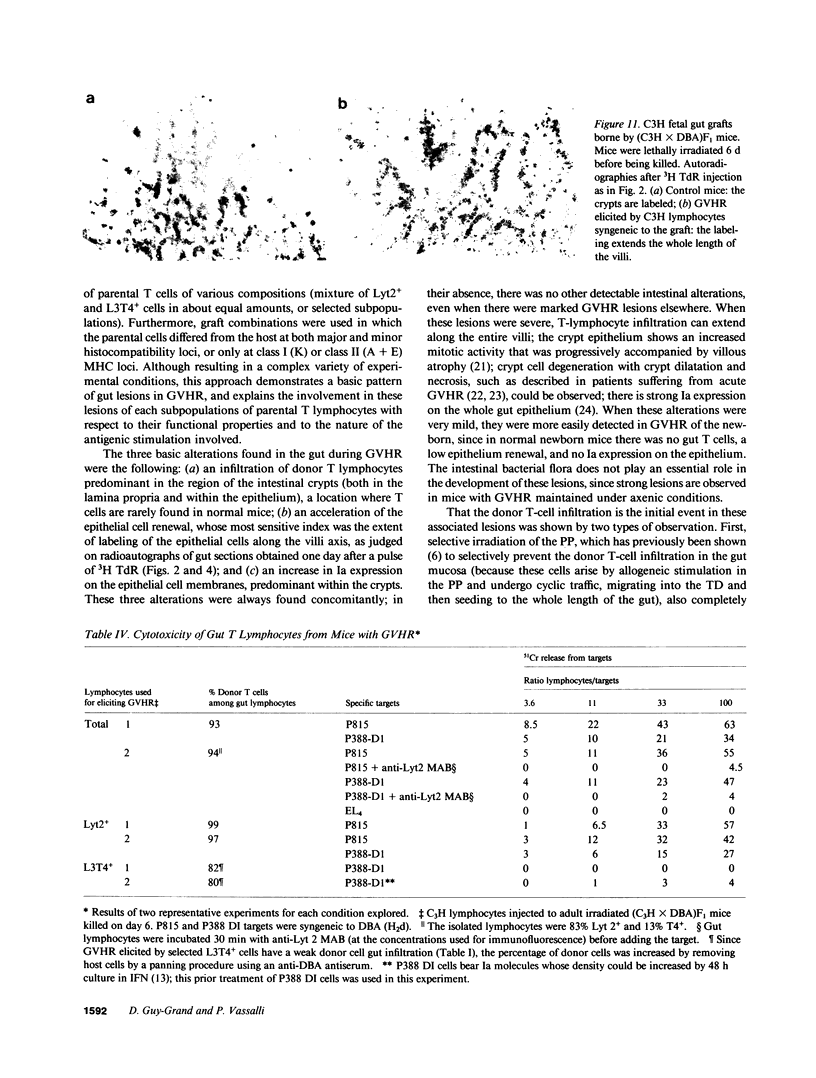
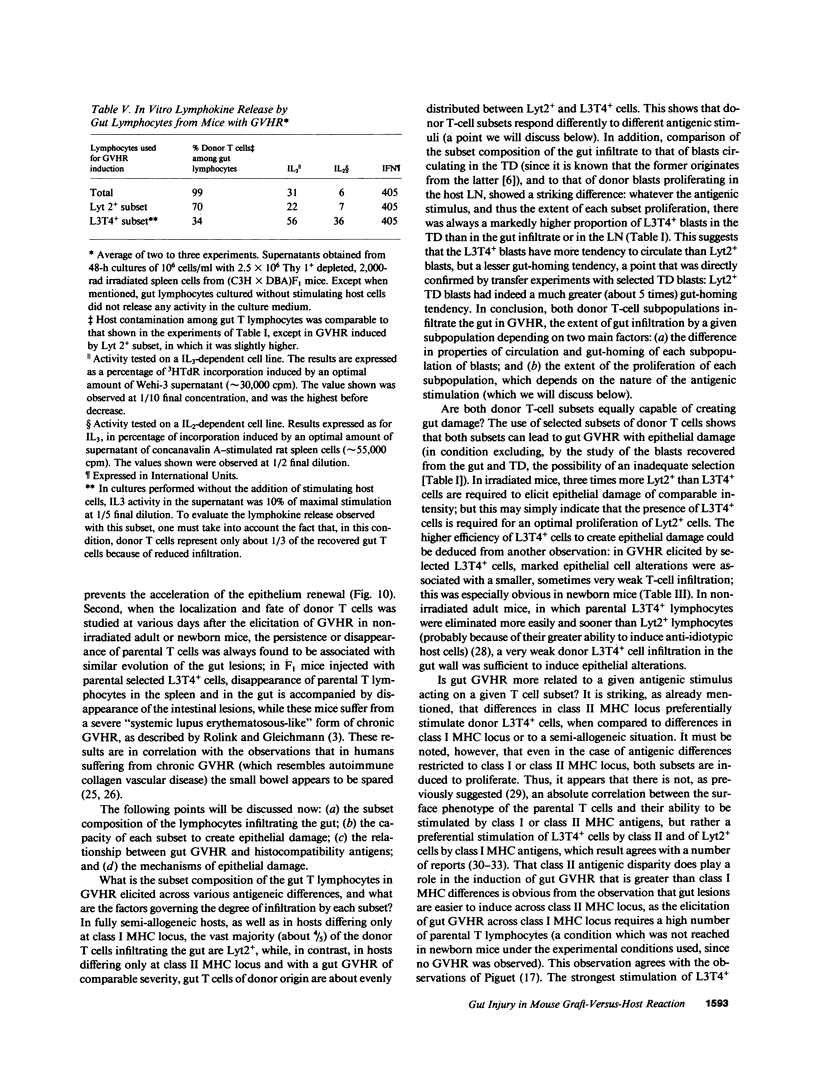
The occurrence, nature, and pathogenesis of intestinal lesions were studied in a number of graft vs. host reaction (GVHR) conditions in mice, combining variations in the nature of the following: the F1 hosts (newborn or adult, normal or lethally irradiated), the injected parental T cells (mixed or selected subsets of Lyt2+ or L3T4+ cells), and the antigenic stimulus (semi-allogeneic or restricted to class I or II MHC loci). The following conclusions were drawn: Three gut alterations are always associated: donor T cell infiltration, predominating in the crypt region; acceleration of the epithelium renewal; and increased epithelial Ia expression. The initial event is T-cell infiltration, which results from stimulation within the Peyer patches followed by cyclic traffic, i.e., migration into the thoracic duct and then seeding to the whole gut mucosa. Both Lyt2+ and L3T4+ cells can infiltrate the gut wall, the extent of the infiltration by a given subset depending upon the capacity of the donor blasts to circulate in the thoracic duct (higher for L3T4+) and then to home in the gut (much higher for Lyt2+ blasts) and the nature of the alloantigenic stimulation that governs the extent of each donor subset proliferation. Both donor T-cell subsets can induce gut epithelial damage, but for a comparable amount of infiltrating cells, L3T4+ cells induce more lesions. When the antigenic stimulation is restricted to class I or class I MHC loci, gut GVHR is much more easily elicited across class II MHC differences, which stimulate preferentially L3T4+ donor cells. The main mechanism of epithelial damage is not direct cytotoxicity, but more probably lymphokine(s) release.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Barclay A. N., Mason D. W. Induction of Ia antigen in rat epidermal cells and gut epithelium by immunological stimuli. J Exp Med. 1982 Dec 1;156(6):1665–1676. doi: 10.1084/jem.156.6.1665. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beschorner W. E., Yardley J. H., Tutschka P. J., Santos G. W. Deficiency of intestinal immunity with graft-vs.-host disease in humans. J Infect Dis. 1981 Jul;144(1):38–46. doi: 10.1093/infdis/144.1.38. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cerf-Bensussan N., Quaroni A., Kurnick J. T., Bhan A. K. Intraepithelial lymphocytes modulate Ia expression by intestinal epithelial cells. J Immunol. 1984 May;132(5):2244–2252. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cerottini J. C., Engers H. D., Macdonald H. R., Brunner T. Generation of cytotoxic T lymphocytes in vitro. I. Response of normal and immune mouse spleen cells in mixed leukocyte cultures. J Exp Med. 1974 Sep 1;140(3):703–717. doi: 10.1084/jem.140.3.703. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crapper R. M., Schrader J. W. Frequency of mast cell precursors in normal tissues determined by an in vitro assay: antigen induces parallel increases in the frequency of P cell precursors and mast cells. J Immunol. 1983 Aug;131(2):923–928. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elson C. O., Reilly R. W., Rosenberg I. H. Small intestinal injury in the graft versus host reaction: an innocent bystander phenomenon. Gastroenterology. 1977 May;72(5 Pt 1):886–889. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Epstein R. J., McDonald G. B., Sale G. E., Shulman H. M., Thomas E. D. The diagnostic accuracy of the rectal biopsy in acute graft-versus-host disease: a prospective study of thirteen patients. Gastroenterology. 1980 Apr;78(4):764–771. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gresser I., Guy-Grand D., Maury C., Maunoury M. T. Interferon induces peripheral lymphadenopathy in mice. J Immunol. 1981 Oct;127(4):1569–1575. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guy-Grand D., Dy M., Luffau G., Vassalli P. Gut mucosal mast cells. Origin, traffic, and differentiation. J Exp Med. 1984 Jul 1;160(1):12–28. doi: 10.1084/jem.160.1.12. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guy-Grand D., Griscelli C., Vassalli P. The gut-associated lymphoid system: nature and properties of the large dividing cells. Eur J Immunol. 1974 Jun;4(6):435–443. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830040610. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guy-Grand D., Griscelli C., Vassalli P. The mouse gut T lymphocyte, a novel type of T cell. Nature, origin, and traffic in mice in normal and graft-versus-host conditions. J Exp Med. 1978 Dec 1;148(6):1661–1677. doi: 10.1084/jem.148.6.1661. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haas W., von Boehmer H. Surface markers of cytotoxic T lymphocyte clones. Eur J Immunol. 1984 Apr;14(4):383–384. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830140421. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Khoury K. A., Floch M. H., Hersh T. Small intestinal mucosal cell proliferation and bacterial flora in the conventionalization of the germfree mouse. J Exp Med. 1969 Sep 1;130(3):659–670. doi: 10.1084/jem.130.3.659. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kimura H., Pickard A., Wilson D. B. Analysis of T cell populations that induce and mediate specific resistance to graft-versus-host disease in rats. J Exp Med. 1984 Sep 1;160(3):652–658. doi: 10.1084/jem.160.3.652. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klein J., Figueroa F., David C. S. H-2 haplotypes, genes and antigens: second listing. II. The H-2 complex. Immunogenetics. 1983;17(6):553–596. doi: 10.1007/BF00366126. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Korngold R., Sprent J. Features of T cells causing H-2-restricted lethal graft-vs.-host disease across minor histocompatibility barriers. J Exp Med. 1982 Mar 1;155(3):872–883. doi: 10.1084/jem.155.3.872. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacDonald T. T., Ferguson A. Hypersensitivity reactions in the small intestine. III. The effects of allograft rejection and of graft-versus-host disease on epithelial cell kinetics. Cell Tissue Kinet. 1977 Jul;10(4):301–312. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mason D. W., Dallman M., Barclay A. N. Graft-versus-host disease induces expression of Ia antigen in rat epidermal cells and gut epithelium. Nature. 1981 Sep 10;293(5828):150–151. doi: 10.1038/293150a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mayrhofer G., Pugh C. W., Barclay A. N. The distribution, ontogeny and origin in the rat of Ia-positive cells with dendritic morphology and of Ia antigen in epithelia, with special reference to the intestine. Eur J Immunol. 1983 Feb;13(2):112–122. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830130206. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller R. A., Stutman O. Monoclonal antibody to Lyt 2 antigen blocks H-2I- and H-2K- specific mouse cytotoxic T cells. Nature. 1982 Mar 4;296(5852):76–78. doi: 10.1038/296076a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mowat A. M., Ferguson A. Hypersensitivity reactions in the small intestine. 6. Pathogenesis of the graft-versus-host reaction in the small intestinal mucosa of the mouse. Transplantation. 1981 Sep;32(3):238–243. doi: 10.1097/00007890-198109000-00011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murray M., Jarrett W. F., Jennings F. W. Mast cells and macromolecular leak in intestinal immunological reactions. The influence of sex of rats infected with Nippostrongylus brasiliensis. Immunology. 1971 Jul;21(1):17–31. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Petit A., Ernst P. B., Befus A. D., Clark D. A., Rosenthal K. L., Ishizaka T., Bienenstock J. Murine intestinal intraepithelial lymphocytes I. Relationship of a novel Thy-1-,Lyt-1-,Lyt-2+, granulated subpopulation to natural killer cells and mast cells. Eur J Immunol. 1985 Mar;15(3):211–215. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830150302. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pierres A., Naquet P., Van Agthoven A., Bekkhoucha F., Denizot F., Mishal Z., Schmitt-Verhulst A. M., Pierres M. A rat anti-mouse T4 monoclonal antibody (H129.19) inhibits the proliferation of Ia-reactive T cell clones and delineates two phenotypically distinct (T4+, Lyt-2,3-, and T4-, Lyt-2,3+) subsets among anti-Ia cytolytic T cell clones. J Immunol. 1984 Jun;132(6):2775–2782. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Piguet P. F. GVHR elicited by products of class I or class II loci of the MHC: analysis of the response of mouse T lymphocytes to products of class I and class II loci of the MHC in correlation with GVHR-induced mortality, medullary aplasia, and enteropathy. J Immunol. 1985 Sep;135(3):1637–1643. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prud'homme G. J., Sohn U., Delovitch T. L. The role of H-2 and Ia antigens in graft-versus-host reactions (GVHR). Presence of host alloantigens on donor cells after GVHR and suppression of GVHR with an anti-Ia antiserum against hose Ia antigens. J Exp Med. 1979 Jan 1;149(1):137–149. doi: 10.1084/jem.149.1.137. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rolink A. G., Gleichmann E. Allosuppressor- and allohelper-T cells in acute and chronic graft-vs.-host (GVH) disease. III. Different Lyt subsets of donor T cells induce different pathological syndromes. J Exp Med. 1983 Aug 1;158(2):546–558. doi: 10.1084/jem.158.2.546. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rolink A. G., Gleichmann H., Gleichmann E. Diseases caused by reactions of T lymphocytes to incompatible structures of the major histocompatibility complex. VII. Immune-complex glomerulonephritis. J Immunol. 1983 Jan;130(1):209–215. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rolink A. G., Pals S. T., Gleichmann E. Allosuppressor and allohelper T cells in acute and chronic graft-vs.-host disease. II. F1 recipients carrying mutations at H-2K and/or I-A. J Exp Med. 1983 Feb 1;157(2):755–771. doi: 10.1084/jem.157.2.755. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rolink A. G., Radaszkiewicz T., Pals S. T., van der Meer W. G., Gleichmann E. Allosuppressor and allohelper T cells in acute and chronic graft-vs-host disease. I. Alloreactive suppressor cells rather than killer T cells appear to be the decisive effector cells in lethal graft-vs.-host disease. J Exp Med. 1982 May 1;155(5):1501–1522. doi: 10.1084/jem.155.5.1501. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rose M. L., Parrott D. M., Bruce R. G. Migration of lymphoblasts to the small intestine. II. Divergent migration of mesenteric and peripheral immunoblasts to sites of inflammation in the mouse. Cell Immunol. 1976 Nov;27(1):36–46. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(76)90151-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sauser D., Anckers C., Bron C. Isolation of mouse thymus-derived lymphocyte specific surface antigens. J Immunol. 1974 Aug;113(2):617–624. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schrader J. W., Scollay R., Battye F. Intramucosal lymphocytes of the gut: Lyt-2 and thy-1 phenotype of the granulated cells and evidence for the presence of both T cells and mast cell precursors. J Immunol. 1983 Feb;130(2):558–564. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shulman H. M., Sullivan K. M., Weiden P. L., McDonald G. B., Striker G. E., Sale G. E., Hackman R., Tsoi M. S., Storb R., Thomas E. D. Chronic graft-versus-host syndrome in man. A long-term clinicopathologic study of 20 Seattle patients. Am J Med. 1980 Aug;69(2):204–217. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(80)90380-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Slavin R. E., Santos G. W. The graft versus host reaction in man after bone marrow transplantation: pathology, pathogenesis, clinical features, and implication. Clin Immunol Immunopathol. 1973 Jul;1(4):472–498. doi: 10.1016/0090-1229(73)90005-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sprent J. Fate of H2-activated T lymphocytes in syngeneic hosts. I. Fate in lymphoid tissues and intestines traced with 3H-thymidine, 125I-deoxyuridine and 51chromium. Cell Immunol. 1976 Feb;21(2):278–302. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(76)90057-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sullivan K. M., Shulman H. M., Storb R., Weiden P. L., Witherspoon R. P., McDonald G. B., Schubert M. M., Atkinson K., Thomas E. D. Chronic graft-versus-host disease in 52 patients: adverse natural course and successful treatment with combination immunosuppression. Blood. 1981 Feb;57(2):267–276. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swain S. L., Dialynas D. P., Fitch F. W., English M. Monoclonal antibody to L3T4 blocks the function of T cells specific for class 2 major histocompatibility complex antigens. J Immunol. 1984 Mar;132(3):1118–1123. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vidović D., Klein J., Nagy Z. A. The role of T cell subsets in the generation of secondary cytolytic responses in vitro against class I and class II major histocompatibility complex antigens. J Immunol. 1984 Mar;132(3):1113–1117. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walker E. B., Maino V., Sanchez-Lanier M., Warner N., Stewart C. Murine gamma interferon activates the release of a macrophage-derived Ia-inducing factor that transfers Ia inductive capacity. J Exp Med. 1984 May 1;159(5):1532–1547. doi: 10.1084/jem.159.5.1532. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]