Abstract
Autoimmunity often involves the abnormal targeting of self-antigens by antibodies, leading to tissue destruction and other pathologies. This process could potentially be disrupted by small ligands that bind specifically to autoantibodies and inhibit their interaction with the target antigen. Here we report the identification of an RNA sequence that binds a mouse monoclonal antibody specific for an autoantigenic epitope of human insulin receptor. The RNA ligand binds specifically and with high affinity (apparent Kd congruent to 2 nM) to the anti-insulin receptor antibody and not to other mouse IgGs. The RNA can also act as a decoy, blocking the antibody from binding the insulin receptor. Thus, it probably binds near the combining site on the antibody. Strikingly, the RNA cross-reacts with autoantibodies from patients with extreme insulin resistance. One simple explanation is that the selected RNA may structurally mimic the antigenic epitope on the insulin receptor protein. These results suggest that decoy RNAs may be used in the treatment of autoimmune diseases.
Full text
PDF

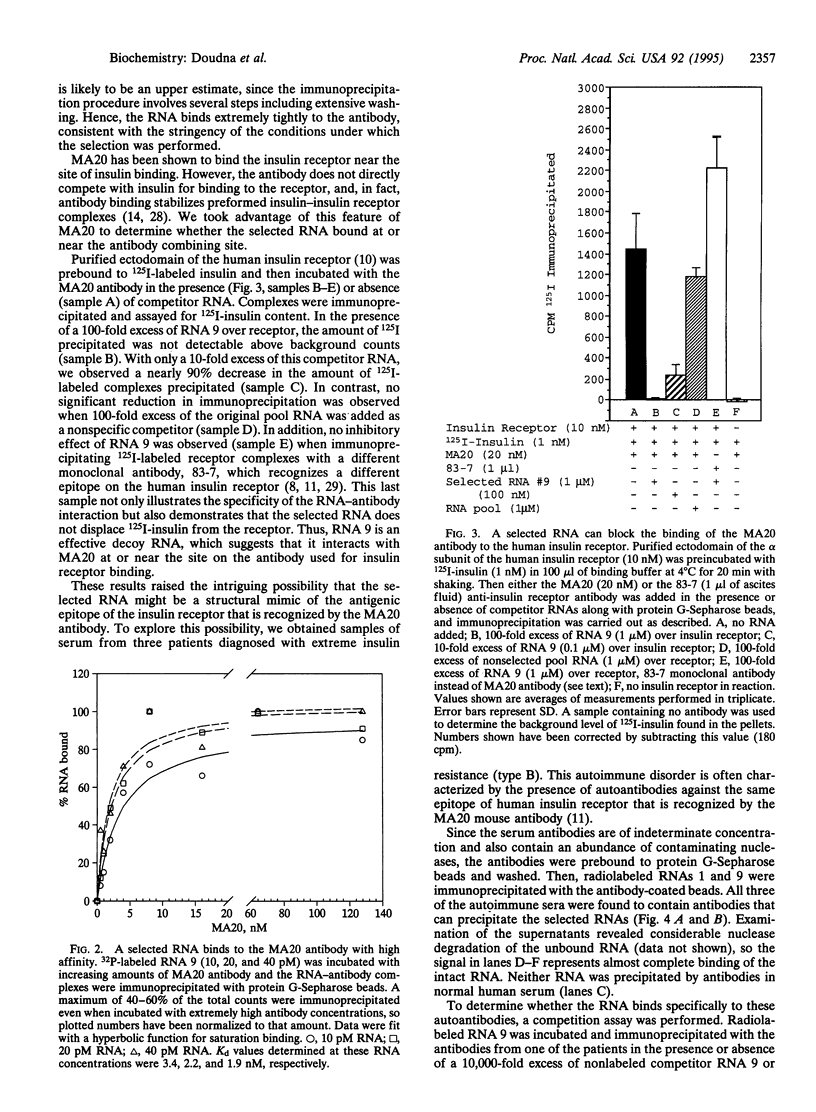
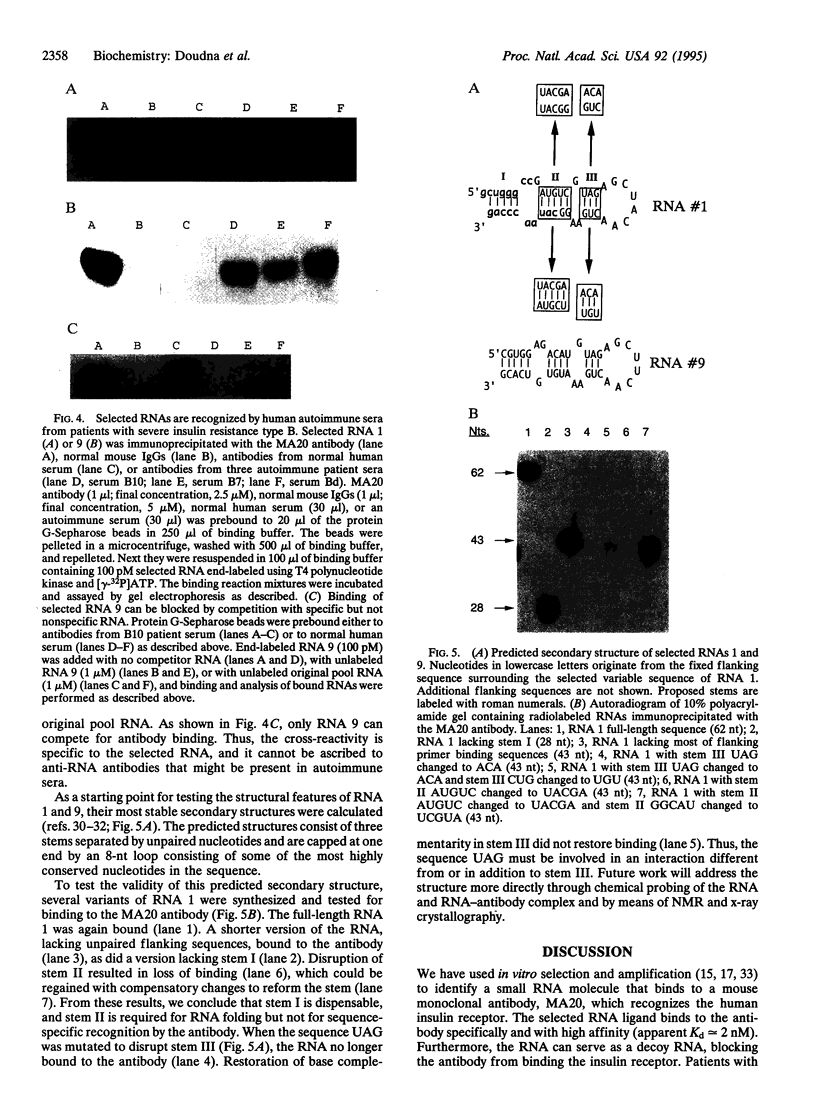

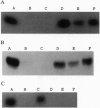
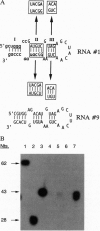
Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bartel D. P., Zapp M. L., Green M. R., Szostak J. W. HIV-1 Rev regulation involves recognition of non-Watson-Crick base pairs in viral RNA. Cell. 1991 Nov 1;67(3):529–536. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90527-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Connell G. J., Illangesekare M., Yarus M. Three small ribooligonucleotides with specific arginine sites. Biochemistry. 1993 Jun 1;32(21):5497–5502. doi: 10.1021/bi00072a002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ebina Y., Ellis L., Jarnagin K., Edery M., Graf L., Clauser E., Ou J. H., Masiarz F., Kan Y. W., Goldfine I. D. The human insulin receptor cDNA: the structural basis for hormone-activated transmembrane signalling. Cell. 1985 Apr;40(4):747–758. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90334-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ellington A. D., Szostak J. W. In vitro selection of RNA molecules that bind specific ligands. Nature. 1990 Aug 30;346(6287):818–822. doi: 10.1038/346818a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ellis L., Tavaré J. M., Levine B. A. Insulin receptor tyrosine kinase structure and function. Biochem Soc Trans. 1991 Apr;19(2):426–432. doi: 10.1042/bst0190426. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flier J. S., Kahn C. R., Roth J., Bar R. S. Antibodies that impair insulin receptor binding in an unusual diabetic syndrome with severe insulin resistance. Science. 1975 Oct 3;190(4209):63–65. doi: 10.1126/science.170678. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forsayeth J. R., Caro J. F., Sinha M. K., Maddux B. A., Goldfine I. D. Monoclonal antibodies to the human insulin receptor that activate glucose transport but not insulin receptor kinase activity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 May;84(10):3448–3451. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.10.3448. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forsayeth J. R., Montemurro A., Maddux B. A., DePirro R., Goldfine I. D. Effect of monoclonal antibodies on human insulin receptor autophosphorylation, negative cooperativity, and down-regulation. J Biol Chem. 1987 Mar 25;262(9):4134–4140. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jaeger J. A., Turner D. H., Zuker M. Improved predictions of secondary structures for RNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Oct;86(20):7706–7710. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.20.7706. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jellinek D., Lynott C. K., Rifkin D. B., Janjić N. High-affinity RNA ligands to basic fibroblast growth factor inhibit receptor binding. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Dec 1;90(23):11227–11231. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.23.11227. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jenison R. D., Gill S. C., Pardi A., Polisky B. High-resolution molecular discrimination by RNA. Science. 1994 Mar 11;263(5152):1425–1429. doi: 10.1126/science.7510417. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Joyce G. F. Amplification, mutation and selection of catalytic RNA. Gene. 1989 Oct 15;82(1):83–87. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(89)90033-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kasuga M., Zick Y., Blith D. L., Karlsson F. A., Häring H. U., Kahn C. R. Insulin stimulation of phosphorylation of the beta subunit of the insulin receptor. Formation of both phosphoserine and phosphotyrosine. J Biol Chem. 1982 Sep 10;257(17):9891–9894. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee T. C., Sullenger B. A., Gallardo H. F., Ungers G. E., Gilboa E. Overexpression of RRE-derived sequences inhibits HIV-1 replication in CEM cells. New Biol. 1992 Jan;4(1):66–74. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Majerfeld I., Yarus M. An RNA pocket for an aliphatic hydrophobe. Nat Struct Biol. 1994 May;1(5):287–292. doi: 10.1038/nsb0594-287. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mohr G., Caprara M. G., Guo Q., Lambowitz A. M. A tyrosyl-tRNA synthetase can function similarly to an RNA structure in the Tetrahymena ribozyme. Nature. 1994 Jul 14;370(6485):147–150. doi: 10.1038/370147a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pilch P. F., Czech M. P. Interaction of cross-linking agents with the insulin effector system of isolated fat cells. Covalent linkage of 125I-insulin to a plasma membrane receptor protein of 140,000 daltons. J Biol Chem. 1979 May 10;254(9):3375–3381. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sassanfar M., Szostak J. W. An RNA motif that binds ATP. Nature. 1993 Aug 5;364(6437):550–553. doi: 10.1038/364550a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schaefer E. M., Erickson H. P., Federwisch M., Wollmer A., Ellis L. Structural organization of the human insulin receptor ectodomain. J Biol Chem. 1992 Nov 15;267(32):23393–23402. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schaefer E. M., Siddle K., Ellis L. Deletion analysis of the human insulin receptor ectodomain reveals independently folded soluble subdomains and insulin binding by a monomeric alpha-subunit. J Biol Chem. 1990 Aug 5;265(22):13248–13253. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schneider D., Tuerk C., Gold L. Selection of high affinity RNA ligands to the bacteriophage R17 coat protein. J Mol Biol. 1992 Dec 5;228(3):862–869. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(92)90870-p. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Soos M. A., Siddle K., Baron M. D., Heward J. M., Luzio J. P., Bellatin J., Lennox E. S. Monoclonal antibodies reacting with multiple epitopes on the human insulin receptor. Biochem J. 1986 Apr 1;235(1):199–208. doi: 10.1042/bj2350199. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strobel S. A., Cech T. R. Minor groove recognition of the conserved G.U pair at the Tetrahymena ribozyme reaction site. Science. 1995 Feb 3;267(5198):675–679. doi: 10.1126/science.7839142. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sullenger B. A., Gallardo H. F., Ungers G. E., Gilboa E. Analysis of trans-acting response decoy RNA-mediated inhibition of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 transactivation. J Virol. 1991 Dec;65(12):6811–6816. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.12.6811-6816.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sullenger B. A., Gallardo H. F., Ungers G. E., Gilboa E. Overexpression of TAR sequences renders cells resistant to human immunodeficiency virus replication. Cell. 1990 Nov 2;63(3):601–608. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90455-n. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Szostak J. W. In vitro genetics. Trends Biochem Sci. 1992 Mar;17(3):89–93. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(92)90242-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor S. I., Barbetti F., Accili D., Roth J., Gorden P. Syndromes of autoimmunity and hypoglycemia. Autoantibodies directed against insulin and its receptor. Endocrinol Metab Clin North Am. 1989 Mar;18(1):123–143. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsai D. E., Kenan D. J., Keene J. D. In vitro selection of an RNA epitope immunologically cross-reactive with a peptide. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Oct 1;89(19):8864–8868. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.19.8864. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tuerk C., Gold L. Systematic evolution of ligands by exponential enrichment: RNA ligands to bacteriophage T4 DNA polymerase. Science. 1990 Aug 3;249(4968):505–510. doi: 10.1126/science.2200121. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tuerk C., MacDougal S., Gold L. RNA pseudoknots that inhibit human immunodeficiency virus type 1 reverse transcriptase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Aug 1;89(15):6988–6992. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.15.6988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ullrich A., Bell J. R., Chen E. Y., Herrera R., Petruzzelli L. M., Dull T. J., Gray A., Coussens L., Liao Y. C., Tsubokawa M. Human insulin receptor and its relationship to the tyrosine kinase family of oncogenes. 1985 Feb 28-Mar 6Nature. 313(6005):756–761. doi: 10.1038/313756a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhang B., Roth R. A. A region of the insulin receptor important for ligand binding (residues 450-601) is recognized by patients' autoimmune antibodies and inhibitory monoclonal antibodies. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Nov 1;88(21):9858–9862. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.21.9858. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zuker M. Computer prediction of RNA structure. Methods Enzymol. 1989;180:262–288. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(89)80106-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zuker M. On finding all suboptimal foldings of an RNA molecule. Science. 1989 Apr 7;244(4900):48–52. doi: 10.1126/science.2468181. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]