Abstract
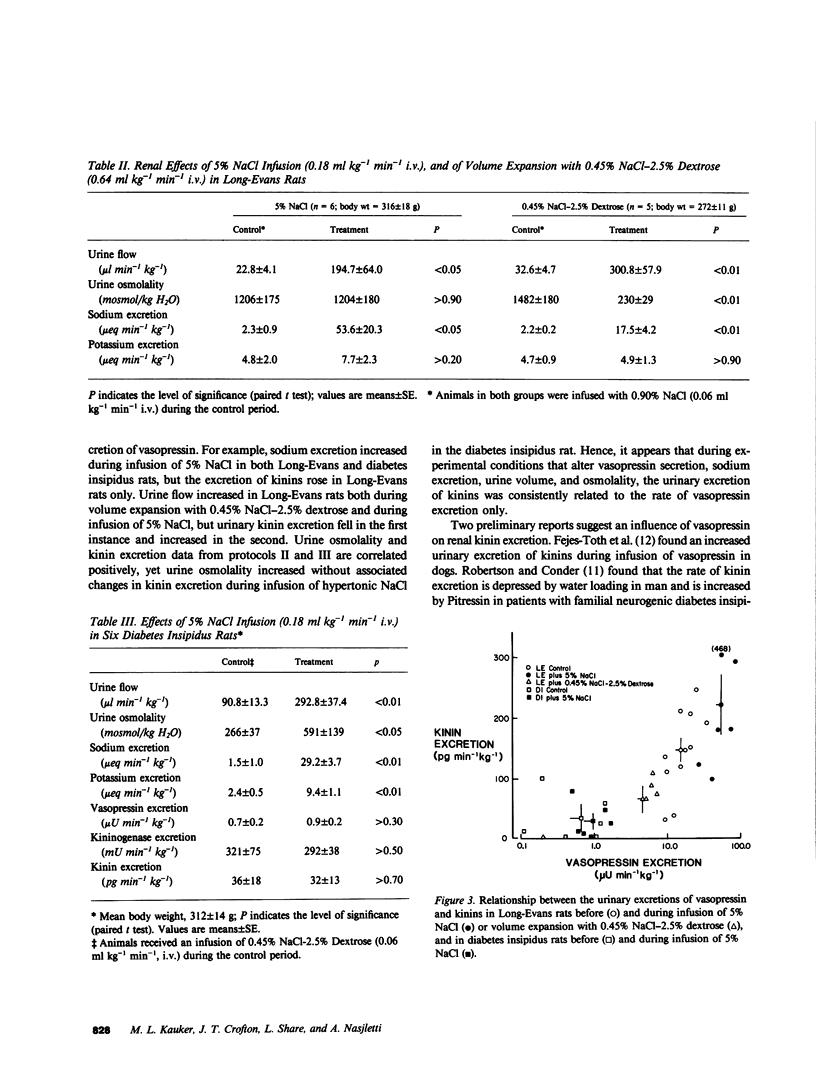
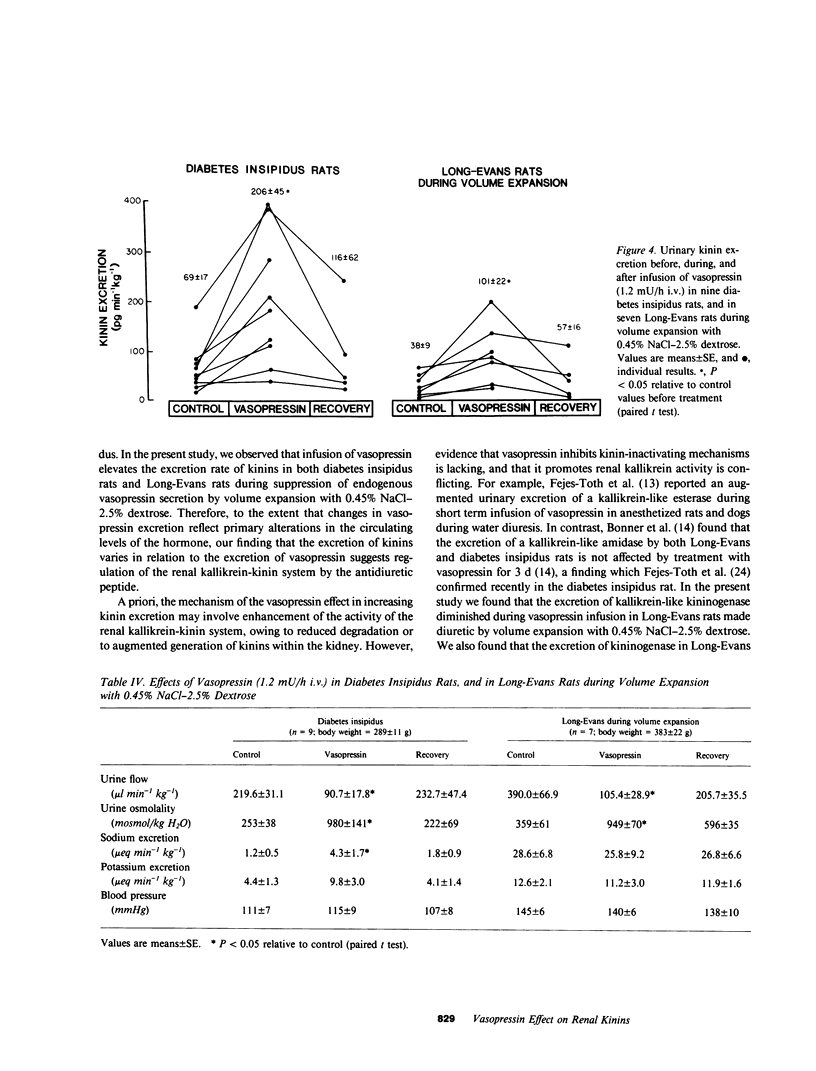
To study the relationship between vasopressin and the renal kallikrein-kinin system we measured the rate of excretion of kinins into the urine of anesthetized rats during conditions of increased and decreased vasopressin level. The excretion of immunoreactive kinins in Brattleboro rats with hereditary diabetes insipidus (DI) (24 +/- 3 pg min-1 kg-1) was lower than in the control Long Evans (LE) rats (182 +/- 22 pg min-1 kg-1; P less than 0.05). The DI rats also exhibited negligible urinary excretion of immunoreactive vasopressin, reduced urine osmolality, and increased urine flow and kininogenase excretion. In LE rats, volume expansion by infusion of 0.45% NaCl-2.5% dextrose to lower vasopressin secretion reduced (P less than 0.05) kinin excretion, vasopressin excretion, and urine osmolality to 41, 26, and 15% of their respective control values, while increasing (P less than 0.05) urine flow and kininogenase excretion. On the other hand, the infusion of 5% NaCl, which promotes vasopressin secretion, increased (P less than 0.05) the urinary excretion of kinins and vasopressin to 165 and 396% of control, while increasing (P less than 0.05) urine flow and kininogenase excretion. Infusion of vasopressin (1.2 mU/h, intravenous) enhanced (P less than 0.05) kinin excretion by two to threefold in DI rats and in LE rats during volume expansion with 0.45% NaCl-2.5% dextrose, while decreasing urine flow and increasing urine osmolality. This study demonstrates that the urinary excretion of immunoreactive kinins varies in relation to the urinary level of vasopressin, irrespective of urine volume and osmolality and of the urinary excretions of sodium and kininogenase. The study suggests a role for vasopressin in promoting the activity of the renal kallikrein-kinin system in the rat.
Full text
PDF





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alhenc-Gelas F., Marchetti J., Allegrini J., Corvol P., Menard J. Measurement of urinary kallikrein activity. Species differences in kinin production. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1981 Nov 5;677(3-4):477–488. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(81)90262-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bönner G., Marin-Grez M., Beck D., Deeg M., Gross F. Changes in renal and urinary kallikrein activity by mannitol-induced osmotic diuresis. Clin Sci (Lond) 1981 Jul;61(1):47–51. doi: 10.1042/cs0610047. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bönner G., Rascher W., Speck G., Marin-Grez M., Gross F. The renal kallikrein-kinin system in Brattleboro rats with hereditary hypothalamic diabetes insipidus. Missing relationship between antidiuretic hormone and the renal kallikrein-kinin system. Acta Endocrinol (Copenh) 1981 Sep;98(1):36–42. doi: 10.1530/acta.0.0980036. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carretero O. A., Oza N. B., Piwonska A., Ocholik T., Scicli A. G. Measurement of urinary kallikrein activity by kinin radioimmunoassay. Biochem Pharmacol. 1976 Oct 15;25(20):2265–2270. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(76)90008-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carvounis C. P., Carvounis G., Arbeit L. A. Role of the endogenous kallikrein-kinin system in modulating vasopressin-stimulated water flow and urea permeability in the toad urinary bladder. J Clin Invest. 1981 Jun;67(6):1792–1796. doi: 10.1172/JCI110219. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chao J. Purification and characterization of rat urinary esterase A, a plasminogen activator. J Biol Chem. 1983 Apr 10;258(7):4434–4439. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chao J., Tanaka S., Margolius H. S. Inhibitory effects of sodium and other monovalent cations on purified versus membrane-bound kallikrein. J Biol Chem. 1983 May 25;258(10):6461–6465. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crofton J. T., Share L., Wang B. C., Shade R. E. Pressor responsiveness to vasopressin in the rat with DOC-salt hypertension. Hypertension. 1980 Jul-Aug;2(4):424–431. doi: 10.1161/01.hyp.2.4.424. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fejes-Toth G., Frölich J. C., Naray-Fejes-Toth A. Effect of aprotinin on the renal response to vasopressin in diabetes insipidus rats. J Physiol. 1983 Jun;339:585–590. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1983.sp014735. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fejes-Tóth G., Magyar A., Walter J. Renal response to vasopressin after inhibition of prostaglandin synthesis. Am J Physiol. 1977 May;232(5):F416–F423. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1977.232.5.F416. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fejes-Tóth G., Zahajszky T., Filep J. Effect of vasopressin on renal kallikrein excretion. Am J Physiol. 1980 Oct;239(4):F388–F392. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1980.239.4.F388. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geiger R., Mann K. A kallikrein-specific inhibitor in rat kidney tubules. Hoppe Seylers Z Physiol Chem. 1976 Apr;357(4):553–558. doi: 10.1515/bchm2.1976.357.1.553. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lieberthal W., Oza N. B., Bernard D. B., Levinsky N. G. The effect of cations on the activity of human urinary kallikrein. J Biol Chem. 1982 Sep 25;257(18):10827–10830. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marks E. S., Frech M., Proud D., Keiser H. R. Effect of alterations in extracellular fluid volume on urinary kallikrein in the conscious rat. Hypertension. 1982 Sep-Oct;4(5):625–633. doi: 10.1161/01.hyp.4.5.625. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McPartland R. P., Sustarsic D. L., Rapp J. P. Evidence for an androgen-dependent urinary arginine esterase in the rat: separation from other urinary arginine esterases including kallikrein. Endocrinology. 1981 May;108(5):1634–1638. doi: 10.1210/endo-108-5-1634. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nasjletti A., McGiff J. C., Colina-Chourio J. Interrelations of the renal kallikrein-kinin system and renal prostaglandins in the conscious rat. Influence of mineralocorticoids. Circ Res. 1978 Nov;43(5):799–807. doi: 10.1161/01.res.43.5.799. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oliver J. A., Sciacca R. R., Le Cren G., Cannon P. J. Modulation by prostaglandins of the renal vascular action of arginine vasopressin. Prostaglandins. 1982 Nov;24(5):641–656. doi: 10.1016/0090-6980(82)90034-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olsen U. B. Changes of urinary kallikrein and kinin excretions induced by adrenalin infusion in conscious dogs. Scand J Clin Lab Invest. 1980 Apr;40(2):173–178. doi: 10.3109/00365518009093022. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Omata K., Carretero O. A., Scicli A. G., Jackson B. A. Localization of active and inactive kallikrein (kininogenase activity) in the microdissected rabbit nephron. Kidney Int. 1982 Dec;22(6):602–607. doi: 10.1038/ki.1982.218. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orce G. G., Castillo G. A., Margolius H. S. Inhibition of short-circuit current in toad urinary bladder by inhibitors of glandular kallikrein. Am J Physiol. 1980 Nov;239(5):F459–F465. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1980.239.5.F459. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pisano J. J., Corthorn J., Yates K., Pierce J. V. The kallikrein-kinin system in the kidney. Contrib Nephrol. 1978;12:116–125. doi: 10.1159/000401659. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Powers C. A., Nasjletti A. A kininogenase resembling glandular kallikrein in the rat pituitary pars intermedia. Endocrinology. 1983 Apr;112(4):1194–1200. doi: 10.1210/endo-112-4-1194. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Powers C. A., Nasjletti A. A novel kinin-generating protease (kininogenase) in the porcine anterior pituitary. J Biol Chem. 1982 May 25;257(10):5594–5600. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Proud D., Perkins M., Pierce J. V., Yates K. N., Highet P. F., Herring P. L., Mangkornkanok/Mark M., Bahu R., Carone F., Pisano J. J. Characterization and localization of human renal kininogen. J Biol Chem. 1981 Oct 25;256(20):10634–10639. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scicli A. G., Carretero O. A., Hampton A., Cortes P., Oza N. B. Site of kininogenase secretion in the dog nephron. Am J Physiol. 1976 Feb;230(2):533–536. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1976.230.2.533. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scicli A. G., Gandolfi R., Carretero O. A. Site of formation of kinins in the dog nephron. Am J Physiol. 1978 Jan;234(1):F36–F40. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1978.234.1.F36. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Valtin H. Animal model of human disease: hereditary hypothalamic diabetes insipidus. Am J Pathol. 1976 Jun;83(3):633–636. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vinci J. M., Zusman R. M., Izzo J. L., Jr, Bowden R. E., Horwitz D., Pisano J. J., Keiser H. R. Human urinary and plasma kinins: relationship to sodium-retaining steroids and plasma renin activity. Circ Res. 1979 Feb;44(2):228–237. doi: 10.1161/01.res.44.2.228. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ward P. E., Erdös E. G., Gedney C. D., Dowben R. M., Reynolds R. C. Isolation of membrane-bound renal enzymes that metabolize kinins and angiotensins. Biochem J. 1976 Sep 1;157(3):643–650. doi: 10.1042/bj1570643. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamada K., Schulz W. W., Page D. S., Erdös E. G. Kallikrein and prekallikrein on the basolateral membrane of rat kidney tubules. Hypertension. 1981 Nov-Dec;3(6 Pt 2):II–59-64. doi: 10.1161/01.hyp.3.6_pt_2.ii-59. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zucker A., Nasjletti A., Schneider E. G. Effect of water deprivation on urinary excretion of PGE2 in the dog. Am J Physiol. 1983 Sep;245(3):R329–R333. doi: 10.1152/ajpregu.1983.245.3.R329. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


