Abstract
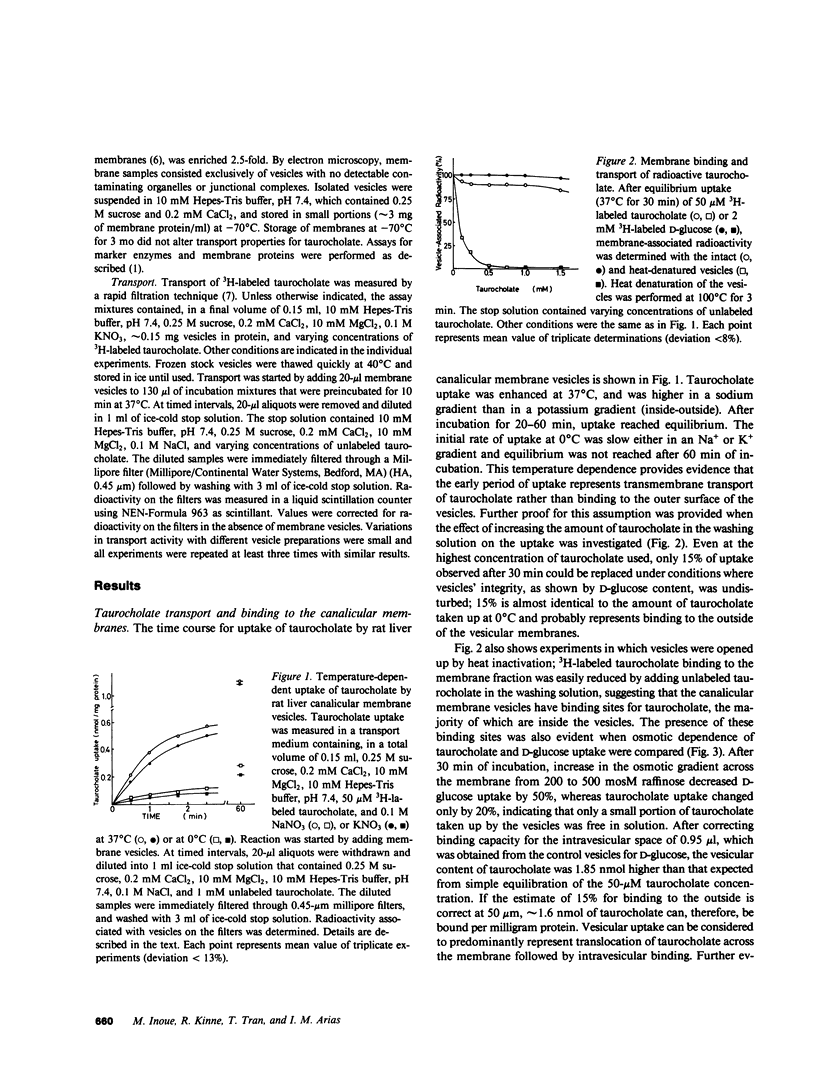
To elucidate the mechanism of vectorial translocation of bile acids in the liver, taurocholate transport was studied in isolated liver canalicular membrane vesicles by a rapid filtration method. The membrane vesicles revealed temperature-dependent, Na+-independent transport of taurocholate into an osmotically reactive intravesicular space. In the absence of sodium, taurocholate uptake followed saturation kinetics (apparent Km for taurocholate = 43 microM and Vmax = 0.22 nmol/mg protein X 20 s at 37 degrees C) and was inhibited by cholate and probenecid. Transstimulation by unlabeled taurocholate was also demonstrated. When the electrical potential difference across the membranes was altered by anion replacement, a more positive intravesicular potential stimulated, and a more negative potential inhibited, transport of taurocholate by the vesicles. Valinomycin-induced K+-diffusion potential (vesicle inside-positive) enhanced the rate of taurocholate uptake that was not altered by imposed pH gradients. These results indicate that rat liver canalicular plasma membrane contains a sodium-independent taurocholate transport system that translocates the bile acid as an anion across the membrane. In intact hepatocytes, the electrical potential difference across the canalicular membrane probably provides the driving force for taurocholate secretion. The contribution of nonionic diffusion to taurocholate secretion appears to be minimal.
Full text
PDF
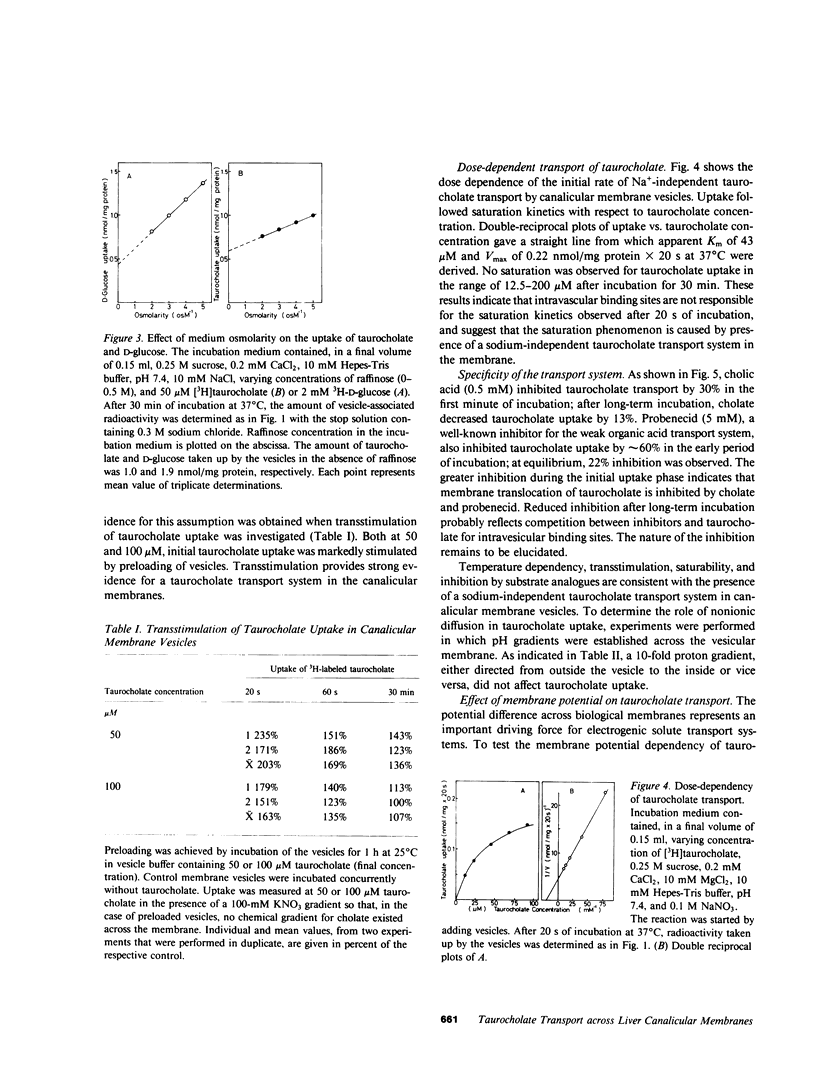

Selected References
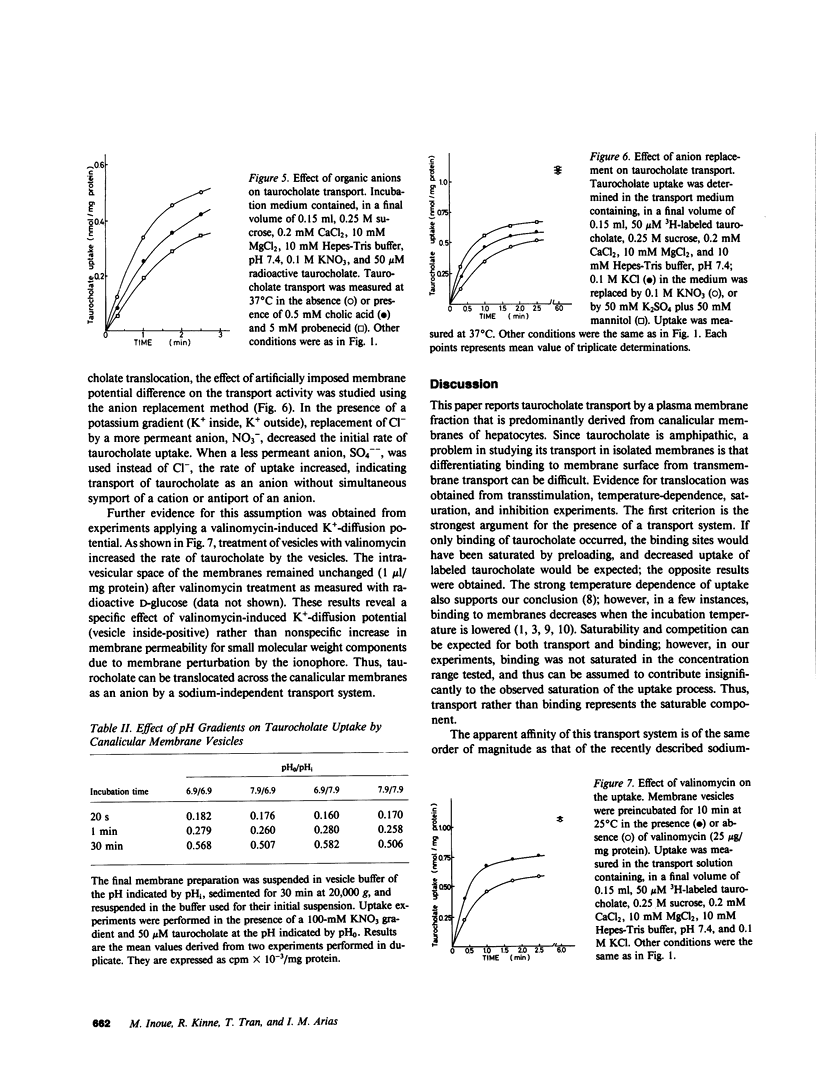
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Accatino L., Simon F. R. Identification and characterization of a bile acid receptor in isolated liver surface membranes. J Clin Invest. 1976 Feb;57(2):496–508. doi: 10.1172/JCI108302. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blitzer B. L., Boyer J. L. Cytochemical localization of Na+, K+-ATPase in the rat hepatocyte. J Clin Invest. 1978 Nov;62(5):1104–1108. doi: 10.1172/JCI109216. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duffy M. C., Blitzer B. L., Boyer J. L. Direct determination of the driving forces for taurocholate uptake into rat liver plasma membrane vesicles. J Clin Invest. 1983 Oct;72(4):1470–1481. doi: 10.1172/JCI111103. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evers J., Murer H., Kinne R. Phenylalanine uptake in isolated renal brush border vesicles. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1976 Apr 5;426(4):598–615. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(76)90124-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inoue M. Cell agglutination mediated by concanavalin A and the dynamic state of the cell surface. J Cell Sci. 1974 Jan;14(1):197–202. doi: 10.1242/jcs.14.1.197. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inoue M., Kinne R., Tran T., Arias I. M. Taurocholate transport by rat liver sinusoidal membrane vesicles: evidence of sodium cotransport. Hepatology. 1982 Sep-Oct;2(5):572–579. doi: 10.1002/hep.1840020510. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inoue M., Kinne R., Tran T., Biempica L., Arias I. M. Rat liver canalicular membrane vesicles. Isolation and topological characterization. J Biol Chem. 1983 Apr 25;258(8):5183–5188. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lücke H., Stange G., Kinne R., Murer H. Taurocholate--sodium co-transport by brush-border membrane vesicles isolated from rat ileum. Biochem J. 1978 Sep 15;174(3):951–958. doi: 10.1042/bj1740951. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruifrok P. G., Meijer D. K. Sodium ion-coupled uptake of taurocholate by rat-liver plasma membrane vesicles. Liver. 1982 Mar;2(1):28–34. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0676.1982.tb00175.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


