Abstract
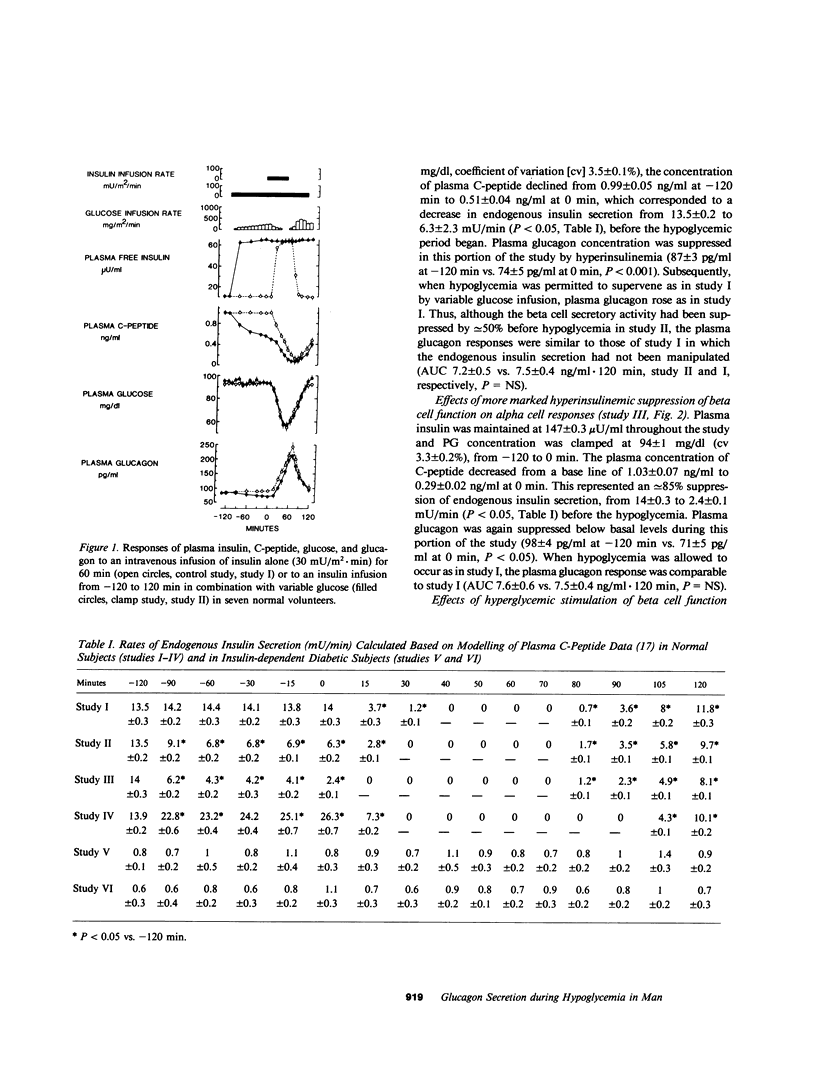
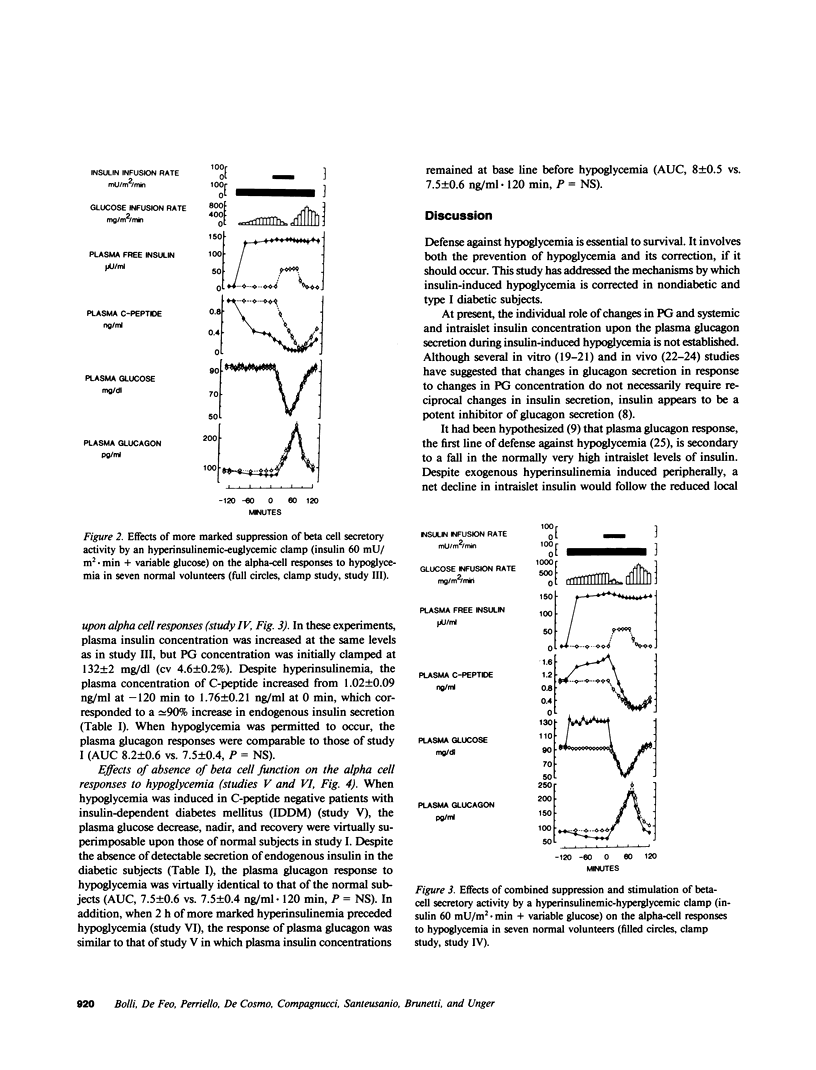
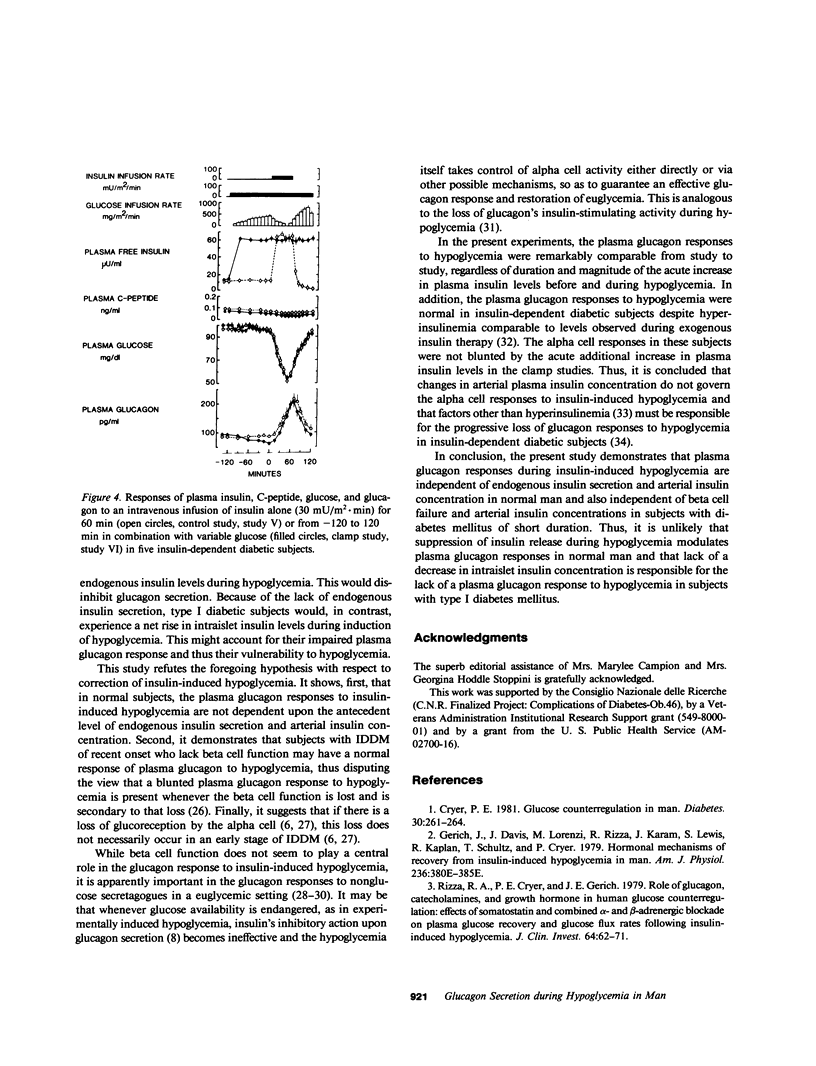
To elucidate the mechanisms controlling the response of glucagon to hypoglycemia, a vital component of the counterregulatory hormonal response, the role of intraislet insulin was studied in seven normal subjects and five subjects with insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus (IDDM) (of less than 15-mo duration). In the normal subjects, hypoglycemia (arterial plasma glucose [PG] 53 +/- 3 mg/dl) induced by an intravenous insulin infusion (30 mU/m2 X min for 1 h, free immunoreactive insulin [FIRI] 58 +/- 2 microU/ml) elicited a 100% fall in insulin secretion and an integrated rise in glucagon of 7.5 ng/ml per 120 min. When endogenous insulin secretion was suppressed by congruent to 50 or congruent to 85% by a hyperinsulinemic-euglycemic clamp (FIRI 63 +/- 1.5 or 147 +/- 0.3 microU/ml, respectively) before hypoglycemia, the alpha cell responses to hypoglycemia were identical to those of the control study. When the endogenous insulin secretion was stimulated by congruent to 100% (hyperinsulinemic-hyperglycemic clamp, FIRI 145 +/- 1.5 microU/ml, PG 132 +/- 2 mg/dl) before hypoglycemia, the alpha cell responses to the hypoglycemia were also superimposable on those of the control study. Finally, in C-peptide negative diabetic subjects made euglycemic by a continuous overnight intravenous insulin infusion, the alpha cell responses to hypoglycemia were comparable to those of normal subjects despite absent beta cell secretion, and were not affected by antecedent hyperinsulinemia (hyperinsulinemic-euglycemic clamp for 2 h, FIRI 61 +/- 2 microU/ml). These results indicate that the glucagon response to insulin-induced hypoglycemia is independent of the level of both endogenous intraislet and exogenous arterial insulin concentration in normal man, and that this response may be normal in the absence of endogenous insulin secretion, in contrast to earlier reports. Thus, loss of beta cell function is not responsible for alpha cell failure during insulin-induced hypoglycemia in IDDM.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Asplin C. M., Paquette T. L., Palmer J. P. In vivo inhibition of glucagon secretion by paracrine beta cell activity in man. J Clin Invest. 1981 Jul;68(1):314–318. doi: 10.1172/JCI110251. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Asplin C., Raghu P., Dornan T., Palmer J. P. Glucose regulation of glucagon secretion independent of B cell activity. Metabolism. 1983 Mar;32(3):292–295. doi: 10.1016/0026-0495(83)90195-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bolli G., Calabrese G., De Feo P., Compagnucci P., Zega G., Angeletti G., Cartechini M. G., Santeusanio F., Brunetti P. Lack of glucagon response in glucose counter-regulation in type 1 (insulin-dependent) diabetics: absence of recovery after prolonged optimal insulin therapy. Diabetologia. 1982 Feb;22(2):100–105. doi: 10.1007/BF00254837. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bolli G., de Feo P., Compagnucci P., Cartechini M. G., Angeletti G., Santeusanio F., Brunetti P., Gerich J. E. Abnormal glucose counterregulation in insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus. Interaction of anti-insulin antibodies and impaired glucagon and epinephrine secretion. Diabetes. 1983 Feb;32(2):134–141. doi: 10.2337/diab.32.2.134. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bolli G., de Feo P., Compagnucci P., Cartechini M. G., Angeletti G., Santeusanio F., Brunetti P. Important role of adrenergic mechanisms in acute glucose counterregulation following insulin-induced hypoglycemia in type I diabetes. Evidence for an effect mediated by beta-adrenoreceptors. Diabetes. 1982 Jul;31(7):641–647. doi: 10.2337/diab.31.7.641. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cryer P. E. Glucose counterregulation in man. Diabetes. 1981 Mar;30(3):261–264. doi: 10.2337/diab.30.3.261. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Feo P., Bolli G., Perriello G., De Cosmo S., Compagnucci P., Angeletti G., Santeusanio F., Gerich J. E., Motolese M., Brunetti P. The adrenergic contribution to glucose counterregulation in type I diabetes mellitus. Dependency on A-cell function and mediation through beta 2-adrenergic receptors. Diabetes. 1983 Oct;32(10):887–893. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eaton R. P., Allen R. C., Schade D. S., Erickson K. M., Standefer J. Prehepatic insulin production in man: kinetic analysis using peripheral connecting peptide behavior. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1980 Sep;51(3):520–528. doi: 10.1210/jcem-51-3-520. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Faber O. K., Hagen C., Binder C., Markussen J., Naithani V. K., Blix P. M., Kuzuya H., Horwitz D. L., Rubenstein A. H., Rossing N. Kinetics of human connecting peptide in normal and diabetic subjects. J Clin Invest. 1978 Jul;62(1):197–203. doi: 10.1172/JCI109106. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Faber O. K., Markussen J., Naithani V. K., Binder C. Production of antisera to synthetic benzyloxycarbonyl-C-peptide of human proinsulin. Hoppe Seylers Z Physiol Chem. 1976 Jun;357(6):751–757. doi: 10.1515/bchm2.1976.357.1.751. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerich J. E., Charles M. A., Grodsky G. M. Characterization of the effects of arginine and glucose on glucagon and insulin release from the perfused rat pancreas. J Clin Invest. 1974 Oct;54(4):833–841. doi: 10.1172/JCI107823. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerich J. E., Langlois M., Noacco C., Karam J. H., Forsham P. H. Lack of glucagon response to hypoglycemia in diabetes: evidence for an intrinsic pancreatic alpha cell defect. Science. 1973 Oct 12;182(4108):171–173. doi: 10.1126/science.182.4108.171. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldfine I. D., Cerasi E., Luft R. Glucagon stimulation of insulin release in man: inhibition during hypoglycemia. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1972 Aug;35(2):312–315. doi: 10.1210/jcem-35-2-312. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuzuya H., Blix P. M., Horwitz D. L., Steiner D. F., Rubenstein A. H. Determination of free and total insulin and C-peptide in insulin-treated diabetics. Diabetes. 1977 Jan;26(1):22–29. doi: 10.2337/diab.26.1.22. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Madsbad S., Hilsted J., Krarup T., Sestoft L., Christensen N. J., Faber O. K., Tronier B. Hormonal, metabolic and cardiovascular responses to hypoglycaemia in Type 1 (insulin-dependent) diabetes with and without residual B cell function. Diabetologia. 1982 Dec;23(6):499–503. doi: 10.1007/BF00254298. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGuire E. A., Helderman J. H., Tobin J. D., Andres R., Berman M. Effects of arterial versus venous sampling on analysis of glucose kinetics in man. J Appl Physiol. 1976 Oct;41(4):565–573. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1976.41.4.565. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pagliara A. S., Stillings S. N., Hover B., Martin D. M., Matschinsky F. M. Glucose modulation of amino acid-induced glucagon and insulin release in the isolated perfused rat pancreas. J Clin Invest. 1974 Oct;54(4):819–832. doi: 10.1172/JCI107822. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pfeifer M. A., Beard J. C., Halter J. B., Judzewitsch R., Best J. D., Porte D., Jr Suppression of glucagon secretion during a tolbutamide infusion in normal and noninsulin-dependent diabetic subjects. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1983 Mar;56(3):586–591. doi: 10.1210/jcem-56-3-586. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rizza R. A., Cryer P. E., Gerich J. E. Role of glucagon, catecholamines, and growth hormone in human glucose counterregulation. Effects of somatostatin and combined alpha- and beta-adrenergic blockade on plasma glucose recovery and glucose flux rates after insulin-induced hypoglycemia. J Clin Invest. 1979 Jul;64(1):62–71. doi: 10.1172/JCI109464. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rizza R. A., Gerich J. E., Haymond M. W., Westland R. E., Hall L. D., Clemens A. H., Service F. J. Control of blood sugar in insulin-dependent diabetes: comparison of an artificial endocrine pancreas, continuous subcutaneous insulin infusion, and intensified conventional insulin therapy. N Engl J Med. 1980 Dec 4;303(23):1313–1318. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198012043032301. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rizza R. A., Mandarino L. J., Gerich J. E. Dose-response characteristics for effects of insulin on production and utilization of glucose in man. Am J Physiol. 1981 Jun;240(6):E630–E639. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.1981.240.6.E630. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Santiago J. V., Clarke W. L., Shah S. D., Cryer P. E. Epinephrine, norepinephrine, glucagon, and growth hormone release in association with physiological decrements in the plasma glucose concentration in normal and diabetic man. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1980 Oct;51(4):877–883. doi: 10.1210/jcem-51-4-877. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sorenson R. L., Elde R. P. Dissociation of glucose stimulation of somatostatin and insulin release from glucose inhibition of glucagon release in the isolated perfused rat pancreas. Diabetes. 1983 Jun;32(6):561–567. doi: 10.2337/diab.32.6.561. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tse T. F., Clutter W. E., Shah S. D., Cryer P. E. Mechanisms of postprandial glucose counterregulation in man. Physiologic roles of glucagon and epinephrine vis-a-vis insulin in the prevention of hypoglycemia late after glucose ingestion. J Clin Invest. 1983 Jul;72(1):278–286. doi: 10.1172/JCI110967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tse T. F., Clutter W. E., Shah S. D., Miller J. P., Cryer P. E. Neuroendocrine responses to glucose ingestion in man. Specificity, temporal relationships, and quantitative aspects. J Clin Invest. 1983 Jul;72(1):270–277. doi: 10.1172/JCI110966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Unger R. H. Meticulous control of diabetes: benefits, risks, and precautions. Diabetes. 1982 Jun;31(6 Pt 1):479–483. doi: 10.2337/diab.31.6.479. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Unger R. H. The Berson memorial lecture. Insulin-glucagon relationships in the defense against hypoglycemia. Diabetes. 1983 Jun;32(6):575–583. doi: 10.2337/diab.32.6.575. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



