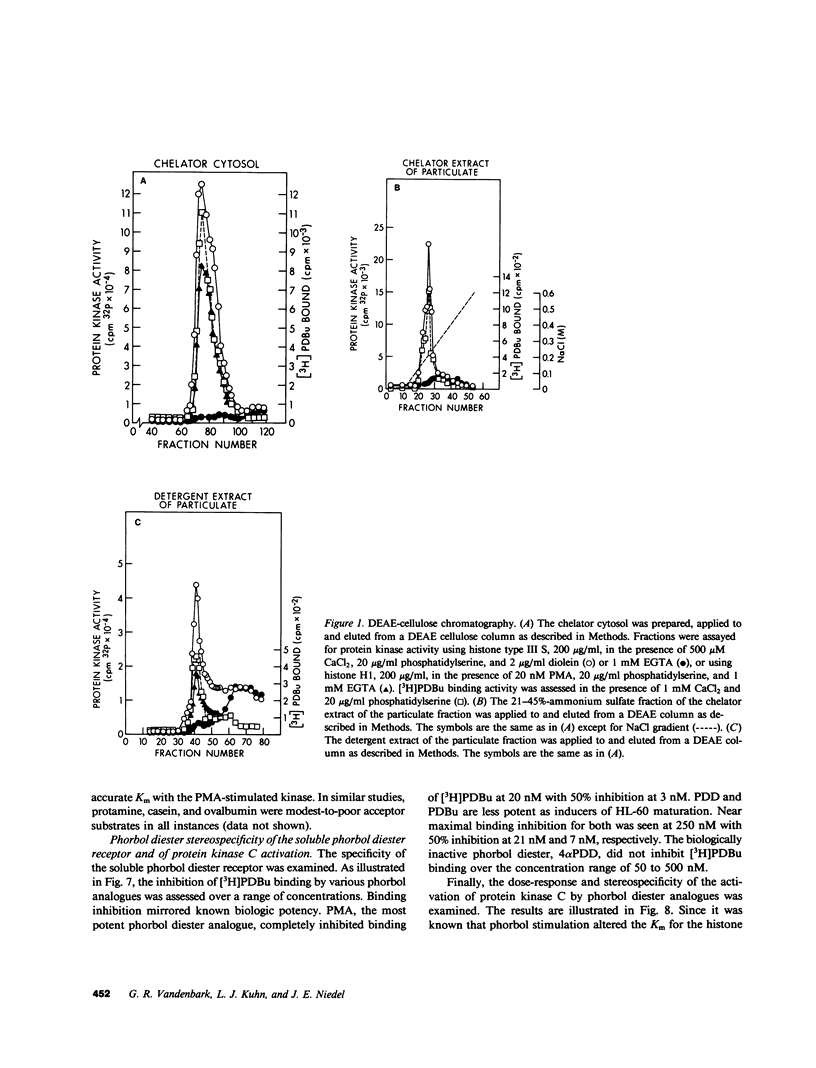
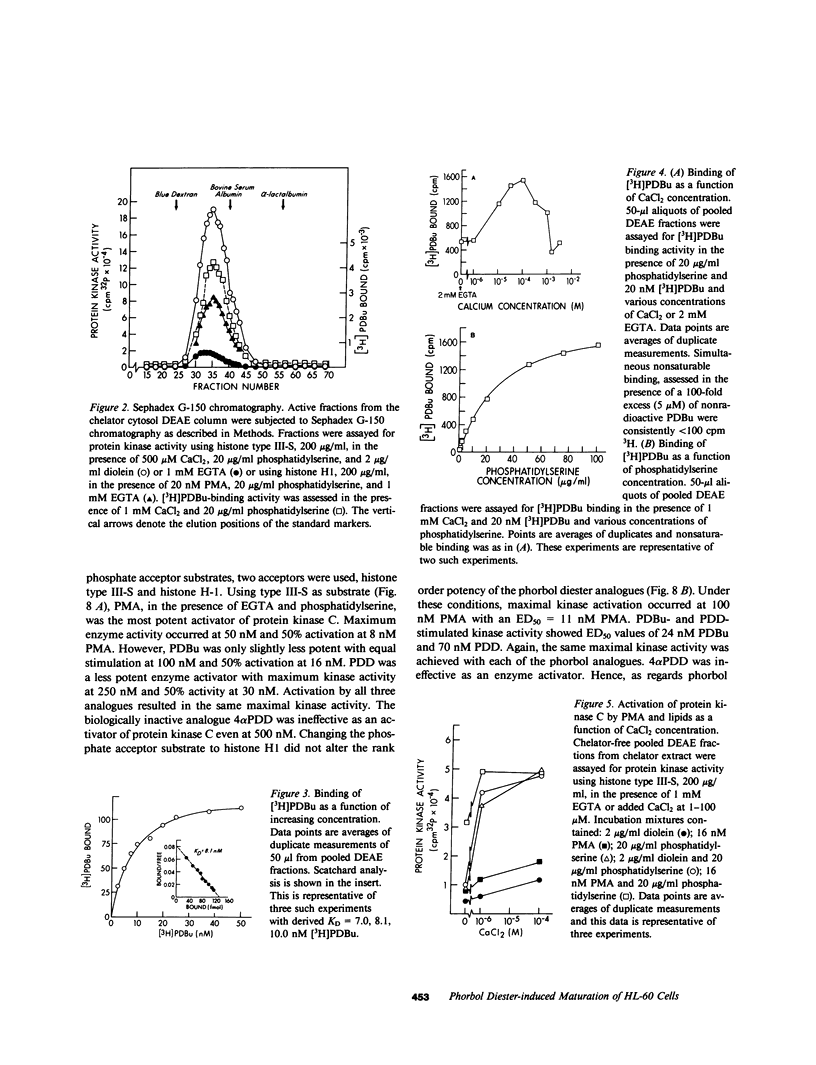
Abstract
The phorbol diesters are the most potent inducers of differentiation of the promyelocytic leukemia cell line, HL-60. Soluble phorbol diester receptors from HL-60 cells were obtained from the cytosolic fraction and from the particulate fraction by either divalent ion chelation or detergent extraction. The partially purified soluble phorbol diester receptors required exogenous Ca2+ and phospholipid for maximal binding and displayed a dissociation constant (KD) of 8.1 nM for [3H]phorbol 12,13-dibutyrate. Phorbol diester analogues inhibited [3H]phorbol 12,13-dibutyrate binding in a stereospecific manner consistent with their biologic potency. The soluble phorbol diester receptors prepared by all three methods copurified in a constant ratio with the Ca2+/phospholipid-dependent protein kinase C through ammonium sulfate precipitation, DEAE ion exchange, and gel filtration chromatography. Partially purified protein kinase C was directly activated by the phorbol diesters even in the absence of exogenous Ca2+. The ability of a series of phorbol analogues to activate the kinase correlated with their known activity as inducers of cell differentiation. In addition, phorbol diester stimulation altered the phosphate acceptor substrate profile of protein kinase C, at least in part, by alteration of the Michaelis constant (Km). These data suggest that protein kinase C is the phorbol diester receptor and that phorbol diester-induced macrophage maturation of HL-60 cells may be mediated by activation of intracellular protein kinase C.
Full text
PDF







Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abrahm J. L., Smiley R. Modification of normal human myelopoiesis by 12-0 tetradecanoylphorbol-13-acetate (TPA). Blood. 1981 Dec;58(6):1119–1126. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Amrein P. C., Stossel T. P. Prevention of degradation of human polymorphonuclear leukocyte proteins by diisopropylfluorophosphate. Blood. 1980 Sep;56(3):442–447. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ashendel C. L., Staller J. M., Boutwell R. K. Identification of a calcium- and phospholipid- dependent phorbol ester binding activity in the soluble fraction of mouse tissues. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1983 Feb 28;111(1):340–345. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(83)80157-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ashendel C. L., Staller J. M., Boutwell R. K. Protein kinase activity associated with a phorbol ester receptor purified from mouse brain. Cancer Res. 1983 Sep;43(9):4333–4337. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ashendel C. L., Staller J. M., Boutwell R. K. Solubilization, purification, and reconstitution of a phorbol ester receptor from the particulate protein fraction of mouse brain. Cancer Res. 1983 Sep;43(9):4327–4332. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BERENBLUM I. A speculative review; the probable nature of promoting action and its significance in the understanding of the mechanism of carcinogenesis. Cancer Res. 1954 Aug;14(7):471–477. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blumberg P. M. In vitro studies on the mode of action of the phorbol esters, potent tumor promoters: part 1. Crit Rev Toxicol. 1980 Dec;8(2):153–197. doi: 10.3109/10408448009037493. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(76)90527-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cabot M. C., Welsh C. J. Fatty acid metabolism in phorbol ester-differentiating human leukemia cells. Cancer Res. 1981 Dec;41(12 Pt 1):4910–4915. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cassileth P. A., Suholet D., Cooper R. A. Early changes in phosphatidylcholine metabolism in human acute promyelocytic leukemia cells stimulated to differentiate by phorbol ester. Blood. 1981 Aug;58(2):237–243. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Castagna M., Takai Y., Kaibuchi K., Sano K., Kikkawa U., Nishizuka Y. Direct activation of calcium-activated, phospholipid-dependent protein kinase by tumor-promoting phorbol esters. J Biol Chem. 1982 Jul 10;257(13):7847–7851. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chiao J. W., Freitag W. F., Steinmetz J. C., Andreeff M. Changes of cellular markers during differentiation of HL-60 promyelocytes to macrophages as induced by T lymphocyte conditioned medium. Leuk Res. 1981;5(6):477–489. doi: 10.1016/0145-2126(81)90118-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collett M. S., Purchio A. F., Erikson R. L. Avian sarcoma virus-transforming protein, pp60src shows protein kinase activity specific for tyrosine. Nature. 1980 May 15;285(5761):167–169. doi: 10.1038/285167a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collins S. J., Gallo R. C., Gallagher R. E. Continuous growth and differentiation of human myeloid leukaemic cells in suspension culture. Nature. 1977 Nov 24;270(5635):347–349. doi: 10.1038/270347a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooper R. A., Braunwald A. D., Kuo A. L. Phorbol ester induction of leukemic cell differentiation is a membrane-mediated process. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 May;79(9):2865–2869. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.9.2865. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cossu G., Kuo A. L., Pessano S., Warren L., Cooper R. A. Decreased synthesis of high-molecular-weight glycopeptides in human promyelocytic leukemic cells (HL-60) during phorbol ester-induced macrophage differentiation. Cancer Res. 1982 Feb;42(2):484–489. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Delclos K. B., Nagle D. S., Blumberg P. M. Specific binding of phorbol ester tumor promoters to mouse skin. Cell. 1980 Apr;19(4):1025–1032. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90093-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Driedger P. E., Blumberg P. M. Specific binding of phorbol ester tumor promoters. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Jan;77(1):567–571. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.1.567. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dunphy W. G., Delclos K. B., Blumberg P. M. Characterization of specific binding of [3H]phorbol 12,13-dibutyrate and [3H]phorbol 12-myristate 13-acetate to mouse brain. Cancer Res. 1980 Oct;40(10):3635–3641. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ek B., Heldin C. H. Characterization of a tyrosine-specific kinase activity in human fibroblast membranes stimulated by platelet-derived growth factor. J Biol Chem. 1982 Sep 10;257(17):10486–10492. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fibach E., Rachmilewitz E. A. Tumour promoters induce macrophage differentiation in human myeloid cells from patients with acute and chronic myelogenous leukaemia. Br J Haematol. 1981 Feb;47(2):203–210. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1981.tb02780.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gallagher R., Collins S., Trujillo J., McCredie K., Ahearn M., Tsai S., Metzgar R., Aulakh G., Ting R., Ruscetti F. Characterization of the continuous, differentiating myeloid cell line (HL-60) from a patient with acute promyelocytic leukemia. Blood. 1979 Sep;54(3):713–733. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodwin B. J., Weinberg J. B. Receptor-mediated modulation of human monocyte, neutrophil, lymphocyte, and platelet function by phorbol diesters. J Clin Invest. 1982 Oct;70(4):699–706. doi: 10.1172/JCI110665. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Helfman D. M., Barnes K. C., Kinkade J. M., Jr, Vogler W. R., Shoji M., Kuo J. F. Phospholipid-sensitive Ca2+-dependent protein phosphorylation system in various types of leukemic cells from human patients and in human leukemic cell lines HL60 and K562, and its inhibition by alkyl-lysophospholipid. Cancer Res. 1983 Jun;43(6):2955–2961. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horowitz A. D., Greenebaum E., Weinstein I. B. Identification of receptors for phorbol ester tumor promoters in intact mammalian cells and of an inhibitor of receptor binding in biologic fluids. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Apr;78(4):2315–2319. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.4.2315. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huberman E., Callaham M. F. Induction of terminal differentiation in human promyelocytic leukemia cells by tumor-promoting agents. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Mar;76(3):1293–1297. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.3.1293. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huberman E., Weeks C., Herrmann A., Callaham M., Slaga T. Alterations in polyamine levels induced by phorbol diesters and other agents that promote differentiation in human promyelocytic leukemia cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Feb;78(2):1062–1066. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.2.1062. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunter T., Sefton B. M. Transforming gene product of Rous sarcoma virus phosphorylates tyrosine. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Mar;77(3):1311–1315. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.3.1311. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inoue M., Kishimoto A., Takai Y., Nishizuka Y. Studies on a cyclic nucleotide-independent protein kinase and its proenzyme in mammalian tissues. II. Proenzyme and its activation by calcium-dependent protease from rat brain. J Biol Chem. 1977 Nov 10;252(21):7610–7616. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kawahara Y., Takai Y., Minakuchi R., Sano K., Nishizuka Y. Possible involvement of Ca2+-activated, phospholipid-dependent protein kinase in platelet activation. J Biochem. 1980 Sep;88(3):913–916. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a133048. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kikkawa U., Takai Y., Minakuchi R., Inohara S., Nishizuka Y. Calcium-activated, phospholipid-dependent protein kinase from rat brain. Subcellular distribution, purification, and properties. J Biol Chem. 1982 Nov 25;257(22):13341–13348. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kishimoto A., Kajikawa N., Shiota M., Nishizuka Y. Proteolytic activation of calcium-activated, phospholipid-dependent protein kinase by calcium-dependent neutral protease. J Biol Chem. 1983 Jan 25;258(2):1156–1164. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koeffler H. P., Bar-Eli M., Territo M. C. Phorbol ester effect on differentiation of human myeloid leukemia cell lines blocked at different stages of maturation. Cancer Res. 1981 Mar;41(3):919–926. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koeffler H. P., Bar-Eli M., Territo M. Phorbol diester-induced macrophage differentiation of leukemic blasts from patients with human myelogenous leukemia. J Clin Invest. 1980 Nov;66(5):1101–1108. doi: 10.1172/JCI109939. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kornberg A., Treves A., Rachmilewitz E. A., Fibach E. Generation of procoagulant activity (PCA) by phorbol-esters-induced macrophages derived from a leukemic promyelocytic cell line (HL-60). Blood. 1982 May;59(5):1061–1066. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kraft A. S., Anderson W. B., Cooper H. L., Sando J. J. Decrease in cytosolic calcium/phospholipid-dependent protein kinase activity following phorbol ester treatment of EL4 thymoma cells. J Biol Chem. 1982 Nov 25;257(22):13193–13196. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kraft A. S., Anderson W. B. Phorbol esters increase the amount of Ca2+, phospholipid-dependent protein kinase associated with plasma membrane. Nature. 1983 Feb 17;301(5901):621–623. doi: 10.1038/301621a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuo J. F., Andersson R. G., Wise B. C., Mackerlova L., Salomonsson I., Brackett N. L., Katoh N., Shoji M., Wrenn R. W. Calcium-dependent protein kinase: widespread occurrence in various tissues and phyla of the animal kingdom and comparison of effects of phospholipid, calmodulin, and trifluoperazine. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Dec;77(12):7039–7043. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.12.7039. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leach K. L., James M. L., Blumberg P. M. Characterization of a specific phorbol ester aporeceptor in mouse brain cytosol. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jul;80(14):4208–4212. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.14.4208. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luk G. D., Civin C. I., Weissman R. M., Baylin S. B. Ornithine decarboxylase: essential in proliferation but not differentiation of human promyelocytic leukemia cells. Science. 1982 Apr 2;216(4541):75–77. doi: 10.1126/science.6950518. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Minakuchi R., Takai Y., Yu B., Nishizuka Y. Widespread occurrence of calcium-activated, phospholipid-dependent protein kinase in mammalian tissues. J Biochem. 1981 May;89(5):1651–1654. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a133362. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mulder A., Alexander S., Engelfriet C. P., von dem Borne A. E., Strominger J. L. Characterization, by immunoprecipitation, of myeloid- and monocyte-specific antigens present on the human promyelocytic cell line (HL-60) in three stages of differentiation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Aug;78(8):5091–5095. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.8.5091. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Newburger P. E., Baker R. D., Hansen S. L., Duncan R. A., Greenberger J. S. Functionally deficient differentiation of HL-60 promyelocytic leukemia cells induced by phorbol myristate acetate. Cancer Res. 1981 May;41(5):1861–1865. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Niedel J. E., Kuhn L. J., Vandenbark G. R. Phorbol diester receptor copurifies with protein kinase C. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jan;80(1):36–40. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.1.36. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishimura J., Huang J. S., Deuel T. F. Platelet-derived growth factor stimulates tyrosine-specific protein kinase activity in Swiss mouse 3T3 cell membranes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Jul;79(14):4303–4307. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.14.4303. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ogawa Y., Takai Y., Kawahara Y., Kimura S., Nishizuka Y. A new possible regulatory system for protein phosphorylation in human peripheral lymphocytes. I. Characterization of a calcium-activated, phospholipid-dependent protein kinase. J Immunol. 1981 Oct;127(4):1369–1374. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olsson I., Olofsson T., Mauritzon N. Characterization of mononuclear blood cell-derived differentiation inducing factors for the human promyelocytic leukemia cell line HL-60. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1981 Dec;67(6):1225–1230. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pegoraro L., Abrahm J., Cooper R. A., Levis A., Lange B., Meo P., Rovera G. Differentiation of human leukemias in response to 12-0-tetradecanoylphorbol-13-acetate in vitro. Blood. 1980 May;55(5):859–862. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rovera G., O'Brien T. G., Diamond L. Induction of differentiation in human promyelocytic leukemia cells by tumor promoters. Science. 1979 May 25;204(4395):868–870. doi: 10.1126/science.286421. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rovera G., Santoli D., Damsky C. Human promyelocytic leukemia cells in culture differentiate into macrophage-like cells when treated with a phorbol diester. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Jun;76(6):2779–2783. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.6.2779. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sando J. J., Young M. C. Identification of high-affinity phorbol ester receptor in cytosol of EL4 thymoma cells: requirement for calcium, magnesium, and phospholipids. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 May;80(9):2642–2646. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.9.2642. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schatzman R. C., Raynor R. L., Fritz R. B., Kuo J. F. Purification to homogeneity, characterization and monoclonal antibodies of phospholipid-sensitive Ca2+-dependent protein kinase from spleen. Biochem J. 1983 Feb 1;209(2):435–443. doi: 10.1042/bj2090435. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sefton B. M., Hunter T., Beemon K., Eckhart W. Evidence that the phosphorylation of tyrosine is essential for cellular transformation by Rous sarcoma virus. Cell. 1980 Jul;20(3):807–816. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90327-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shoyab M., Todaro G. J. Specific high affinity cell membrane receptors for biologically active phorbol and ingenol esters. Nature. 1980 Dec 4;288(5790):451–455. doi: 10.1038/288451a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Solanki V., Slaga T. J., Callaham M., Huberman E. Down regulation of specific binding of [20-3H]phorbol 12,13-dibutyrate and phorbol ester-induced differentiation of human promyelocytic leukemia cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Mar;78(3):1722–1725. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.3.1722. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsuchiya S., Kobayashi Y., Goto Y., Okumura H., Nakae S., Konno T., Tada K. Induction of maturation in cultured human monocytic leukemia cells by a phorbol diester. Cancer Res. 1982 Apr;42(4):1530–1536. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ushiro H., Cohen S. Identification of phosphotyrosine as a product of epidermal growth factor-activated protein kinase in A-431 cell membranes. J Biol Chem. 1980 Sep 25;255(18):8363–8365. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weinberg J. B. Tumor cell killing by phorbol ester--differentiated human leukemia cells. Science. 1981 Aug 7;213(4508):655–657. doi: 10.1126/science.7196085. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wise B. C., Raynor R. L., Kuo J. F. Phospholipid-sensitive Ca2+-dependent protein kinase from heart. I. Purification and general properties. J Biol Chem. 1982 Jul 25;257(14):8481–8488. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Witte O. N., Dasgupta A., Baltimore D. Abelson murine leukaemia virus protein is phosphorylated in vitro to form phosphotyrosine. Nature. 1980 Feb 28;283(5750):826–831. doi: 10.1038/283826a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


