Abstract
Mammals vary dramatically in lifespan, by at least two-orders of magnitude, but the molecular basis for this difference remains largely unknown. The bowhead whale Balaena mysticetus is the longest-lived mammal known, with an estimated maximal lifespan in excess of two hundred years. It is also one of the two largest animals and the most cold-adapted baleen whale species. Here, we report the first genome-wide gene expression analyses of the bowhead whale, based on the de novo assembly of its transcriptome. Bowhead whale or cetacean-specific changes in gene expression were identified in the liver, kidney and heart, and complemented with analyses of positively selected genes. Changes associated with altered insulin signaling and other gene expression patterns could help explain the remarkable longevity of bowhead whales as well as their adaptation to a lipid-rich diet. The data also reveal parallels in candidate longevity adaptations of the bowhead whale, naked mole rat and Brandt's bat. The bowhead whale transcriptome is a valuable resource for the study of this remarkable animal, including the evolution of longevity and its important correlates such as resistance to cancer and other diseases.
Keywords: bowhead whale, transcriptome, insulin/IGF1-axis, aging, evolution
INTRODUCTION
The bowhead whale (Balaena mysticetus) is a sentinel baleen whale species of the Arctic [1]. It has a suite of adaptations for life in an intensely cold and ice-bound habitat. These include the thickest blubber of any whale, primarily for lipid storage but also for effective thermoregulation, and a unique bow-shaped head that allows creation of breathing holes by breaking thick sea ice from beneath. Whales belong to the order Cetacea, which includes the suborders Mysticeti (baleen whales) and Odontoceti (toothed whales, including dolphins, porpoises, sperm whales, etc.), and is a subgroup nested within Artiodactyla (even-toed ungulates such as the hippopotamus, camels, pig, cow, etc.) [2, 3].
Cetaceans are generally long-lived species and, similarly to humans, display traits such as delayed sexual maturity, low fecundity and high survival rates. In contrast to their terrestrial relatives within the order Artiodactyla, which feed on a carbohydrate-rich diet, cetaceans subsist on a lipid-rich diet of krill and other small marine animals. The bowhead whale is the longest-lived mammal known, with an estimated maximal lifespan up to 211 years [4, 5]. The bowhead's lifespan far exceeds that of other renowned long-lived species of mammals studied for molecular insights into aging, including the naked mole rat (31 years) (Heterocephalus glaber) [6] and Brandt's bat (41 years) (Myotis brandtii) [7]. The genomic sequences of only a few cetaceans, including the minke whale (Balaenoptera acutorostrata) [8], bottlenose dolphin (Tursiops truncatus) [9], killer whale (Orcinus orca) [10] and Yangtze River dolphin (baiji; Lipotes vexillifer) [11], have been determined. However, limited access to tissues of these animals has precluded detailed analyses of biological functions based on gene expression.
As a first step in identifying such patterns, we present the liver, kidney and heart transcriptomes of the bowhead whale. Comparison of the bowhead whale transcriptome with that of the related minke whale and other mammals enabled us to identify candidate genes for the exceptional longevity of the bowhead whale as well as molecular adaptations to a lipid-rich diet. Analyses of gene sequen-ces and expression patterns also informed on various aspects of the biology and evolution of bowhead whales.
RESULTS AND DISCUSSION
We sequenced the liver, kidney and heart transcriptomes of bowhead whales by Illumina RNA-seq technology. The tissue samples (Fig. 1 and Supplemental Table 1) were sourced from native Iñupiaq Eskimo subsistence harvests in Barrow, Alaska. Using the de novo assembler Trinity [12, 13], approximately 659 million paired-end short reads from the bowhead whale were assembled into a single transcriptome per tissue (Supplemental Table 2). Using the Ensembl mouse gene dataset [14] as reference, we identified 9,395 protein-coding genes with one-to-one orthology between diverse mammalian taxa, including whales, a bat, rodents, a tree shrew and a primate (Fig. 2A).
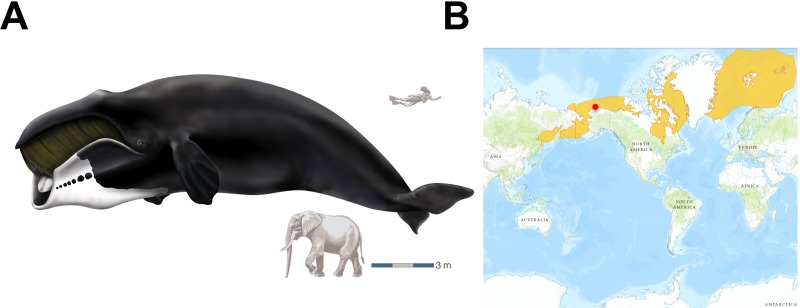
Figure 1. The bowhead whale and overview of its geographic range.
(A) Bowhead whale (Balaena mysticetus). Reproduced courtesy of Encyclopaedia Britannica, Inc., copyright 2002. Human and elephant are shown for size comparison. (B) Occurrence of B. mysticetus in Arctic waters. The site of sample collection (Barrow, Alaska) is shown as a red dot.
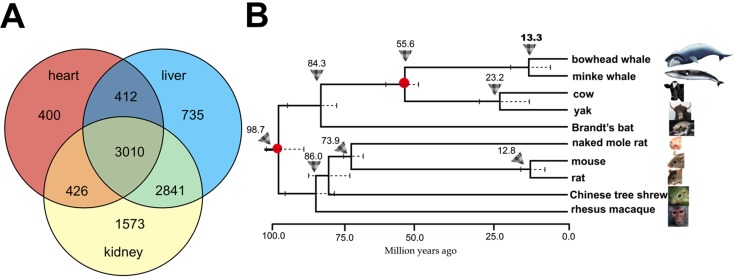
Figure 2. Overview of orthologous genes shared between the bowhead whale and other mammals and the phylogenetic position of the bowhead whale.
(A) Venn diagram showing the number of common and unique orthologs identified in the liver, kidney and heart. (B) Estimation of divergence time using phylogenetic analysis of 10 species based on 6,998 orthologous genes from the liver. Triangle arrows and the numbers above denote the most recent common ancestor (MRCA), and the scale units are million years ago. The standard error range for each divergence time is represented by a dashed line. The red solid circles on the branch nodes denote the node as an ‘age constraint’ used in the estimation of the time of divergence.
Phylogenetic analysis of the gene expression dataset revealed that the bowhead and minke whales cluster within one evolutionary branch, with a sister group comprising the cow and yak. The bowhead whale and minke whale diverged approximately 13.3 million years ago (Mya) (Fig. 2B). The estimated molecular divergence time of bowhead and minke whales is slightly less than the estimates from comprehensive morphological and molecular phylogenetic analyses of cetacean phylogeny, examining both extant and fossil lineages in simultaneous analyses [15, 16]. It is thus likely that the common ancestor of the bowhead and minke whales lived approximately 13-27 million years ago.
To reveal candidate genes important in the bowhead's longevity, we compared the bowhead whale transcriptome with that of the minke whale (maximum lifespan of 50 years in the wild [17]), cow, yak, Brandt's bat, Chinese tree shrew, naked mole rat, rhesus macaque, mouse and rat. We also identified unique amino acid changes and rapidly evolving genes in the bowhead whale that may contribute to slow aging in this species.
Liver
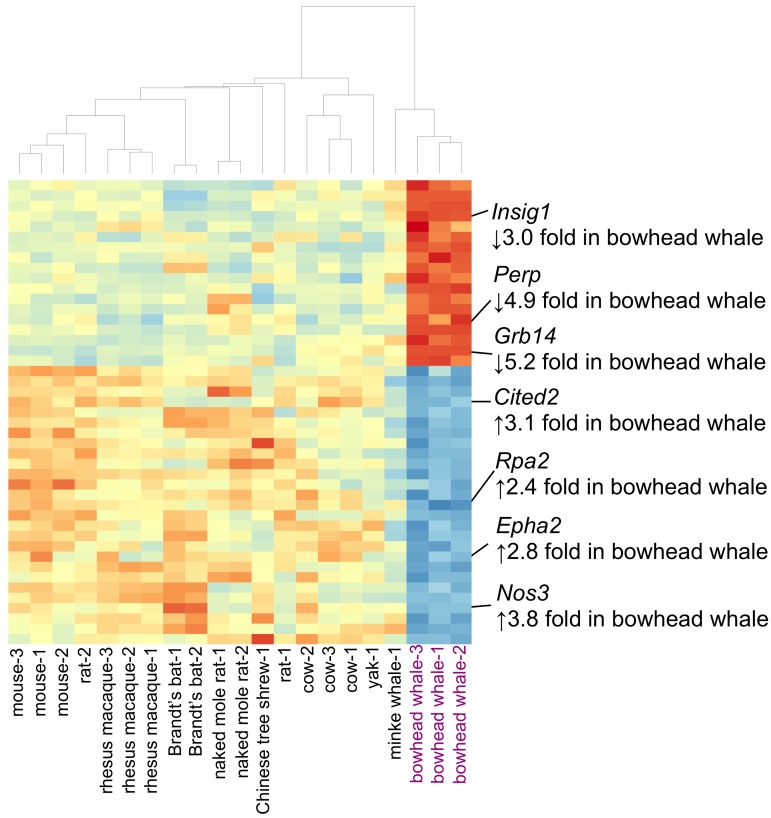
The liver performs several functions vital to whole-body homeostasis. The integrity of liver function is thus important to longevity, and this organ has gained considerable attention in aging research. A total of 45 genes were differentially expressed in the bowhead whale liver compared to other mammals (Fig. 3, and Tables 1 and 2). In particular, the bowhead whale showed greatly reduced expression of growth factor receptor-bound protein 14 (Grb14) (Fig. 4A). Grb14 is normally highly expressed in the liver and kidney of rodents and humans [18]. In contrast to the liver, Grb14 showed moderate expression in the kidney of the bowhead whale (data not shown). GRB14 binds the receptors for insulin (IR) and IGF1 (IGF1R) to modulate downstream signaling [19-22]. Insulin itself decreases endogenous glucose production (gluconeogenesis) and promotes lipogenesis. Knockout of Grb14 in mouse reduces the amount of circulating insulin and enhances insulin responsiveness in the liver [21]. Similar effects were observed in primary murine hepatocytes, where RNAi knockdown of Grb14 augmented insulin-activated signaling and associated decreased expression of genes associated with gluconeogenesis [23]. During fasting and calorie restriction hepatic gluconeogenesis is required for tissues that lack enzymes required to metabolize free fatty acids (e.g. the brain) [24]. Elevated expression of Cited2 was observed in the bowhead whale (Fig. 4B).
Figure 3. Heat map displaying 45 genes differentially expressed in the bowhead whale liver.
Genes with ≥2 log2-fold change and with a Benjamini–Hochberg false discovery rate ≤ 0.05) are shown. The color scheme was used wherein the gradient of red indicates decreased expression, and blue increased expression. Selected genes discussed in the text are highlighted. Hierarchical clustering of samples was based on Pearson's correlation of gene expression data.
Table 1. Genes differentially expressed in the liver of bowhead whales compared to other mammals.
For each gene, gene counts were normalized across all replicates. We used an absolute value of log2 Ratio≥2, a Benjamini-Hochberg corrected P-value≤ 0.05, and a B-value of at least 2.945 (representing a 95% probability that a gene is differentially expressed) as the threshold to judge the significance of gene expression difference between the bowhead whale and other mammals. A negative fold change denotes a higher gene expression compared to the other mammals examined, and vice versa.
| Gene symbol (mouse) | Ensembl transcript ID | Name | logFC | P-value | BH-adj. P-value | B-value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Adamts13 | ENSMUST00000102891 | a disintegrin-like and metallopeptidase (reprolysin type) with thrombospondin type 1 motif | −3.84 | 5.55E-006 | 8.95E-004 | 4.06 |
| Arap3 | ENSMUST00000042944 | ArfGAP with RhoGAP domain | −2.40 | 9.01E-007 | 1.96E-004 | 5.81 |
| Atp6v1b2 | ENSMUST00000006435 | ATPase | 2.94 | 1.42E-008 | 1.34E-005 | 9.66 |
| BC027231 | ENSMUST00000048788 | cDNA sequence BC027231 | −3.12 | 6.29E-007 | 1.61E-004 | 6.15 |
| Bgn | ENSMUST00000033741 | biglycan | −2.45 | 8.00E-006 | 1.13E-003 | 3.70 |
| Card10 | ENSMUST00000164826 | caspase recruitment domain family | −3.61 | 2.61E-007 | 8.67E-005 | 7.00 |
| Cited2 | ENSMUST00000038107 | Cbp/p300-interacting transactivator | −3.08 | 1.14E-005 | 1.37E-003 | 3.37 |
| Cxx1b | ENSMUST00000088778 | CAAX box 1B | −3.87 | 3.26E-007 | 9.67E-005 | 6.78 |
| Cyp2r1 | ENSMUST00000032908 | cytochrome P450 | 3.42 | 5.80E-007 | 1.56E-004 | 6.21 |
| Dtd1 | ENSMUST00000028917 | D-tyrosyl-tRNA deacylase 1 | −2.16 | 6.96E-007 | 1.64E-004 | 6.06 |
| Epg5 | ENSMUST00000044622 | ectopic P-granules autophagy protein 5 homolog (C. elegans) | −4.10 | 2.70E-006 | 5.26E-004 | 4.76 |
| Epha2 | ENSMUST00000006614 | Eph receptor A2 | −2.76 | 5.78E-006 | 8.98E-004 | 4.03 |
| Fam129b | ENSMUST00000028135 | family with sequence similarity 129 | −2.97 | 3.10E-007 | 9.67E-005 | 6.83 |
| Fam92a | ENSMUST00000108285 | family with sequence similarity 92 | 2.96 | 6.59E-007 | 1.62E-004 | 6.09 |
| Fbln5 | ENSMUST00000021603 | fibulin 5 | −4.57 | 5.76E-008 | 4.65E-005 | 8.43 |
| Grb14 | ENSMUST00000028252 | growth factor receptor bound protein 14 | 5.21 | 4.61E-009 | 5.20E-006 | 10.73 |
| Ift122 | ENSMUST00000112923 | intraflagellar transport 122 | −3.02 | 6.41E-006 | 9.52E-004 | 3.93 |
| Igj | ENSMUST00000087033 | immunoglobulin joining chain | −3.30 | 9.15E-006 | 1.20E-003 | 3.59 |
| Insig1 | ENSMUST00000059155 | insulin induced gene 1 | 3.04 | 8.94E-006 | 1.20E-003 | 3.63 |
| Ints2 | ENSMUST00000018212 | integrator complex subunit 2 | −2.85 | 5.89E-006 | 8.98E-004 | 4.01 |
| Iqsec1 | ENSMUST00000189881 | IQ motif and Sec7 domain 1 | 5.16 | 2.00E-007 | 7.52E-005 | 7.22 |
| Lgals3 | ENSMUST00000142734 | lectin | −3.58 | 1.15E-007 | 6.48E-005 | 7.78 |
| Lrrfip2 | ENSMUST00000035078 | leucine rich repeat (in FLII) interacting protein 2 | 2.61 | 2.52E-007 | 8.67E-005 | 6.99 |
| Masp2 | ENSMUST00000052060 | mannan-binding lectin serine peptidase 2 | 3.46 | 2.63E-009 | 4.94E-006 | 11.32 |
| Med28 | ENSMUST00000156481 | mediator complex subunit 28 | 3.16 | 1.93E-006 | 3.89E-004 | 5.08 |
| Nemf | ENSMUST00000021368 | nuclear export mediator factor | 3.48 | 3.17E-006 | 5.77E-004 | 4.61 |
| Ngef | ENSMUST00000068681 | neuronal guanine nucleotide exchange factor | 5.16 | 1.26E-007 | 6.48E-005 | 7.65 |
| Nos3 | ENSMUST00000030834 | nitric oxide synthase 3 | −3.58 | 7.94E-006 | 1.13E-003 | 3.72 |
| Orc5 | ENSMUST00000030872 | origin recognition complex | 2.69 | 1.92E-006 | 3.89E-004 | 5.09 |
| Pdgfrb | ENSMUST00000115274 | platelet derived growth factor receptor | −4.44 | 3.62E-006 | 6.38E-004 | 4.48 |
| Perp | ENSMUST00000019998 | PERP | 4.91 | 6.10E-010 | 3.44E-006 | 12.57 |
| Pglyrp2 | ENSMUST00000170392 | peptidoglycan recognition protein 2 | 6.23 | 1.25E-009 | 3.52E-006 | 11.93 |
| Rasip1 | ENSMUST00000057927 | Ras interacting protein 1 | −4.69 | 9.75E-008 | 6.11E-005 | 7.94 |
| Rnase4 | ENSMUST00000022428 | ribonuclease | 3.21 | 3.60E-007 | 1.01E-004 | 6.69 |
| Rpa2 | ENSMUST00000102561 | replication protein A2 | −2.42 | 2.87E-006 | 5.41E-004 | 4.70 |
| Rpusd4 | ENSMUST00000034543 | RNA pseudouridylate synthase domain containing 4 | −4.13 | 1.84E-007 | 7.52E-005 | 7.33 |
| Slc25a38 | ENSMUST00000035106 | solute carrier family 25 | 2.90 | 8.36E-007 | 1.89E-004 | 5.87 |
| Smad2 | ENSMUST00000168423 | SMAD family member 2 | 2.12 | 1.58E-005 | 1.81E-003 | 3.09 |
| Ssbp4 | ENSMUST00000049908 | single stranded DNA binding protein 4 | −2.50 | 8.39E-006 | 1.15E-003 | 3.68 |
| Tie1 | ENSMUST00000047421 | tyrosine kinase with immunoglobulin-like and EGF-like domains 1 | −3.79 | 8.04E-008 | 5.67E-005 | 8.12 |
| Timp2 | ENSMUST00000017610 | tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinase 2 | −5.09 | 3.71E-009 | 5.20E-006 | 11.02 |
| Top1 | ENSMUST00000109468 | topoisomerase (DNA) I | 2.18 | 1.07E-005 | 1.35E-003 | 3.45 |
| Vac14 | ENSMUST00000034190 | Vac14 homolog (S. cerevisiae) | −2.27 | 1.87E-007 | 7.52E-005 | 7.32 |
| Wsb1 | ENSMUST00000017821 | WD repeat and SOCS box-containing 1 | −4.40 | 1.57E-007 | 7.40E-005 | 7.48 |
| Zfp143 | ENSMUST00000084727 | zinc finger protein 143 | −2.43 | 5.19E-006 | 8.62E-004 | 4.13 |
Table 2. Enrichment of biological process (BP) Gene Ontology (GO) terms for genes differentially expressed in the bowhead liver compared to other mammals.
| GO Category | Term | Count | Genes | Fold Enrichment | Fisher's exact P-value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| GO:0001501 | skeletal system development | 4 | Epha2, Insig1, Lgals3, Pdgfrb | 7.3 | 2.00E-003 |
| GO:0048568 | embryonic organ development | 3 | Epha2, Cited2, Insig1 | 7.4 | 7.20E-003 |
| GO:0006260 | DNA replication | 3 | Orc5, Rpa2, Top1 | 6.1 | 1.30E-002 |
| GO:0040013 | negative regulation of locomotion | 2 | Arap3, Tie1 | 22.1 | 3.50E-003 |
| GO:0030336 | negative regulation of cell migration | 2 | Arap3, Tie1 | 22.1 | 3.50E-003 |
| GO:0001570 | vasculogenesis | 2 | Epha2, Cited2 | 20.6 | 4.00E-003 |
| GO:0051271 | negative regulation of cell motion | 2 | Arap3, Tie1 | 19.2 | 4.60E-003 |
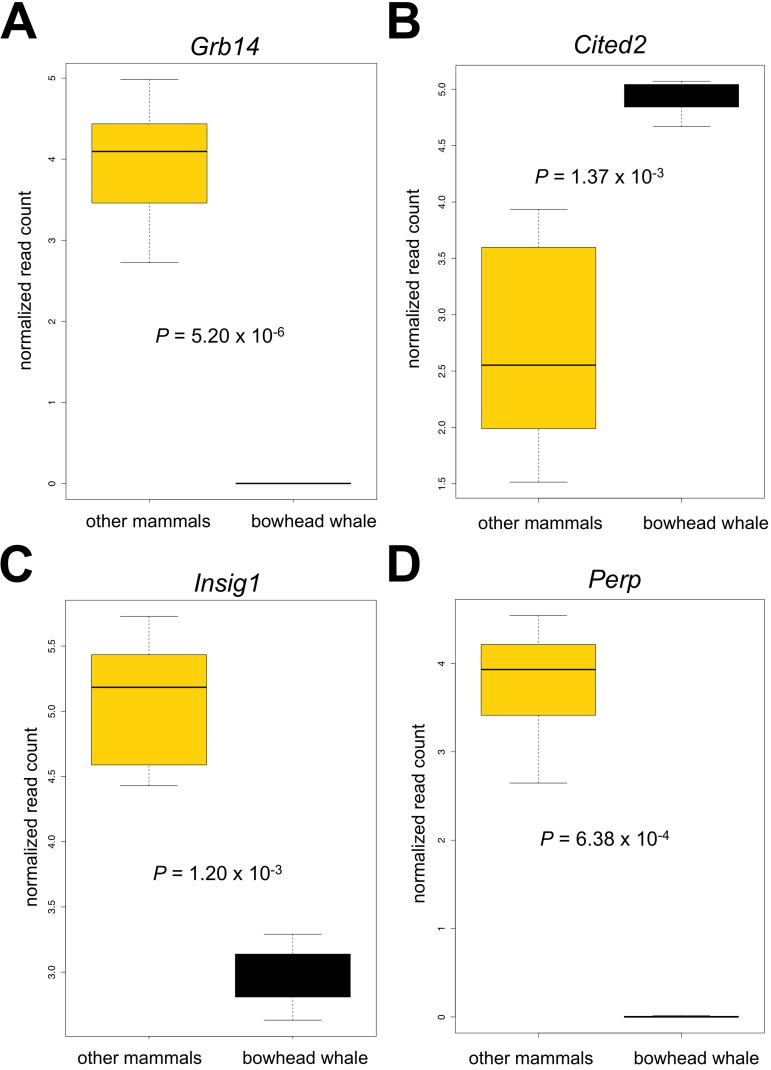
Figure 4. Boxplots of selected genes differentially expressed in the bowhead whale liver.
(A) Growth factor receptor bound protein 14 (Grb14). (B) Insulin induced gene 1 (Insig1). (C) Cbp/p300-interacting transactivator (Cited2). (D) TP53 Apoptosis Effector (Perp). Genes were subjected to limma analysis at 5% FDR and 2.0 fold-change cut-off. Normalized log2 read counts and P-values adjusted for multiple comparisons (Benjamini and Hochberg) are shown.
CITED2 is upregulated during fasting, increases the activity of transcriptional co-activator PGC-1α,and directly induces hepatic gluconeogenesis [25]. Interestingly, a recent study found that elevated PGC-1αactivity retards aging in Drosophila (26) and it has been hypothesized to also influence longevity in mammals (27). These data suggest that gluconeogenesis is sustained in the bowhead whale despite reduced expression of Grb14. Surprisingly, knockdown of Grb14 in mouse hepatocytes also potently inhibits maturation of sterol regulatory element binding transcription factor 1 (Srebf1, often denoted as SREBP1) and decreases lipogenesis, rendering lipogenic genes unresponsive to insulin [23]. In agreement, we observed decreased expression of insulin-induced gene 1 (Insig1, a downstream target of SREBP1 [23, 28-29]) in the bowhead whale liver (Fig. 4C), indicative of reduced activities along the GRB14/SREBP1 axis.
Calorie restriction and modulation of the insulin/IGF1-signaling pathway are key modulators of aging and have potent effects on lipid homeostasis [30]. Lipid metabolism, therefore, plays a central role in lifespan regulation in metazoan eukaryotes. While carbohydrates are a major contributor to metabolism of terrestrial mammals, marine mammals subsist on a high-energy, lipid-rich diet [31]. Notably, the bowhead whale diet consists of zooplankton with very high lipid content [32, 33]. Toothed whales, such as the common bottlenose dolphin, which has a maximum lifespan of ~52 years in captivity [34], can exhibit pathology that parallels type two diabetes (T2D) and metabolic syndrome of humans. This includes a high prevalence of insulin resistance, fatty liver disease, and chronic overproduction of Very-low-density lipoprotein (VLDL) by the liver (dyslipidemia) [35-37]. Our data suggest that reduced Grb14 expression in the bowhead whale improves energy homeostasis in an animal that depends on an exceptionally lipid-rich diet. This beneficial adaptation may serve to protect the long-lived bowhead whale against chronic dietary diseases.
It has been proposed that the longevity of large mammals, such as the bowhead whale and elephant, stem from a lack of non-human predators, slow development and concomitant tight control of nutrient sensing pathways, in particular the insulin/TOR signaling axis [38]. Small African mole rats and many bats live in protected environments and are long-lived relative to animals of similar size, but may in contrast have evolved genetic changes that allow them to slow down aging after a comparatively rapid development [38]. Sequence and expression changes of genes involved in hepatic metabolism have been reported for Brandt's bat [39] and naked mole rat [40], two terrestrial species in our dataset that are long-lived compared to related species. Interestingly, in agreement with the previous studies that compared a smaller set of species, we found that Foxo1 (forkhead box O1) and Fto (fat mass and obesity associated) were differentially expressed in liver of the Brandt's bat and naked mole rat, respectively (Supplemental Tables 3-6). The transcription factor FOXO1, like PGC-1α, is a classical mediator of gluconeogenesis in species ranging from worms to mammals, and Foxo1 and its upstream regulator Creb1 [24] are expressed at a higher level in the Brandt's bat liver (Supplemental Table 3). Elevated hepatic Foxo1 mRNA expression in the Brandt's bat reconciles with increased longevity in calorie restricted and growth hormone receptor knockout mice [41], the worm C. elegans [42] and the fruit fly Drosophila melanogaster [43]. This result strongly suggests that elevated hepatic Foxo1 expression contributes to the longevity of the Brandt's bat. The naked mole rat has a highly divergent insulin peptide that may be compensated by autocrine/paracrine IGF2 in the adult liver and displays physiological changes consistent with an altered insulin/IGF1 axis [40, 44]. In the naked mole rat, fat mass and obesity associated mRNA (encoded by Fto) is expressed at a lower level compared to the other species examined (Supplemental Table 5). Fto regulates glucose metabolism in the liver and its reduced expression protects against obesity and metabolic syndrome, and associated pathology such as insulin resistance [45-47]. Taken together, we propose that fundamental longevity-promoting mechanisms in the long-lived bowhead whale, Brandt's bat and naked mole rat stem from overlapping but distinct expression and sequence changes in metabolism genes.
Living under water also entails a unique set of challenges. Compared with the other mammals, the bowhead liver had lower expression of the apoptosis-associated p53 target gene Perp (TP53 Apoptosis Effector) (Fig. 4D). Under hypoxic stress, p53 is activated to trigger cellular apoptosis as a protective response, but this may not be appropriate for mammals with only intermittent assess to oxygen. It has been shown in mouse kidney that Perp knockdown protected cells from hypoxia-induced apoptosis [48]. Low levels of Perp may therefore increase stress tolerance in the bowhead whale liver. In addition, we observed increased expression of genes that enhance vasculature maintenance (EPH receptor A2 (Epha2) [49]), regulate vascular tone and proliferation (endothelial nitric oxide synthase (eNOS) (Nos3) [50, 51]) and promote DNA repair (replication protein A2 (Rpa2) [52, 53]) (Fig. 3, Tables 1 and 2), which may also represent adaptations to limited oxygen availability and water pressure in the aquatic environment.
Cardiovascular system
Other extraordinarily long-lived species, such as the naked mole rat, possess biological adaptations endowing resilience to aging-related diseases, including cardiovascular disease and cancer [54, 55]. The availability of a single heart sample precluded differential gene expression analysis of the bowhead whale alone. Using transcriptome data from a bowhead whale heart and a minke whale heart [8], we compared these marine mammals to the terrestrial ones and identified four differentially expressed genes in whales (Table 3). Of these, argininosuccinate lyase (Asl) is particularly interesting. The expression of Asl, which is essential for NO production in the heart [56], was 4.4-fold higher in the whales (Table 3). Reduction of nitrite to nitric oxide (NO) provides cytoprotection of tissues during hypoxic events [57] and serves to preserve cardiac function in the diving and hibernating red-eared slider turtle (Trachemys scripta elegans) [58]. Cardiovascular regulation is critical during diving in all marine mammal species, and evidence suggests that hypoxia-sensitive tissues such as the brain and heart have adapted to low oxygen conditions while diving [59]. We speculate that elevated expression of Asl improves cardiac metabolism and function of diving cetaceans.
Table 3. Genes differentially expressed in the bowhead and minke whale heart compared to other mammals.
For each gene, gene counts were normalized across all replicates. We used an absolute value of log2 Ratio≥2, a Benjamini-Hochberg corrected P-value≤ 0.05, and a B-value of at least 2.945 (representing a 95% probability that a gene is differentially expressed) as the threshold to judge the significance of gene expression difference between whales and other mammals. A negative fold change denotes a higher gene expression compared to the other mammals examined, and vice versa.
| Gene symbol (mouse) | Ensembl transcript ID | Name | logFC | P-value | BH-adj. P-value | B-value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Asl | ENSMUST00000161094 | argininosuccinate lyase | −4.40 | 1.43E-005 | 1.50E-002 | 3.19 |
| Brk1 | ENSMUST00000035725 | BRICK1, SCAR/WAVE actin-nucleating complex subunit | −2.85 | 5.69E-006 | 7.93E-003 | 3.96 |
| Eif3l | ENSMUST00000040518 | eukaryotic translation initiation factor 3, subunit L | −2.46 | 2.28E-006 | 4.77E-003 | 4.95 |
| Htatip2 | ENSMUST00000085272 | HIV-1 tat interactive protein 2, homolog (human) | −6.00 | 1.40E-007 | 5.87E-004 | 6.99 |
Amino-acid residues that are uniquely altered in a lineage can reveal clues to functional adaptations [39, 60]. In addition to differential gene expression patterns, we identified a unique amino acid change with potential relevance to vascular aging in the bowhead whale (Table 4). An examination of 68 vertebrate genomes, including 6 cetaceans (Supplemental Table 7), revealed a unique amino acid change in bowhead whale c-fos induced growth factor (Figf, coding for vascular endothelial growth factor D, VEGFD) (Fig. 5). VEGFD plays a role in the maintenance of vascular homeostasis [61, 62]. The radical amino acid change, neutral polar residues replaced by a charged residue (SerThrGln174Arg), in bowhead whale VEGFD flanks a large hydrophobic surface that interacts with the cognate receptor VEGFR-2 [63]. Although this finding must be corroborated with experimental data, we speculate that the arginine substitution may serve to improve the interaction of VEGFD with its cognate receptor, potentially aiding maintenance of vascular health in bowhead whales.
Table 4. Proteins with unique amino acids in the bowhead whale compared to 67 vertebrates.
AA changes correspond to residue locations in the translated human RefSeq mRNA entry (typically the longest RefSeq entry of each gene). Genes shown in bold were checked by BLAST analysis of raw sequence data. Some of the genes in this table, especially those not shown in bold, may be false-positives.
| Gene name | Symbol (human) | RefSeq ID | AA change(s) |
|---|---|---|---|
| actin-binding Rho activating protein | ABRA | NM_139166 | HKR283P |
| adaptor-related protein complex 3, beta 1 subunit | AP3B1 | NM_003664 | R1086Q |
| annexin A7 | ANXA7 | NM_001156 | Y410C |
| arachidonate 5-lipoxygenase | ALOX5 | NM_000698 | D204N |
| calcium homeostasis modulator 2 | CALHM2 | NM_015916 | F172C |
| calsyntenin 2 | CLSTN2 | NM_022131 | Q362H |
| cell division cycle associated 7 | CDCA7 | NM_145810 | ED257K |
| c-fos induced growth factor (vascular endothelial growth factor D) | FIGF | NM_004469 | STQ174R |
| ClpB caseinolytic peptidase B homolog (E. coli) | CLPB | NM_001258392 | HR226W |
| complement component 5 | C5 | NM_001735 | I760K |
| cytidine and dCMP deaminase domain containing 1 | CDADC1 | NM_030911 | YQ367C |
| derlin 1 | DERL1 | NM_024295 | R197G |
| enhancer of polycomb homolog 1 (Drosophila) | EPC1 | NM_001272004 | G562R |
| erythrocyte membrane protein band 4.1-like 1 | EPB41L1 | NM_001258329 | K478M |
| fucose-1-phosphate guanylyltransferase | FPGT | NM_003838 | HK339E |
| gem (nuclear organelle) associated protein 4 | GEMIN4 | NM_015721 | KR721T |
| gigaxonin | GAN | NM_022041 | E74V |
| glutamate receptor, ionotropic, kainate 2 | GRIK2 | NM_175768 | Y571C, Q621R |
| glutamate receptor, metabotropic 1 | GRM1 | NM_001278066 | E559D |
| heat shock protein 90kDa alpha (cytosolic), class B member 1 | HSP90AB1 | NM_001271971 | H121T |
| homeodomain interacting protein kinase 1 | HIPK1 | NM_181358 | SP465C |
| homeodomain interacting protein kinase 3 | HIPK3 | NM_005734 | Q698H |
| ligase III, DNA, ATP-dependent | LIG3 | NM_013975 | D255N |
| mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase kinase 7 | MAP3K7 | NM_145331 | V424D |
| MMS19 nucleotide excision repair homolog (S. cerevisiae) | MMS19 | NM_022362 | SLT202C |
| Nance-Horan syndrome (congenital cataracts and dental anomalies) | NHS | NM_001291868 | R388Q |
| NEDD4 binding protein 3 | N4BP3 | NM_015111 | Q384H |
| neuronal pentraxin II | NPTX2 | NM_002523 | Q375H |
| NOP2 nucleolar protein | NOP2 | NM_001258310 | YF516C |
| NRDE-2, necessary for RNA interference, domain containing | NRDE2 | NM_017970 | H592Q |
| nuclear receptor coactivator 2 | NCOA2 | NM_006540 | F441C |
| nuclear receptor coactivator 7 | NCOA7 | NM_181782 | SAT160D |
| nucleolar protein 6 (RNA-associated) | NOL6 | NM_022917 | R582L |
| oncoprotein induced transcript 3 | OIT3 | NM_152635 | P353R |
| oxidative stress induced growth inhibitor family member 2 | OSGIN2 | NM_004337 | ED194K |
| PALM2-AKAP2 readthrough | PALM2-AKAP2 | NM_147150 | ED488G |
| patched 1 | PTCH1 | NM_000264 | S1185C |
| phosphodiesterase 4D interacting protein | PDE4DIP | NM_001002811 | SGNTP264R |
| polymerase (DNA-directed), delta interacting protein 3 | POLDIP3 | NM_032311 | Q198R |
| potassium voltage-gated channel, Shal-related subfamily, member 2 | KCND2 | NM_012281 | L457R |
| protein kinase, cAMP-dependent, regulatory, type I, alpha | PRKAR1A | NM_212472 | N26D |
| protocadherin alpha subfamily C, 2 | PCDHAC2 | NM_018899 | K884Q |
| serpin peptidase inhibitor, clade C (antithrombin), member 1 | SERPINC1 | NM_000488 | E359D |
| striatin, calmodulin binding protein | STRN | NM_003162 | ED279V |
| transmembrane protein 214 | TMEM214 | NM_017727 | R251Q |
| transmembrane protein 25 | TMEM25 | NM_032780 | G162D |
| tripartite motif containing 29 | TRIM29 | NM_012101 | Q250H |
| tyrosine aminotransferase | TAT | NM_000353 | Y442H |
| vacuolar protein sorting 13 homolog B (yeast) | VPS13B | NM_015243 | G567R |
Figure 5. Evolution of vertebrate VEGFD protein sequences.
(A) Alignment of vertebrate VEGFD protein sequences. VEGFD residues at the VEGFR-2 receptor-ligand interface are highlighted in yellow, highly conserved cysteine residues that stabilize VEGFD in orange, and a radical amino acid in the bowhead whale, but not in 67 other species, is shown in red. (B) Modeled VEGFD structure. Location of the unique arginine residue in the bowhead whale protein is shown.
Kidney
Aging-induced changes in the kidney include reduced repair and/or regeneration of cells, which is concomitant with decreases in glomerular filtration rate and blood flow [64, 65]. Comparison of the bowhead whale kidney transcriptome with those of other mammals revealed that 53 genes were differentially expressed in the bowhead whale kidney (Tables 5 and 6). Among these was a battery of DNA repair associated genes. For example, SprT-like N-terminal domain (Sprtn) [66]; non-SMC condensin I complex, subunit D2 (Ncapd2) [67]; ligase I, DNA, ATP-dependent (Lig1) [68]; and Rpa2 [52, 53] which also was elevated in the liver, were expressed at higher levels in the bowhead whale kidney (Table 5). The mitochondrial stress inhibitor Junb [69], as well as genes associated with tumor suppression, was also expressed at higher levels in the bowhead whale kidney. These latter genes included E4F transcription factor 1 (E4fl) which directly interacts with the tumor suppressors p53, RASSF1A, pRB and p14ARF [70]; ADP-ribosylation factor-like 2 (Arl2) [71]; protein kinase C, delta binding protein (Prkcdbp; also known as hSRBC) [72, 73]; and Egr1 [74]. We speculate that this series of genes protect against age-related kidney tissue decline in the bowhead whale.
Table 5. Genes differentially expressed in the kidney of bowhead whales compared to other mammals.
For each gene, gene counts were normalized across all replicates. We used an absolute value of log2 Ratio≥2, Benjamini-Hochberg corrected P-value≤ 0.05 a B-value of at least 2.945 (representing a 95% probability that a gene is differentially expressed) as the threshold to judge the significance of gene expression difference between the bowhead whale and other mammals. A negative fold change denotes a higher gene expression compared to the other mammals examined, and vice versa.
| Gene symbol (mouse) | Ensembl transcript ID | Name | logFC | P-value | BH-adj. P-value | B-value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Adamts1 | ENSMUST00000023610 | a disintegrin-like and metallopeptidase (reprolysin type) with thrombospondin type 1 motif, 1 | −2.08 | 2.6E-07 | 1.0E-04 | 6.98 |
| Ankrd6 | ENSMUST00000035719 | ankyrin repeat domain 6 | −3.37 | 2.5E-06 | 3.2E-04 | 4.84 |
| Arhgef19 | ENSMUST00000006618 | Rho guanine nucleotide exchange factor (GEF) 19 | −3.41 | 2.9E-07 | 1.0E-04 | 6.89 |
| Arl2 | ENSMUST00000025893 | ADP-ribosylation factor-like 2 | −2.36 | 1.2E-06 | 2.2E-04 | 5.52 |
| Atp5g2 | ENSMUST00000185641 | ATP synthase, H+ transporting, mitochondrial F0 complex, subunit C2 (subunit 9) | −2.22 | 8.6E-07 | 1.8E-04 | 5.83 |
| Cdh3 | ENSMUST00000080797 | cadherin 3 | −3.41 | 7.6E-06 | 6.6E-04 | 3.73 |
| Cep170 | ENSMUST00000057037 | centrosomal protein 170 | −2.71 | 1.5E-06 | 2.3E-04 | 5.36 |
| Cpsf3l | ENSMUST00000030901 | cleavage and polyadenylation specific factor 3-like | −2.44 | 3.3E-06 | 3.9E-04 | 4.52 |
| Cxx1b | ENSMUST00000088778 | CAAX box 1B | −2.29 | 1.6E-06 | 2.3E-04 | 5.25 |
| Dennd4b | ENSMUST00000098914 | DENN/MADD domain containing 4B | −2.68 | 2.3E-06 | 3.0E-04 | 4.92 |
| E4f1 | ENSMUST00000056032 | E4F transcription factor 1 | −2.08 | 1.7E-05 | 1.1E-03 | 2.99 |
| Egr1 | ENSMUST00000064795 | early growth response 1 | −4.04 | 2.2E-07 | 9.4E-05 | 7.16 |
| Epb4.1l2 | ENSMUST00000053748 | erythrocyte protein band 4.1-like 2 | −2.41 | 2.2E-08 | 2.0E-05 | 9.36 |
| Fancg | ENSMUST00000030165 | Fanconi anemia, complementation group G | −3.22 | 1.0E-05 | 7.6E-04 | 3.51 |
| Galnt11 | ENSMUST00000045737 | UDP-N-acetyl-alpha-D-galactosamine:polypeptide N-acetylgalactosaminyltransferase 11 | 2.33 | 7.9E-06 | 6.6E-04 | 3.69 |
| Gja4 | ENSMUST00000053753 | gap junction protein, alpha 4 | −3.17 | 7.3E-08 | 4.8E-05 | 8.21 |
| Gltscr2 | ENSMUST00000044158 | glioma tumor suppressor candidate region gene 2 | −2.60 | 2.2E-08 | 2.0E-05 | 9.40 |
| Hdac11 | ENSMUST00000041736 | histone deacetylase 11 | −2.01 | 8.3E-07 | 1.8E-04 | 5.89 |
| Heatr1 | ENSMUST00000059270 | HEAT repeat containing 1 | 2.60 | 1.2E-06 | 2.2E-04 | 5.47 |
| Hecw2 | ENSMUST00000120904 | HECT, C2 and WW domain containing E3 ubiquitin protein ligase 2 | −2.62 | 7.8E-07 | 1.8E-04 | 5.94 |
| Hoxa5 | ENSMUST00000048794 | homeobox A5 | −3.44 | 7.9E-06 | 6.6E-04 | 3.73 |
| Igsf11 | ENSMUST00000023478 | immunoglobulin superfamily, member 11 | 4.09 | 9.2E-07 | 1.9E-04 | 5.72 |
| Junb | ENSMUST00000064922 | jun B proto-oncogene | −3.44 | 1.5E-06 | 2.3E-04 | 5.29 |
| Klf9 | ENSMUST00000036884 | Kruppel-like factor 9 | 2.26 | 9.3E-06 | 7.2E-04 | 3.60 |
| Lig1 | ENSMUST00000177588 | ligase I, DNA, ATP-dependent | −2.50 | 9.3E-06 | 7.2E-04 | 3.54 |
| Lrfn4 | ENSMUST00000113822 | leucine rich repeat and fibronectin type III domain containing 4 | −2.78 | 5.0E-07 | 1.4E-04 | 6.37 |
| Marc2 | ENSMUST00000068725 | mitochondrial amidoxime reducing component 2 | 5.01 | 2.6E-07 | 1.0E-04 | 6.90 |
| Ncapd2 | ENSMUST00000043848 | non-SMC condensin I complex, subunit D2 | −2.14 | 1.3E-08 | 1.5E-05 | 9.91 |
| Ncs1 | ENSMUST00000000199 | neuronal calcium sensor 1 | −2.40 | 8.7E-07 | 1.8E-04 | 5.84 |
| Nfya | ENSMUST00000046719 | nuclear transcription factor-Y alpha | 3.45 | 2.2E-07 | 9.4E-05 | 7.02 |
| Nipsnap3b | ENSMUST00000015391 | nipsnap homolog 3B (C. elegans) | −2.47 | 5.0E-06 | 5.0E-04 | 4.18 |
| Nle1 | ENSMUST00000103213 | notchless homolog 1 (Drosophila) | −3.32 | 7.1E-10 | 2.6E-06 | 12.57 |
| Nme6 | ENSMUST00000035053 | NME/NM23 nucleoside diphosphate kinase 6 | 2.34 | 4.7E-07 | 1.4E-04 | 6.30 |
| Nr4a1 | ENSMUST00000023779 | nuclear receptor subfamily 4, group A, member 1 | −5.09 | 1.5E-07 | 7.7E-05 | 7.53 |
| Palld | ENSMUST00000121785 | palladin, cytoskeletal associated protein | 4.13 | 7.0E-09 | 1.3E-05 | 10.13 |
| Pmf1 | ENSMUST00000056370 | polyamine-modulated factor 1 | −2.39 | 8.1E-06 | 6.7E-04 | 3.72 |
| Pomk | ENSMUST00000061850 | protein-O-mannose kinase | −2.21 | 1.0E-06 | 2.0E-04 | 5.72 |
| Por | ENSMUST00000005651 | P450 (cytochrome) oxidoreductase | 2.49 | 4.8E-06 | 5.0E-04 | 4.18 |
| Prelid1 | ENSMUST00000021942 | PRELI domain containing 1 | 2.72 | 1.4E-07 | 7.7E-05 | 7.56 |
| Prkcdbp | ENSMUST00000047040 | protein kinase C, delta binding protein | −3.03 | 1.6E-06 | 2.3E-04 | 5.25 |
| Psmg3 | ENSMUST00000031531 | proteasome (prosome, macropain) assembly chaperone 3 | −2.12 | 3.8E-06 | 4.3E-04 | 4.43 |
| Rpa2 | ENSMUST00000102561 | replication protein A2 | −2.61 | 1.2E-08 | 1.5E-05 | 9.95 |
| Rpl10 | ENSMUST00000008826 | ribosomal protein L10 | −2.37 | 7.7E-07 | 1.8E-04 | 5.93 |
| Rps17 | ENSMUST00000080813 | ribosomal protein S17 | −2.34 | 1.1E-05 | 7.9E-04 | 3.33 |
| Scg5 | ENSMUST00000024005 | secretogranin V | −2.81 | 6.8E-07 | 1.7E-04 | 6.07 |
| Sema4c | ENSMUST00000114991 | sema domain, immunoglobulin domain (Ig), transmembrane domain (TM) and short cytoplasmic domain, (semaphorin) 4C | −2.55 | 1.4E-07 | 7.7E-05 | 7.58 |
| Sprtn | ENSMUST00000034467 | SprT-like N-terminal domain | −2.14 | 1.6E-06 | 2.3E-04 | 5.25 |
| St7 | ENSMUST00000081635 | suppression of tumorigenicity 7 | 2.56 | 9.5E-06 | 7.3E-04 | 3.58 |
| Syf2 | ENSMUST00000030622 | SYF2 homolog, RNA splicing factor (S. cerevisiae) | 2.03 | 1.2E-05 | 8.6E-04 | 3.33 |
| Tle2 | ENSMUST00000146358 | transducin-like enhancer of split 2, homolog of Drosophila E(spl) | −2.60 | 1.6E-06 | 2.3E-04 | 5.25 |
| Traf1 | ENSMUST00000172159 | TNF receptor-associated factor 1 | −3.11 | 1.2E-06 | 2.2E-04 | 5.56 |
| Usp9x | ENSMUST00000089302 | ubiquitin specific peptidase 9, X chromosome | 5.60 | 5.1E-11 | 3.7E-07 | 14.39 |
| Zdhhc1 | ENSMUST00000044286 | zinc finger, DHHC domain containing 1 | −2.16 | 3.7E-09 | 8.9E-06 | 11.09 |
Table 6. Enrichment of biological process (BP) Gene Ontology (GO) terms for genes differentially expressed in the kidney of bowhead whales compared to other mammals.
| GO Category | Term | Count | Genes | Fold Enrichment | Fisher's exact P-value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| GO:0000087 | M phase of mitotic cell cycle | 8 | Usp9x, E4f1, Pmf1, Ncapd2 | 6.1 | 3.80E-003 |
| GO:0007067 | mitosis | 8 | Usp9x, E4f1, Pmf1, Ncapd2 | 6.1 | 3.80E-003 |
| GO:0000280 | nuclear division | 8 | Usp9x, E4f1, Pmf1, Ncapd2 | 6.1 | 3.80E-003 |
| GO:0006350 | transcription | 20 | Egr1, Klf9, Hoxa5, Nr4a1, Tle2, E4f1, Hdac11, Nfya, Pmf1, Junb | 2.2 | 1.10E-002 |
| GO:0048285 | organelle fission | 8 | Usp9x, E4f1, Pmf1, Ncapd2 | 5.9 | 4.40E-003 |
| GO:0000279 | M phase | 8 | Usp9x, E4f1, Pmf1, Ncapd2 | 4.9 | 8.40E-003 |
| GO:0000278 | mitotic cell cycle | 8 | Usp9x, E4f1, Pmf1, Ncapd2 | 4.8 | 8.80E-003 |
| GO:0022403 | cell cycle phase | 8 | Usp9x, E4f1, Pmf1, Ncapd2 | 4.2 | 1.40E-002 |
| GO:0051301 | cell division | 8 | Usp9x, E4f1, Pmf1, Ncapd2 | 4.1 | 1.60E-002 |
| GO:0001825 | blastocyst formation | 4 | Nle1, Junb | 24.7 | 2.80E-003 |
| GO:0045449 | regulation of transcription | 20 | Egr1, Klf9, Hoxa5, Nr4a1, Tle2, E4f1, Hdac11, Nfya, Pmf1, Junb | 1.8 | 4.00E-002 |
Expanding on the theme of improved genome integrity and repair, we found a radical amino acid change SerLeuThr202Cys in the HEAT2 domain of bowhead whale MMS19 nucleotide excision repair homolog (encoded by Mms19) (Table 4). This highly conserved protein plays an essential role in genome stability by facilitating iron-sulfur (FeS) cluster insertion into proteins involved in methionine biosynthesis, DNA replication and repair and telomere maintenance [75, 76]. Reactive cysteines in assembly complex proteins, such as MMS19, assist in the transfer of FeS clusters to target proteins [77]. The amino acid change in bowhead whale MMS19 may confer systemic robustness to damage and/or longevity.
Rapid gene evolution analysis
Identification of positively selected genes can reveal insights into unique adaptations. Of the 9,395 1:1 orthologs from the species shown in Fig. 2B, eight genes showed evidence of positive selection in the bowhead whale lineage (Table 7). Similar to comparisons between human and other primates [78], the small number of positively selected genes in the Arctic bowhead whale may reflect a reduced efficacy of natural selection. Indeed, the bowhead whale has a long generation time (~50 years) and a small population size compared to the common minke whale and the other mammals examined here [79]. Unique amino acid changes were recently identified in cetacean haptoglobin (encoded by Hp) [8], a protein that protects against hemoglobin-driven oxidative stress [80]. Hp is under positive selection in the bowhead whale (Table 7), suggesting that this gene is rapidly evolving in the long-lived bowhead. Four positively selected genes in the bowhead whale lineage have roles in cancer: mitochondrial tumor suppressor 1 (Mtus1) [81]; glycogen synthase kinase 3 alpha (Gsk3a) and prune exopolyphosphatase (Prune), which act in concert to regulate cell migration [82]; and cytoplasmic FMR1 interacting protein 1 (Cyfip1) [83].
Table 7. Positively selected genes in the bowhead whale.
| Gene symbol (mouse) | Ensembl transcript ID | Gene description |
|---|---|---|
| BC026585 | ENSMUST00000046743 | quinone oxidoreductase-like protein 2-like |
| Cyfip1 | ENSMUST00000032629 | cytoplasmic FMR1 interacting protein 1 |
| Ecm1 | ENSMUST00000117507 | extracellular matrix protein 1 |
| Gsk3a | ENSMUST00000071739 | glycogen synthase kinase 3 alpha |
| Gtf2i | ENSMUST00000059042 | general transcription factor II I |
| Hp | ENSMUST00000074898 | haptoglobin |
| Mtus1 | ENSMUST00000059115 | mitochondrial tumor suppressor 1 |
| Prune | ENSMUST00000015855 | prune exopolyphosphatase |
Concluding comments
Here, we report the transcriptome of the bowhead whale, the longest-lived mammal known. We compared the gene expression of the bowhead whale to shorter-lived mammals, including the minke whale which we estimate to have diverged from a common ancestor approximately 13-27 million years ago (Mya). This is similar to the great apes (gorillas, chimpanzees, orangutans and humans) which share a common ancestor ~13 Mya [84], or human and rhesus macaques which diverged ~25 Mya [85]. Among higher primates, humans are exceptionally long-lived [86]. Similarly, the bowhead whale has increased maximum lifespan compared to related cetaceans. It has been proposed that the difference in longevity between humans and other primates stems from differential expression of a small number of genes [87]. A recent study comparing humans to eight other mammals, including primates, revealed that 93 liver and 253 kidney genes showed evidence of human lineage-specific expression changes [88]. The number of genes differentially expressed in the bowhead whale liver (45 genes) and kidney (53 genes) compared to other mammals is similar, albeit obtained using a different computational method. We speculate that the genes differentially expressed, with unique coding sequence changes and rapidly evolving in the bowhead whale, represent candidate longevity-promoting genes. We particularly stress the findings suggestive of altered insulin signaling and adaptation to a lipid-rich diet. The availability of a single heart tissue sample from the bowhead whale precluded identification of distinct gene expression patterns in the long-lived bowhead whale, but revealed that argininosuccinate lyase (Asl) may protect the heart of cetaceans during hypoxic events such as diving. The bowhead whale transcriptome provides valuable resource for further research, including genome annotation and analysis, the evolution of longevity, adaptation to an aquatic environment, conservation efforts and as a reference for closely related species.
METHODS
Animals
Kidney (n=4), liver (n=3) and heart (n=1) tissues were obtained from bowhead whales (Balaena mysticetus) captured during the 2010 native Iñupiaq Eskimo subsistence harvests in Barrow, AK, USA. See Supplemental Table 1 for details. A species range map, which includes all five stocks of bowhead whales, was obtained from the IUCN Red List of Threatened Species (http://www.iucnredlist.org).
Transcriptome sequencing
Total RNA was isolated from frozen tissues using a RNAqueous kit (Life Technologies, Carlsland, CA, USA). Short-insert ‘paired-end’ libraries were prepared using the Illumina TruSeq Sample Preparation Kit v2 and Illumina HiSeq 2000 next-generation sequencing was performed following the manufacturer's instructions (Illumina, San Diego, CA, USA). Libraries were sequenced bi-directionally (101 bp in each direction) on the Illumina HiSeq 2000 Genome Analyzer platform.
de novo transcriptome assembly
We obtained and performed RNA-seq on independent biological replicates of bowhead whales (3 liver, 4 kidney and 1 heart samples) (Supplemental Table 1). In addition, publicly available Illumina HiSeq 2000 RNA-seq data were obtained from the following species: the common minke whale Balaenoptera acutorostrata (1 liver, 1 kidney, 1 heart) [8], cow Bos taurus (3 livers, 3 kidneys, 3 hearts) [89], (domestic) yak Bos grunniens (1 liver, 1 heart) [90], Brandt's bat Myotis brandtii (2 livers, 2 kidneys – all from summer active bats) [39], naked mole rat Heterocephalus glaber (2 livers, 2 kidneys) [91], Chinese tree shrew Tupaia chinensis (1 liver, 1 kidney, 1 heart) [92], mouse Mus musculus (3 livers, 3 kidneys, 2 hearts) [93], rat Rattus norvegicus (2 livers, 3 kidneys, 2 hearts) [89] and rhesus macaque Macaca mulatta (3 livers, 3 kidneys, 2 hearts) [89]. Prior to assembly, all reads (in FASTQ format) were filtered for adapter contamination, ambiguous residues (N's) and low quality regions using nesoni v0.123 (http://www.vicbioinformatics.com/software.nesoni.shtml) with default settings. Trimmed read quality was visualized using FastQC (http://www.bioinformatics.bbsrc.ac.uk/projects/fastqc). For each species, trimmed reads from a tissue were pooled and assembled using Trinity v20140717 [12,13] with default parameters. Assembly statistics can be found in Supplemental Table 2.
Ortholog annotation
To identify orthologous protein-coding transcripts we employed a custom pipeline written in the R statistical computing language [93]. First, we extracted the longest open reading frame for each gene in Mouse Ensembl gene data set GRCm38.p2 (hereafter termed “Reference ORF”) and confirmed they were all in frame, had start and stop codons, and did not have internal stop codons. For genes with multiple alternatively spliced transcripts, the longest transcript was kept. Putative orthologs between the mouse and Trinity assembled transcriptomes (each Trinity transcriptome contains a set of Trinity Transcripts) were identified by a bidirectional best-hit method by discontiguous MegaBLAST. MegaBLAST is bundled in v2.2.29 of the BLAST+ suite and optimized to find long cross-species alignments of highly similar sequences [94]. An “ortholog pair” was declared if a Reference ORF and a Trinity Transcript were mutual best hits and an “ortholog set” was declared if such ortholog pairs could be identified in all species. We further refined the sequences in each ortholog set as follows: they must have a start and stop codons in at least 80% of the sequences in the set; and they must be within ±50% of the median length of the sequences in the set.
Analysis of differential gene expression
For each species, trimmed RNA-seq reads (in FASTQ format) for each biological replicate were aligned to ortholog sets using TopHat2 [95] and read counting was performed using featureCounts [96]. Raw counts were normalized by Trimmed Mean of M-values (TMM) correction [97] using the R package edgeR [98]. Library size normalized read counts were next subjected to the voom function (variance modeling at the observation-level) function in limma R package v3.18.13 [99] with trend=TRUE for the eBayes function and correction for multiple testing (Benjamini–Hochberg false discovery rate of 0.05). Following limma analysis, strict parameters were set to denote genes as differentially expressed between the bowhead whale and other mammals: significant genes required a log2 fold-change of at least 2.0, a Benjamini Hochberg-adjusted P-value less than or equal to 0.05, and a B-value of least 2.945; representing a 95% probability that each gene was differentially expressed.
Phylogenetic analysis
Orthologs identified from ten de novo liver transcriptome assemblies were joined into one ‘super gene’ for each species. Briefly, nucleotide sequences were aligned with ClustalO v1.2.1 [100] and trimmed using Gblocks v0.91b, preserving codon information [101, 102]. A ML (Maximal Likelihood) phylogenetic tree was constructed in RAxML8.0.0 [103] using all codons included and the first and second codon respectively. The best likelihood trees were searched under the GTR-GAMMA model with six categories of rate variation (500 bootstrap replicates were undertaken for estimation of node support). Bayesian molecular dating was adopted to estimate species divergence time using MCMCTree implemented in PAML (v4.4b) [104]. For each Bayesian analysis, 2,000,000 generations of MCMC (Markov chain Monte Carlo) analysis of phylogenetic trees were performed, with the first 2,000 generations discarded as burn-in. The remaining trees were sampled every 100 generations to build consensus trees. Calibration times (50-60 Mya) of divergence between Cetacea (includes the bowhead whale and minke whale) and Artiodactyla (includes the cow and yak) were obtained from fossil records [2, 3].
Identification of proteins with unique amino acid changes
To obtain single best orthologs to human RefSeq proteins, as in the UCSC human 100 species multiple alignment track [105], Trinity FASTA files of the bowhead whale kidney (n=4) and liver (n=3) were concatenated and putative open reading frames (ORFs) identified using the Perl script TransDecoder bundled with Trinity [13]. Next, to associate predicted bowhead whale peptide sequences with human RefSeq IDs, tBLASTn v2.2.29+ of the BLAST+ suite [94] with an E-value cut-off set at 1e-5 was employed. The best match (>50% overall amino acid sequence identity along the entire sequence and spanning >75% of the length of the query sequence) was used to annotate the sequences. Protein sequences from the the toothed whales the bottlenose dolphin (Tursiops truncatus) and the killer whale (Orcinus orca) were available in the UCSC multiple alignment track. The genomes of an additional baleen whale, the minke whale (Balaenoptera acutorostrata) [8] (GenBank Assembly GCF_000493695.1), and two toothed whales: the sperm whale (Physeter catodon) (NCBI Assembly GCF_000472045.1) and the Yangtze River dolphin (Lipotes vexillifer) [11] (GenBank Assembly GCF_000442215.1) were queried using human UCSC multiway coding sequences and gmap v2014-07-28 (a genomic mapping and alignment program for mRNA and EST sequences) [106] with the parameters --cross-species --align --direction=sense_force -Y. The gmap output was parsed using custom Perl scripts. Bowhead whale proteins were aligned to orthologs from 67 vertebrate species (Supplemental Table 7) using ClustalO v1.2.1 [100].
In-house Perl scripts were used to parse the ClustalO output and identify unique amino acids. A Perl script scanned orthologous proteins for sites where types/groups of residues unique to the bowhead whale. The script groups residues into four groups: acidic (ED), basic (KHR), cysteine (C) and “other” (STYNQGAVLIFPMW). For example, it identifies cases where the bowhead whale harbors E or D, whilst the other organisms contain exclusively basic, cysteine, or “other” residues at that particular site. The false positive rate of the detection of unique amino acids is approximately 1.33 per analysis; or in other words, one false positive per 315 unique amino acid residue candidates [39]. To validate the results pertaining to specific genes, we manually inspected multiple sequence alignments and interrogated raw bowhead whale transcriptome data for selected genes. We appreciate that, in lieu of lack of bowhead whale genome data, unique amino acid inferences are putative when supported by a limited number of RNA-sequencing reads.
Identification of genes under positive selection in the bowhead whale
The orthologous gene set (9,395 protein-coding genes) identified in our R pipeline was aligned by ClustalO [100]. We next employed Gblocks [101, 102] to minimise the impact of multiple sequence alignment errors and divergent regions. We used the program CodeML in the PAML v4.6 package to perform the optimized branch-site test [104, 107], as described previously [39]. Briefly, we compared PAML modelA1 (where codons evolve neutrally and under purifying selection) with ModelA (where codons on the branch of interest can be under positive selection). Following PAML analysis, likelihood ratio test (LRT) P-values were computed assuming that the null distribution was a chi-squared distribution with 1 degree of freedom at a false discovery rate of 0.05. We applied a sequential Bonferroni correction to account for the multiple comparisons made in these analyses. Manual inspection of positive selection data is currently recommended in the literature [108, 109], and we manually examined all significant alignments.
SUPPLEMENTAL DATA TABLES
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank the Iñupiaq Eskimo hunters of Barrow for access to captured bowhead whales and for their extraordinary cooperation and involvement. We hope our work is helpful to the conservation of bowhead whales and communities that rely on them. We acknowledge the efforts of Wesley Warren and the Genome Institute at the Washington University School of Medicine, and the Broad Institute in assembling the genome sequence of the sperm whale (Physeter catodon). Next generation sequencing data was submitted to the NCBI Sequence Read Archive (study number PRJNA263931).
Footnotes
Sources of funding
This work was supported by NIH grants AG047745 and AG047200.
Conflict of interest statement
There is no conflict of interest disclosed for any author.
SUPPLEMENTAL DATA
Please browse the full text version of this manuscript to see the Supplemental Tables.
REFERENCES
- 1.Ferguson SH, Dueck L, Loseto LL, Luque SP. Bowhead whale Balaena mysticetus seasonal selection of sea ice. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2010;411:285–297. [Google Scholar]
- 2.Gingerich PD, Haq M, Zalmout IS, Khan IH, Malkani MS. Origin of whales from early artiodactyls: hands and feet of Eocene Protocetidae from Pakistan. Science. 2001;293:2239–2242. doi: 10.1126/science.1063902. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Thewissen JG, Cooper LN, Clementz MT, Bajpai S, Tiwari BN. Whales originated from aquatic artiodactyls in the Eocene epoch of India. Nature. 2007;450:1190–1194. doi: 10.1038/nature06343. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.George JC, Bada J, Zeh J, Scott L, Brown SE, O'Hara T, Suydam R. Age and growth estimates of bowhead whales (Balaena mysticetus) via aspartic acid racemization. Can. J. Zool. 1999;77:571–580. [Google Scholar]
- 5.George JC, Bockstoce JR. Two historical weapon fragments as an aid to estimating the longevity and movements of bowhead whales. Polar Biol. 2008;31:751–754. [Google Scholar]
- 6.Lewis KN, Andziak B, Yang T, Buffenstein R. The naked mole-rat response to oxidative stress: just deal with it. Antioxid. Redox Signal. 2013;19:1388–1399. doi: 10.1089/ars.2012.4911. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Podlutsky AJ, Khritankov AM, Ovodov ND, Austad SN. A new field record for bat longevity. J. Gerontol. A Biol. Sci. Med. Sci. 2005;60:1366–1368. doi: 10.1093/gerona/60.11.1366. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Yim HS, Cho YS, Guang X, Kang SG, Jeong JY, Cha SS, Oh HM, Lee JH, Yang EC, Kwon KK, Kim YJ, Kim TW, Kim W, et al. Minke whale genome and aquatic adaptation in cetaceans. Nat. Genet. 2014;46:88–92. doi: 10.1038/ng.2835. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.McGowen MR, Grossman LI, Wildman DE. Dolphin genome provides evidence for adaptive evolution of nervous system genes and a molecular rate slowdown. Proc. Biol. Sci. 2012;279:3643–3651. doi: 10.1098/rspb.2012.0869. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Moura AE, Janse van Rensburg C, Pilot M, Tehrani A, Best PB, Thornton M, Plon S, de Bruyn PJ, Worley KC, Gibbs RA, Dahlheim ME, Hoelzel AR. Killer whale nuclear genome and mtDNA reveal widespread population bottleneck during the last glacial maximum. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2014;31:1121–1131. doi: 10.1093/molbev/msu058. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Zhou X, Sun F, Xu S, Fan G, Zhu K, Liu X, Chen Y, Shi C, Yang Y, Huang Z, Chen J, Hou H, Guo X, et al. Baiji genomes reveal low genetic variability and new insights into secondary aquatic adaptations. Nat. Commun. 2013;4:2708. doi: 10.1038/ncomms3708. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Grabherr MG, Haas BJ, Yassour M, Levin JZ, Thompson DA, Amit I, Adiconis X, Fan L, Raychowdhury R, Zeng Q, Chen Z, Mauceli E, Hacohen N, et al. Full-length transcriptome assembly from RNA-Seq data without a reference genome. Nat. Biotechnol. 2011;29:644–652. doi: 10.1038/nbt.1883. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Haas BJ, Papanicolaou A, Yassour M, Grabherr M, Blood PD, Bowden J, Couger MB, Eccles D, Li B, Lieber M, Macmanes MD, Ott M, Orvis J, et al. De novo transcript sequence reconstruction from RNA-seq using the Trinity platform for reference generation and analysis. Nat. Protoc. 2013;8:1494–1512. doi: 10.1038/nprot.2013.084. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Flicek P, Amode MR, Barrell D, Beal K, Billis K, Brent S, Carvalho-Silva D, Clapham P, Coates G, Fitzgerald S, Gil L, Giron CG, Gordon L, et al. Ensembl. Nucleic Acids Res. 2014;42:D749–755. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkt1196. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Geisler JH, McGowen MR, Yang G, Gatesy J. A supermatrix analysis of genomic, morphological, and paleontological data from crown Cetacea. BMC Evol. Biol. 2011;11:112. doi: 10.1186/1471-2148-11-112. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Gatesy J, Geisler JH, Chang J, Buell C, Berta A, Meredith RW, Springer MS, McGowen MR. A phylogenetic blueprint for a modern whale. Mol. Phylogenet. Evol. 2013;66:479–506. doi: 10.1016/j.ympev.2012.10.012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Grzimek B, Schlager N, Olendorf D, McDade MC. Grzimek's animal life encyclopedia (Gale) 2004.
- 18.Cariou B, Capitaine N, Le Marcis V, Vega N, Bereziat V, Kergoat M, Laville M, Girard J, Vidal H, Burnol AF. Increased adipose tissue expression of Grb14 in several models of insulin resistance. FASEB J. 2004;18:965–967. doi: 10.1096/fj.03-0824fje. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Béréziat V, Kasus-Jacobi A, Perdereau D, Cariou B, Girard J, Burnol AF. Inhibition of insulin receptor catalytic activity by the molecular adapter Grb14. J. Biol. Chem. 2002;277:4845–4852. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M106574200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Depetris RS, Hu J, Gimpelevich I, Holt LJ, Daly RJ, Hubbard SR. Structural basis for inhibition of the insulin receptor by the adaptor protein Grb14. Mol Cell. 2005;20:325–333. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2005.09.001. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Cooney GJ, Lyons RJ, Crew AJ, Jensen TE, Molero JC, Mitchell CJ, Biden TJ, Ormandy CJ, James DE, Daly RJ. Improved glucose homeostasis and enhanced insulin signalling in Grb14-deficient mice. EMBO J. 2004;23:582–593. doi: 10.1038/sj.emboj.7600082. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Goenaga D, Hampe C, Carre N, Cailliau K, Browaeys-Poly E, Perdereau D, Holt LJ, Daly RJ, Girard J, Broutin I, Issad T, Burnol AF. Molecular determinants of Grb14-mediated inhibition of insulin signaling. Mol. Endocrinol. 2009;23:1043–1051. doi: 10.1210/me.2008-0360. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Carre N, Cauzac M, Girard J, Burnol AF. Dual effect of the adapter growth factor receptor-bound protein 14 (grb14) on insulin action in primary hepatocytes. Endocrinology. 2008;149:3109–3117. doi: 10.1210/en.2007-1196. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Altarejos JY, Montminy M. CREB and the CRTC co-activators: sensors for hormonal and metabolic signals. Nat. Rev Mol. Cell Biol. 2011;12:141–151. doi: 10.1038/nrm3072. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Sakai M, Matsumoto M, Tujimura T, Yongheng C, Noguchi T, Inagaki K, Inoue H, Hosooka T, Takazawa K, Kido Y, Yasuda K, Hiramatsu R, Matsuki Y, Kasuga M. CITED2 links hormonal signaling to PGC-1alpha acetylation in the regulation of gluconeogenesis. Nat. Med. 2012;18:612–617. doi: 10.1038/nm.2691. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Rera M, Bahadorani S, Cho J, Koehler CL, Ulgherait M, Hur JH, Ansari WS, Lo T, Jr, Jones DL, Walker DW. Modulation of longevity and tissue homeostasis by the Drosophila PGC-1 homolog. Cell Metab. 2011;14:623–634. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2011.09.013. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Mukherjee S, Basar MA, Davis C, Duttaroy A. Emerging functional similarities and divergences between Drosophila Spargel/dPGC-1 and mammalian PGC-1 protein. Front. Genet. 2014;5:216. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2014.00216. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Haas JT, Miao J, Chanda D, Wang Y, Zhao E, Haas ME, Hirschey M, Vaitheesvaran B, Farese RV, Jr., Kurland IJ, Graham M, Crooke R, Foufelle F, et al. Hepatic insulin signaling is required for obesity-dependent expression of SREBP-1c mRNA but not for feeding-dependent expression. Cell Metab. 2012;15:873–884. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2012.05.002. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Engelking LJ, Kuriyama H, Hammer RE, Horton JD, Brown MS, Goldstein JL, Liang G. Overexpression of Insig-1 in the livers of transgenic mice inhibits SREBP processing and reduces insulin-stimulated lipogenesis. J. Clin. Invest. 2004;113:1168–1175. doi: 10.1172/JCI20978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Wang L, Karpac J, Jasper H. Promoting longevity by maintaining metabolic and proliferative homeostasis. J. Exp. Biol. 2014;217:109–118. doi: 10.1242/jeb.089920. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Bluhm BA, Gradinger R. Regional variability in food availability for Arctic marine mammals. Ecol. Appl. 2008;18:S77–96. doi: 10.1890/06-0562.1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Berge J, Gabrielsen TM, Moline M, Renaud PE. Evolution of the Arctic Calanus complex: an Arctic marine avocado? J. Plankton Res. 2012;34:191–195. doi: 10.1093/plankt/fbr103. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Clarke A, Holmes LJ, Gore DJ. Proximate and elemental composition of gelatinous zooplankton from the Southern Ocean. J. Exp. Mar. Biol. Ecol. 1992;155:55–68. [Google Scholar]
- 34.Weigl R. Longevity of Mammals in Captivity: From the Living Collections of the World: A List of Mammalian Longevity in Captivity (E. Schweizerbartsche Verlagsbuchhandlung) 2005.
- 35.Venn-Watson S, Benham C, Carlin K, DeRienzo D, St Leger J. Hemochromatosis and fatty liver disease: building evidence for insulin resistance in bottlenose dolphins (Tursiops truncatus) J. Zoo Wildl. Med. 2012;43:S35–47. doi: 10.1638/2011-0146.1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Venn-Watson S, Smith CR, Stevenson S, Parry C, Daniels R, Jensen E, Cendejas V, Balmer B, Janech M, Neely BA, Wells R. Blood-Based Indicators of Insulin Resistance and Metabolic Syndrome in Bottlenose Dolphins (Tursiops truncatus) Front. Endocrinol. (Lausanne) 2013;4:136. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2013.00136. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Venn-Watson S, Carlin K, Ridgway S. Dolphins as animal models for type 2 diabetes: sustained, post-prandial hyperglycemia and hyperinsulinemia. Gen. Comp. Endocrinol. 2011;170:193–199. doi: 10.1016/j.ygcen.2010.10.005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Blagosklonny MV. Big mice die young but large animals live longer. Aging (Albany NY) 2013;5:227–233. doi: 10.18632/aging.100551. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Seim I, Fang X, Xiong Z, Lobanov AV, Huang Z, Ma S, Feng Y, Turanov AA, Zhu Y, Lenz TL, Gerashchenko MV, Fan D, Yim SH, et al. Genome analysis reveals insights into physiology and longevity of the Brandt's bat Myotis brandtii. Nat. Commun. 2013;4:2212. doi: 10.1038/ncomms3212. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Fang X, Seim I, Huang Z, Gerashchenko MV, Xiong Z, Turanov AA, Zhu Y, Lobanov AV, Fan D, Yim SH, Yao X, Ma S, Yang L, et al. Adaptations to a subterranean environment and longevity revealed by the analysis of mole rat genomes. Cell Rep. 2014;8:1354–1364. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2014.07.030. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Al-Regaiey KA, Masternak MM, Bonkowski M, Sun L, Bartke A. Long-lived growth hormone receptor knockout mice: interaction of reduced insulin-like growth factor i/insulin signaling and caloric restriction. Endocrinology. 2005;146:851–860. doi: 10.1210/en.2004-1120. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Ogg S, Paradis S, Gottlieb S, Patterson GI, Lee L, Tissenbaum HA, Ruvkun G. The Fork head transcription factor DAF-16 transduces insulin-like metabolic and longevity signals in C. elegans. Nature. 1997;389:994–999. doi: 10.1038/40194. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Giannakou ME, Goss M, Junger MA, Hafen E, Leevers SJ, Partridge L. Long-lived Drosophila with overexpressed dFOXO in adult fat body. Science. 2004;305:361. doi: 10.1126/science.1098219. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Buffenstein R, Kang H, Biney A. Glucose tolerance and insulin sensitivity in an extremely long-living rodent, the naked mole-rat. FASEB J. 2007;21:A1423. [Google Scholar]
- 45.Bravard A, Vial G, Chauvin MA, Rouille Y, Bailleul B, Vidal H, Rieusset J. FTO contributes to hepatic metabolism regulation through regulation of leptin action and STAT3 signalling in liver. Cell Commun. Signal. 2014;12:4. doi: 10.1186/1478-811X-12-4. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Poritsanos NJ, Lew PS, Mizuno TM. Relationship between blood glucose levels and hepatic Fto mRNA expression in mice. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2010;400:713–717. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2010.08.133. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Ikels K, Kuschel S, Fischer J, Kaisers W, Eberhard D, Ruther U. FTO is a relevant factor for the development of the metabolic syndrome in mice. PloS ONE. 2014;9:e105349. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0105349. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Singaravelu K, Devalaraja-Narashimha K, Lastovica B, Padanilam BJ. PERP, a p53 proapoptotic target, mediates apoptotic cell death in renal ischemia. Am. J. Physiol. Renal Physiol. 2009;296:F847–858. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.90438.2008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Brantley-Sieders DM, Caughron J, Hicks D, Pozzi A, Ruiz JC, Chen J. EphA2 receptor tyrosine kinase regulates endothelial cell migration and vascular assembly through phosphoinositide 3-kinase-mediated Rac1 GTPase activation. J. Cell. Sci. 2004;117:2037–2049. doi: 10.1242/jcs.01061. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.McNaughton L, Puttagunta L, Martinez-Cuesta MA, Kneteman N, Mayers I, Moqbel R, Hamid Q, Radomski MW. Distribution of nitric oxide synthase in normal and cirrhotic human liver. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 2002;99:17161–17166. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0134112100. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51.Mei Y, Thevananther S. Endothelial nitric oxide synthase is a key mediator of hepatocyte proliferation in response to partial hepatectomy in mice. Hepatology. 2011;54:1777–1789. doi: 10.1002/hep.24560. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52.Anantha RW, Vassin VM, Borowiec JA. Sequential and synergistic modification of human RPA stimulates chromosomal DNA repair. J. Biol. Chem. 2007;282:35910–35923. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M704645200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53.Yin JY, Dong ZZ, Liu RY, Chen J, Liu ZQ, Zhang JT. Translational regulation of RPA2 via internal ribosomal entry site and by eIF3a. Carcinogenesis. 2013;34:1224–1231. doi: 10.1093/carcin/bgt052. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 54.Anson RM, Willcox B, Austad S, Perls T. Within- and between-species study of extreme longevity--comments, commonalities, and goals. J. Gerontol. A Biol. Sci. Med. Sci. 2012;67:347–350. doi: 10.1093/gerona/gls010. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 55.Grimes KM, Reddy AK, Lindsey ML, Buffenstein R. And the beat goes on: maintained cardiovascular function during aging in the longest-lived rodent, the naked mole-rat. Am. J. Physiol. Heart Circ. Physiol. 2014;307:H284–291. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.00305.2014. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 56.Erez A, Nagamani SC, Shchelochkov OA, Premkumar MH, Campeau PM, Chen Y, Garg HK, Li L, Mian A, Bertin TK, Black JO, Zeng H, Tang Y, et al. Requirement of argininosuccinate lyase for systemic nitric oxide production. Nat. Med. 2011;17:1619–1626. doi: 10.1038/nm.2544. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 57.Jensen FB. The role of nitrite in nitric oxide homeostasis: a comparative perspective. Biochim. Biophys. Acta. 2009;1787:841–848. doi: 10.1016/j.bbabio.2009.02.010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 58.Misfeldt M, Fago A, Gesser H. Nitric oxide increases myocardial efficiency in the hypoxia-tolerant turtle Trachemys scripta. J. Exp. Biol. 2009;212:954–960. doi: 10.1242/jeb.025171. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 59.Berta A, Sumich JL. Academic Press; 2005. Marine mammals: evolutionary biology. [Google Scholar]
- 60.Parker J, Tsagkogeorga G, Cotton JA, Liu Y, Provero P, Stupka E, Rossiter SJ. Genome-wide signatures of convergent evolution in echolocating mammals. Nature. 2013;502:228–231. doi: 10.1038/nature12511. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 61.Rutanen J, Leppanen P, Tuomisto TT, Rissanen TT, Hiltunen MO, Vajanto I, Niemi M, Hakkinen T, Karkola K, Stacker SA, Achen MG, Alitalo K, Yla-Herttuala S. Vascular endothelial growth factor-D expression in human atherosclerotic lesions. Cardiovasc. Res. 2003;59:971–979. doi: 10.1016/s0008-6363(03)00518-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 62.Koch S, Tugues S, Li X, Gualandi L, Claesson-Welsh L. Signal transduction by vascular endothelial growth factor receptors. Biochem. J. 2011;437:169–183. doi: 10.1042/BJ20110301. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 63.Leppanen VM, Jeltsch M, Anisimov A, Tvorogov D, Aho K, Kalkkinen N, Toivanen P, Yla-Herttuala S, Ballmer-Hofer K, Alitalo K. Structural determinants of vascular endothelial growth factor-D receptor binding and specificity. Blood. 2011;117:1507–1515. doi: 10.1182/blood-2010-08-301549. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 64.Weinstein JR, Anderson S. The aging kidney: physiological changes. Adv Chronic Kidney Dis. 2010;17:302–307. doi: 10.1053/j.ackd.2010.05.002. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 65.Lans H, Hoeijmakers JH. Genome stability, progressive kidney failure and aging. Nat. Genet. 2012;44:836–838. doi: 10.1038/ng.2363. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 66.Juhasz S, Balogh D, Hajdu I, Burkovics P, Villamil MA, Zhuang Z, Haracska L. Characterization of human Spartan/C1orf124, an ubiquitin-PCNA interacting regulator of DNA damage tolerance. Nucleic Acids Res. 2012;40:10795–10808. doi: 10.1093/nar/gks850. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 67.Kong X, Stephens J, Ball AR, Jr., Heale JT, Newkirk DA, Berns MW, Yokomori K. Condensin I recruitment to base damage-enriched DNA lesions is modulated by PARP1. PLoS ONE. 2011;6:e23548. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0023548. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 68.Soza S, Leva V, Vago R, Ferrari G, Mazzini G, Biamonti G, Montecucco A. DNA ligase I deficiency leads to replication-dependent DNA damage and impacts cell morphology without blocking cell cycle progression. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2009;29:2032–2041. doi: 10.1128/MCB.01730-08. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 69.Son YO, Heo JS, Kim TG, Jeon YM, Kim JG, Lee JC. Over-expression of JunB inhibits mitochondrial stress and cytotoxicity in human lymphoma cells exposed to chronic oxidative stress. BMB Rep. 2010;43:57–61. doi: 10.5483/bmbrep.2010.43.1.057. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 70.Le Cam L, Linares LK, Paul C, Julien E, Lacroix M, Hatchi E, Triboulet R, Bossis G, Shmueli A, Rodriguez MS, Coux O, Sardet C. E4F1 is an atypical ubiquitin ligase that modulates p53 effector functions independently of degradation. Cell. 2006;127:775–788. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2006.09.031. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 71.Beghin A, Matera EL, Brunet-Manquat S, Dumontet C. Expression of Arl2 is associated with p53 localization and chemosensitivity in a breast cancer cell line. Cell Cycle. 2008;7:3074–3082. doi: 10.4161/cc.7.19.6777. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 72.Lee JH, Byun DS, Lee MG, Ryu BK, Kang MJ, Chae KS, Lee KY, Kim HJ, Park H, Chi SG. Frequent epigenetic inactivation of hSRBC in gastric cancer and its implication in attenuated p53 response to stresses. Int. J. Cancer. 2008;122:1573–1584. doi: 10.1002/ijc.23166. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 73.Lee JH, Kang MJ, Han HY, Lee MG, Jeong SI, Ryu BK, Ha TK, Her NG, Han J, Park SJ, Lee KY, Kim HJ, Chi SG. Epigenetic alteration of PRKCDBP in colorectal cancers and its implication in tumor cell resistance to TNFalpha-induced apoptosis. Clin. Cancer Res. 2011;17:7551–7562. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-11-1026. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 74.Zwang Y, Oren M, Yarden Y. Consistency test of the cell cycle: roles for p53 and EGR1. Cancer Res. 2012;72:1051–1054. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-11-3382. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 75.Gari K, León Ortiz AM, Borel V, Flynn H, Skehel JM, Boulton SJ. MMS19 links cytoplasmic iron-sulfur cluster assembly to DNA metabolism. Science. 2012;337:243–245. doi: 10.1126/science.1219664. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 76.Stehling O, Vashisht AA, Mascarenhas J, Jonsson ZO, Sharma T, Netz DJ, Pierik AJ, Wohlschlegel JA, Lill R. MMS19 assembles iron-sulfur proteins required for DNA metabolism and genomic integrity. Science. 2012;337:195–199. doi: 10.1126/science.1219723. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 77.Weerapana E, Wang C, Simon GM, Richter F, Khare S, Dillon MB, Bachovchin DA, Mowen K, Baker D, Cravatt BF. Quantitative reactivity profiling predicts functional cysteines in proteomes. Nature. 2010;468:790–795. doi: 10.1038/nature09472. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 78.Bakewell MA, Shi P, Zhang J. More genes underwent positive selection in chimpanzee evolution than in human evolution. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 2007;104:7489–7494. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0701705104. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 79.Phillips CD, Hoffman JI, George JC, Suydam RS, Huebinger RM, Patton JC, Bickham JW. Molecular insights into the historic demography of bowhead whales: understanding the evolutionary basis of contemporary management practices. Ecol. Evol. 2012;3:18–37. doi: 10.1002/ece3.374. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 80.Schaer CA, Deuel JW, Bittermann AG, Rubio IG, Schoedon G, Spahn DR, Wepf RA, Vallelian F, Schaer DJ. Mechanisms of haptoglobin protection against hemoglobin peroxidation triggered endothelial damage. Cell Death Differ. 2013;20:1569–1579. doi: 10.1038/cdd.2013.113. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 81.Molina A, Velot L, Ghouinem L, Abdelkarim M, Bouchet BP, Luissint AC, Bouhlel I, Morel M, Sapharikas E, Di Tommaso A, Honore S, Braguer D, Gruel N, et al. ATIP3, a novel prognostic marker of breast cancer patient survival, limits cancer cell migration and slows metastatic progression by regulating microtubule dynamics. Cancer Res. 2013;73:2905–2915. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-12-3565. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 82.Kobayashi T, Hino S, Oue N, Asahara T, Zollo M, Yasui W, Kikuchi A. Glycogen synthase kinase 3 and h-prune regulate cell migration by modulating focal adhesions. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2006;26:898–911. doi: 10.1128/MCB.26.3.898-911.2006. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 83.Silva JM, Ezhkova E, Silva J, Heart S, Castillo M, Campos Y, Castro V, Bonilla F, Cordon-Cardo C, Muthuswamy SK, Powers S, Fuchs E, Hannon GJ. Cyfip1 is a putative invasion suppressor in epithelial cancers. Cell. 2009;137:1047–1061. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2009.04.013. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 84.Moya-Sola S, Kohler M, Alba DM, Casanovas-Vilar I, Galindo J. Pierolapithecus catalaunicus, a new Middle Miocene great ape from Spain. Science. 2004;306:1339–1344. doi: 10.1126/science.1103094. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 85.Gibbs RA, Rogers J, Katze MG, Bumgarner R, Weinstock GM, Mardis ER, Remington KA, Strausberg RL, Venter JC, Wilson RK, Batzer MA, Bustamante CD, et al. Evolutionary and biomedical insights from the rhesus macaque genome. Science. 2007;316:222–234. doi: 10.1126/science.1139247. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 86.Robson SL, Wood B. Hominin life history: reconstruction and evolution. Journal Anat. 2008;212:394–425. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-7580.2008.00867.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 87.Cutler RG. Evolution of human longevity and the genetic complexity governing aging rate. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 1975;72:4664–4668. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.11.4664. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 88.Brawand D, Soumillon M, Necsulea A, Julien P, Csardi G, Harrigan P, Weier M, Liechti A, Aximu-Petri A, Kircher M, Albert FW, Zeller U, Khaitovich P, et al. The evolution of gene expression levels in mammalian organs. Nature. 2011;478:343–348. doi: 10.1038/nature10532. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 89.Merkin J, Russell C, Chen P, Burge CB. Evolutionary dynamics of gene and isoform regulation in Mammalian tissues. Science. 2012;338:1593–1599. doi: 10.1126/science.1228186. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 90.Qiu Q, Zhang G, Ma T, Qian W, Wang J, Ye Z, Cao C, Hu Q, Kim J, Larkin DM, Auvil L, Capitanu B, Ma J, et al. The yak genome and adaptation to life at high altitude. Nat. Genet. 2012;44:946–949. doi: 10.1038/ng.2343. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 91.Kim EB, Fang X, Fushan AA, Huang Z, Lobanov AV, Han L, Marino SM, Sun X, Turanov AA, Yang P, Yim SH, Zhao X, Kasaikina MV, et al. Genome sequencing reveals insights into physiology and longevity of the naked mole rat. Nature. 2011;479:223–227. doi: 10.1038/nature10533. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 92.Fan Y, Huang ZY, Cao CC, Chen CS, Chen YX, Fan DD, He J, Hou HL, Hu L, Hu XT, Jiang XT, Lai R, Lang YS, et al. Genome of the Chinese tree shrew. Nat Commun. 2013;4:1426. doi: 10.1038/ncomms2416. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 93.RDevelopment CoreTeam . R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing. R Foundation for Statistical Computing; Vienna, Austria: 2012. [Google Scholar]
- 94.Sayers EW, Barrett T, Benson DA, Bolton E, Bryant SH, Canese K, Chetvernin V, Church DM, Dicuccio M, Federhen S, Feolo M, Fingerman IM, Geer LY, et al. Database resources of the National Center for Biotechnology Information. Nucleic Acids Res. 2012;40:D13–25. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkr1184. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 95.Kim D, Pertea G, Trapnell C, Pimentel H, Kelley R, Salzberg SL. TopHat2: accurate alignment of transcriptomes in the presence of insertions, deletions and gene fusions. Genome Biol. 2013;14:R36. doi: 10.1186/gb-2013-14-4-r36. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 96.Liao Y, Smyth GK, Shi W. featureCounts: an efficient general purpose program for assigning sequence reads to genomic features. Bioinformatics. 2014;30:923–930. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btt656. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 97.Robinson MD, Oshlack A. A scaling normalization method for differential expression analysis of RNA-seq data. Genome Biol. 2010;11:R25. doi: 10.1186/gb-2010-11-3-r25. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 98.Robinson MD, McCarthy DJ, Smyth GK. edgeR: a Bioconductor package for differential expression analysis of digital gene expression data. Bioinformatics. 2010;26:139–140. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btp616. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 99.Law CW, Chen Y, Shi W, Smyth GK. voom: precision weights unlock linear model analysis tools for RNA-seq read counts. Genome Biol. 2014;15:R29. doi: 10.1186/gb-2014-15-2-r29. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 100.Sievers F, Wilm A, Dineen D, Gibson TJ, Karplus K, Li W, Lopez R, McWilliam H, Remmert M, Soding J, Thompson JD, Higgins DG. Fast, scalable generation of high-quality protein multiple sequence alignments using Clustal Omega. Mol. Syst. Biol. 2011;7:539. doi: 10.1038/msb.2011.75. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 101.Castresana J. Selection of conserved blocks from multiple alignments for their use in phylogenetic analysis. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2000;17:540–552. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.molbev.a026334. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 102.Talavera G, Castresana J. Improvement of phylogenies after removing divergent and ambiguously aligned blocks from protein sequence alignments. Syst. Biol. 2007;56:564–577. doi: 10.1080/10635150701472164. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 103.Stamatakis A. RAxML version 8: a tool for phylogenetic analysis and post-analysis of large phylogenies. Bioinformatics. 2014;30:1312–1313. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btu033. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 104.Yang Z. PAML 4: phylogenetic analysis by maximum likelihood. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2007;24:1586–1591. doi: 10.1093/molbev/msm088. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 105.Miller W, Rosenbloom K, Hardison RC, Hou M, Taylor J, Raney B, Burhans R, King DC, Baertsch R, Blankenberg D, Kosakovsky Pond SL, Nekrutenko A, Giardine B, et al. 28-way vertebrate alignment and conservation track in the UCSC Genome Browser. Genome Res. 2007;17:1797–1808. doi: 10.1101/gr.6761107. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 106.Wu TD, Watanabe CK. GMAP: a genomic mapping and alignment program for mRNA and EST sequences. Bioinformatics. 2005;21:1859–1875. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/bti310. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 107.Yang Z, dos Reis M. Statistical properties of the branch-site test of positive selection. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2011;28:1217–1228. doi: 10.1093/molbev/msq303. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 108.Markova-Raina P, Petrov D. High sensitivity to aligner and high rate of false positives in the estimates of positive selection in the 12 Drosophila genomes. Genome Res. 2011;21:863–874. doi: 10.1101/gr.115949.110. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 109.Vamathevan JJ, Hasan S, Emes RD, Amrine-Madsen H, Rajagopalan D, Topp SD, Kumar V, Word M, Simmons MD, Foord SM, Sanseau P, Yang Z, Holbrook JD. The role of positive selection in determining the molecular cause of species differences in disease. BMC Evol. Biol. 2008;8:273. doi: 10.1186/1471-2148-8-273. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.