Abstract
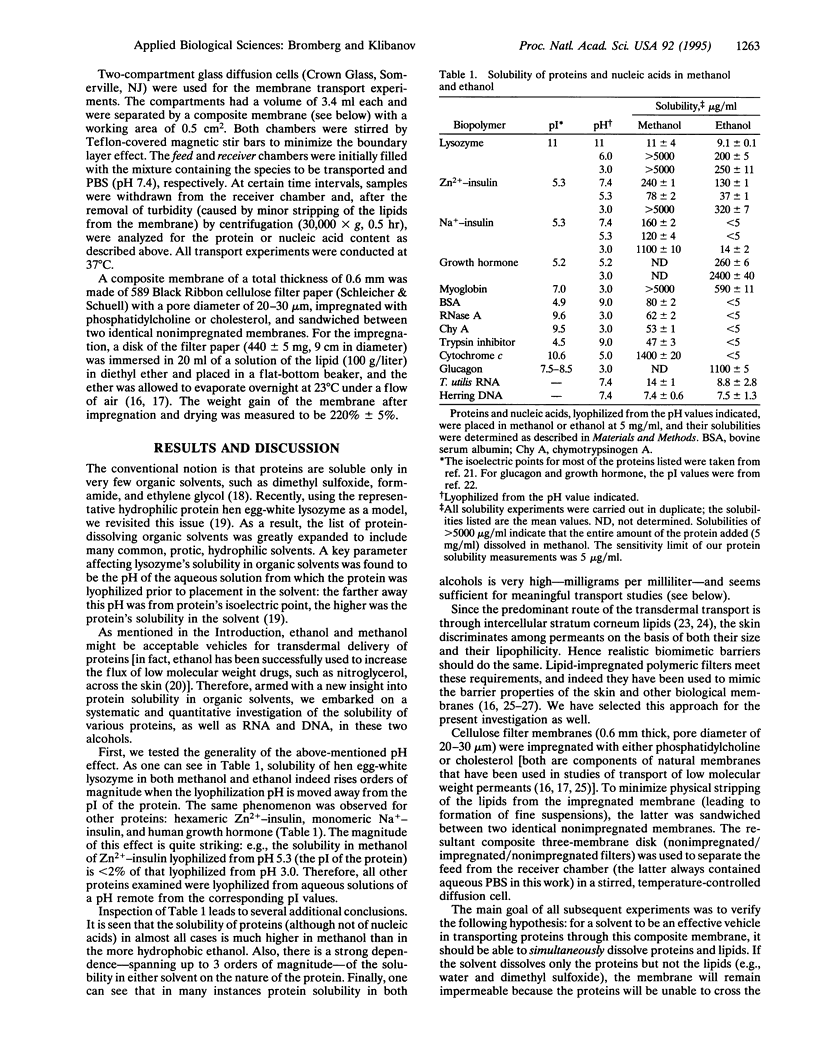
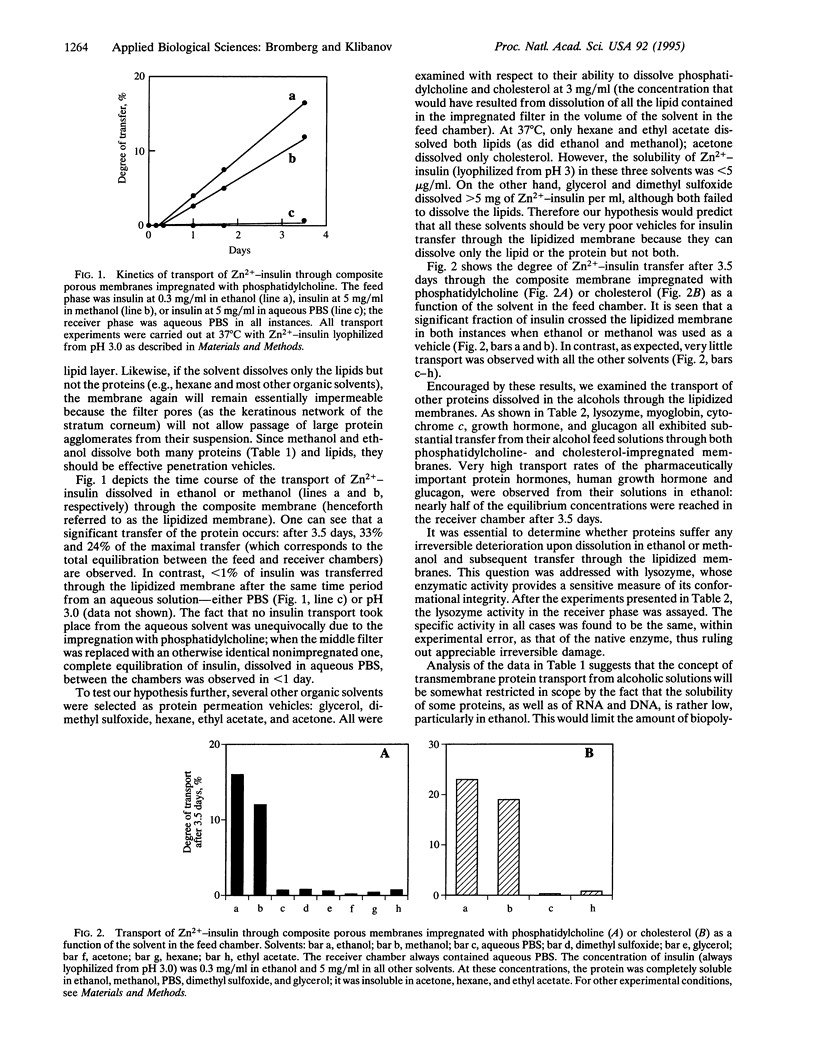
Using lipid-impregnated porous cellulose membranes as biomimetic barriers, we tested the hypothesis that to afford effective transmembrane transfer of proteins and nucleic acids, the vehicle solvent should be able to dissolve both the biopolymers and the lipids. While the majority of solvents dissolve one or the other, ethanol and methanol were found to dissolve both, especially if the protein had been lyophilized from an aqueous solution of a pH remote from the protein's isoelectric point. A number of proteins, as well as RNA and DNA, dissolved in these alcohols readily crossed the lipidized membranes, whereas the same biopolymers placed in nondissolving solvents (e.g., hexane and ethyl acetate) or in those unable to dissolve lipids (e.g., water and dimethyl sulfoxide) exhibited little transmembrane transport. The solubility of biopolymers in ethanol and methanol was further enhanced by complexation with detergents and poly(ethylene glycol); significant protein and nucleic acid transport through the lipidized membranes was observed from these solvents but not from water.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bromberg L. E., Klibanov A. M. Detergent-enabled transport of proteins and nucleic acids through hydrophobic solvents. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 Jan 4;91(1):143–147. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.1.143. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burnette R. R., Marrero D. Comparison between the iontophoretic and passive transport of thyrotropin releasing hormone across excised nude mouse skin. J Pharm Sci. 1986 Aug;75(8):738–743. doi: 10.1002/jps.2600750803. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Del Terzo S., Behl C. R., Nash R. A. Iontophoretic transport of a homologous series of ionized and nonionized model compounds: influence of hydrophobicity and mechanistic interpretation. Pharm Res. 1989 Jan;6(1):85–90. doi: 10.1023/a:1015812005467. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green P. G., Hinz R. S., Cullander C., Yamane G., Guy R. H. Iontophoretic delivery of amino acids and amino acid derivatives across the skin in vitro. Pharm Res. 1991 Sep;8(9):1113–1120. doi: 10.1023/a:1015894016235. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guy R. H., Hadgraft J. Physicochemical aspects of percutaneous penetration and its enhancement. Pharm Res. 1988 Dec;5(12):753–758. doi: 10.1023/a:1015980516564. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kari B. Control of blood glucose levels in alloxan-diabetic rabbits by iontophoresis of insulin. Diabetes. 1986 Feb;35(2):217–221. doi: 10.2337/diab.35.2.217. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Potts R. O., Guy R. H. Predicting skin permeability. Pharm Res. 1992 May;9(5):663–669. doi: 10.1023/a:1015810312465. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SHUGAR D. The measurement of lysozyme activity and the ultra-violet inactivation of lysozyme. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1952 Mar;8(3):302–309. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(52)90045-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sandermann H., Jr Preparation of stable and solvent-free model membranes. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1979 Apr 13;87(3):789–794. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(79)92027-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shieh P. K., Lanyi J., Packer L. Lipid-impregnated filter membranes: a stable planar membrane system for assay of electrical properties across reconstituted liposomes and natural membrane vesicles. Methods Enzymol. 1979;55:604–613. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(79)55069-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith P. K., Krohn R. I., Hermanson G. T., Mallia A. K., Gartner F. H., Provenzano M. D., Fujimoto E. K., Goeke N. M., Olson B. J., Klenk D. C. Measurement of protein using bicinchoninic acid. Anal Biochem. 1985 Oct;150(1):76–85. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(85)90442-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TOBIAS J. M., AGIN D. P., PAWLOWSKI R. Phospholipidcholesterol membrane model. Control of resistance by ions or current flow. J Gen Physiol. 1962 May;45:989–1001. doi: 10.1085/jgp.45.5.989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walter J. S., Wheeler J. S., Jr, Dunn R. B. Dynamic bulbocavernosus reflex: dyssynergia evaluation following SCI. J Am Paraplegia Soc. 1994 Jul;17(3):140–145. doi: 10.1080/01952307.1994.11735924. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



