Abstract
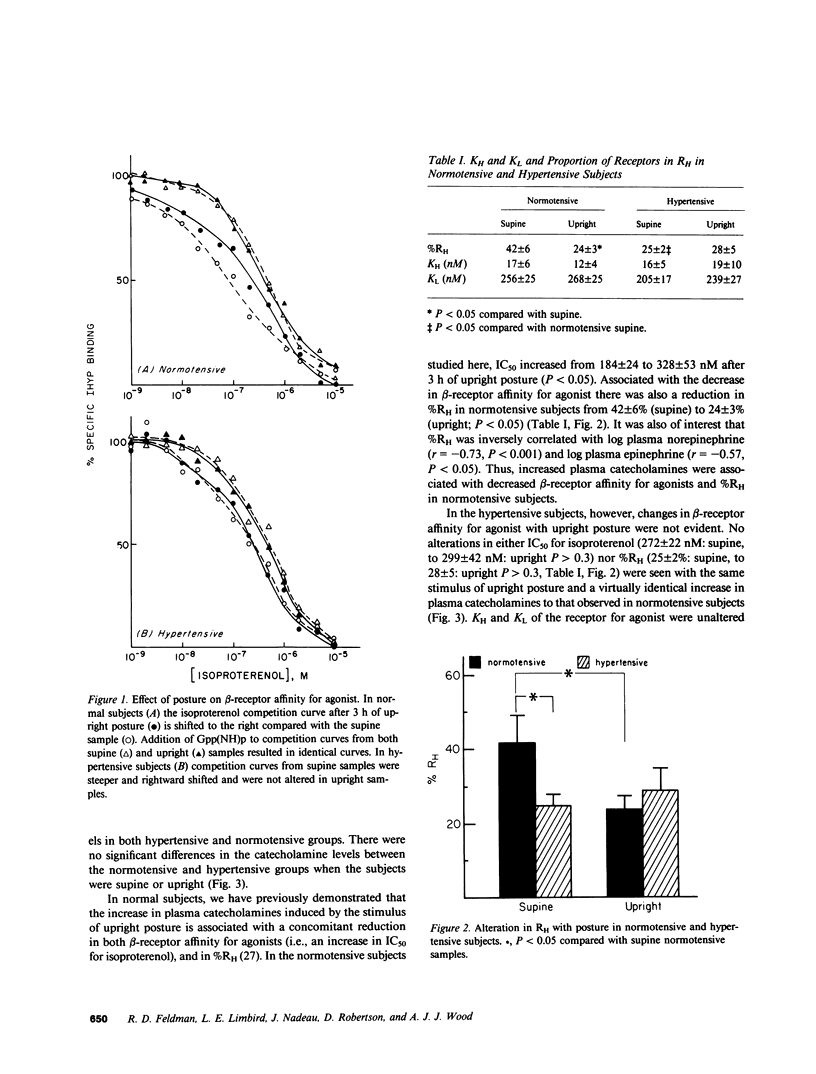
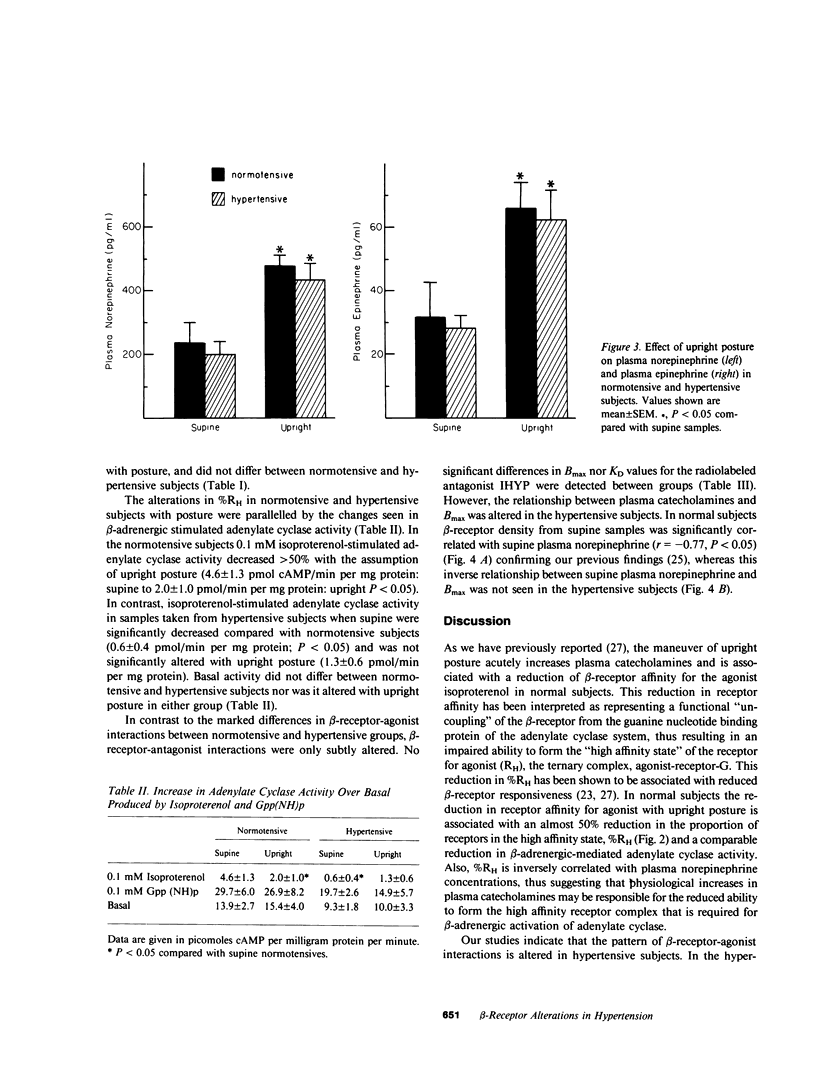
It has been suggested that beta-adrenergic responsiveness is reduced in hypertension. To evaluate a possible alteration in human beta-receptors that might account for diminished beta-adrenergic responsiveness, we studied leukocytes from hypertensive and normotensive subjects after an overnight rest supine, and then after being ambulatory, a maneuver that increases plasma catecholamines approximately twofold. In supine samples, beta-receptor affinity for the agonist isoproterenol was significantly reduced in hypertensives and was associated with a reduction in the proportion of beta-receptors binding agonist with a high affinity from 42 +/- 6% in normotensive subjects to 25 +/- 2% in hypertensives (P less than 0.05). Alterations in beta-adrenergic-mediated adenylate cyclase activity parallelled the differences seen in the beta-receptor affinity for agonist. In normotensive subjects, beta-receptor density and the proportion of receptors binding agonist with high affinity were reciprocally correlated with plasma catecholamines. However, in the hypertensive subjects these correlations were not evident. Thus, our data suggest an alteration in leukocyte beta-receptor interactions in hypertensive subjects, and may represent a generalized defect in beta-receptor function in hypertension.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aarons R. D., Molinoff P. B. Changes in the density of beta adrenergic receptors in rat lymphocytes, heart and lung after chronic treatment with propranolol. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1982 May;221(2):439–443. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aarons R. D., Nies A. S., Gal J., Hegstrand L. R., Molinoff P. B. Elevation of beta-adrenergic receptor density in human lymphocytes after propranolol administration. J Clin Invest. 1980 May;65(5):949–957. doi: 10.1172/JCI109781. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Abboud F. M. The sympathetic system in hypertension. State-of-the-art review. Hypertension. 1982 May-Jun;4(3 Pt 2):208–225. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bertel O., Bühler F. R., Kiowski W., Lütold B. E. Decreased Beta-adrenoreceptor responsiveness as related to age, blood pressure, and plasma catecholamines in patients with essential hypertension. Hypertension. 1980 Mar-Apr;2(2):130–138. doi: 10.1161/01.hyp.2.2.130. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bhalla R. C., Sharma R. V. Characteristics of hormone-stimulated adenylate cyclase in vascular smooth muscle: altered activity in spontaneously hypertensive rat. Blood Vessels. 1982;19(3):109–116. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bhalla R. C., Sharma R. V., Ramanathan S. Ontogenetic development of isoproterenol subsensitivity of myocardial adenylate cyclase and beta-adrenergic receptors in spontaneously hypertensive rats. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1980 Nov 3;632(4):497–506. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(80)90326-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Böyum A. Isolation of mononuclear cells and granulocytes from human blood. Isolation of monuclear cells by one centrifugation, and of granulocytes by combining centrifugation and sedimentation at 1 g. Scand J Clin Lab Invest Suppl. 1968;97:77–89. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen M. L., Berkowitz B. A. Decreased vascular relaxation in hypertension. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1976 Feb;196(2):396–406. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colucci W. S., Alexander R. W., Williams G. H., Rude R. E., Holman B. L., Konstam M. A., Wynne J., Mudge G. H., Jr, Braunwald E. Decreased lymphocyte beta-adrenergic-receptor density in patients with heart failure and tolerance to the beta-adrenergic agonist pirbuterol. N Engl J Med. 1981 Jul 23;305(4):185–190. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198107233050402. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Lean A., Stadel J. M., Lefkowitz R. J. A ternary complex model explains the agonist-specific binding properties of the adenylate cyclase-coupled beta-adrenergic receptor. J Biol Chem. 1980 Aug 10;255(15):7108–7117. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feldman R. D., Limbird L. E., Nadeau J., FitzGerald G. A., Robertson D., Wood A. J. Dynamic regulation of leukocyte beta adrenergic receptor-agonist interactions by physiological changes in circulating catecholamines. J Clin Invest. 1983 Jul;72(1):164–170. doi: 10.1172/JCI110954. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fraser J., Nadeau J., Robertson D., Wood A. J. Regulation of human leukocyte beta receptors by endogenous catecholamines: relationship of leukocyte beta receptor density to the cardiac sensitivity to isoproterenol. J Clin Invest. 1981 Jun;67(6):1777–1784. doi: 10.1172/JCI110217. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Godfraind T., Dieu D. Influence of ageing on the isoprenaline relaxation of aortae from normal and hypertensive rats. Arch Int Pharmacodyn Ther. 1978 Dec;236(2):300–302. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hancock A. A., DeLean A. L., Lefkowitz R. J. Quantitative resolution of beta-adrenergic receptor subtypes by selective ligand binding: application of a computerized model fitting technique. Mol Pharmacol. 1979 Jul;16(1):1–9. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katovich M. J., Fregly M. J., Barney C. C. Reduced responsiveness to beta-adrenergic stimulation in renal hypertensive rats. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1978 Jul;158(3):363–369. doi: 10.3181/00379727-158-40205. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kent R. S., De Lean A., Lefkowitz R. J. A quantitative analysis of beta-adrenergic receptor interactions: resolution of high and low affinity states of the receptor by computer modeling of ligand binding data. Mol Pharmacol. 1980 Jan;17(1):14–23. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kunos G., Robertson B., Kan W. H., Preiksaitis H., Mucci L. Adrenergic reactivity of the myocardium in hypertension. Life Sci. 1978 Mar;22(10):847–854. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(78)90608-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leenen F. H., Boer P., Dorhout Mees E. J. Peripheral beta-adrenoceptor responsiveness in young normotensive and hypertensive subjects. Clin Exp Hypertens. 1981;3(3):539–553. doi: 10.3109/10641968109033681. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Limbird L. E. Activation and attenuation of adenylate cyclase. The role of GTP-binding proteins as macromolecular messengers in receptor--cyclase coupling. Biochem J. 1981 Apr 1;195(1):1–13. doi: 10.1042/bj1950001. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Limbird L. E., Gill D. M., Lefkowitz R. J. Agonist-promoted coupling of the beta-adrenergic receptor with the guanine nucleotide regulatory protein of the adenylate cyclase system. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Feb;77(2):775–779. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.2.775. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McAllister R. G., Jr, Love D. W., Guthrie G. P., Jr, Dominic J. A., Kotchen T. A. Peripheral beta-receptor responsiveness in patients with essential hypertension. Arch Intern Med. 1979 Aug;139(8):879–881. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mendlowitz M. Vascular reactivity in systemic arterial hypertension. Am Heart J. 1973 Feb;85(2):252–259. doi: 10.1016/0002-8703(73)90467-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Passon P. G., Peuler J. D. A simplified radiometric assay for plasma norepinephrine and epinephrine. Anal Biochem. 1973 Feb;51(2):618–631. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(73)90517-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Passon P. G., Peuler J. D. A simplified radiometric assay for plasma norepinephrine and epinephrine. Anal Biochem. 1973 Feb;51(2):618–631. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(73)90517-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robberecht P., Winand J., Chatelain P., Poloczek P., Camus J. C., De Neef P., Christophe J. Comparison of beta-adrenergic receptors and the adenylate cyclase system with muscarinic receptors and guanylate cyclase activities in the heart of spontaneously hypertensive rats. Biochem Pharmacol. 1981 Feb 15;30(4):385–387. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(81)90071-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robertson D., Johnson G. A., Robertson R. M., Nies A. S., Shand D. G., Oates J. A. Comparative assessment of stimuli that release neuronal and adrenomedullary catecholamines in man. Circulation. 1979 Apr;59(4):637–643. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.59.4.637. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ross E. M., Gilman A. G. Biochemical properties of hormone-sensitive adenylate cyclase. Annu Rev Biochem. 1980;49:533–564. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.49.070180.002533. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strecker R. B., Hubbard W. C., Michelakis A. M. Dissociation constant of the norepinephrine-receptor complex in normotensive and hypertensive rats. Circ Res. 1975 Nov;37(5):658–663. doi: 10.1161/01.res.37.5.658. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vlachakis N. D. Blood pressure response to norepinephrine infusion in relationship to plasma catecholamines and renin activity in man. J Clin Pharmacol. 1979 Oct;19(10):654–661. doi: 10.1002/j.1552-4604.1979.tb01628.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Webb R. C., Bohr D. F. Recent advances in the pathogenesis of hypertension: consideration of structural, functional, and metabolic vascular abnormalities resulting in elevated arterial resistance. Am Heart J. 1981 Aug;102(2):251–264. doi: 10.1016/s0002-8703(81)80016-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woodcock E. A., Funder J. W., Johnston C. I. Decreased cardiac beta-adrenergic receptors in deoxycorticosterone-salt and renal hypertensive rats. Circ Res. 1979 Oct;45(4):560–565. doi: 10.1161/01.res.45.4.560. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamada S., Yamamura H. I., Roeske W. R. Alterations in central and peripheral adrenergic receptors in deoxycorticosterone/salt hypertensive rats. Life Sci. 1980 Dec 15;27(24):2405–2416. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(80)90512-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


