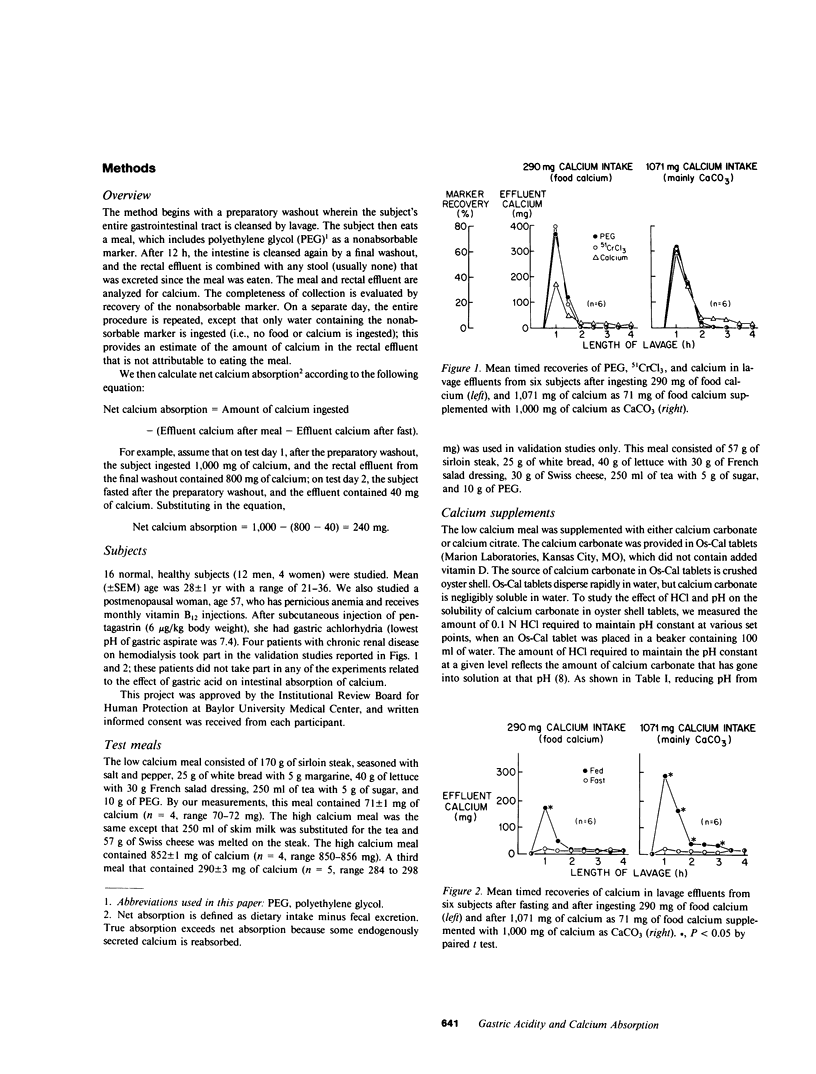
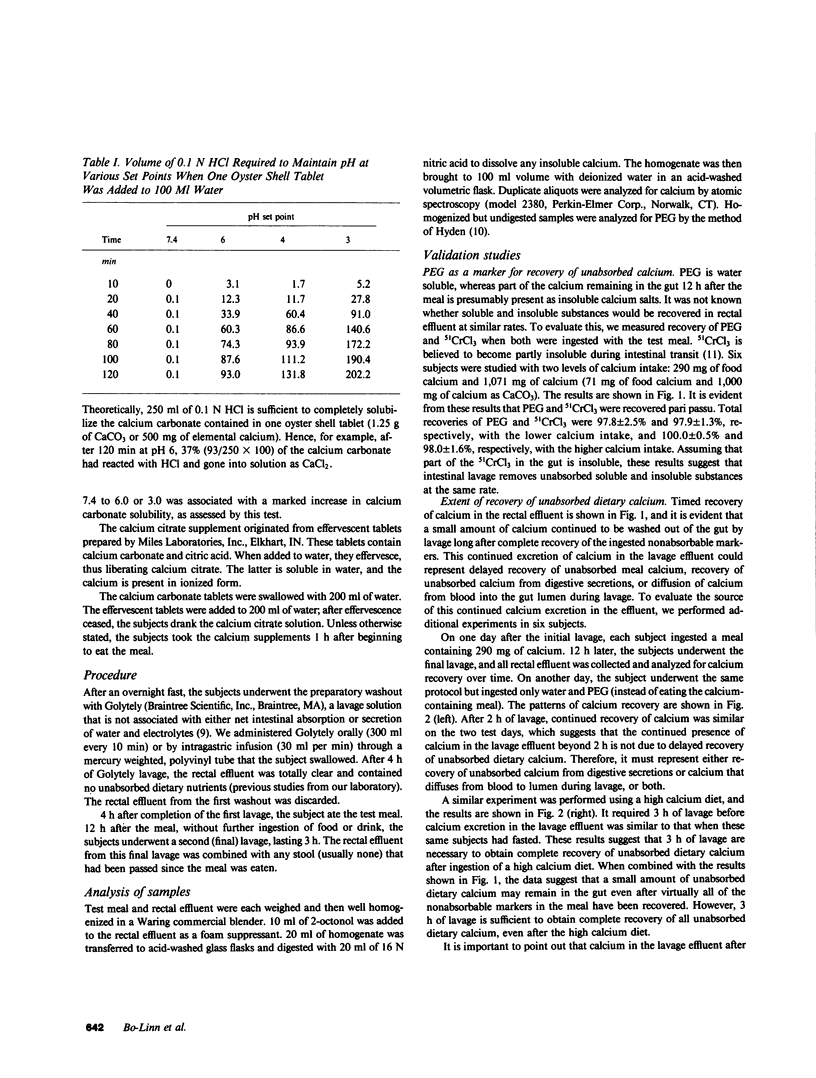
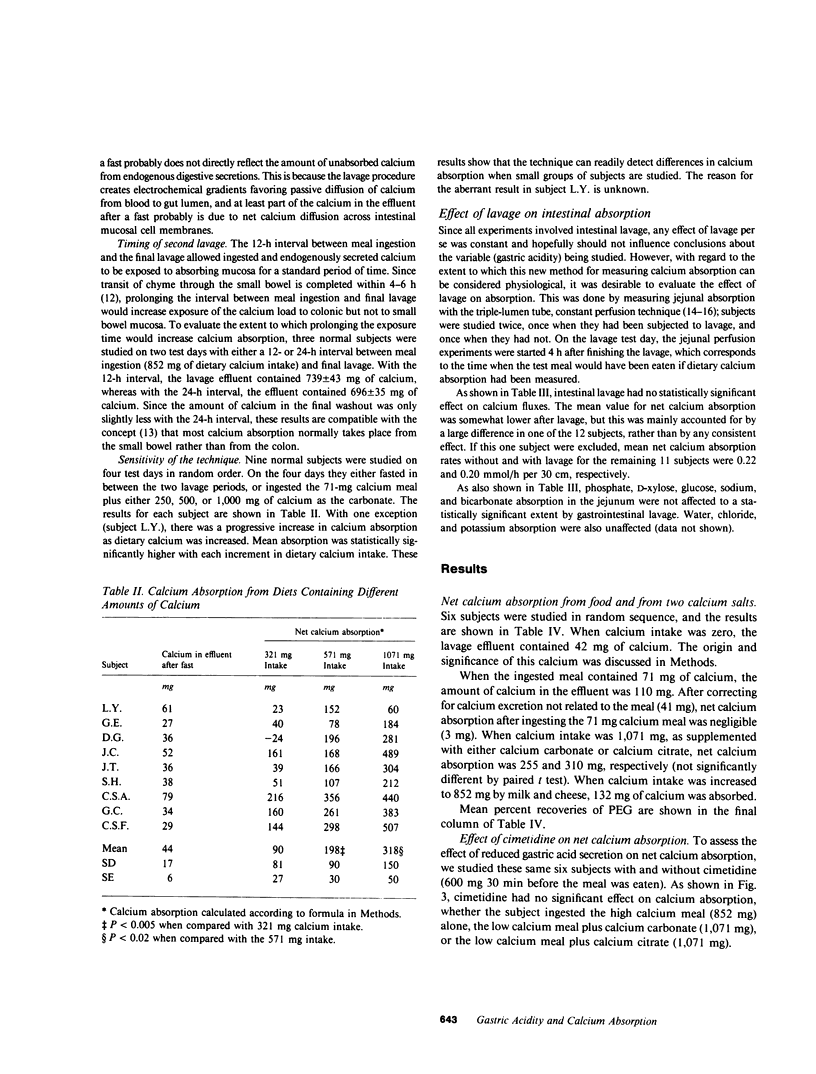
Abstract
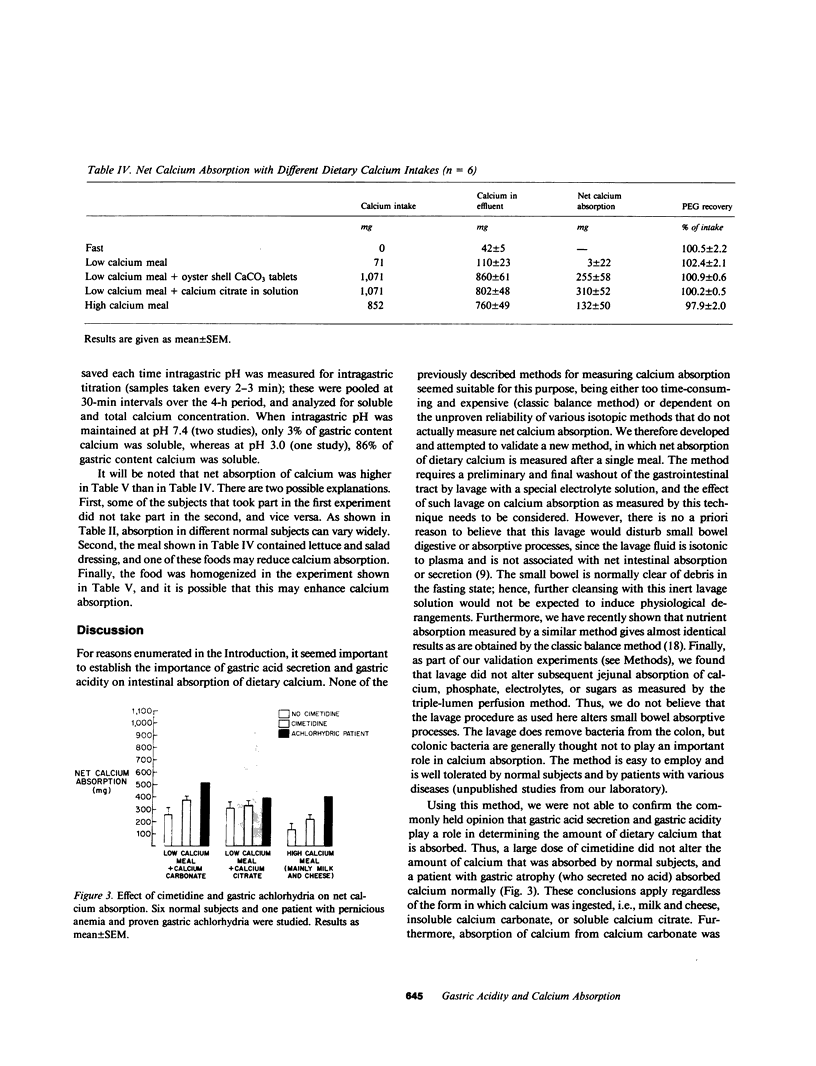
Since calcium solubility is a prerequisite to calcium absorption, and since solubility of calcium is highly pH-dependent, it has been generally assumed that gastric acid secretion and gastric acidity play an important role in the intestinal absorption of calcium from ingested food or calcium salts such as CaCO3. To evaluate this hypothesis, we developed a method wherein net gastrointestinal absorption of calcium can be measured after ingestion of a single meal. A large dose of cimetidine, which markedly reduced gastric acid secretion, had no effect on calcium absorption in normal subjects, and an achlorhydric patient with pernicious anemia absorbed calcium normally. This was true regardless of the major source of dietary calcium (i.e., milk, insoluble calcium carbonate, or soluble calcium citrate). Moreover, calcium absorption after CaCO3 ingestion was the same when intragastric contents were maintained at pH 7.4 (by in vivo titration) as when intragastric pH was 3.0. On the basis of these results, we conclude that gastric acid secretion and gastric acidity do not normally play a role in the absorption of dietary calcium. Other possible mechanisms by which the gastrointestinal tract might solubilize ingested calcium complexes and salts are discussed.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BARON J. H. Studies of basal and peak acid output with an augmented histamine test. Gut. 1963 Jun;4:136–144. doi: 10.1136/gut.4.2.136. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bo-Linn G. W., Santa Ana C. A., Morawski S. G., Fordtran J. S. Starch blockers--their effect on calorie absorption from a high-starch meal. N Engl J Med. 1982 Dec 2;307(23):1413–1416. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198212023072301. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clarkson E. M., McDonald S. J., De Wardener H. E. The effect of a high intake of calcium carbonate in normal subjects and patients with chronic renal failure. Clin Sci. 1966 Jun;30(3):425–438. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis G. R., Santa Ana C. A., Morawski S. G., Fordtran J. S. Development of a lavage solution associated with minimal water and electrolyte absorption or secretion. Gastroenterology. 1980 May;78(5 Pt 1):991–995. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis G. R., Santa Ana C. A., Morawski S., Fordtran J. S. Active chloride secretion in the normal human jejunum. J Clin Invest. 1980 Dec;66(6):1326–1333. doi: 10.1172/JCI109985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis G. R., Zerwekh J. E., Parker T. F., Krejs G. J., Pak C. Y., Fordtran J. S. Absorption of phosphate in the jejunum of patients with chronic renal failure before and after correction of vitamin D deficiency. Gastroenterology. 1983 Oct;85(4):908–916. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fordtran J. S., Morawski S. G., Richardson C. T. In vivo and in vitro evaluation of liquid antacids. N Engl J Med. 1973 May 3;288(18):923–928. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197305032881801. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fromm H., Thomas P. J., Hofmann A. F. Sensitivity and specificity in tests of distal ileal function: prospective comparison of bile acid and vitamin B 12 absorption in ileal resection patients. Gastroenterology. 1973 Jun;64(6):1077–1090. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HOGBEN C. A., TOCCO D. J., BRODIE B. B., SCHANKER L. S. On the mechanism of intestinal absorption of drugs. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1959 Apr;125(4):275–282. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ivanovich P., Fellows H., Rich C. The absorption of calcium carbonate. Ann Intern Med. 1967 May;66(5):917–923. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-66-5-917. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krejs G. J., Walsh J. H., Morawski S. G., Fordtran J. S. Intractable diarrhea. Intestinal perfusion studies and plasma VIP concentrations in patients with pancreatic cholera syndrome and surreptitious ingestion of laxatives and diuretics. Am J Dig Dis. 1977 Apr;22(4):280–292. doi: 10.1007/BF01072184. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nordin B. E. Measurement and meaning of calcium absorption. Gastroenterology. 1968 Feb;54(2):294–301. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Read N. W., Miles C. A., Fisher D., Holgate A. M., Kime N. D., Mitchell M. A., Reeve A. M., Roche T. B., Walker M. Transit of a meal through the stomach, small intestine, and colon in normal subjects and its role in the pathogenesis of diarrhea. Gastroenterology. 1980 Dec;79(6):1276–1282. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richardson C. T., Walsh J. H., Cooper K. A., Feldman M., Fordtran J. S. Studies on the role of cephalic-vagal stimulation in the acid secretory response to eating in normal human subjects. J Clin Invest. 1977 Aug;60(2):435–441. doi: 10.1172/JCI108793. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SCHACHTER D., DOWDLE E. B., SCHENKER H. Active transport of calcium by the small intestine of the rat. Am J Physiol. 1960 Feb;198:263–268. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1960.198.2.263. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith R. H., McAllan A. B. Binding of magnesium and calcium in the contents of the small intestine of the calf. Br J Nutr. 1966;20(4):703–718. doi: 10.1079/bjn19660072. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Turnberg L. A., Fordtran J. S., Carter N. W., Rector F. C., Jr Mechanism of bicarbonate absorption and its relationship to sodium transport in the human jejunum. J Clin Invest. 1970 Mar;49(3):548–556. doi: 10.1172/JCI106265. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- VASSAR P. S. THE ELECTRIC CHARGE DENSITY OF HUMAN TUMOR CELL SURFACES. Lab Invest. 1963 Nov;12:1072–1077. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vergne-Marini P., Parker T. F., Pak C. Y., Hull A. R., DeLuca H. F., Fordtran J. S. Jejunal and ileal absorption in patients with chronic renal disease. Effect of 1alpha-hydroxycholecalciferol. J Clin Invest. 1976 Apr;57(4):861–866. doi: 10.1172/JCI108362. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Webling D. D., Holdsworth E. S. Bile salts and calcium absorption. Biochem J. 1966 Sep;100(3):652–660. doi: 10.1042/bj1000652. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Webling D. D., Holdsworth E. S. The effect of bile, bile acids and detergents on calcium absorption in the chick. Biochem J. 1965 Nov;97(2):408–421. doi: 10.1042/bj0970408. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]