Abstract
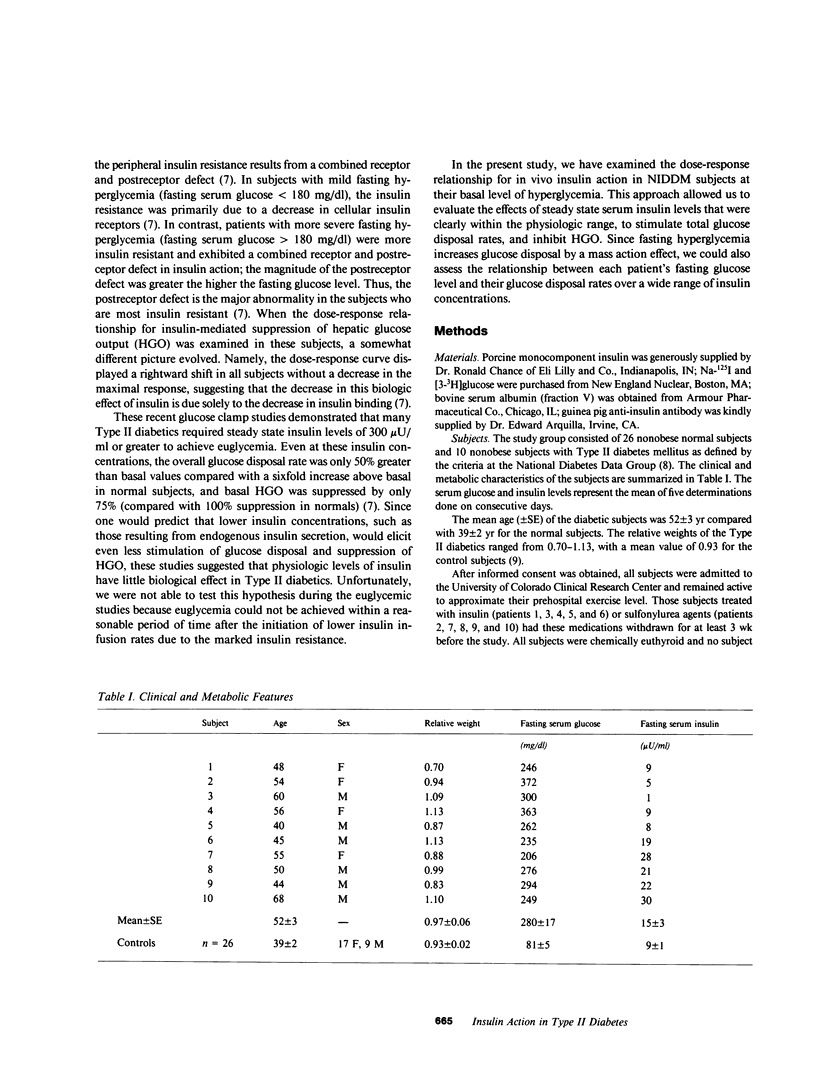
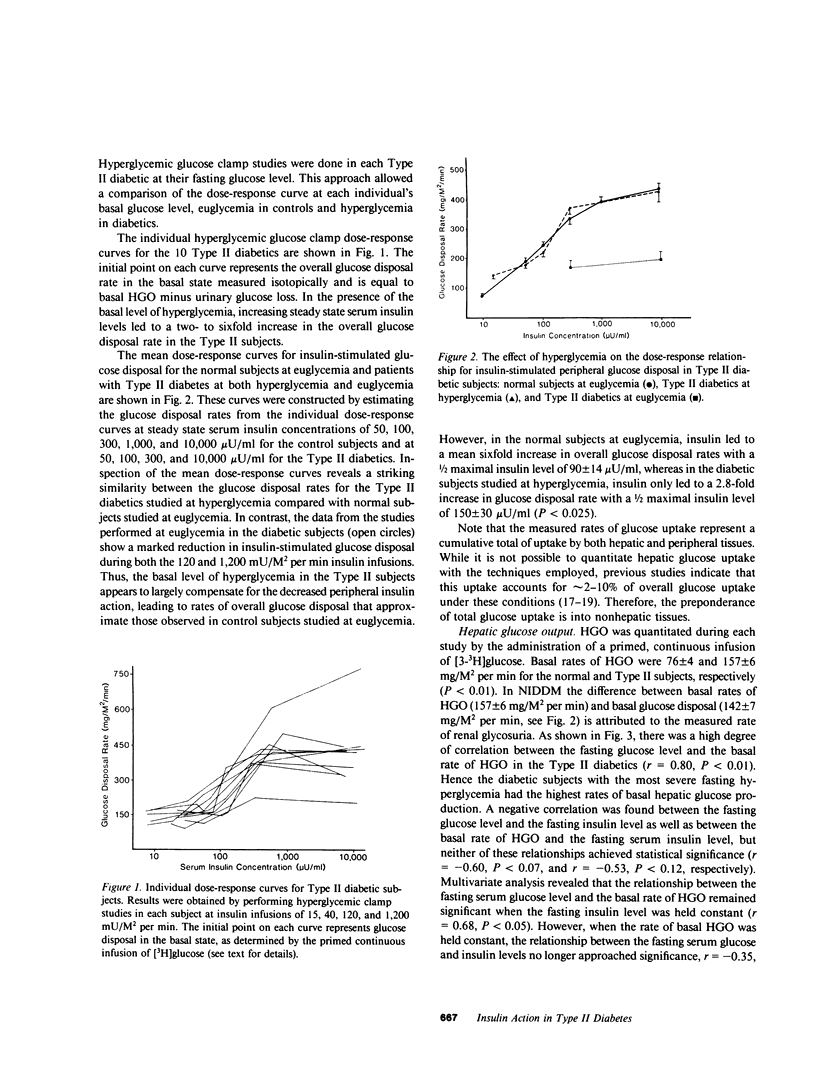
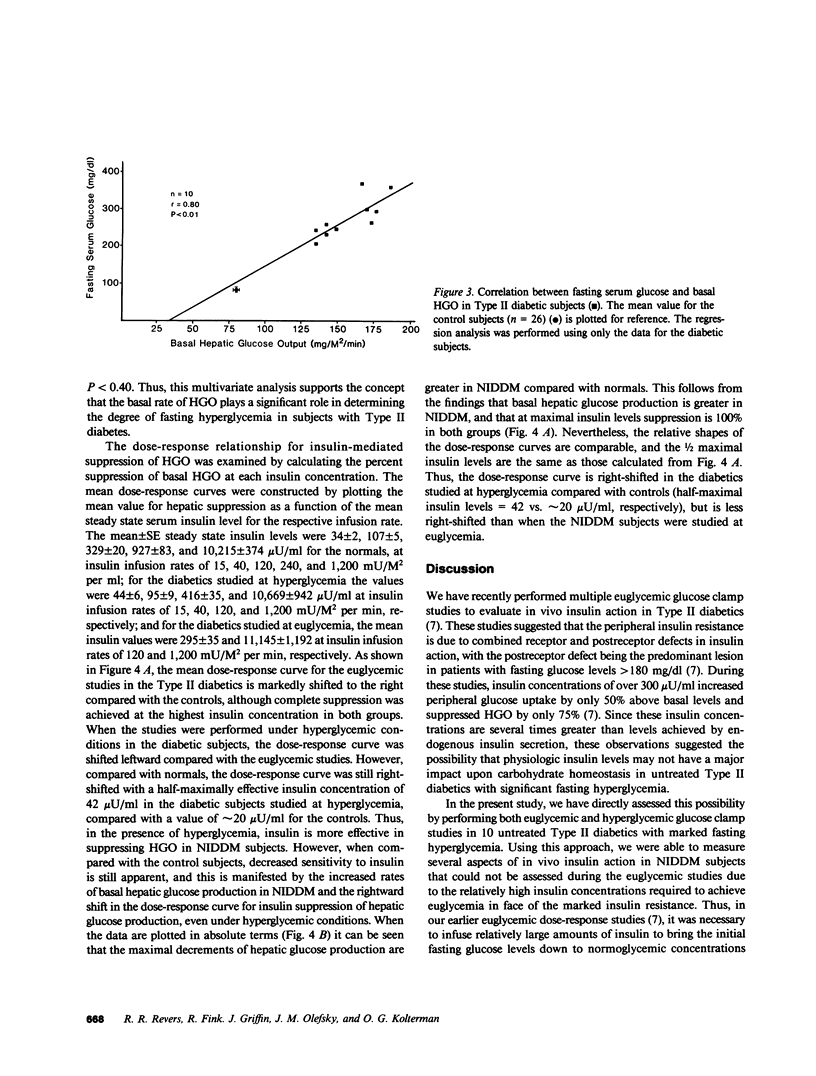
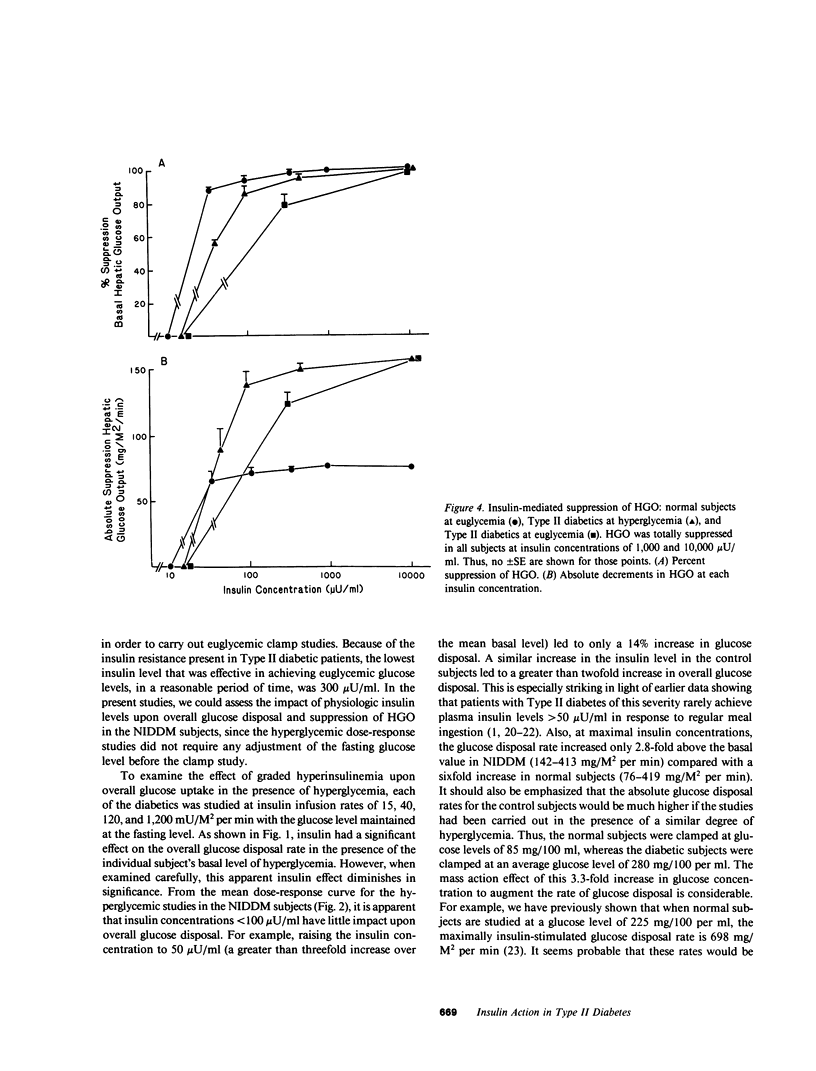
The present study was designed to quantitate the interaction between the decrease in target tissue insulin action seen in subjects with Type II diabetes and the mass action effect of glucose exerted via the prevailing hyperglycemic state. To this end, euglycemic glucose clamp studies were performed in 26 control subjects using insulin infusion rates of 15, 40, 120, 240, and 1,200 mU/M2 per min and in 10 Type II diabetic subjects using insulin infusion rates of 120 and 1,200 mU/M2 per min. The results of these euglycemic studies indicated that insulin-stimulated peripheral glucose disposal was decreased in the Type II diabetics due to a combined receptor (rightward shift in the dose-response curve) and postreceptor defect in insulin action (decreased maximal response), whereas the decrease in insulin-mediated suppression of hepatic glucose output (HGO) was consistent with a defect in insulin binding (rightward shift in dose-response curve). Hyperglycemic glucose clamp studies were also performed in the Type II diabetics at their respective fasting serum glucose levels (mean [+/- SE] 280 +/- 17 mg/dl) employing insulin infusion rates of 15, 40, 120, and 1,200 mU/M2 per min. In the presence of their basal level of hyperglycemia, the noninsulin-dependent diabetes mellitus (NIDDM) subjects exhibited rates of overall glucose disposal that were similar to those observed in control subjects studied at euglycemia at similar steady state insulin concentrations. This suggests that in Type II diabetics, the mass action effect of glucose partially compensates for the marked decrease in insulin-stimulated glucose uptake observed under euglycemic conditions. However, even in the presence of hyperglycemia, insulin levels below 100 microU/ml had little effect and maximally effective insulin levels increased peripheral glucose disposal only 2.8-fold (142 +/- 7-413 +/- 47 mg/M2 per min) above basal in the Type II diabetics, compared with a sixfold increase (75 +/- 4-419 +/- 34 mg/M2 per min) in the control subjects studied at euglycemia. Thus, the severe insulin resistance that is a characteristic feature of NIDDM remains apparent. Basal HGO was elevated in the NIDDM subjects (157 +/- 6 vs. 76 +/- 4 mg/M2 per min for controls) and a high degree of correlation was found between the basal rate of HGO and the fasting glucose level (r = 0.80, P less than 0.01). The presence of hyperglycemia augmented insulin-mediated suppression of HGO, but did not restore it to normal. We concluded that: (a) in the presence of basal hyperglycemia, physiologic insulin levels exerts a diminished effect to suppress HGO and stimulate peripheral glucose disposal in NIDDM; (b) basal HGO is elevated in untreated Type II diabetics, and this may serve to maintain the level of hyperglycemia required to compensate for the decrease in peripheral insulin action; and (c) fasting hyperglycemia exerts a suppressive effect on HGO but does not completely compensate for the decrease in hepatic insulin action in Type II diabetics.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Best J. D., Judzewitsch R. G., Pfeifer M. A., Beard J. C., Halter J. B., Porte D., Jr The effect of chronic sulfonylurea therapy on hepatic glucose production in non-insulin-dependent diabetes. Diabetes. 1982 Apr;31(4 Pt 1):333–338. doi: 10.2337/diab.31.4.333. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bowen H. F., Moorhouse J. A. Glucose turnover and disposal in maturity-onset diabetes. J Clin Invest. 1973 Dec;52(12):3033–3045. doi: 10.1172/JCI107502. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cherrington A. D., Williams P. E., Harris M. S. Relationship between the plasma glucose level and glucose uptake in the conscious dog. Metabolism. 1978 Jul;27(7):787–791. doi: 10.1016/0026-0495(78)90213-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chiasson J. L., Liljenquist J. E., Lacy W. W., Jennings A. S., Cherrington A. D. Gluconeogenesis: methodological approaches in vivo. Fed Proc. 1977 Feb;36(2):229–235. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crapo P. A., Insel J., Sperling M., Kolterman O. G. Comparison of serum glucose, insulin, and glucagon responses to different types of complex carbohydrate in noninsulin-dependent diabetic patients. Am J Clin Nutr. 1981 Feb;34(2):184–190. doi: 10.1093/ajcn/34.2.184. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davidson M. B. The effect of aging on carbohydrate metabolism: a review of the English literature and a practical approach to the diagnosis of diabetes mellitus in the elderly. Metabolism. 1979 Jun;28(6):688–705. doi: 10.1016/0026-0495(79)90024-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeFronzo R. A., Ferrannini E., Hendler R., Felig P., Wahren J. Regulation of splanchnic and peripheral glucose uptake by insulin and hyperglycemia in man. Diabetes. 1983 Jan;32(1):35–45. doi: 10.2337/diab.32.1.35. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeFronzo R. A., Ferrannini E., Hendler R., Wahren J., Felig P. Influence of hyperinsulinemia, hyperglycemia, and the route of glucose administration on splanchnic glucose exchange. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Oct;75(10):5173–5177. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.10.5173. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeFronzo R. A. Glucose intolerance and aging. Diabetes Care. 1981 Jul-Aug;4(4):493–501. doi: 10.2337/diacare.4.4.493. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeFronzo R. A., Tobin J. D., Andres R. Glucose clamp technique: a method for quantifying insulin secretion and resistance. Am J Physiol. 1979 Sep;237(3):E214–E223. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.1979.237.3.E214. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeFronzo R., Deibert D., Hendler R., Felig P., Soman V. Insulin sensitivity and insulin binding to monocytes in maturity-onset diabetes. J Clin Invest. 1979 May;63(5):939–946. doi: 10.1172/JCI109394. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar] [Retracted]
- Doberne L., Greenfield M. S., Schulz B., Reaven G. M. Enhanced glucose utilization during prolonged glucose clamp studies. Diabetes. 1981 Oct;30(10):829–835. doi: 10.2337/diab.30.10.829. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fink R. I., Kolterman O. G., Griffin J., Olefsky J. M. Mechanisms of insulin resistance in aging. J Clin Invest. 1983 Jun;71(6):1523–1535. doi: 10.1172/JCI110908. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Genuth S. M. Plasma insulin and glucose profiles in normal, obese, and diabetic persons. Ann Intern Med. 1973 Dec;79(6):812–822. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-79-6-812. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ginsberg H., Kimmerling G., Olefsky J. M., Reaven G. M. Demonstration of insulin resistance in untreated adult onset diabetic subjects with fasting hyperglycemia. J Clin Invest. 1975 Mar;55(3):454–461. doi: 10.1172/JCI107951. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang S. C., Phelps M. E., Hoffman E. J., Sideris K., Selin C. J., Kuhl D. E. Noninvasive determination of local cerebral metabolic rate of glucose in man. Am J Physiol. 1980 Jan;238(1):E69–E82. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.1980.238.1.E69. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Insel P. A., Liljenquist J. E., Tobin J. D., Sherwin R. S., Watkins P., Andres R., Berman M. Insulin control of glucose metabolism in man: a new kinetic analysis. J Clin Invest. 1975 May;55(5):1057–1066. doi: 10.1172/JCI108006. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KALANT N., CSORBA T. R., HELLER N. EFFECT OF INSULIN ON GLUCOSE PRODUCTION AND UTILIZATION IN DIABETES. Metabolism. 1963 Dec;12:1100–1111. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kolterman O. G., Gray R. S., Griffin J., Burstein P., Insel J., Scarlett J. A., Olefsky J. M. Receptor and postreceptor defects contribute to the insulin resistance in noninsulin-dependent diabetes mellitus. J Clin Invest. 1981 Oct;68(4):957–969. doi: 10.1172/JCI110350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kolterman O. G., Insel J., Saekow M., Olefsky J. M. Mechanisms of insulin resistance in human obesity: evidence for receptor and postreceptor defects. J Clin Invest. 1980 Jun;65(6):1272–1284. doi: 10.1172/JCI109790. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuzuya H., Blix P. M., Horwitz D. L., Steiner D. F., Rubenstein A. H. Determination of free and total insulin and C-peptide in insulin-treated diabetics. Diabetes. 1977 Jan;26(1):22–29. doi: 10.2337/diab.26.1.22. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liljenquist J. E., Mueller G. L., Cherrington A. D., Perry J. M., Rabinowitz D. Hyperglycemia per se (insulin and glucagon withdrawn) can inhibit hepatic glucose production in man. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1979 Jan;48(1):171–175. doi: 10.1210/jcem-48-1-171. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Sullivan J. B., Mahan C. M., Freedlender A. E., Williams R. F. Effect of age on corbohydrate metabolism. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1971 Oct;33(4):619–623. doi: 10.1210/jcem-33-4-619. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olefsky J. M. The insulin receptor: its role in insulin resistance of obesity and diabetes. Diabetes. 1976 Dec;25(12):1154–1162. doi: 10.2337/diab.25.12.1154. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perley M. J., Kipnis D. M. Plasma insulin responses to oral and intravenous glucose: studies in normal and diabetic sujbjects. J Clin Invest. 1967 Dec;46(12):1954–1962. doi: 10.1172/JCI105685. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reaven G. M., Bernstein R., Davis B., Olefsky J. M. Nonketotic diabetes mellitus: insulin deficiency or insulin resistance? Am J Med. 1976 Jan;60(1):80–88. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(76)90536-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reaven G. M., Olefsky J. M. The role of insulin resistance in the pathogenesis of diabetes mellitus. Adv Metab Disord. 1978;9:313–331. doi: 10.1016/b978-0-12-027309-6.50021-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- STEELE R. Influences of glucose loading and of injected insulin on hepatic glucose output. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1959 Sep 25;82:420–430. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1959.tb44923.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sacca L., Hendler R., Sherwin R. S. Hyperglycemia inhibits glucose production in man independent of changes in glucoregulatory hormones. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1978 Nov;47(5):1160–1163. doi: 10.1210/jcem-47-5-1160. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sherwin R. S., Kramer K. J., Tobin J. D., Insel P. A., Liljenquist J. E., Berman M., Andres R. A model of the kinetics of insulin in man. J Clin Invest. 1974 May;53(5):1481–1492. doi: 10.1172/JCI107697. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Verdonk C. A., Rizza R. A., Gerich J. E. Effects of plasma glucose concentration on glucose utilization and glucose clearance in normal man. Diabetes. 1981 Jun;30(6):535–537. doi: 10.2337/diab.30.6.535. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waldhäusl W. K., Gasić S., Bratusch-Marrain P., Korn A., Nowotny P. Feedback inhibition by biosynthetic human insulin of insulin release in healthy human subjects. Am J Physiol. 1982 Dec;243(6):E476–E482. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.1982.243.6.E476. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


