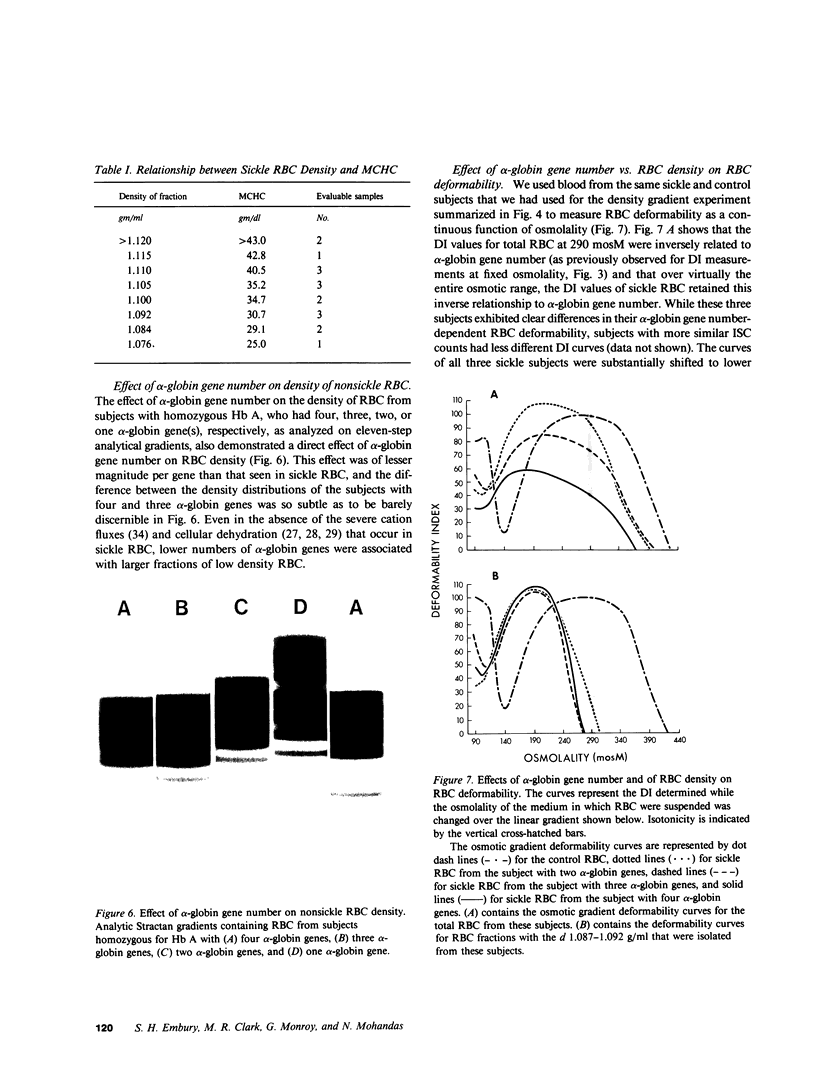
Abstract
The concurrence of sickle cell anemia and alpha-thalassemia results in less severe hemolytic anemia apparently as a result of reduced intraerythrocytic concentration of hemoglobin S and its retarded polymerization. We have evaluated the effect of alpha-globin gene number on several interrelated properties of sickle erythrocytes (RBC) that are expected to correlate with the hemolytic and rheologic consequences of sickle cell disease. The irreversibly sickled cell number, proportion of very dense sickle RBC, and diminished deformability of sickle RBC each varied directly with alpha-globin gene number. Sickle RBC density was a direct function of the mean corpuscular hemoglobin concentration (MCHC). Even in nonsickle RBC, alpha-globin gene number varied directly with RBC density. Despite differences in alpha-globin gene number, sickle RBC of the same density had the same degree of deformability and dehydration. These data indicate that the fundamental effect of alpha-thalassemia is to inhibit the generation of sickle RBC having high density and MCHC, and that the other beneficial effects of sickle RBC are secondary to this process. The less consistent effect on overall clinical severity reported for subjects with this concurrence may reflect an undefined detrimental effect of alpha-thalassemia, possibly on the whole blood viscosity or on sickle RBC membrane-mediated adherence phenomena.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alter B. P., Goff S. C., Efremov G. D., Gravely M. E., Huisman T. H. Globin chain electrophoresis: a new approach to the determination of the G gamma/A gamma ratio in fetal haemoglobin and to studies of globin synthesis. Br J Haematol. 1980 Apr;44(4):527–534. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1980.tb08706.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bank A., Mears G., Weiss R., O'Donnell J. V., Natta C. Preferential binding of beta s globin chains associated with stroma in sickle cell disorders. J Clin Invest. 1974 Oct;54(4):805–809. doi: 10.1172/JCI107820. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bertles J. F., Milner P. F. Irreversibly sickled erythrocytes: a consequence of the heterogeneous distribution of hemoglobin types in sickle-cell anemia. J Clin Invest. 1968 Aug;47(8):1731–1741. doi: 10.1172/JCI105863. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chien S., Usami S., Bertles J. F. Abnormal rheology of oxygenated blood in sickle cell anemia. J Clin Invest. 1970 Apr;49(4):623–634. doi: 10.1172/JCI106273. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chiu D., Lubin B., Roelofsen B., van Deenen L. L. Sickled erythrocytes accelerate clotting in vitro: an effect of abnormal membrane lipid asymmetry. Blood. 1981 Aug;58(2):398–401. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark M. R., Mohandas N., Embury S. H., Lubin B. H. A simple laboratory alternative to irreversibly sickled cell (ISC) counts. Blood. 1982 Sep;60(3):659–662. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark M. R., Mohandas N., Shohet S. B. Deformability of oxygenated irreversibly sickled cells. J Clin Invest. 1980 Jan;65(1):189–196. doi: 10.1172/JCI109650. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark M. R., Mohandas N., Shohet S. B. Osmotic gradient ektacytometry: comprehensive characterization of red cell volume and surface maintenance. Blood. 1983 May;61(5):899–910. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark M. R., Unger R. C., Shohet S. B. Monovalent cation composition and ATP and lipid content of irreversibly sickled cells. Blood. 1978 Jun;51(6):1169–1178. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dean J., Schechter A. N. Sickle-cell anemia: molecular and cellular bases of therapeutic approaches (first of three parts). N Engl J Med. 1978 Oct 5;299(14):752–763. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197810052991405. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dozy A. M., Kan Y. W., Embury S. H., Mentzer W. C., Wang W. C., Lubin B., Davis J. R., Jr, Koenig H. M. alpha-Globin gene organisation in blacks precludes the severe form of alpha-thalassaemia. Nature. 1979 Aug 16;280(5723):605–607. doi: 10.1038/280605a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eaton J. W., Jacob H. S., White J. G. Membrane abnormalities of irreversibly sickled cells. Semin Hematol. 1979 Jan;16(1):52–64. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eaton J. W., Skelton T. D., Swofford H. S., Kolpin C. E., Jacob H. S. Elevated erythrocyte calcium in sickle cell disease. Nature. 1973 Nov 9;246(5428):105–106. doi: 10.1038/246105a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Embury S. H., Dozy A. M., Miller J., Davis J. R., Jr, Kleman K. M., Preisler H., Vichinsky E., Lande W. N., Lubin B. H., Kan Y. W. Concurrent sickle-cell anemia and alpha-thalassemia: effect on severity of anemia. N Engl J Med. 1982 Feb 4;306(5):270–274. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198202043060504. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glader B. E., Lux S. E., Muller-Soyano A., Platt O. S., Propper R. D., Nathan D. G. Energy reserve and cation composition of irreversibly sickled cells in vivo. Br J Haematol. 1978 Dec;40(4):527–532. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1978.tb05828.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glader B. E., Nathan D. G. Cation permeability alterations during sickling: relationship to cation composition and cellular hydration of irreversibly sickled cells. Blood. 1978 May;51(5):983–989. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hawker H., Neilson H., Hayes R. J., Serjeant G. R. Haematological factors associated with avascular necrosis of the femoral head in homozygous sickle cell disease. Br J Haematol. 1982 Jan;50(1):29–34. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1982.tb01887.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hayes R. J., Condon P. I., Serjeant G. R. Haematological factors associated with proliferative retinopathy in homozygous sickle cell disease. Br J Ophthalmol. 1981 Jan;65(1):29–35. doi: 10.1136/bjo.65.1.29. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hebbel R. P., Boogaerts M. A., Eaton J. W., Steinberg M. H. Erythrocyte adherence to endothelium in sickle-cell anemia. A possible determinant of disease severity. N Engl J Med. 1980 May 1;302(18):992–995. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198005013021803. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hebbel R. P., Eaton J. W., Balasingam M., Steinberg M. H. Spontaneous oxygen radical generation by sickle erythrocytes. J Clin Invest. 1982 Dec;70(6):1253–1259. doi: 10.1172/JCI110724. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hebbel R. P., Yamada O., Moldow C. F., Jacob H. S., White J. G., Eaton J. W. Abnormal adherence of sickle erythrocytes to cultured vascular endothelium: possible mechanism for microvascular occlusion in sickle cell disease. J Clin Invest. 1980 Jan;65(1):154–160. doi: 10.1172/JCI109646. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Higgs D. R., Aldridge B. E., Lamb J., Clegg J. B., Weatherall D. J., Hayes R. J., Grandison Y., Lowrie Y., Mason K. P., Serjeant B. E. The interaction of alpha-thalassemia and homozygous sickle-cell disease. N Engl J Med. 1982 Jun 17;306(24):1441–1446. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198206173062402. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Higgs D. R., Goodbourn S. E., Wainscoat J. S., Clegg J. B., Weatherall D. J. Highly variable regions of DNA flank the human alpha globin genes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Sep 11;9(17):4213–4224. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.17.4213. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hofrichter J., Ross P. D., Eaton W. A. Kinetics and mechanism of deoxyhemoglobin S gelation: a new approach to understanding sickle cell disease. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Dec;71(12):4864–4868. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.12.4864. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoover R., Rubin R., Wise G., Warren R. Adhesion of normal and sickle erythrocytes to endothelial monolayer cultures. Blood. 1979 Oct;54(4):872–876. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horne M. K., 3rd Sickle cell anemia as a rheologic disease. Am J Med. 1981 Feb;70(2):288–298. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(81)90764-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jensen M., Shohet S. B., Nathan D. G. The role of red cell energy metabolism in the generation of irreversibly sickled cells in vitro. Blood. 1973 Dec;42(6):835–842. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaul D. K., Fabry M. E., Windisch P., Baez S., Nagel R. L. Erythrocytes in sickle cell anemia are heterogeneous in their rheological and hemodynamic characteristics. J Clin Invest. 1983 Jul;72(1):22–31. doi: 10.1172/JCI110960. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lubin B., Chiu D., Bastacky J., Roelofsen B., Van Deenen L. L. Abnormalities in membrane phospholipid organization in sickled erythrocytes. J Clin Invest. 1981 Jun;67(6):1643–1649. doi: 10.1172/JCI110200. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lux S. E., John K. M. Isolation and partial characterization of a high molecular weight red cell membrane protein complex normally removed by the spleen. Blood. 1977 Oct;50(4):625–641. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lux S. E., John K. M., Karnovsky M. J. Irreversible deformation of the spectrin-actin lattice in irreversibly sickled cells. J Clin Invest. 1976 Oct;58(4):955–963. doi: 10.1172/JCI108549. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maniatis T., Jeffrey A., Kleid D. G. Nucleotide sequence of the rightward operator of phage lambda. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Mar;72(3):1184–1188. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.3.1184. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mears J. G., Lachman H. M., Labie D., Nagel R. L. Alpha-thalassemia is related to prolonged survival in sickle cell anemia. Blood. 1983 Aug;62(2):286–290. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mohandas N., Clark M. R., Jacobs M. S., Shohet S. B. Analysis of factors regulating erythrocyte deformability. J Clin Invest. 1980 Sep;66(3):563–573. doi: 10.1172/JCI109888. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Noguchi C. T., Torchia D. A., Schechter A. N. Determination of deoxyhemoglobin S polymer in sickle erythrocytes upon deoxygenation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Sep;77(9):5487–5491. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.9.5487. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Noguchi C. T., Torchia D. A., Schechter A. N. Intracellular polymerization of sickle hemoglobin. Effects of cell heterogeneity. J Clin Invest. 1983 Sep;72(3):846–852. doi: 10.1172/JCI111055. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz R. S., Düzgünes N., Chiu D. T., Lubin B. Interaction of phosphatidylserine-phosphatidylcholine liposomes with sickle erythrocytes. Evidence for altered membrane surface properties. J Clin Invest. 1983 Jun;71(6):1570–1580. doi: 10.1172/JCI110913. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Serjeant G. R. Fetal haemoglobin in homozygous sickle cell disease. Clin Haematol. 1975 Feb;4(1):109–122. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Serjeant G. R., Serjeant B. E., Milner P. F. The irreversibly sickled cell; a determinant of haemolysis in sickle cell anaemia. Br J Haematol. 1969 Dec;17(6):527–533. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1969.tb01403.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern E. M. Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol. 1975 Nov 5;98(3):503–517. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80083-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steinberg M. H., Dreiling B. J., Morrison F. S., Necheles T. F. Mild sickle cell disease. Clinical and laboratory studies. JAMA. 1973 Apr 16;224(3):317–321. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stockman J. A., Nigro M. A., Mishkin M. M., Oski F. A. Occlusion of large cerebral vessels in sickle-cell anemia. N Engl J Med. 1972 Oct 26;287(17):846–849. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197210262871703. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson J. T., Wilson L. B., deRiel J. K., Villa-komaroff L., Efstratiadis A., Forget B. G., Weissman S. M. Insertion of synthetic copies of human globin genes into bacterial plasmids. Nucleic Acids Res. 1978 Feb;5(2):563–581. doi: 10.1093/nar/5.2.563. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]





