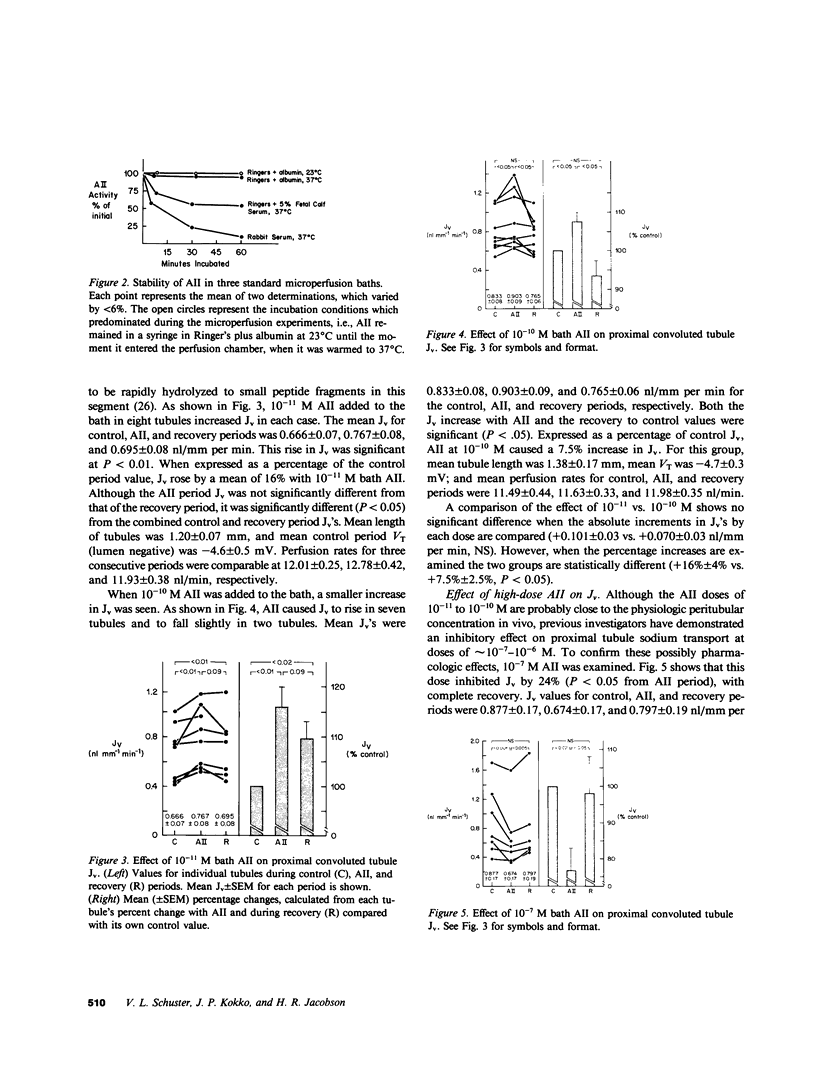
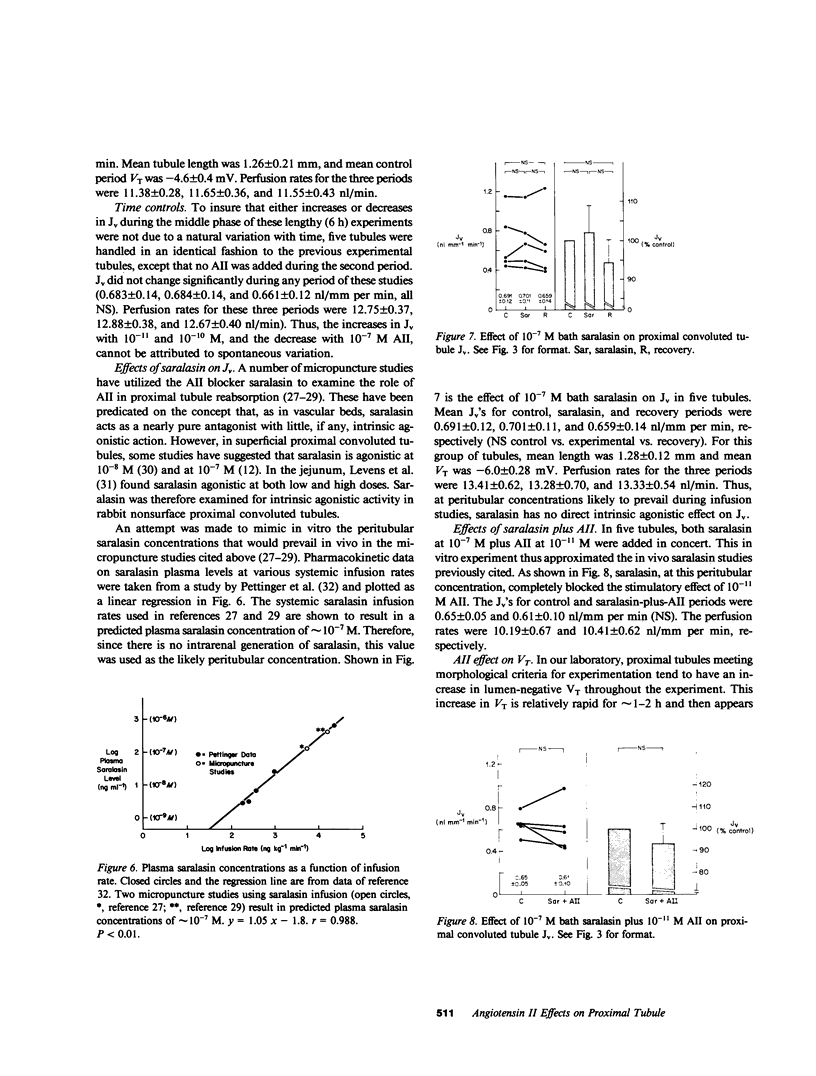
Abstract
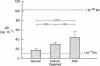
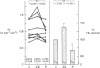
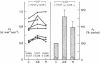
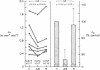
Numerous previous studies have proposed a role for angiotensin II (AII) in the renal regulation of salt balance. At least one nephron site, the proximal convoluted segment, has been implicated in this role. We used in vitro microperfusion of rabbit proximal convoluted tubules to further examine this question. To insure use of appropriate in vivo concentrations as well as potency of the hormone in vitro, we measured plasma AII levels by radioimmunoassay in normal, sodium-depleted, and adrenalectomized rabbits, and measured AII activity by bioassay after incubation in various microperfusion baths. Plasma levels ranged from approximately 2 X 10(-11) to 5 X 10(-11) M. AII activity was stable in Ringer's solution plus albumin, but not in rabbit serum or Ringer's solution plus fetal calf serum. In Ringer's solution plus albumin, physiologic concentrations of AII stimulated volume reabsorption (Jv). 10(-11) M AII increased Jv by 16% (P less than 0.01). 10(-10) M AII produced a lesser increase, 7.5% (P less than 0.05). At a frequently studied, but probably pharmacologic dose, 10(-7) M AII inhibited Jv by 24% (P less than 0.001). AII at 10(-11) M did not stimulate Jv in the presence of 10(-7) M saralasin. Though previous studies have suggested agonistic effects of saralasin alone in epithelia, we found no significant effect of 10(-7) M saralasin on Jv. None of the AII doses measurably changed transepithelial voltage. We conclude that AII in physiologic doses directly stimulates Jv in proximal convoluted tubules and this effect is probably receptor mediated and, within the limits of detection, electroneutral.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bolton J. E., Munday K. A., Parsons B. J., York B. G. Effects of angiotensin II on fluid transport, transmural potential difference and blood flow by rat jejunum in vivo. J Physiol. 1975 Dec;253(2):411–428. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1975.sp011197. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown G. P., Douglas J. G. Angiotensin II-binding sites in rat and primate isolated renal tubular basolateral membranes. Endocrinology. 1983 Jun;112(6):2007–2014. doi: 10.1210/endo-112-6-2007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burg M. B., Orloff J. Control of fluid absorption in the renal proximal tubule. J Clin Invest. 1968 Sep;47(9):2016–2024. doi: 10.1172/JCI105888. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burg M., Patlak C., Green N., Villey D. Organic solutes in fluid absorption by renal proximal convoluted tubules. Am J Physiol. 1976 Aug;231(2):627–637. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1976.231.2.627. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burghardt W., Schweisfurth H., Dahlheim H. Juxtaglomerular angiotensin II formation. Kidney Int Suppl. 1982 Aug;12:S49–S54. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davies N. T., Munday K. A., Parsons B. J. The effect of angiotensin on rat intestinal fluid transfer. J Endocrinol. 1970 Sep;48(1):39–46. doi: 10.1677/joe.0.0480039. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flamenbaum W., Hamburger R. J. Superficial and deep juxtaglomerular apparatus renin activity of the rat kidney. Effect of surgical preparation and NaCl intake. J Clin Invest. 1974 Dec;54(6):1373–1381. doi: 10.1172/JCI107884. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friedman P. A., Figueiredo J. F., Maack T., Windhager E. E. Sodium-calcium interactions in the renal proximal convoluted tubule of the rabbit. Am J Physiol. 1981 Jun;240(6):F558–F568. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1981.240.6.F558. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HUGHES-JONES N. C., PICKERING G. W. The nature of the action of renin and hypertensin on renal function in the rabbit. J Physiol. 1949 Sep;109(3-4):288–307. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1949.sp004393. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harris P. J., Young J. A. Dose-dependent stimulation and inhibition of proximal tubular sodium reabsorption by angiotensin II in the rat kidney. Pflugers Arch. 1977 Jan 17;367(3):295–297. doi: 10.1007/BF00581370. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hornych A., Meyer P., Milliez P. Angiotensin, vasopressin, and cyclic AMP: effects on sodium and water fluxes in rat colon. Am J Physiol. 1973 May;224(5):1223–1229. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1973.224.5.1223. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horster M., Nagel W., Schnermann J., Thurau K. Zur Frage einer direkten Angiotensinwirkung auf die Natriumresorption im proximalen Tubulus und in der Henleschen Schleife der Rattenniere. Pflugers Arch Gesamte Physiol Menschen Tiere. 1966;292(2):118–128. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang W. C., Ploth D. W., Navar L. G. Angiotensin-mediated alterations in nephron function in Goldblatt hypertensive rats. Am J Physiol. 1982 Dec;243(6):F553–F560. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1982.243.6.F553. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Imai M., Seldin D. W., Kokko J. P. Effect of perfusion rate on the fluxes of water, sodium, chloride and urea across the proximal convoluted tubule. Kidney Int. 1977 Jan;11(1):18–27. doi: 10.1038/ki.1977.3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacobson H. R. Altered permeability in the proximal tubule response to cyclic AMP. Am J Physiol. 1979 Jan;236(1):F71–F79. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1979.236.1.F71. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacobson H. R. Characteristics of volume reabsorption in rabbit superficial and juxtamedullary proximal convoluted tubules. J Clin Invest. 1979 Mar;63(3):410–418. doi: 10.1172/JCI109317. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacobson H. R. Effects of CO2 and acetazolamide on bicarbonate and fluid transport in rabbit proximal tubules. Am J Physiol. 1981 Jan;240(1):F54–F62. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1981.240.1.F54. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jensen P. K., Steven K. Angiotensin II induced reduction of peritubular capillary diameter in the rat kidney. Pflugers Arch. 1977 Nov 23;371(3):245–250. doi: 10.1007/BF00586264. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kokko J. P. Effect of prostaglandins on renal epithelial electrolyte transport. Kidney Int. 1981 Jun;19(6):791–796. doi: 10.1038/ki.1981.82. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levens N. R., Peach M. J., Carey R. M. Interactions between angiotensin peptides and the sympathetic nervous system mediating intestinal sodium and water absorption in the rat. J Clin Invest. 1981 Apr;67(4):1197–1207. doi: 10.1172/JCI110135. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levens N. R., Peach M. J., Carey R. M., Poat J. A., Munday K. A. Changes in an electroneutral transport process mediated by angiotensin II in the rat distal colon in vivo. Endocrinology. 1981 Apr;108(4):1497–1504. doi: 10.1210/endo-108-4-1497. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levens N. R., Peach M. J., Carey R. M., Poat J. A., Munday K. A. Response of rat jejunum to angiotensin II: role of norepinephrine and prostaglandins. Am J Physiol. 1981 Jan;240(1):G17–G24. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.1981.240.1.G17. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leyssac P. P., Kristensen L. O., Christensen P., Frederiksen O. The effect of angiotensin on isosmotic fluid absorption by the rabbit gall-bladder in vitro. Acta Physiol Scand. 1974 Dec;92(4):508–516. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1974.tb05772.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lowitz H. D., Stumpe K. O., Ochwadt B. Micropuncture study of the action of angiotensin-II on tubular sodium and water reabsorption in the rat. Nephron. 1969;6(3):173–187. doi: 10.1159/000179727. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGiff J. C. Natriuretic effect of angiotensin in dogs revealed after administration of reserpine and guanethidine. Circ Res. 1967 Jun;20(6):664–675. doi: 10.1161/01.res.20.6.664. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Munday K. A., Parsons B. J., Poat J. A., d'Auriac G. A., Meyer P. The role of cyclic 3':5'-adenosine monophosphate in the responses of the intestine and kidney to angiotensin. J Endocrinol. 1976 May;69(2):297–298. doi: 10.1677/joe.0.0690297. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Myers B. D., Deen W. M., Brenner B. M. Effects of norepinephrine and angiotensin II on the determinants of glomerular ultrafiltration and proximal tubule fluid reabsorption in the rat. Circ Res. 1975 Jul;37(1):101–110. doi: 10.1161/01.res.37.1.101. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakajima T., Nakayama T., Sokabe H. Examination of angiotensin-like substances from renal and extrarenal sources in mammalian and nonmammalian species. Gen Comp Endocrinol. 1971 Dec;17(3):458–466. doi: 10.1016/0016-6480(71)90180-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peach M. J. Molecular actions of angiotensin. Biochem Pharmacol. 1981 Oct;30(20):2745–2751. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(81)90410-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peterson D. R., Chrabaszcz G., Peterson W. R., Oparil S. Mechanism for renal tubular handling of angiotensin. Am J Physiol. 1979 Apr;236(4):F365–F372. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1979.236.4.F365. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pettinger W. A., Keeton K., Tanaka K. Radioimmunoassay and pharmacokinetics of saralasin in the rat and hypertensive patients. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 1975 Feb;17(2):146–158. doi: 10.1002/cpt1975172146. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ploth D. W., Roy R. N. Renal and tubuloglomerular feedback effects of [Sar1,Ala8]angiotensin II in the rat. Am J Physiol. 1982 Feb;242(2):F149–F157. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1982.242.2.F149. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- REGOLI D., VANE J. R. A SENSITIVE METHOD FOR THE ASSAY OF ANGIOTENSIN. Br J Pharmacol Chemother. 1964 Oct;23:351–359. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1964.tb01591.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schafer J. A., Troutman S. L., Andreoli T. E. Volume reabsorption, transepithelial potential differences, and ionic permeability properties in mammalian superficial proximal straight tubules. J Gen Physiol. 1974 Nov;64(5):582–607. doi: 10.1085/jgp.64.5.582. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steiner R. W., Tucker B. J., Blantz R. C. Glomerular hemodynamics in rats with chronic sodium depletion. Effect of saralasin. J Clin Invest. 1979 Aug;64(2):503–512. doi: 10.1172/JCI109488. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steven K. Effect of peritubular infusion of angiotensin II on rat proximal nephron function. Kidney Int. 1974 Aug;6(2):73–80. doi: 10.1038/ki.1974.82. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taub M., Saier M. H., Jr Regulation of 22Na+ transport by calcium in an established kidney epithelial cell line. J Biol Chem. 1979 Nov 25;254(22):11440–11444. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Torres V. E., Northrup T. E., Edwards R. M., Shah S. V., Dousa T. P. Modulation of cyclic nucleotides in islated rat glomeruli: role of histamine, carbamylcholine, parathyroid hormone, and angiotensin-II. J Clin Invest. 1978 Dec;62(6):1334–1343. doi: 10.1172/JCI109254. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Warnock D. G., Eveloff J. NaCl entry mechanisms in the luminal membrane of the renal tubule. Am J Physiol. 1982 Jun;242(6):F561–F574. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1982.242.6.F561. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waugh W. H. Angiotensin II: local renal effects of physiological increments in concentration. Can J Physiol Pharmacol. 1972 Jul;50(7):711–716. doi: 10.1139/y72-103. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wingo C. S., Seldin D. W., Kokko J. P., Jacobson H. R. Dietary modulation of active potassium secretion in the cortical collecting tubule of adrenalectomized rabbits. J Clin Invest. 1982 Sep;70(3):579–586. doi: 10.1172/JCI110650. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woodcock E. A., Johnston C. I. Inhibition of adenylate cyclase by angiotensin II in rat renal cortex. Endocrinology. 1982 Nov;111(5):1687–1691. doi: 10.1210/endo-111-5-1687. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]