Abstract
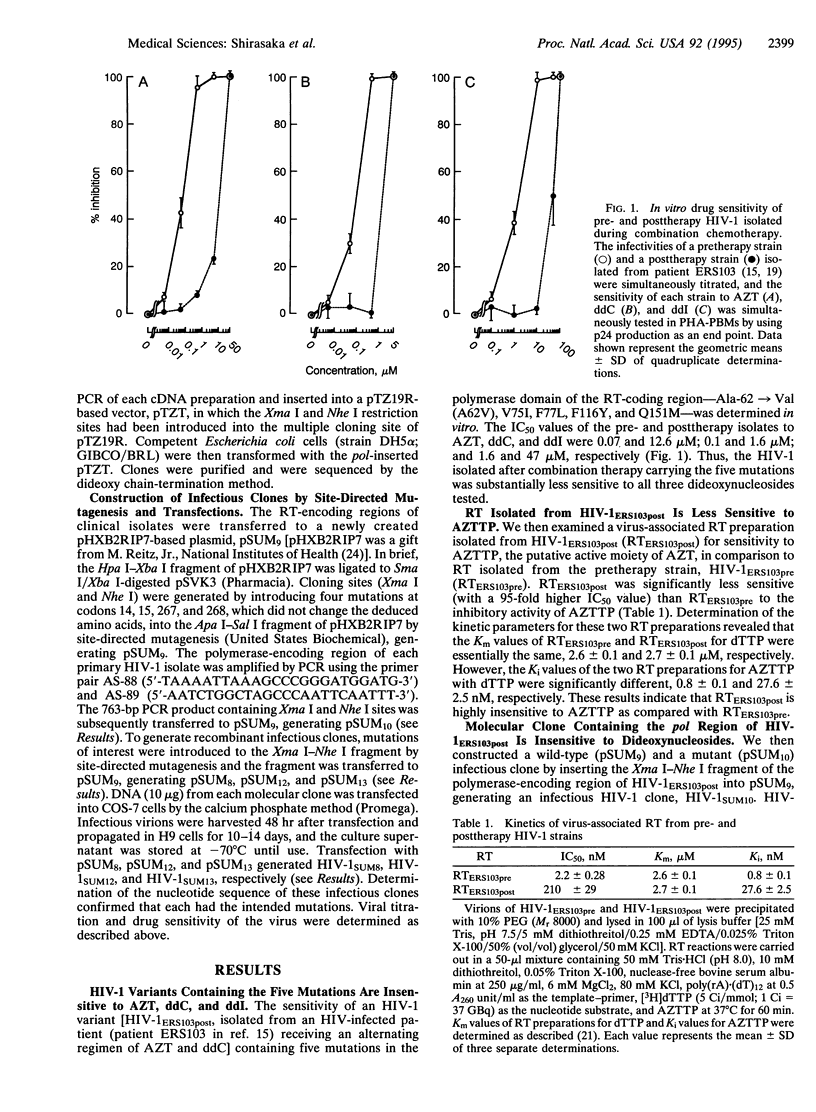
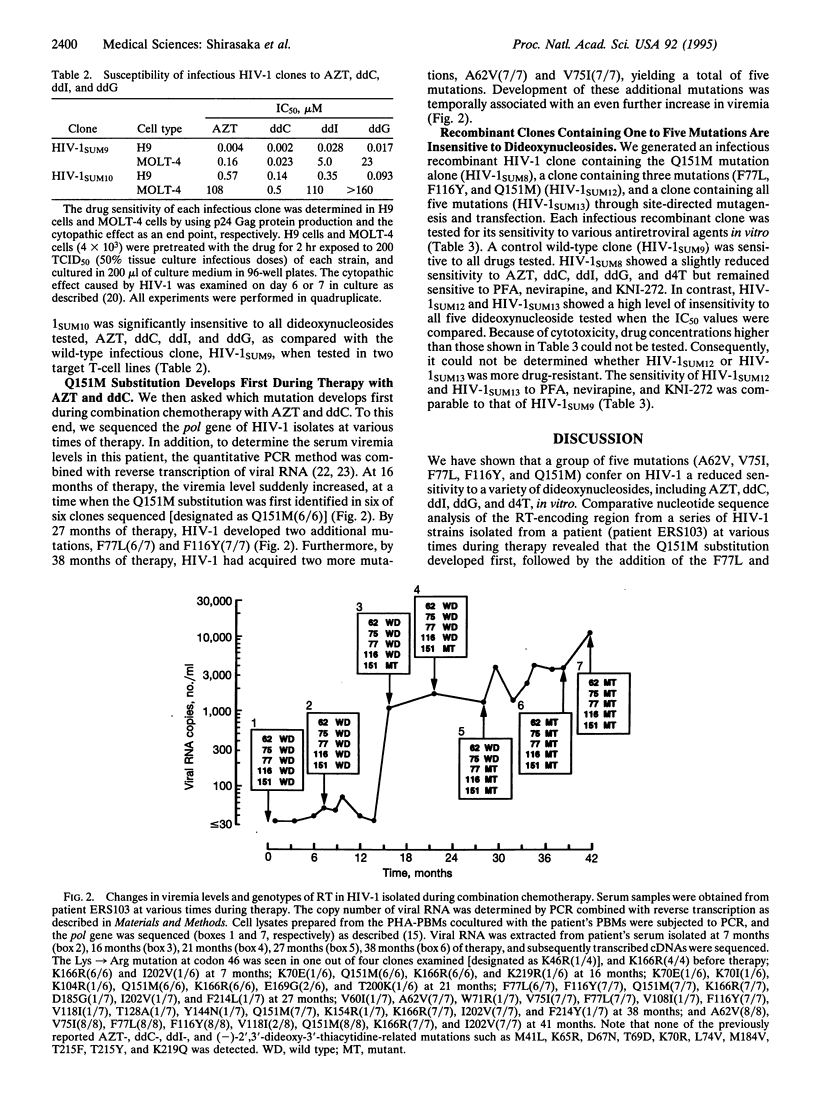
A set of mutations [Ala-62-->Val(A62V), V75I, F77L, F116Y, and Q151M] in the polymerase domain of reverse transcriptase (RT) of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 (HIV-1) confers on the virus a reduced sensitivity to multiple antiretroviral dideoxynucleosides and has been seen in HIV-1 variants isolated from patients receiving combination chemotherapy with 3'-azido-3'-deoxythymidine (AZT) plus 2',3'-dideoxycytidine (ddC) or 2',3'-dideoxyinosine (ddI). The IC50 values of AZT, ddC, ddI, 2',3'-dideoxyguanosine, and 2',3'-didehydro-3'-deoxythymidine against an infectious clone constructed to include the five mutations were significantly higher than those of a wild-type infectious clone. The K1 value for AZT 5'-triphosphate determined for the virus-associated RT from a posttherapy strain was 35-fold higher than that of RT from a pretherapy strain. Detailed analysis of HIV-1 strains isolated at various times during therapy showed that the Q151M mutation developed first in vivo, at the time when the viremia level suddenly increased, followed by the F116Y and F77L mutations. All five mutations ultimately developed, and the viremia level rose even further. Analyses based on the three-dimensional structure of HIV-1 RT suggest that the positions where at least several of the five mutations occur are located in close proximity to the proposed dNTP-binding site of RT and the first nucleotide position of the single-stranded template.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aoki-Sei S., Yarchoan R., Kageyama S., Hoekzema D. T., Pluda J. M., Wyvill K. M., Broder S., Mitsuya H. Plasma HIV-1 viremia in HIV-1 infected individuals assessed by polymerase chain reaction. AIDS Res Hum Retroviruses. 1992 Jul;8(7):1263–1270. doi: 10.1089/aid.1992.8.1263. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boyer P. L., Tantillo C., Jacobo-Molina A., Nanni R. G., Ding J., Arnold E., Hughes S. H. Sensitivity of wild-type human immunodeficiency virus type 1 reverse transcriptase to dideoxynucleotides depends on template length; the sensitivity of drug-resistant mutants does not. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 May 24;91(11):4882–4886. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.11.4882. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collier A. C., Coombs R. W., Fischl M. A., Skolnik P. R., Northfelt D., Boutin P., Hooper C. J., Kaplan L. D., Volberding P. A., Davis L. G. Combination therapy with zidovudine and didanosine compared with zidovudine alone in HIV-1 infection. Ann Intern Med. 1993 Oct 15;119(8):786–793. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-119-8-199310150-00003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Clercq E. HIV resistance to reverse transcriptase inhibitors. Biochem Pharmacol. 1994 Jan 20;47(2):155–169. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(94)90001-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Emini E. A., Graham D. J., Gotlib L., Condra J. H., Byrnes V. W., Schleif W. A. HIV and multidrug resistance. Nature. 1993 Aug 19;364(6439):679–679. doi: 10.1038/364679b0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fitzgibbon J. E., Howell R. M., Haberzettl C. A., Sperber S. J., Gocke D. J., Dubin D. T. Human immunodeficiency virus type 1 pol gene mutations which cause decreased susceptibility to 2',3'-dideoxycytidine. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1992 Jan;36(1):153–157. doi: 10.1128/aac.36.1.153. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gu Z., Gao Q., Fang H., Salomon H., Parniak M. A., Goldberg E., Cameron J., Wainberg M. A. Identification of a mutation at codon 65 in the IKKK motif of reverse transcriptase that encodes human immunodeficiency virus resistance to 2',3'-dideoxycytidine and 2',3'-dideoxy-3'-thiacytidine. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1994 Feb;38(2):275–281. doi: 10.1128/aac.38.2.275. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacobo-Molina A., Ding J., Nanni R. G., Clark A. D., Jr, Lu X., Tantillo C., Williams R. L., Kamer G., Ferris A. L., Clark P. Crystal structure of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 reverse transcriptase complexed with double-stranded DNA at 3.0 A resolution shows bent DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Jul 1;90(13):6320–6324. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.13.6320. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kageyama S., Mimoto T., Murakawa Y., Nomizu M., Ford H., Jr, Shirasaka T., Gulnik S., Erickson J., Takada K., Hayashi H. In vitro anti-human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) activities of transition state mimetic HIV protease inhibitors containing allophenylnorstatine. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1993 Apr;37(4):810–817. doi: 10.1128/aac.37.4.810. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kojima E., Shirasaka T., Anderson B., Chokekijchai S., Sei S., Yarchoan R., Mitsuya H. Monitoring the activity of antiviral therapy for HIV infection using a polymerase chain reaction method coupled with reverse transcription. AIDS. 1993 Nov;7 (Suppl 2):S101–S105. doi: 10.1097/00002030-199311002-00019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozal M. J., Shafer R. W., Winters M. A., Katzenstein D. A., Merigan T. C. A mutation in human immunodeficiency virus reverse transcriptase and decline in CD4 lymphocyte numbers in long-term zidovudine recipients. J Infect Dis. 1993 Mar;167(3):526–532. doi: 10.1093/infdis/167.3.526. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Larder B. A., Kemp S. D. Multiple mutations in HIV-1 reverse transcriptase confer high-level resistance to zidovudine (AZT). Science. 1989 Dec 1;246(4934):1155–1158. doi: 10.1126/science.2479983. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Larder B. A., Kemp S. D., Purifoy D. J. Infectious potential of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 reverse transcriptase mutants with altered inhibitor sensitivity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Jul;86(13):4803–4807. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.13.4803. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin J. L., Wilson J. E., Haynes R. L., Furman P. A. Mechanism of resistance of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 to 2',3'-dideoxyinosine. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Jul 1;90(13):6135–6139. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.13.6135. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCune J. M., Rabin L. B., Feinberg M. B., Lieberman M., Kosek J. C., Reyes G. R., Weissman I. L. Endoproteolytic cleavage of gp160 is required for the activation of human immunodeficiency virus. Cell. 1988 Apr 8;53(1):55–67. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90487-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Merluzzi V. J., Hargrave K. D., Labadia M., Grozinger K., Skoog M., Wu J. C., Shih C. K., Eckner K., Hattox S., Adams J. Inhibition of HIV-1 replication by a nonnucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitor. Science. 1990 Dec 7;250(4986):1411–1413. doi: 10.1126/science.1701568. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Montaner J. S., Singer J., Schechter M. T., Raboud J. M., Tsoukas C., O'Shaughnessy M., Ruedy J., Nagai K., Salomon H., Spira B. Clinical correlates of in vitro HIV-1 resistance ot zidovudine. Results of the Multicentre Canadian AZT Trial. AIDS. 1993 Feb;7(2):189–196. doi: 10.1097/00002030-199302000-00006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nunberg J. H., Schleif W. A., Boots E. J., O'Brien J. A., Quintero J. C., Hoffman J. M., Emini E. A., Goldman M. E. Viral resistance to human immunodeficiency virus type 1-specific pyridinone reverse transcriptase inhibitors. J Virol. 1991 Sep;65(9):4887–4892. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.9.4887-4892.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poch O., Sauvaget I., Delarue M., Tordo N. Identification of four conserved motifs among the RNA-dependent polymerase encoding elements. EMBO J. 1989 Dec 1;8(12):3867–3874. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb08565.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schinazi R. F., Lloyd R. M., Jr, Nguyen M. H., Cannon D. L., McMillan A., Ilksoy N., Chu C. K., Liotta D. C., Bazmi H. Z., Mellors J. W. Characterization of human immunodeficiency viruses resistant to oxathiolane-cytosine nucleosides. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1993 Apr;37(4):875–881. doi: 10.1128/aac.37.4.875. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shafer R. W., Kozal M. J., Winters M. A., Iversen A. K., Katzenstein D. A., Ragni M. V., Meyer W. A., 3rd, Gupta P., Rasheed S., Coombs R. Combination therapy with zidovudine and didanosine selects for drug-resistant human immunodeficiency virus type 1 strains with unique patterns of pol gene mutations. J Infect Dis. 1994 Apr;169(4):722–729. doi: 10.1093/infdis/169.4.722. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shirasaka T., Yarchoan R., O'Brien M. C., Husson R. N., Anderson B. D., Kojima E., Shimada T., Broder S., Mitsuya H. Changes in drug sensitivity of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 during therapy with azidothymidine, dideoxycytidine, and dideoxyinosine: an in vitro comparative study. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Jan 15;90(2):562–566. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.2.562. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- St Clair M. H., Martin J. L., Tudor-Williams G., Bach M. C., Vavro C. L., King D. M., Kellam P., Kemp S. D., Larder B. A. Resistance to ddI and sensitivity to AZT induced by a mutation in HIV-1 reverse transcriptase. Science. 1991 Sep 27;253(5027):1557–1559. doi: 10.1126/science.1716788. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tantillo C., Ding J., Jacobo-Molina A., Nanni R. G., Boyer P. L., Hughes S. H., Pauwels R., Andries K., Janssen P. A., Arnold E. Locations of anti-AIDS drug binding sites and resistance mutations in the three-dimensional structure of HIV-1 reverse transcriptase. Implications for mechanisms of drug inhibition and resistance. J Mol Biol. 1994 Oct 28;243(3):369–387. doi: 10.1006/jmbi.1994.1665. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tudor-Williams G., St Clair M. H., McKinney R. E., Maha M., Walter E., Santacroce S., Mintz M., O'Donnell K., Rudoll T., Vavro C. L. HIV-1 sensitivity to zidovudine and clinical outcome in children. Lancet. 1992 Jan 4;339(8784):15–19. doi: 10.1016/0140-6736(92)90140-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yarchoan R., Lietzau J. A., Nguyen B. Y., Brawley O. W., Pluda J. M., Saville M. W., Wyvill K. M., Steinberg S. M., Agbaria R., Mitsuya H. A randomized pilot study of alternating or simultaneous zidovudine and didanosine therapy in patients with symptomatic human immunodeficiency virus infection. J Infect Dis. 1994 Jan;169(1):9–17. doi: 10.1093/infdis/169.1.9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yarchoan R., Perno C. F., Thomas R. V., Klecker R. W., Allain J. P., Wills R. J., McAtee N., Fischl M. A., Dubinsky R., McNeely M. C. Phase I studies of 2',3'-dideoxycytidine in severe human immunodeficiency virus infection as a single agent and alternating with zidovudine (AZT). Lancet. 1988 Jan 16;1(8577):76–81. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(88)90283-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- di Marzo Veronese F., Copeland T. D., DeVico A. L., Rahman R., Oroszlan S., Gallo R. C., Sarngadharan M. G. Characterization of highly immunogenic p66/p51 as the reverse transcriptase of HTLV-III/LAV. Science. 1986 Mar 14;231(4743):1289–1291. doi: 10.1126/science.2418504. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]




