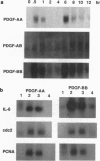
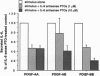
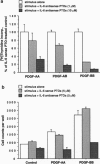
Abstract
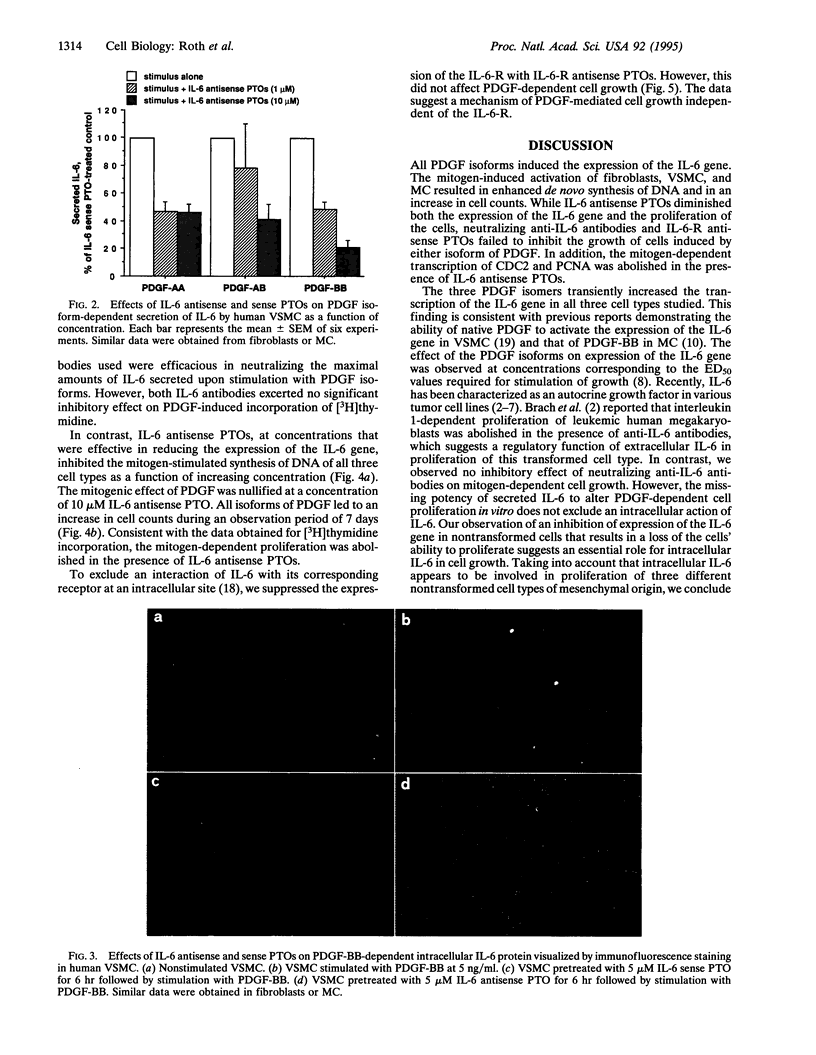
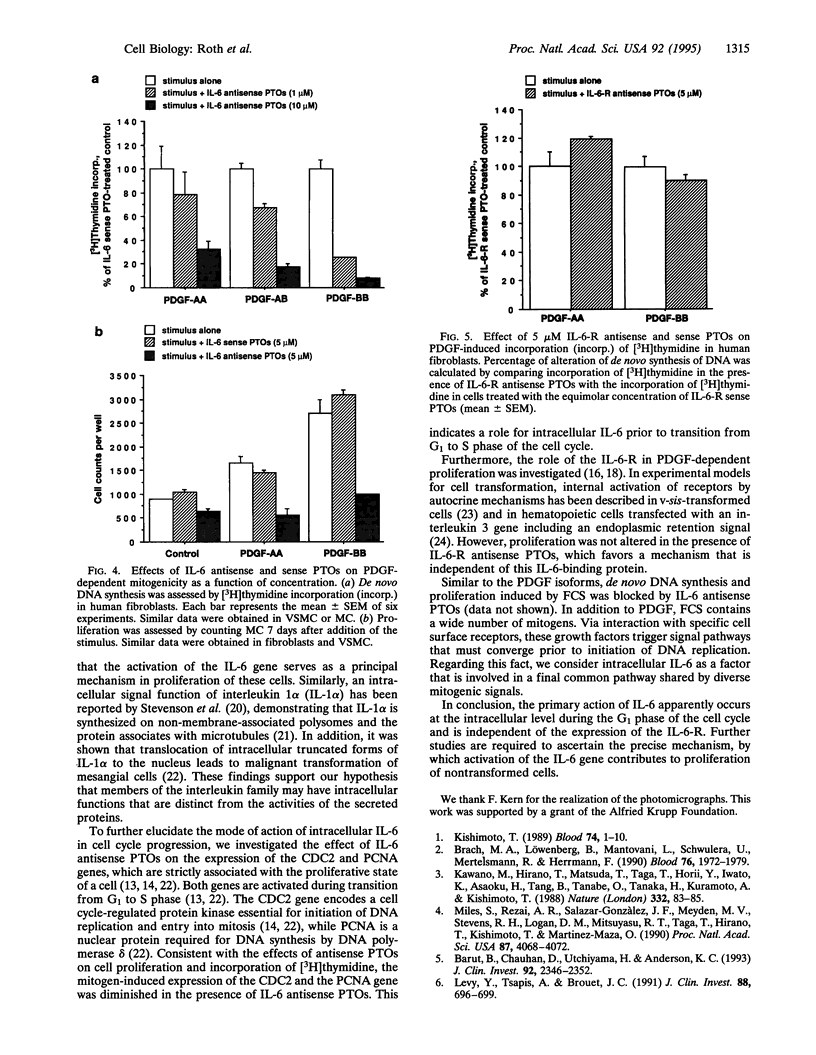
The functional relevance of interleukin 6 (IL-6) in platelet-derived growth factor (PDGF)-induced cell growth was evaluated in cultures of human fibroblasts, vascular smooth muscle cells, and mesangial cells. The three isoforms of the PDGF--namely, PDGF-AA, -AB, and -BB--induced the expression of the IL-6 gene and proliferation of the nontransformed cells. PDGF-induced transcription, translation, and secretion of IL-6 were diminished in the presence of IL-6 antisense oligonucleotides. While neutralizing anti-IL-6 antibodies failed to affect the growth factor-dependent cell proliferation, IL-6 antisense oligonucleotides inhibited cell division. In addition, IL-6 antisense oligonucleotides abolished PDGF-induced transcription of the genes coding for the cell division cycle 2-related protein (CDC2) and proliferating cell nuclear antigen (PCNA), both of which are regulated in a cell cycle-dependent manner. It is concluded that PDGF-dependent proliferation of nontransformed cells involves the action of intracellular IL-6.
Full text
PDF
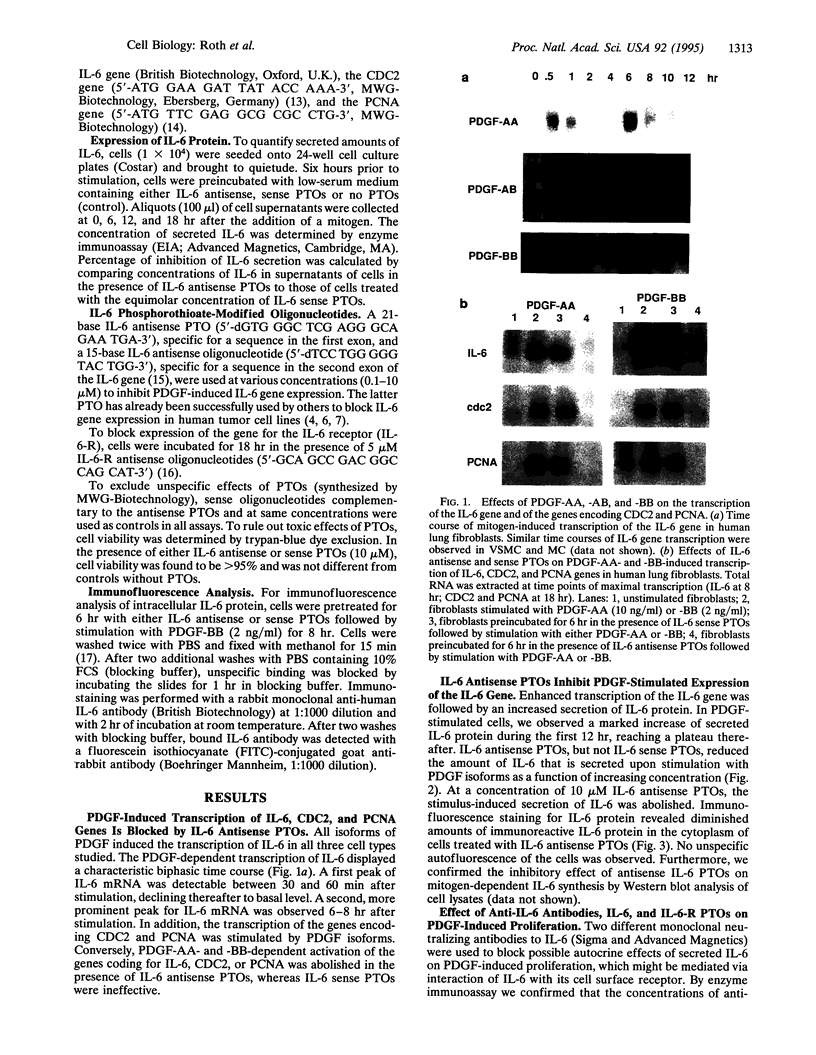

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Barut B., Chauhan D., Uchiyama H., Anderson K. C. Interleukin-6 functions as an intracellular growth factor in hairy cell leukemia in vitro. J Clin Invest. 1993 Nov;92(5):2346–2352. doi: 10.1172/JCI116839. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bejcek B. E., Li D. Y., Deuel T. F. Transformation by v-sis occurs by an internal autoactivation mechanism. Science. 1989 Sep 29;245(4925):1496–1499. doi: 10.1126/science.2551043. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brach M. A., Löwenberg B., Mantovani L., Schwulera U., Mertelsmann R., Herrmann F. Interleukin-6 (IL-6) is an intermediate in IL-1-induced proliferation of leukemic human megakaryoblasts. Blood. 1990 Nov 15;76(10):1972–1979. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Browder T. M., Abrams J. S., Wong P. M., Nienhuis A. W. Mechanism of autocrine stimulation in hematopoietic cells producing interleukin-3 after retrovirus-mediated gene transfer. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Jan;9(1):204–213. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.1.204. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dalton S. Cell cycle regulation of the human cdc2 gene. EMBO J. 1992 May;11(5):1797–1804. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05231.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jaskulski D., Gatti C., Travali S., Calabretta B., Baserga R. Regulation of the proliferating cell nuclear antigen cyclin and thymidine kinase mRNA levels by growth factors. J Biol Chem. 1988 Jul 25;263(21):10175–10179. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jaskulski D., deRiel J. K., Mercer W. E., Calabretta B., Baserga R. Inhibition of cellular proliferation by antisense oligodeoxynucleotides to PCNA cyclin. Science. 1988 Jun 10;240(4858):1544–1546. doi: 10.1126/science.2897717. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kawano M., Hirano T., Matsuda T., Taga T., Horii Y., Iwato K., Asaoku H., Tang B., Tanabe O., Tanaka H. Autocrine generation and requirement of BSF-2/IL-6 for human multiple myelomas. Nature. 1988 Mar 3;332(6159):83–85. doi: 10.1038/332083a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kishimoto T., Akira S., Taga T. Interleukin-6 and its receptor: a paradigm for cytokines. Science. 1992 Oct 23;258(5082):593–597. doi: 10.1126/science.1411569. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kishimoto T. The biology of interleukin-6. Blood. 1989 Jul;74(1):1–10. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levy Y., Tsapis A., Brouet J. C. Interleukin-6 antisense oligonucleotides inhibit the growth of human myeloma cell lines. J Clin Invest. 1991 Aug;88(2):696–699. doi: 10.1172/JCI115355. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loppnow H., Libby P. Proliferating or interleukin 1-activated human vascular smooth muscle cells secrete copious interleukin 6. J Clin Invest. 1990 Mar;85(3):731–738. doi: 10.1172/JCI114498. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lu C., Kerbel R. S. Interleukin-6 undergoes transition from paracrine growth inhibitor to autocrine stimulator during human melanoma progression. J Cell Biol. 1993 Mar;120(5):1281–1288. doi: 10.1083/jcb.120.5.1281. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miles S. A., Rezai A. R., Salazar-González J. F., Vander Meyden M., Stevens R. H., Logan D. M., Mitsuyasu R. T., Taga T., Hirano T., Kishimoto T. AIDS Kaposi sarcoma-derived cells produce and respond to interleukin 6. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Jun;87(11):4068–4072. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.11.4068. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roth M., Emmons L. R., Perruchoud A., Block L. H. Expressions of the low density lipoprotein receptor and 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl coenzyme A reductase genes are stimulated by recombinant platelet-derived growth factor isomers. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Mar 1;88(5):1888–1892. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.5.1888. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roth M., Keul R., Emmons L. R., Hörl W. H., Block L. H. Manidipine regulates the transcription of cytokine genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 May 1;89(9):4071–4075. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.9.4071. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roth M., Solèr M., Hornung M., Emmons L. R., Stulz P., Perruchoud A. P. Cell cultures from cryopreserved human lung tissue. Tissue Cell. 1992;24(4):455–459. doi: 10.1016/0040-8166(92)90061-b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stevenson F. T., Torrano F., Locksley R. M., Lovett D. H. Interleukin 1: the patterns of translation and intracellular distribution support alternative secretory mechanisms. J Cell Physiol. 1992 Aug;152(2):223–231. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041520202. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamasaki K., Taga T., Hirata Y., Yawata H., Kawanishi Y., Seed B., Taniguchi T., Hirano T., Kishimoto T. Cloning and expression of the human interleukin-6 (BSF-2/IFN beta 2) receptor. Science. 1988 Aug 12;241(4867):825–828. doi: 10.1126/science.3136546. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zilberstein A., Ruggieri R., Korn J. H., Revel M. Structure and expression of cDNA and genes for human interferon-beta-2, a distinct species inducible by growth-stimulatory cytokines. EMBO J. 1986 Oct;5(10):2529–2537. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04531.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]