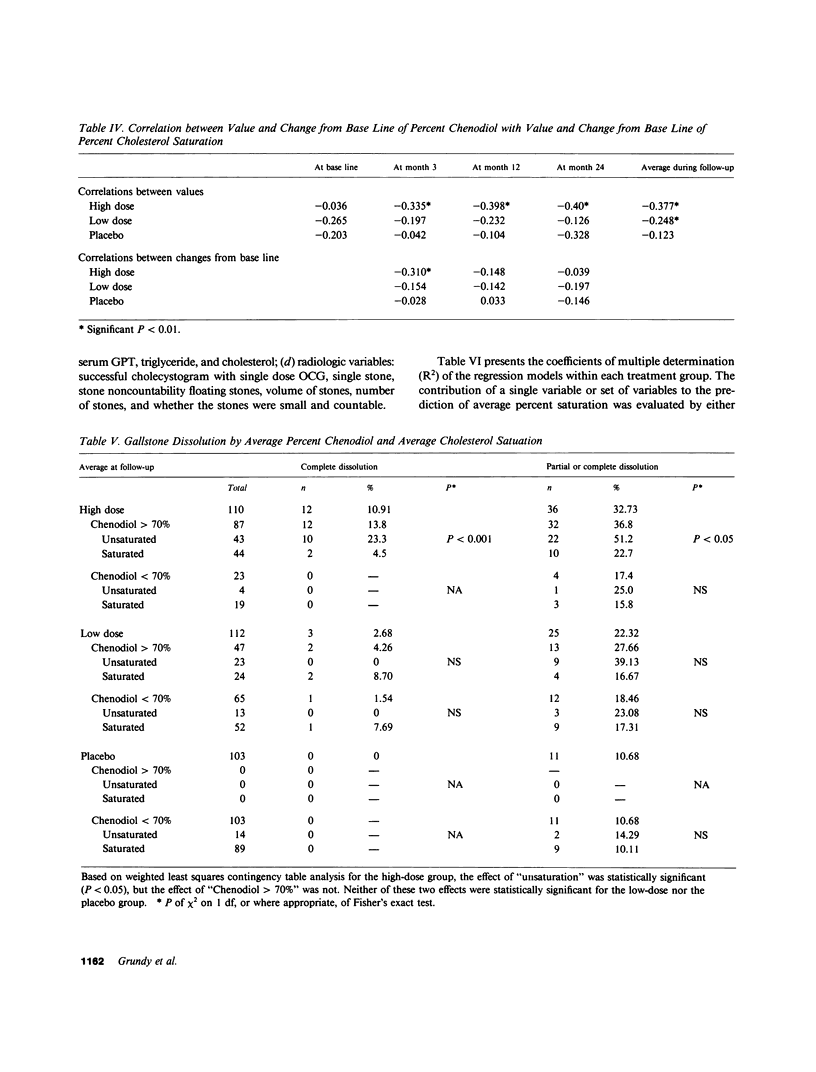
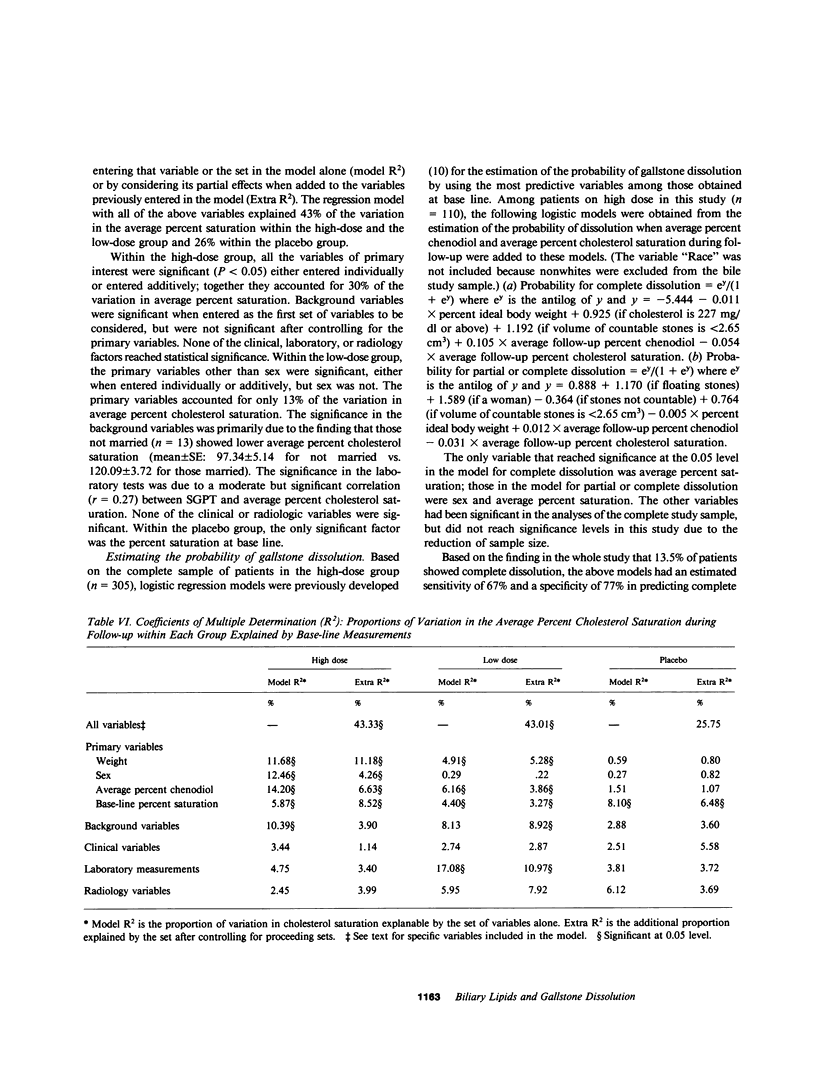
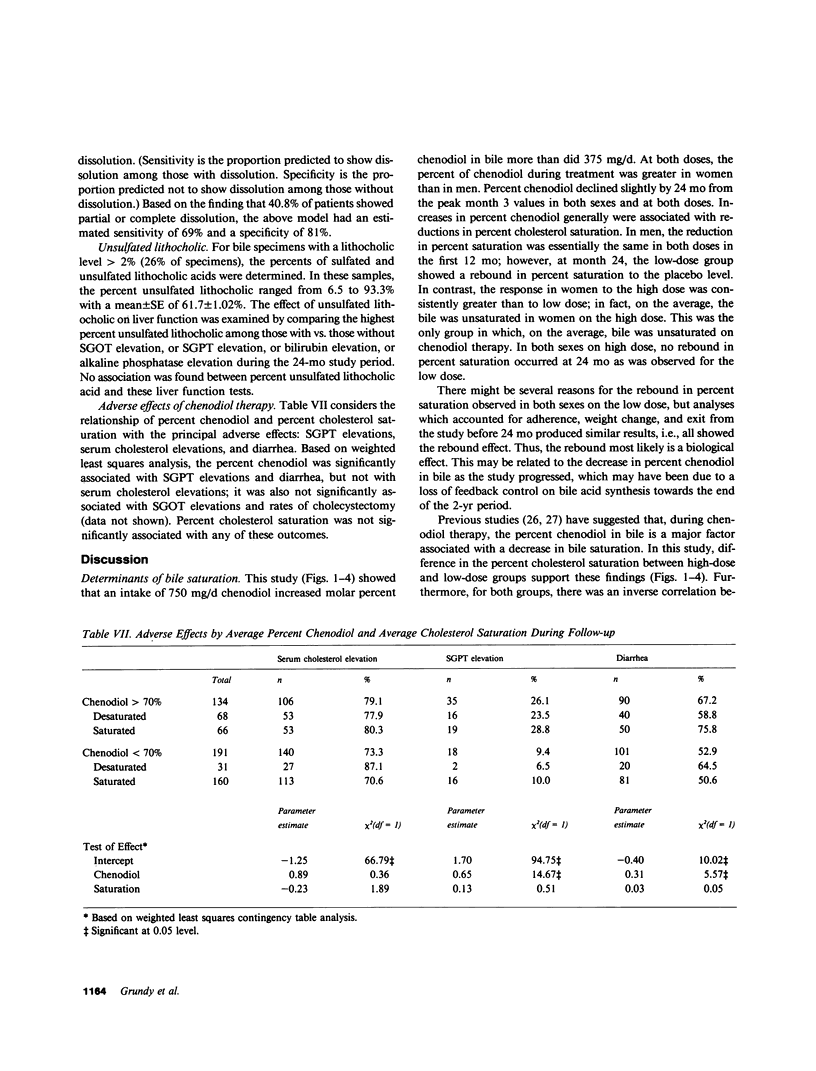
Abstract
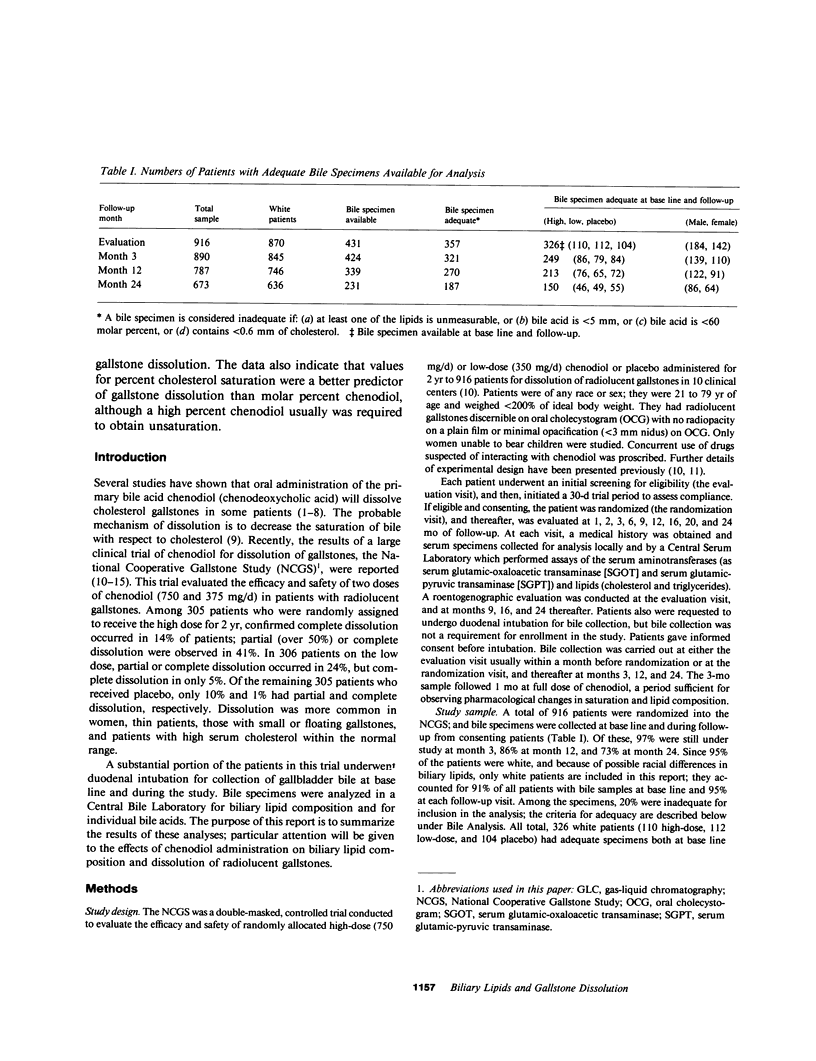
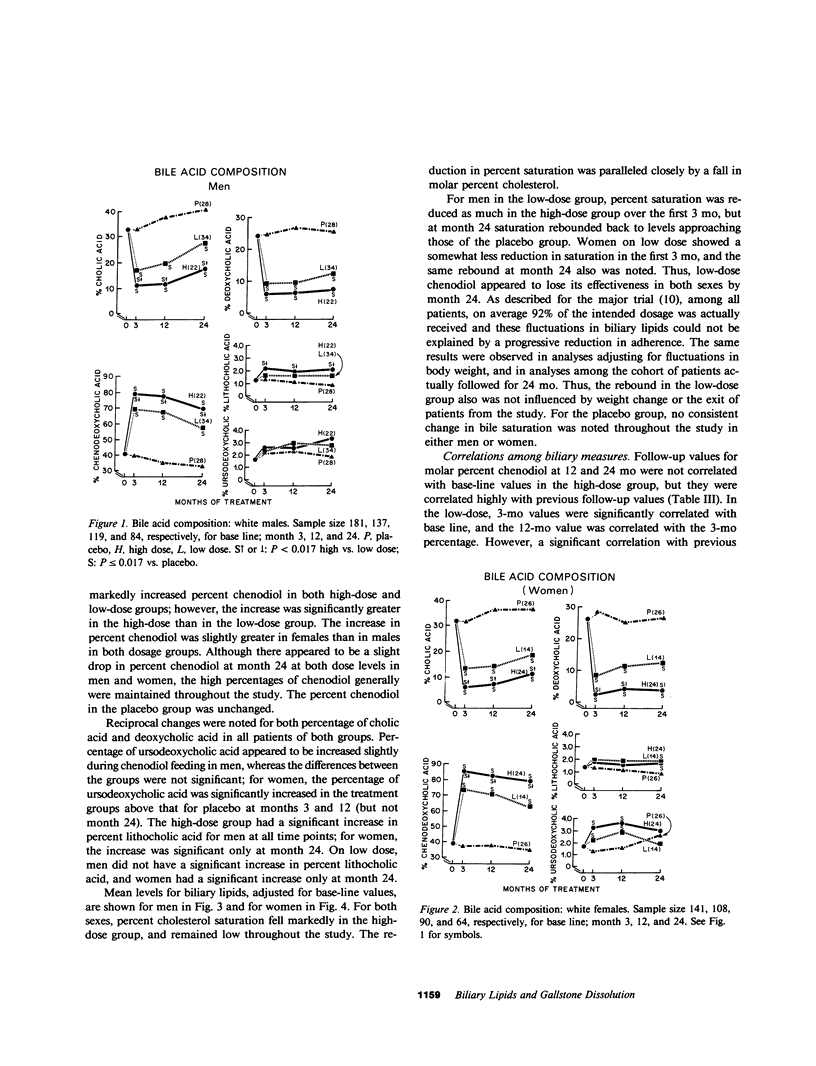
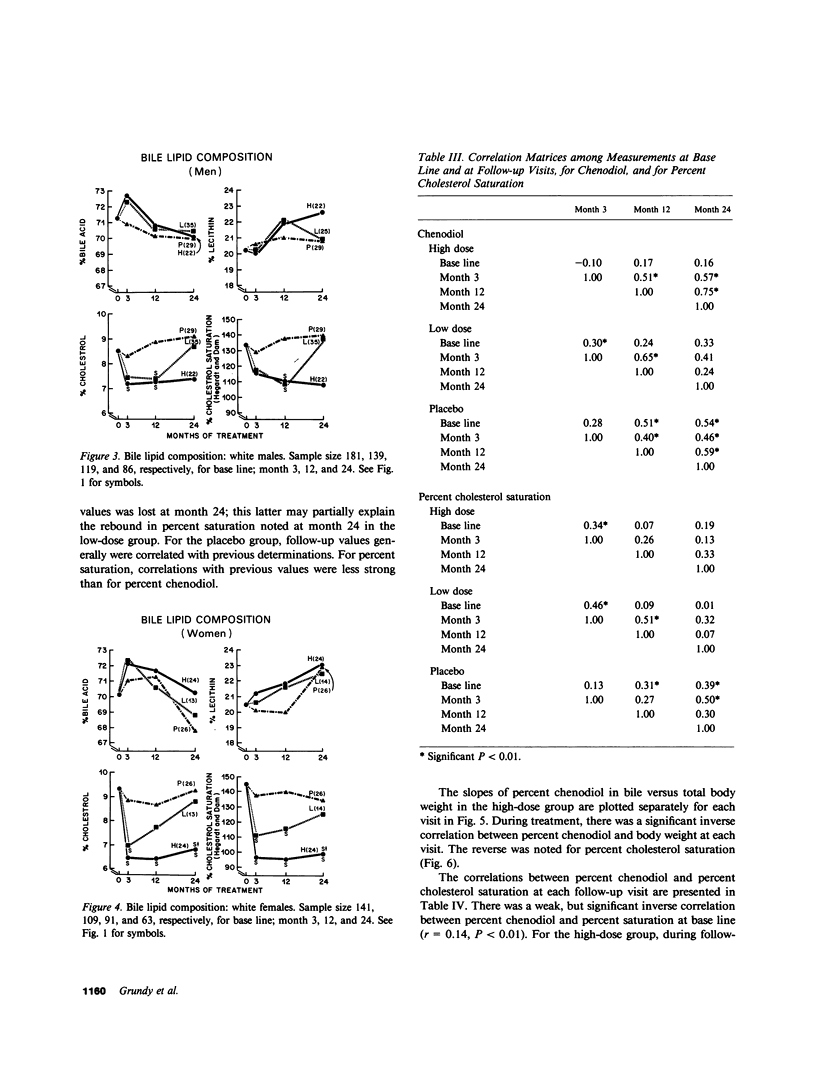
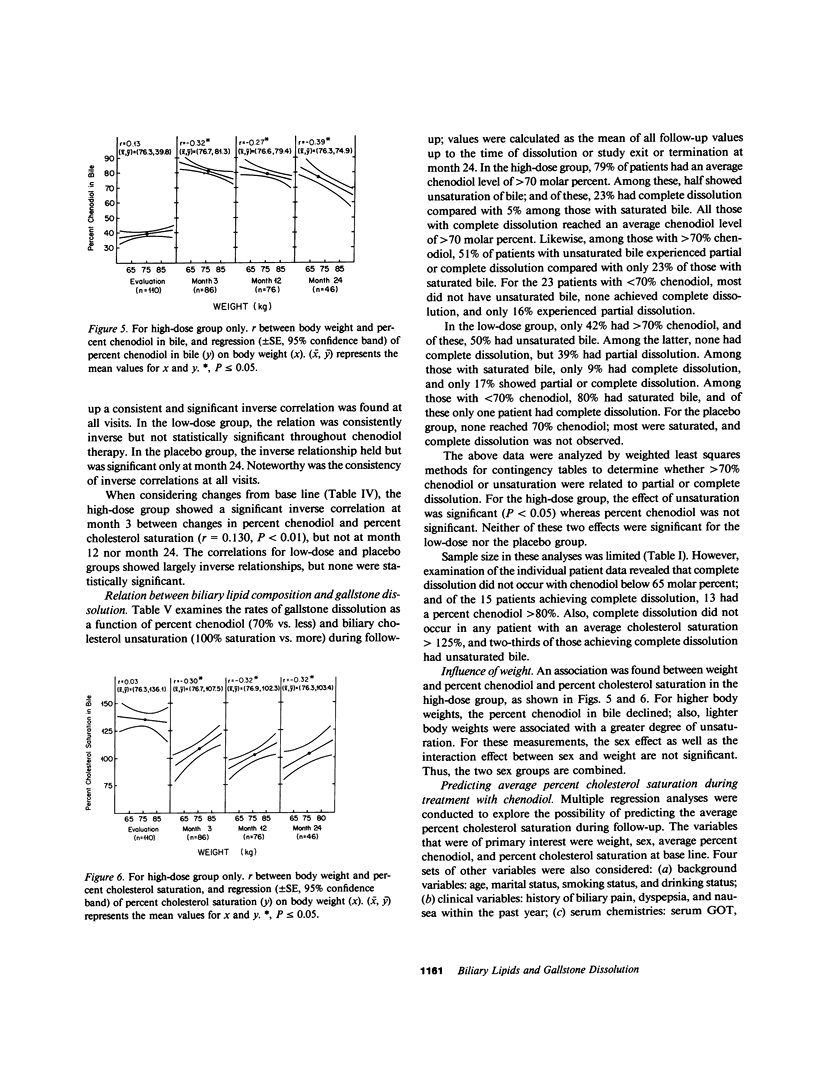
The National Cooperative Gallstone Study was a double-masked trial conducted to determine the efficacy and safety of chenodeoxycholic acid (chenodiol) for dissolution of cholesterol gallstones. Patients with radiolucent gallstones were randomly allocated to either a high dose (750 mg/d, n = 305) or low dose (375 mg/d, n = 306) of chenodiol or placebo (n = 305) administered for 2 yr. Specimens of gallbladder bile were obtained for biliary lipid analysis on 50% of all white obtained for biliary lipid analysis on 50% of all white patients at base line and after 3-mo therapy, on 45% at 12 mo, and on 36% at 24 mo. Among these specimens, 20% were inadequate for analysis. For analysis of data, available values during therapy were averaged up to time of dissolution, study exit, or study termination. In the high-dose group, percent chenodiol (molar percent of all bile acids) increased markedly and remained high during the 2 yr of follow-up. Also, molar percent cholesterol decreased significantly and remained low during the 2 yr of follow-up. In the low-dose group, percent chenodiol increased and remained significantly increased. Percent cholesterol saturation decreased at 3 mo, but at 24 mo it was not different from that in the placebo group, suggesting a physiological adaptation to the low dose by 2 yr. 79% of patients on high dose had greater than 70% chenodiol. Among these, half showed unsaturated bile (less than 100% cholesterol saturation) while the remainder were supersaturated; in the former group with unsaturated bile, 23% had complete dissolution and 51% had partial (greater than 50% reduction in stone size) or complete dissolution. In contrast, those with over 70% chenodiol and supersaturated bile had only 5% complete dissolution. Thus, development of unsaturated bile was a major factor associated with gallstone dissolution. The data also indicate that values for percent cholesterol saturation were a better predictor of gallstone dissolution than molar percent chenodiol, although a high percent chenodiol usually was required to obtain unsaturation.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Albers J. J., Grundy S. M., Cleary P. A., Small D. M., Lachin J. M., Schoenfield L. J. National Cooperative Gallstone Study: the effect of chenodeoxycholic acid on lipoproteins and apolipoproteins. Gastroenterology. 1982 Apr;82(4):638–646. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barbara L., Roda E., Roda A., Casanova S., Festi D., Sama C., Mazella G., Aldini R. Il trattamento medico della calcolosi biliare colesterolica nell'uomo con acido chenodesossicolico. Minerva Med. 1977 Oct 17;68(49):3355–3382. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bateson M. C., Ross P. E., Murison J., Bouchier I. A. Comparison of fixed doses of chenodeoxycholic acid for gallstone dissolution. Lancet. 1978 May 27;1(8074):1111–1114. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bell G. D., Whitney B., Dowling R. H. Gallstone dissolution in man using chenodeoxycholic acid. Lancet. 1972 Dec 9;2(7789):1213–1216. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(72)92266-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bennion L. J., Grundy S. M. Effects of obesity and caloric intake on biliary lipid metabolism in man. J Clin Invest. 1975 Oct;56(4):996–1011. doi: 10.1172/JCI108180. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carey M. C. Critical tables for calculating the cholesterol saturation of native bile. J Lipid Res. 1978 Nov;19(8):945–955. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carey M. C., Small D. M. The physical chemistry of cholesterol solubility in bile. Relationship to gallstone formation and dissolution in man. J Clin Invest. 1978 Apr;61(4):998–1026. doi: 10.1172/JCI109025. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Danzinger R. G., Hofmann A. F., Schoenfield L. J., Thistle J. L. Dissolution of cholesterol gallstones by chenodeoxycholic acid. N Engl J Med. 1972 Jan 6;286(1):1–8. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197201062860101. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fisher R. L., Anderson D. W., Boyer J. L., Ishak K., Klatskin G., Lachin J. M., Phillips M. J. A prospective morphologic evaluation of hepatic toxicity of chenodeoxycholic acid in patients with cholelithiasis: the National Cooperative Gallstone Study. Hepatology. 1982 Mar-Apr;2(2):187–201. doi: 10.1002/hep.1840020202. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerolami A., Sarles H., Brette R., Paraf A., Rautureau J., Debray C., Bermann C., Etienne J. P., Chaput J. C., Petite J. P. Controlled trial of chenodeoxycholic therapy for radiolucent gallstones. A multicenter study. Digestion. 1977;16(4):299–307. doi: 10.1159/000198082. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grizzle J. E., Starmer C. F., Koch G. G. Analysis of categorical data by linear models. Biometrics. 1969 Sep;25(3):489–504. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grundy S. M., Metzger A. L., Adler R. D. Mechanisms of lithogenic bile formation in American Indian women with cholesterol gallstones. J Clin Invest. 1972 Dec;51(12):3026–3043. doi: 10.1172/JCI107130. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hegardt F. G., Dam H. The solubility of cholesterol in aqueous solutions of bile salts and lecithin. Z Ernahrungswiss. 1971 Apr;10(3):223–233. doi: 10.1007/BF02020933. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hofmann A. F., Grundy S. M., Lachin J. M., Lan S. P., Baum R. A., Hanson R. F., Hersh T., Hightower N. C., Jr, Marks J. W., Mekhjian H. Pretreatment biliary lipid composition in white patients with radiolucent gallstones in the National Cooperative Gallstone Study. Gastroenterology. 1982 Oct;83(4):738–752. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iser J. H., Maton P. N., Murphy G. M., Dowling R. H. Resistance to chenodeoxycholic acid (CDCA) treatment in obese patients with gall stones. Br Med J. 1978 Jun 10;1(6126):1509–1512. doi: 10.1136/bmj.1.6126.1509. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iser J. H., Murphy G. M., Dowling R. H. Speed of change in biliary lipids and bile acids with chenodeoxycholic acid--is intermittent therapy feasible? Gut. 1977 Jan;18(1):7–15. doi: 10.1136/gut.18.1.7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lachin J. M., Marks J. W., Schoenfield L. J., Tyor M. P., Bennett P. H., Grundy S. M., Hardison W. G., Shaw L. W., Thistle J. L., Vlahcevic Z. R. Design and methodological considerations in the National Cooperative Gallstone Study: a multicenter clinical trial. Control Clin Trials. 1981 Sep;2(3):177–229. doi: 10.1016/0197-2456(81)90012-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mabee T. M., Meyer P., DenBesten L., Mason E. E. The mechanism of increased gallstone formation in obese human subjects. Surgery. 1976 Apr;79(4):460–468. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Makino I., Hashimoto H., Shinozaki K., Yoshino K., Nakagawa S. Sulfated and nonsulfated bile acids in urine, serum, and bile of patients with hepatobiliary diseases. Gastroenterology. 1975 Mar;68(3):545–553. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marks J. W., Sherman J. H., Bonorris G. G., Chung A., Coyne M. J., Schoenfield L. J. Gallstone dissolution by chenodeoxycholic acid and phenobarbital. Am J Gastroenterol. 1978 Feb;69(2):160–165. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marks J. W., Sue S. O., Pearlman B. J., Bonorris G. G., Varady P., Lachin J. M., Schoenfield L. J. Sulfation of lithocholate as a possible modifier of chenodeoxycholic acid-induced elevations of serum transaminase in patients with gallstones. J Clin Invest. 1981 Nov;68(5):1190–1196. doi: 10.1172/JCI110364. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mok H. Y., von Bergmann K., Crouse J. R., Grundy S. M. Bilary lipid metabolism in obesity. Effects of bile acid feeding before and during weight reduction. Gastroenterology. 1979 Mar;76(3):556–567. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Phillips M. J., Fisher R. L., Anderson D. W., Lan S. P., Lachin J. M., Boyer J. L. Ultrastructural evidence of intrahepatic cholestasis before and after chenodeoxycholic acid therapy in patients with cholelithiasis: the national cooperative gallstone study. Hepatology. 1983 Mar-Apr;3(2):209–220. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schoenfield L. J., Lachin J. M. Chenodiol (chenodeoxycholic acid) for dissolution of gallstones: the National Cooperative Gallstone Study. A controlled trial of efficacy and safety. Ann Intern Med. 1981 Sep;95(3):257–282. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-95-3-257. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shaffer E. A., Small D. M. Biliary lipid secretion in cholesterol gallstone disease. The effect of cholecystectomy and obesity. J Clin Invest. 1977 May;59(5):828–840. doi: 10.1172/JCI108705. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thistle J. L., Hofmann A. F. Efficacy and specificity of chenodeoxycholic acid therapy for dissolving gallstones. N Engl J Med. 1973 Sep 27;289(13):655–659. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197309272891303. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thistle J. L., Hofmann A. F., Yu P. Y., Ott B. Effect of varying doses of chenodeoxycholic acid on bile lipid and biliary bile acid composition in gallstone patients: a dose-response study. Am J Dig Dis. 1977 Jan;22(1):1–6. doi: 10.1007/BF01077389. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thistle J. L., Schoenfield L. J. Induced alterations in composition of bile of persons having cholelithiasis. Gastroenterology. 1971 Oct;61(4):488–496. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas P. J., Hofmann A. F. Letter: A simple calculation of the lithogenic index of bile: expressing biliary lipid composition on rectangular coordinates. Gastroenterology. 1973 Oct;65(4):698–700. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Waes L., de Weert M., Schurgers M., Beeckman P., Barbier F., Demeulenaere L. Traitement de la lithiase biliaire par l'acide chénique. Etat actuel d'une étude prospective. Acta Gastroenterol Belg. 1975 Jan-Feb;38(1-2):24–33. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



