Abstract
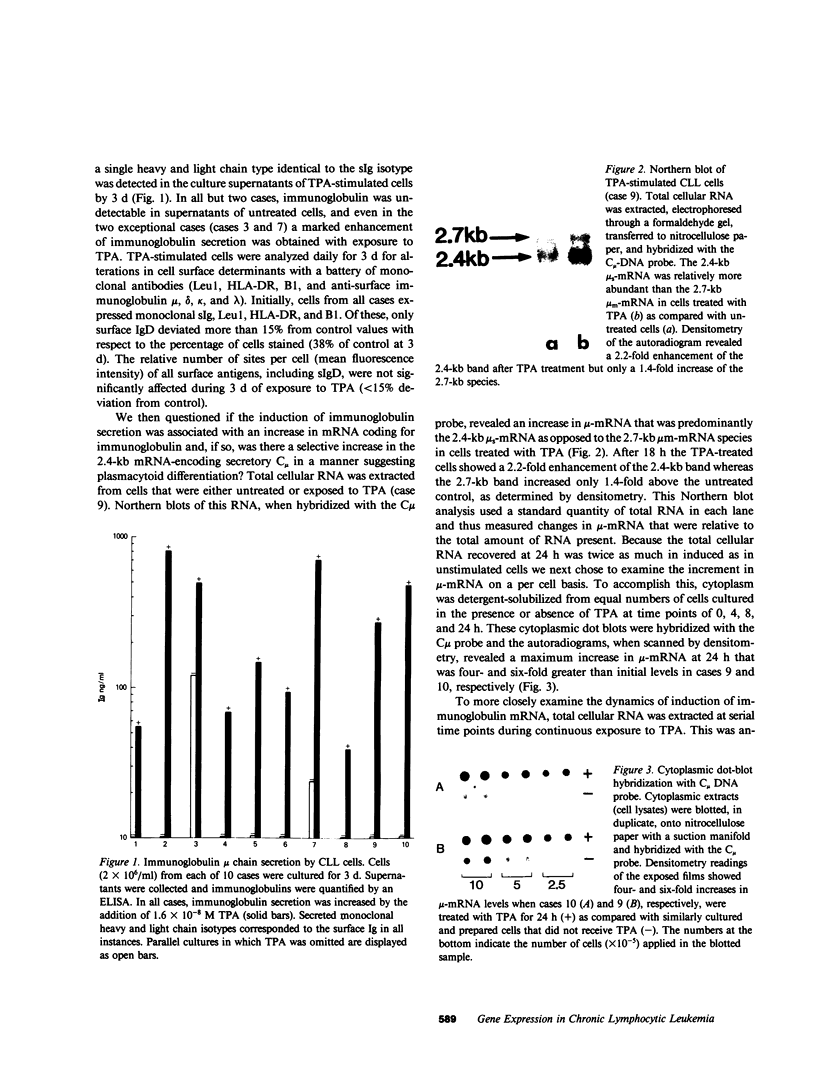
B cell chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) cells appear to be arrested in their differentiation so that little immunoglobulin is secreted in most cases. To determine their capacity for further differentiation we stimulated cells from a series of 10 cases of CLL with a phorbol ester and assayed for production of immunoglobulin protein, accumulation of immunoglobulin mRNA, and alterations in cell surface markers. We found that cells from all cases were induced to secret monoclonal immunoglobulin of the same heavy and light chain type as the surface membrane immunoglobulin type. Immunoglobulin secretion was preceded by a rapid increase in the levels of mRNA coding for IgM, predominantly the secretory form, mu s-mRNA, rather than the membrane form, mu m-mRNA. A similar selection of mu s- over mu m-mRNA is known to occur in plasma cells by a mechanism of differential processing of mRNA from a single mu-chain gene. Except for a decline in the expression of surface IgD, cell surface determinants remained unaffected both in terms of the percentage of positive cells and the relative number of sites per cell. In contrast to previous studies, these results indicate that CLL cells consistently retain the capacity to further differentiate toward plasma cells and secrete immunoglobulin. The immunoglobulin secretion is mediated, at least in part, by a developmentally regulated increment in mu s-mRNA.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ashendel C. L., Staller J. M., Boutwell R. K. Identification of a calcium- and phospholipid- dependent phorbol ester binding activity in the soluble fraction of mouse tissues. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1983 Feb 28;111(1):340–345. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(83)80157-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Castagna M., Takai Y., Kaibuchi K., Sano K., Kikkawa U., Nishizuka Y. Direct activation of calcium-activated, phospholipid-dependent protein kinase by tumor-promoting phorbol esters. J Biol Chem. 1982 Jul 10;257(13):7847–7851. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chirgwin J. M., Przybyla A. E., MacDonald R. J., Rutter W. J. Isolation of biologically active ribonucleic acid from sources enriched in ribonuclease. Biochemistry. 1979 Nov 27;18(24):5294–5299. doi: 10.1021/bi00591a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collins S. J., Ruscetti F. W., Gallagher R. E., Gallo R. C. Terminal differentiation of human promyelocytic leukemia cells induced by dimethyl sulfoxide and other polar compounds. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 May;75(5):2458–2462. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.5.2458. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cossman J., Neckers L. M., Arnold A., Korsmeyer S. J. Induction of differentiation in a case of common acute lymphoblastic leukemia. N Engl J Med. 1982 Nov 11;307(20):1251–1254. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198211113072006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Early P., Rogers J., Davis M., Calame K., Bond M., Wall R., Hood L. Two mRNAs can be produced from a single immunoglobulin mu gene by alternative RNA processing pathways. Cell. 1980 Jun;20(2):313–319. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90617-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Engleman E. G., Warnke R., Fox R. I., Dilley J., Benike C. J., Levy R. Studies of a human T lymphocyte antigen recognized by a monoclonal antibody. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Mar;78(3):1791–1795. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.3.1791. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farmer S. R., Ben-Ze'av A., Benecke B. J., Penman S. Altered translatability of messenger RNA from suspended anchorage-dependent fibroblasts: reversal upon cell attachment to a surface. Cell. 1978 Oct;15(2):627–637. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90031-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friend C., Scher W., Holland J. G., Sato T. Hemoglobin synthesis in murine virus-induced leukemic cells in vitro: stimulation of erythroid differentiation by dimethyl sulfoxide. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1971 Feb;68(2):378–382. doi: 10.1073/pnas.68.2.378. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fu S. M., Chiorazzi N., Kunkel H. G. Differentiation capacity and other properties of the leukemic cells of chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Immunol Rev. 1979;48:23–44. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1979.tb00297.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamblin T. J., Abdul-Ahad A. K., Gordon J., Stevenson F. K., Stevenson G. T. Preliminary experience in treating lymphocytic leukaemia with antibody to immunoglobulin idiotypes on the cell surfaces. Br J Cancer. 1980 Oct;42(4):495–502. doi: 10.1038/bjc.1980.271. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hsu S. M., Raine L., Fanger H. A comparative study of the peroxidase-antiperoxidase method and an avidin-biotin complex method for studying polypeptide hormones with radioimmunoassay antibodies. Am J Clin Pathol. 1981 May;75(5):734–738. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/75.5.734. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Korsmeyer S. J., Hieter P. A., Ravetch J. V., Poplack D. G., Waldmann T. A., Leder P. Developmental hierarchy of immunoglobulin gene rearrangements in human leukemic pre-B-cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Nov;78(11):7096–7100. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.11.7096. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kraft A. S., Anderson W. B. Phorbol esters increase the amount of Ca2+, phospholipid-dependent protein kinase associated with plasma membrane. Nature. 1983 Feb 17;301(5901):621–623. doi: 10.1038/301621a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller R. A., Maloney D. G., Warnke R., Levy R. Treatment of B-cell lymphoma with monoclonal anti-idiotype antibody. N Engl J Med. 1982 Mar 4;306(9):517–522. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198203043060906. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nadler L. M., Ritz J., Bates M. P., Park E. K., Anderson K. C., Sallan S. E., Schlossman S. F. Induction of human B cell antigens in non-T cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia. J Clin Invest. 1982 Aug;70(2):433–442. doi: 10.1172/JCI110633. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nagasawa K., Mak T. W. Phorbol esters induce differentiation in human malignant T lymphoblasts. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 May;77(5):2964–2968. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.5.2964. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Niedel J. E., Kuhn L. J., Vandenbark G. R. Phorbol diester receptor copurifies with protein kinase C. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jan;80(1):36–40. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.1.36. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okamura J., Letarte M., Stein L. D., Sigal N. H., Gelfand E. W. Modulation of chronic lymphocytic leukemia cells by phorbol ester: increase in Ia expression, IgM secretion and MLR stimulatory capacity. J Immunol. 1982 May;128(5):2276–2280. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robèrt K. H., Möller E., Gahrton G., Eriksson H., Nilsson B. B-cell activation of peripheral blood lymphocytes from patients with chronic lymphatic leukaemia. Clin Exp Immunol. 1978 Aug;33(2):302–308. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sidman C. B lymphocyte differentiation and the control of IgM mu chain expression. Cell. 1981 Feb;23(2):379–389. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90133-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stashenko P., Nadler L. M., Hardy R., Schlossman S. F. Characterization of a human B lymphocyte-specific antigen. J Immunol. 1980 Oct;125(4):1678–1685. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stevenson F. K., Hamblin T. J., Stevenson G. T., Tutt A. L. Extracellular idiotypic immunoglobulin arising from human leukemic B lymphocytes. J Exp Med. 1980 Dec 1;152(6):1484–1496. doi: 10.1084/jem.152.6.1484. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Storti R. V., Scott M. P., Rich A., Pardue M. L. Translational control of protein synthesis in response to heat shock in D. melanogaster cells. Cell. 1980 Dec;22(3):825–834. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90559-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas P. S. Hybridization of denatured RNA and small DNA fragments transferred to nitrocellulose. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Sep;77(9):5201–5205. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.9.5201. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tötterman T. H., Nilsson K., Sundström C. Phorbol ester-induced differentiation of chronic lymphocytic leukaemia cells. Nature. 1980 Nov 13;288(5787):176–178. doi: 10.1038/288176a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White B. A., Bancroft F. C. Cytoplasmic dot hybridization. Simple analysis of relative mRNA levels in multiple small cell or tissue samples. J Biol Chem. 1982 Aug 10;257(15):8569–8572. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yuan D., Tucker P. W. Effect of lipopolysaccharide stimulation on the transcription and translation of messenger RNA for cell surface immunoglobulin M. J Exp Med. 1982 Oct 1;156(4):962–974. doi: 10.1084/jem.156.4.962. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]





