Abstract
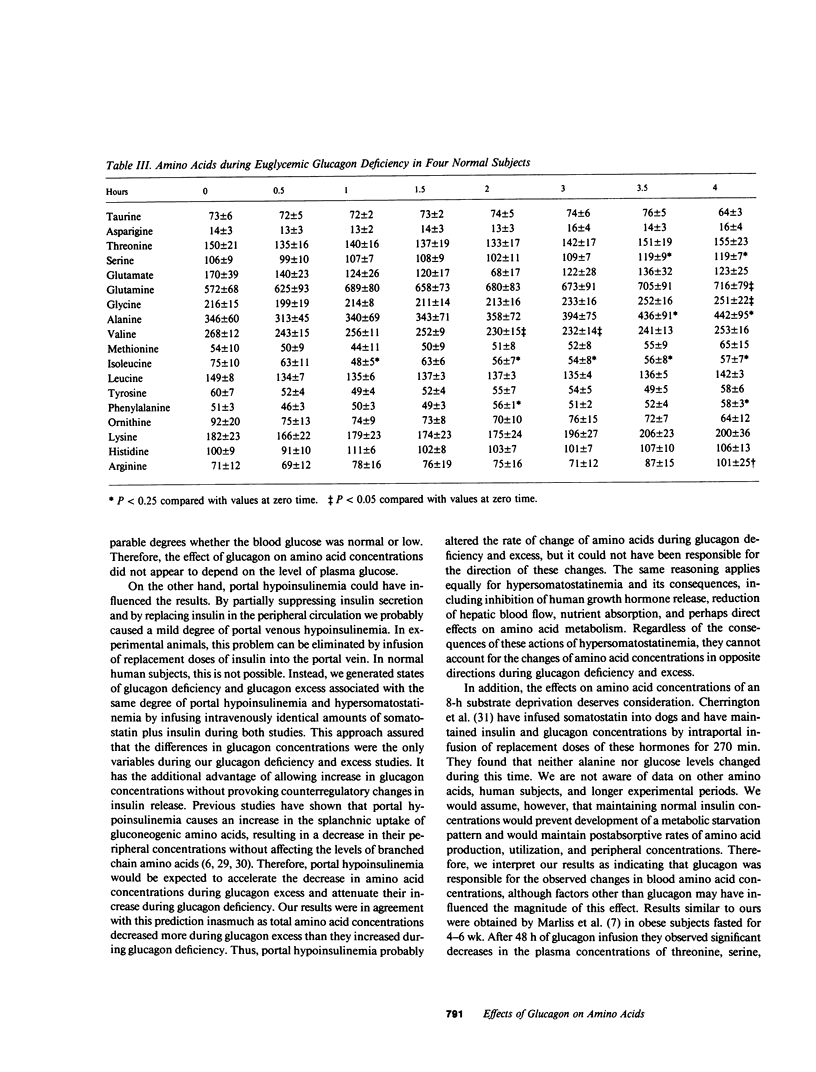
The effects of glucagon deficiency and excess on plasma concentrations of 21 amino acids were studied in six normal human subjects for 8 h. During glucagon deficiency, produced by intravenous infusion of somatostatin (0.5 mg/h) and insulin (5 mU/kg per h), amino acid concentration (sum of 21 amino acids) rose from 2,607 +/- 76 to 2,922 +/- 133 microM after 4 h (P less than 0.025). The largest increases occurred in lysine (+26%), glycine (+24%), alanine (+23%), and arginine (+23%) concentrations. During glucagon excess produced by intravenous infusion of somatostatin (0.5 mg/h), insulin (5 mU/kg per h), and glucagon (60 ng/kg per h), amino acid concentration decreased from 2,774 +/- 166 to 2,388 +/- 102 microM at 8 h (P less than 0.01). The largest decreases occurred in citrulline (-37%), proline (-32%), ornithine (-30%), tyrosine (-23%), glycine (-20%), threonine (-21%), and alanine (18%) concentrations. Urinary urea nitrogen and total nitrogen excretions were lower during glucagon deficiency than during glucagon excess (3.1 +/- 0.2 vs. 6.3 +/- 2.3 g/8 h, P less than 0.05 and 4.8 +/- 1.0 vs 7.0 +/- 2.6 g/8 h, respectively, P less than 0.05). Biostator-controlled euglycemic glucagon deficiency was produced in four normal subjects for 4 h to eliminate possible effects of changes in glucose concentration on amino acids. Amino acid concentration (sum of 18 amino acids) increases occurred in arginine (+42%), alanine (+28%), glutamine (+25%), and glycine (+16%) concentrations. The data show that small changes (-66 pg/ml and +50 pg/ml) in basal glucagon concentrations cause plasma amino acid concentrations to change in opposite directions. The finding that urinary excretion of nitrogen and urea nitrogen was greater during glucagon excess than during glucagon deficiency suggested alterations in the rate of gluconeogenesis from amino acids as one mechanism by which glucagon controls blood amino acid levels.
Full text
PDF

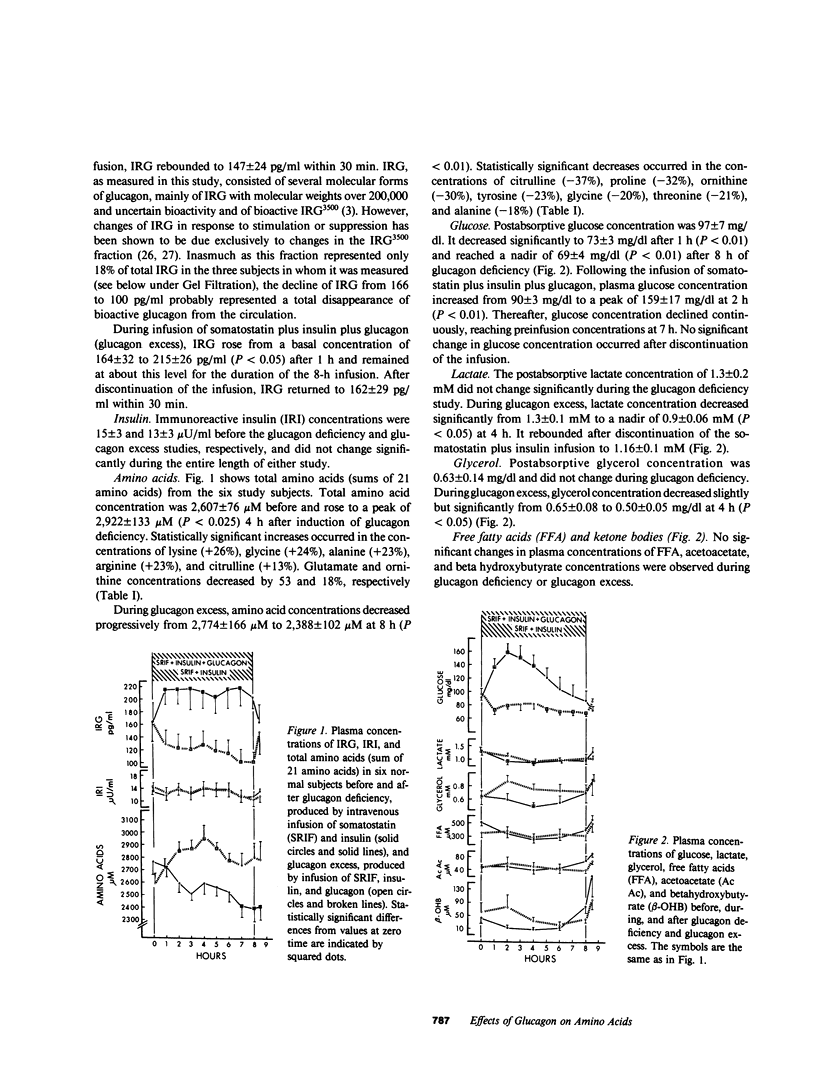
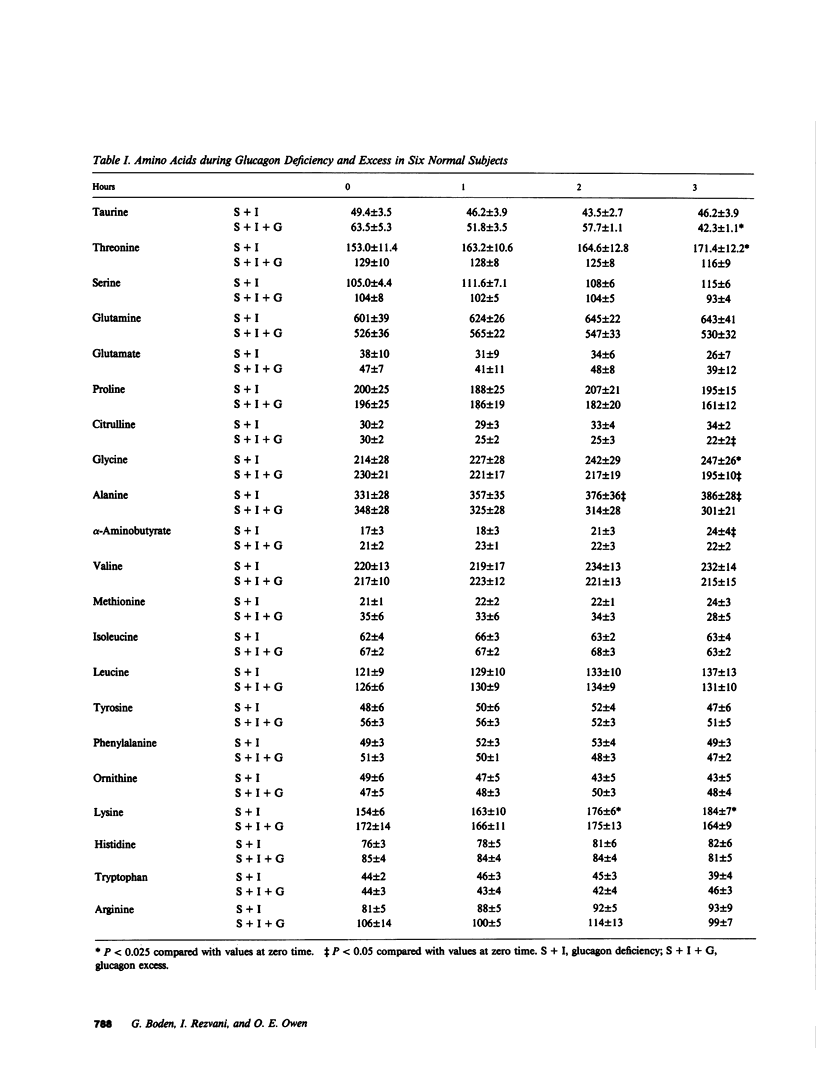
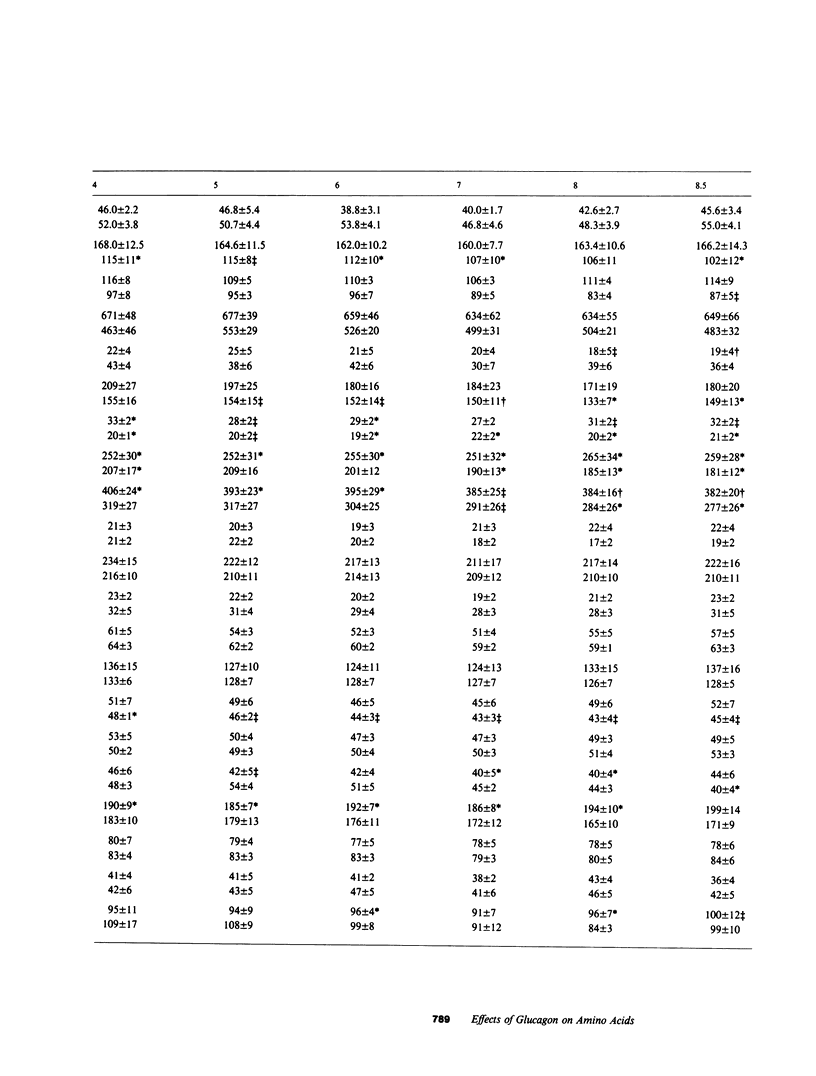
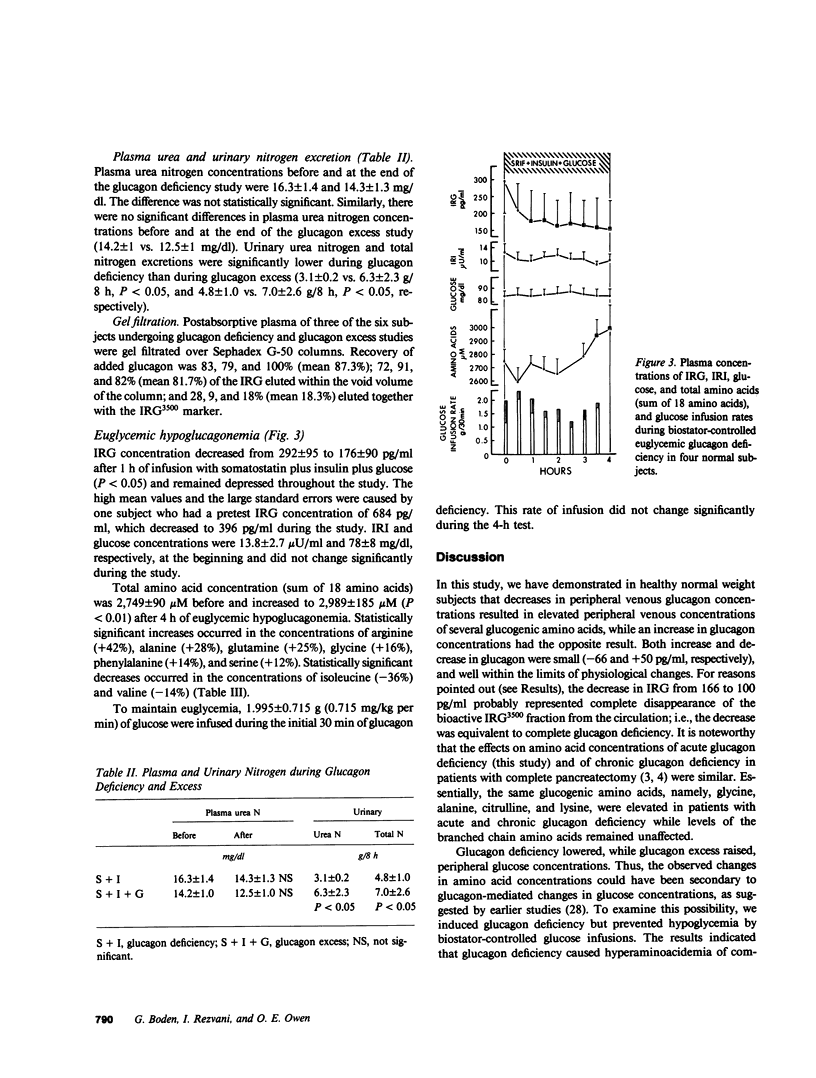


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aoki T. T., Muller W. A., Brennan M. F., Cahill G. F., Jr Blood cell and plasma amino acid levels across forearm muscle during a protein meal. Diabetes. 1973 Oct;22(10):768–775. doi: 10.2337/diab.22.10.768. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boden G., Master R. W., Rezvani I., Palmer J. P., Lobe T. E., Owen O. E. Glucagon deficiency and hyperaminoacidemia after total pancreatectomy. J Clin Invest. 1980 Mar;65(3):706–716. doi: 10.1172/JCI109717. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boden G., Owen O. E., Rezvani I., Elfenbein B. I., Quickel K. E. An islet cell carcinoma containing glucagon and insulin. Chronic glucagon excess and glucose homeostasis. Diabetes. 1977 Feb;26(2):128–137. doi: 10.2337/diab.26.2.128. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boden G., Wilson R. M., Owen O. E. Effects of chronic glucagon excess on hepatic metabolism. Diabetes. 1978 Jun;27(6):643–648. doi: 10.2337/diab.27.6.643. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bomboy J. D., Jr, Lewis S. B., Lacy W. W., Sinclair-Smith B. C., Liljenquist J. E. Transient stimulatory effect of sustained hyperglucagonemia on splanchnic glucose production in normal and diabetic man. Diabetes. 1977 Mar;26(3):177–174. doi: 10.2337/diab.26.3.177. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CROFFORD O. B., FELTS P. W., LACY W. W. EFFECT OF GLUCOSE INFUSION ON THE INDIVIDUAL PLASMA FREE AMINO ACIDS IN MAN. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1964 Oct;117:11–14. doi: 10.3181/00379727-117-29483. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cahill G. F., Jr, Herrera M. G., Morgan A. P., Soeldner J. S., Steinke J., Levy P. L., Reichard G. A., Jr, Kipnis D. M. Hormone-fuel interrelationships during fasting. J Clin Invest. 1966 Nov;45(11):1751–1769. doi: 10.1172/JCI105481. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cherrington A. D., Lacy W. W., Chiasson J. L. Effect of glucagon on glucose production during insulin deficiency in the dog. J Clin Invest. 1978 Sep;62(3):664–677. doi: 10.1172/JCI109174. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clemens A. H. Feedback control dynamics for glucose controlled insulin infusion system. Med Prog Technol. 1979 Jun 15;6(3):91–98. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DOLE V. P., MEINERTZ H. Microdetermination of long-chain fatty acids in plasma and tissues. J Biol Chem. 1960 Sep;235:2595–2599. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eggstein M. Eine neue Bestimmung der Neutralfette im Blutserum und Gewebe. II. Zuverlässigkeit der Methode, andere Neutralfettbestimmungen, Normalwerte für Triglyceride und Glycerin im menschlichen Blut. Klin Wochenschr. 1966 Mar 1;44(5):267–273. doi: 10.1007/BF01747717. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eggstein M., Kreutz F. H. Eine neue Bestimmung der Neutralfette im Blutserum und Gewebe. I. Prinzip, Durchführung und Besprechung der Methode. Klin Wochenschr. 1966 Mar 1;44(5):262–267. doi: 10.1007/BF01747716. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Felig P. Amino acid metabolism in man. Annu Rev Biochem. 1975;44:933–955. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.44.070175.004441. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Felig P., Owen O. E., Wahren J., Cahill G. F., Jr Amino acid metabolism during prolonged starvation. J Clin Invest. 1969 Mar;48(3):584–594. doi: 10.1172/JCI106017. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Felig P., Wahren J. Amino acid metabolism in exercising man. J Clin Invest. 1971 Dec;50(12):2703–2714. doi: 10.1172/JCI106771. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerich J. E., Lorenzi M., Bier D. M., Tsalikian E., Schneider V., Karam J. H., Forsham P. H. Effects of physiologic levels of glucagon and growth hormone on human carbohydrate and lipid metabolism. Studies involving administration of exogenous hormone during suppression of endogenous hormone secretion with somatostatin. J Clin Invest. 1976 Apr;57(4):875–884. doi: 10.1172/JCI108364. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodenberger D. M., Lawley T. J., Strober W., Wyatt L., Sangree M. H., Jr, Sherwin R., Rosenbaum H., Braverman I., Katz S. I. Necrolytic migratory erythema without glucagonoma. Arch Dermatol. 1979 Dec;115(12):1429–1432. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jennings A. S., Cherrington A. D., Liljenquist J. E., Keller U., Lacy W. W., Chiasson J. L. The roles of insulin and glucagon in the regulation of gluconeogenesis in the postabsorptive dog. Diabetes. 1977 Sep;26(9):847–856. doi: 10.2337/diab.26.9.847. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuku S. F., Jaspan J. B., Emmanouel D. S., Zeidler A., Katz A. I., Rubenstein A. H. Heterogeneity of plasma glucagon. Circulating components in normal subjects and patients with chronic renal failure. J Clin Invest. 1976 Sep;58(3):742–750. doi: 10.1172/JCI108521. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lefebvre P. J., Luyckx A. S. Effect of insulin on glucagon enhanced lipolysis in vitro. Diabetologia. 1969 Jun;5(3):195–197. doi: 10.1007/BF01213680. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liljenquist J. E., Mueller G. L., Cherrington A. D., Keller U., Chiasson J-L, Perry J. M., Lacy W. W., Rabinowitz D. Evidence for an important role of glucagon in the regulation of hepatic glucose production in normal man. J Clin Invest. 1977 Feb;59(2):369–374. doi: 10.1172/JCI108649. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lorch E., Gey K. F. Photometric "titration" of free fatty acids with the Technicon AutoAnalyzer. Anal Biochem. 1966 Aug;16(2):244–252. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(66)90152-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MARSH W. H., FINGERHUT B., MILLER H. AUTOMATED AND MANUAL DIRECT METHODS FOR THE DETERMINATION OF BLOOD UREA. Clin Chem. 1965 Jun;11:624–627. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mallinson C. N., Bloom S. R., Warin A. P., Salmon P. R., Cox B. A glucagonoma syndrome. Lancet. 1974 Jul 6;2(7871):1–5. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(74)91343-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marliss E. B., Aoki T. T., Unger R. H., Soeldner J. S., Cahill G. F., Jr Glucagon levels and metabolic effects in fasting man. J Clin Invest. 1970 Dec;49(12):2256–2270. doi: 10.1172/JCI106445. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muller W. A., Berger M., Suter P., Cüppers H. J., Reiter J., Wyss T., Berchtold P., Schmidt F. H., Assal J. P., Renold A. E. Glucagon immunoreactivities and amino acid profile in plasma of duodenopancreatectomized patients. J Clin Invest. 1979 May;63(5):820–827. doi: 10.1172/JCI109381. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oliver J. R., Wagle S. R. Studies on the inhibition of insulin release, glycogenolysis and gluconeogenesis by somatostatin in the rat islets of langerhans and isolated hepatocytes. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1975 Feb 3;62(3):772–777. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(75)90466-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PIEZ K. A., MORRIS L. A modified procedure for the automatic analysis of amino acids. Anal Biochem. 1960 Nov;1:187–201. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(60)90045-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pagliara A. S., Goodman A. D. Elevation of plasma glutamate in gout. Its possible role in the pathogenesis of hyperuricemia. N Engl J Med. 1969 Oct 2;281(14):767–770. doi: 10.1056/NEJM196910022811405. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pozefsky T., Tancredi R. G., Moxley R. T., Dupre J., Tobin J. D. Metabolism of forearm tissues in man. Studies with glucagon. Diabetes. 1976 Feb;25(2):128–135. doi: 10.2337/diab.25.2.128. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sacks H., Waligora K., Matthews J., Pimstone B. Inhibition by somatostatin of glucagon-induced glucose release from the isolated perfused rat liver. Endocrinology. 1977 Dec;101(6):1751–1759. doi: 10.1210/endo-101-6-1751. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schusdziarra V., Zyznar E., Rouiller D., Boden G., Brown J. C., Arimura A., Unger R. H. Splanchnic somatostatin: a hormonal regulator of nutrient homeostasis. Science. 1980 Feb 1;207(4430):530–532. doi: 10.1126/science.7352262. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sherwin R. S., Bastl C., Finkelstein F. O., Fisher M., Black H., Hendler R., Felig P. Influence of uremia and hemodialysis on the turnover and metabolic effects of glucagon. J Clin Invest. 1976 Mar;57(3):722–731. doi: 10.1172/JCI108330. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Soeldner J. S., Slone D. Critical variables in the radioimmunoassay of serum insulin using the double antibody technic. Diabetes. 1965 Dec;14(12):771–779. doi: 10.2337/diab.14.12.771. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Valverde I., Dobbs R., Unger R. H. Heterogeneity of plasma glucagon immunoreactivity in normal, depancreatized, and alloxan-diabetic dogs. Metabolism. 1975 Sep;24(9):1021–1028. doi: 10.1016/0026-0495(75)90095-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WILLIAMSON D. H., MELLANBY J., KREBS H. A. Enzymic determination of D(-)-beta-hydroxybutyric acid and acetoacetic acid in blood. Biochem J. 1962 Jan;82:90–96. doi: 10.1042/bj0820090. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wahren J., Efendić S., Luft R., Hagenfeldt L., Björkman O., Felig P. Influence of somatostatin on splanchnic glucose metabolism in postabsorptive and 60-hour fasted humans. J Clin Invest. 1977 Feb;59(2):299–307. doi: 10.1172/JCI108641. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wahren J., Felig P., Cerasi E., Luft R. Splanchnic and peripheral glucose and amino acid metabolism in diabetes mellitus. J Clin Invest. 1972 Jul;51(7):1870–1878. doi: 10.1172/JCI106989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


