Abstract
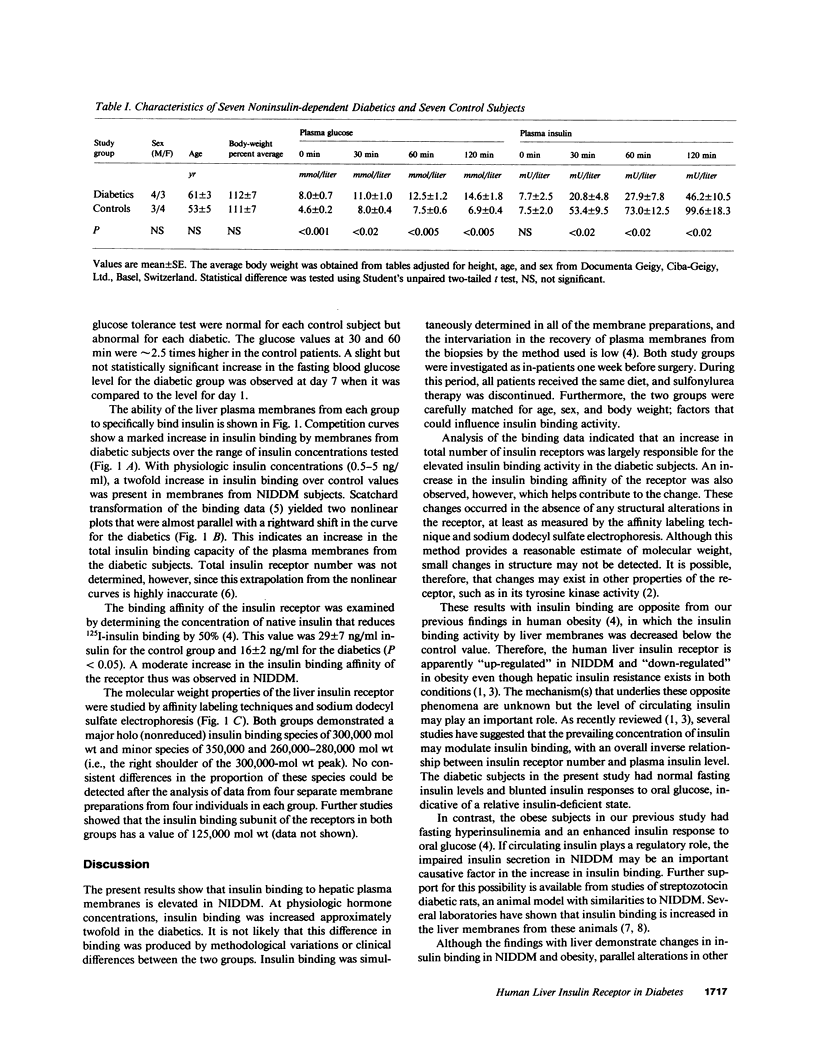
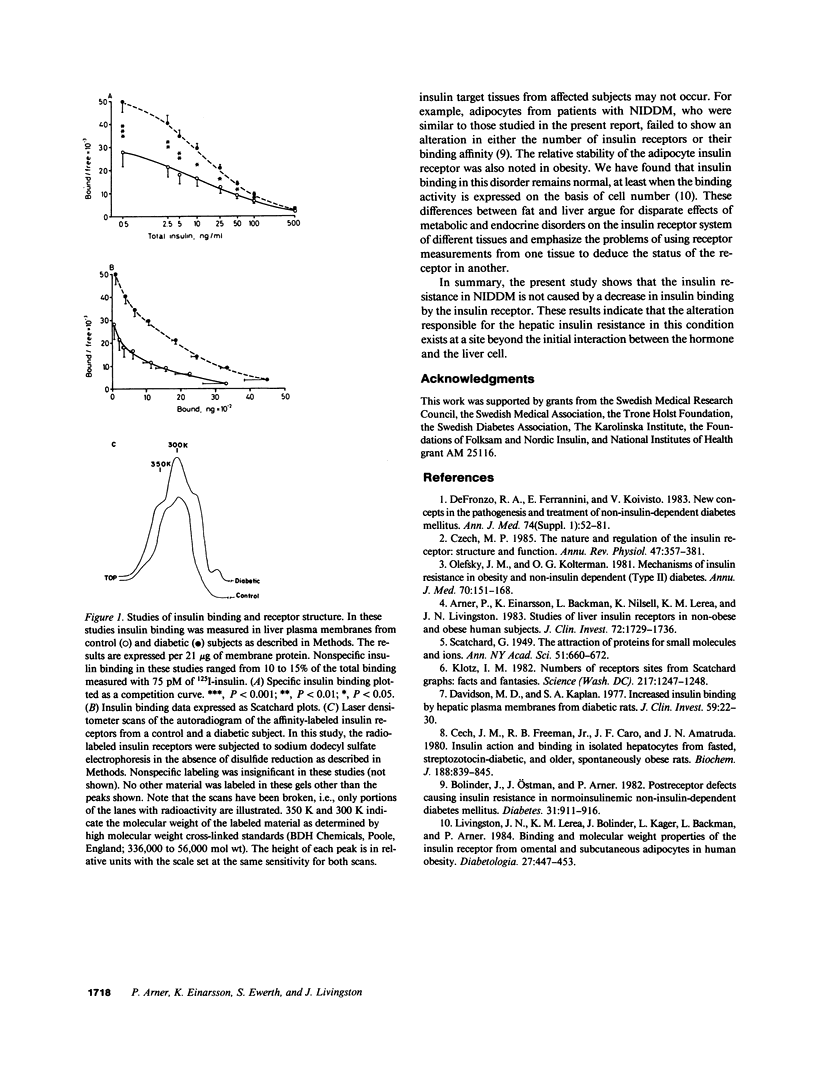
The insulin binding characteristics and the structural components of the insulin receptor were studied in the purified liver plasma membranes from seven patients with noninsulin-dependent diabetes (NIDDM) and seven control subjects. In comparison to the controls, diabetic subjects had a 65% reduction in plasma insulin levels in response to an oral glucose load. Specific insulin binding by liver membranes from diabetic patients was, however, twofold greater than the binding activity by membranes from control subjects. This alteration resulted largely from an increase in the number of insulin receptors and a modest increase in receptor binding affinity. Holo (nonreduced) receptor species of similar molecular weights were detected by an affinity labeling technique in the two membrane preparations and sulfhydryl reduction demonstrated an insulin binding subunit of 125,000 mol wt. Overall, these results show that the hepatic insulin resistance of NIDDM cannot be explained by a deficiency in insulin binding.
Full text
PDF
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arner P., Einarsson K., Backman L., Nilsell K., Lerea K. M., Livingston J. N. Studies of liver insulin receptors in non-obese and obese human subjects. J Clin Invest. 1983 Nov;72(5):1729–1736. doi: 10.1172/JCI111132. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bolinder J., Ostman J., Arner P. Postreceptor defects causing insulin resistance in normoinsulinemic non-insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus. Diabetes. 1982 Oct;31(10):911–916. doi: 10.2337/diab.31.10.911. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cech J. M., Freeman R. B., Jr, Caro J. F., Amatruda J. M. Insulin action and binding in isolated hepatocytes from fasted, streptozotocin-diabetic, and older, spontaneously obese rats. Biochem J. 1980 Jun 15;188(3):839–845. doi: 10.1042/bj1880839. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Czech M. P. The nature and regulation of the insulin receptor: structure and function. Annu Rev Physiol. 1985;47:357–381. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ph.47.030185.002041. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davidson M. B., Kaplan S. A. Increased insulin binding by hepatic plasma membranes from diabetic rats: normalization by insulin therapy. J Clin Invest. 1977 Jan;59(1):22–30. doi: 10.1172/JCI108618. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeFronzo R. A., Ferrannini E., Koivisto V. New concepts in the pathogenesis and treatment of noninsulin-dependent diabetes mellitus. Am J Med. 1983 Jan 17;74(1A):52–81. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(83)90654-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klotz I. M. Numbers of receptor sites from Scatchard graphs: facts and fantasies. Science. 1982 Sep 24;217(4566):1247–1249. doi: 10.1126/science.6287580. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Livingston J. N., Lerea K. M., Bolinder J., Kager L., Backman L., Arner P. Binding and molecular weight properties of the insulin receptor from omental and subcutaneous adipocytes in human obesity. Diabetologia. 1984 Oct;27(4):447–453. doi: 10.1007/BF00273909. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olefsky J. M., Kolterman O. G. Mechanisms of insulin resistance in obesity and noninsulin-dependent (type II) diabetes. Am J Med. 1981 Jan;70(1):151–168. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(81)90422-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


