Abstract
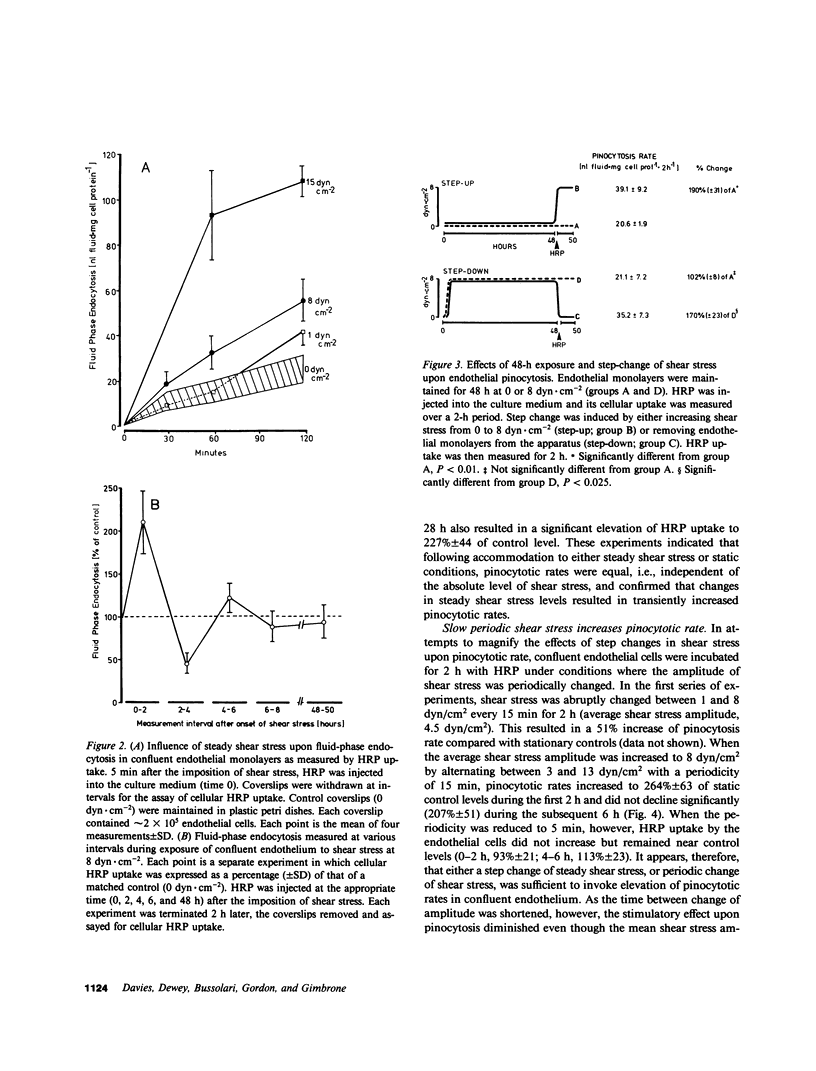
The relationships between fluid shear stress, a physiologically relevant mechanical force in the circulatory system, and pinocytosis (fluid-phase endocytosis) were investigated in cultured bovine aortic endothelial cells using a specially designed apparatus. Continuous exposure to steady shear stresses (1-15 dyn/cm2) in laminar flow stimulated time- and amplitude-dependent increases in pinocytotic rate which returned to control levels after several hours. After 48 h continuous exposure to steady shear stress, removal to static conditions also resulted in a transient increase in pinocytotic rate, suggesting that temporal fluctuations in shear stress may influence endothelial cell function. Endothelial pinocytotic rates remained constant during exposure to rapidly oscillating shear stress at near physiological frequency (1 Hz) in laminar flow. In contrast, however, a sustained elevation of pinocytotic rate occurred when cells were subjected to fluctuations in shear stress amplitude (3-13 dyn/cm2) of longer cycle time (15 min), suggesting that changes in blood flow of slower periodicity may influence pinocytotic vesicle formation. As determined by [3H]thymidine autoradiography, neither steady nor oscillating shear stress stimulated the proliferation of confluent endothelial cells. These observations indicate that: (a) alterations in fluid shear stress can significantly influence the rate of formation of pinocytotic vesicles in vascular endothelial cells, (b) this process is force- and time-dependent and shows accommodation, (c) certain patterns of fluctuation in shear stress result in sustained elevation of pinocytotic rate, and (d) shear stresses can modulate endothelial pinocytosis independent of growth stimulation. These findings are relevant to (i) transendothelial transport and the metabolism of macromolecules in normal endothelium and (ii) the role of hemodynamic factors in the localization of atherosclerotic lesions in vivo.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Björkerud S., Bondjers G. Endothelial integrity and viability in the aorta of the normal rabbit and rat as evaluated with dye exclusion tests and interference contrast microscopy. Atherosclerosis. 1972 May-Jun;15(3):285–300. doi: 10.1016/0021-9150(72)90019-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
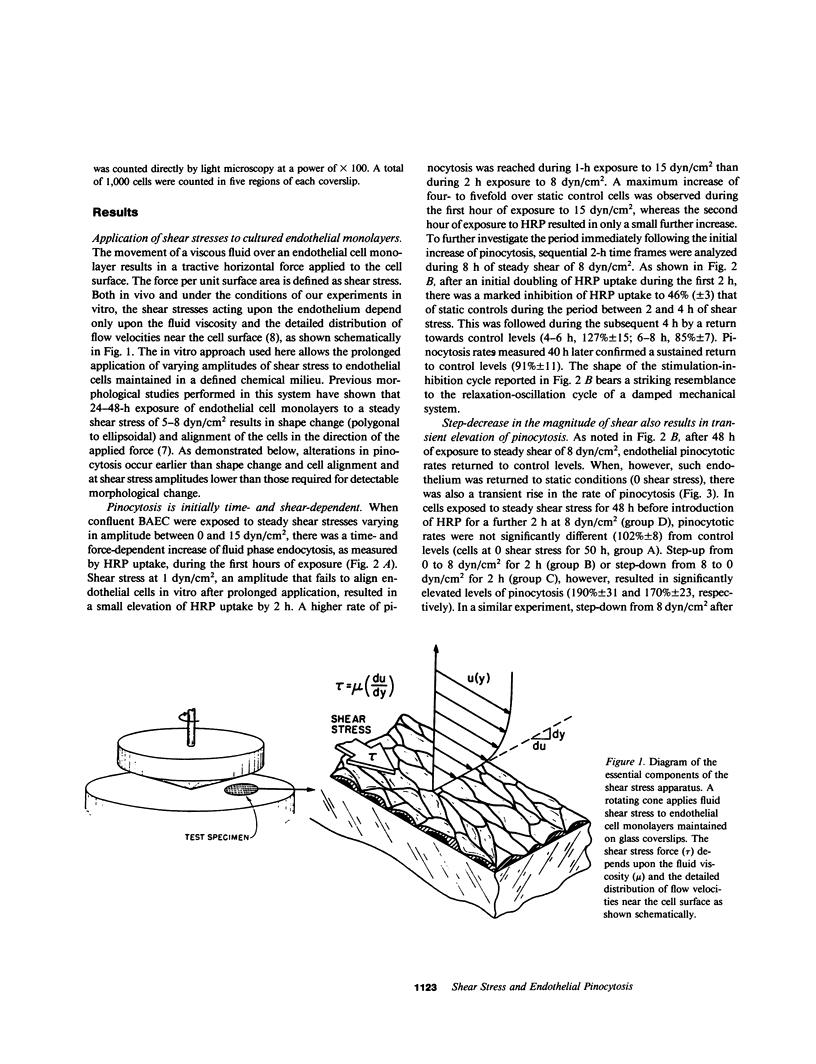
- Bussolari S. R., Dewey C. F., Jr, Gimbrone M. A., Jr Apparatus for subjecting living cells to fluid shear stress. Rev Sci Instrum. 1982 Dec;53(12):1851–1854. doi: 10.1063/1.1136909. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caro C. G., Fitz-Gerald J. M., Schroter R. C. Atheroma and arterial wall shear. Observation, correlation and proposal of a shear dependent mass transfer mechanism for atherogenesis. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1971 Feb 16;177(1046):109–159. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1971.0019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davies P. F., Reidy M. A., Goode T. B., Bowyer D. E. Scanning electron microscopy in the evaluation of endothelial integrity of the fatty lesion in atherosclerosis. Atherosclerosis. 1976 Oct;25(1):125–130. doi: 10.1016/0021-9150(76)90054-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davies P. F., Rennke H. G., Cotran R. S. Influence of molecular charge upon the endocytosis and intracellular fate of peroxidase activity in cultured arterial endothelium. J Cell Sci. 1981 Jun;49:69–86. doi: 10.1242/jcs.49.1.69. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davies P. F., Ross R. Mediation of pinocytosis in cultured arterial smooth muscle and endothelial cells by platelet-derived growth factor. J Cell Biol. 1978 Dec;79(3):663–671. doi: 10.1083/jcb.79.3.663. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davies P. F., Selden S. C., 3rd, Schwartz S. M. Enhanced rates of fluid pinocytosis during exponential growth and monolayer regeneration by cultured arterial endothelial cells. J Cell Physiol. 1980 Feb;102(2):119–127. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041020204. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dewey C. F., Jr, Bussolari S. R., Gimbrone M. A., Jr, Davies P. F. The dynamic response of vascular endothelial cells to fluid shear stress. J Biomech Eng. 1981 Aug;103(3):177–185. doi: 10.1115/1.3138276. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duncan R., Lloyd J. B. Pinocytosis in the rat visceral yolk sac. Effects of temperature, metabolic inhibitors and some other modifiers. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1978 Dec 18;544(3):647–655. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(78)90339-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fry D. L. Acute vascular endothelial changes associated with increased blood velocity gradients. Circ Res. 1968 Feb;22(2):165–197. doi: 10.1161/01.res.22.2.165. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gimbrone M. A., Jr Culture of vascular endothelium. Prog Hemost Thromb. 1976;3:1–28. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldstein J. L., Brown M. S. The low-density lipoprotein pathway and its relation to atherosclerosis. Annu Rev Biochem. 1977;46:897–930. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.46.070177.004341. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goode T. B., Davies P. F., Reidy M. A., Bowyer D. E. Aortic endothelial cell morphology observed in situ by scanning electron microscopy during atherogenesis in the rabbit. Atherosclerosis. 1977 Jun;27(2):235–251. doi: 10.1016/0021-9150(77)90061-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graham R. C., Jr, Karnovsky M. J. The early stages of absorption of injected horseradish peroxidase in the proximal tubules of mouse kidney: ultrastructural cytochemistry by a new technique. J Histochem Cytochem. 1966 Apr;14(4):291–302. doi: 10.1177/14.4.291. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gutstein W. H., Farrell G. A., Armellini C. Blood flow disturbance and endothelial cell injury in preatherosclerotic swine. Lab Invest. 1973 Aug;29(2):134–149. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lutz R. J., Cannon J. N., Bischoff K. B., Dedrick R. L., Stiles R. K., Fry D. L. Wall shear stress distribution in a model canine artery during steady flow. Circ Res. 1977 Sep;41(3):391–399. doi: 10.1161/01.res.41.3.391. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Newman D. L., Batten J. R., Bowden N. L. Influence of experimental stenosis on uptake of albumin by the abdominal aorta. Atherosclerosis. 1977 Feb;26(2):195–204. doi: 10.1016/0021-9150(77)90102-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pratten M. K., Lloyd J. B. Effects of temperature, metabolic inhibitors and some other factors on fluid-phase and adsorptive pinocytosis by rat peritoneal macrophages. Biochem J. 1979 Jun 15;180(3):567–571. doi: 10.1042/bj1800567. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rittgers S. E., Karayannacos P. E., Guy J. F., Nerem R. M., Shaw G. M., Hostetler J. R., Vasko J. S. Velocity distribution and intimal proliferation in autologous vein grafts in dogs. Circ Res. 1978 Jun;42(6):792–801. doi: 10.1161/01.res.42.6.792. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salisbury J. L., Condeelis J. S., Satir P. Receptor-mediated endocytosis: machinery and regulation of the clathrin-coated vesicle pathway. Int Rev Exp Pathol. 1983;24:1–62. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steinman R. M., Brodie S. E., Cohn Z. A. Membrane flow during pinocytosis. A stereologic analysis. J Cell Biol. 1976 Mar;68(3):665–687. doi: 10.1083/jcb.68.3.665. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steinman R. M., Cohn Z. A. The interaction of soluble horseradish peroxidase with mouse peritoneal macrophages in vitro. J Cell Biol. 1972 Oct;55(1):186–204. doi: 10.1083/jcb.55.1.186. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor R. F., Price T. H., Schwartz S. M., Dale D. C. Neutrophil-endothelial cell interactions on endothelial monolayers grown on micropore filters. J Clin Invest. 1981 Feb;67(2):584–587. doi: 10.1172/JCI110071. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vasile E., Simionescu M., Simionescu N. Visualization of the binding, endocytosis, and transcytosis of low-density lipoprotein in the arterial endothelium in situ. J Cell Biol. 1983 Jun;96(6):1677–1689. doi: 10.1083/jcb.96.6.1677. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White G. E., Gimbrone M. A., Jr, Fujiwara K. Factors influencing the expression of stress fibers in vascular endothelial cells in situ. J Cell Biol. 1983 Aug;97(2):416–424. doi: 10.1083/jcb.97.2.416. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]





