Abstract
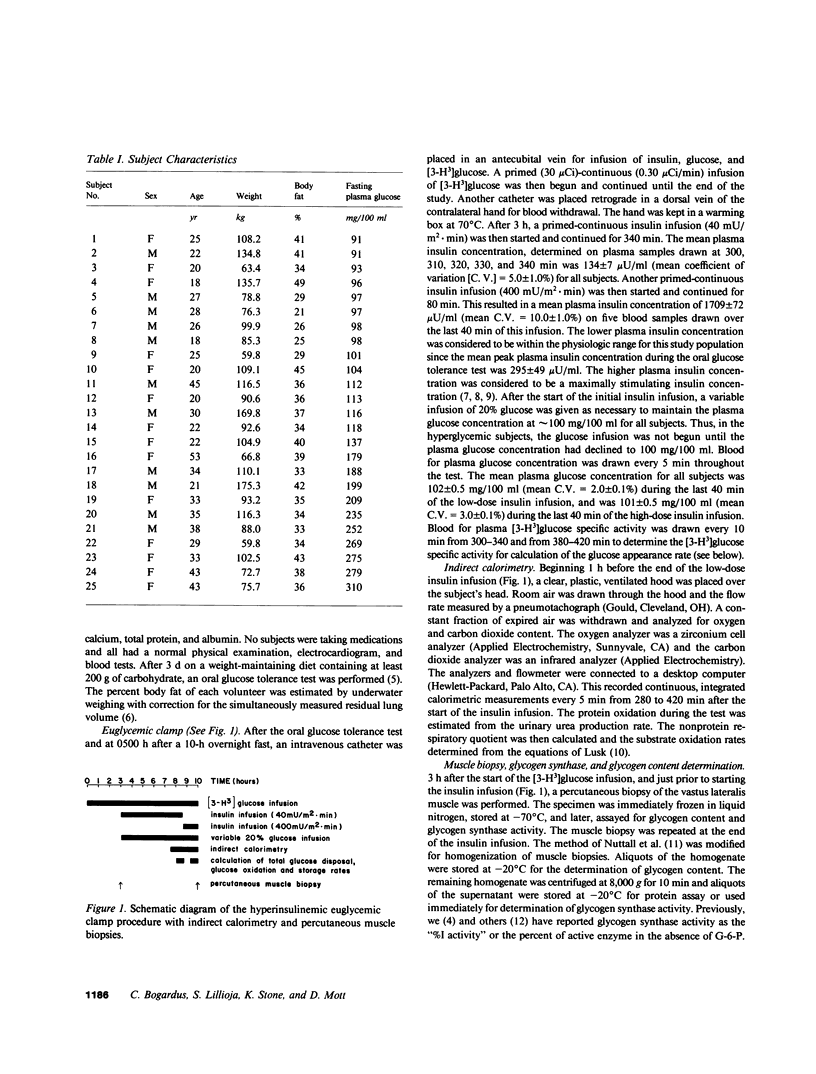
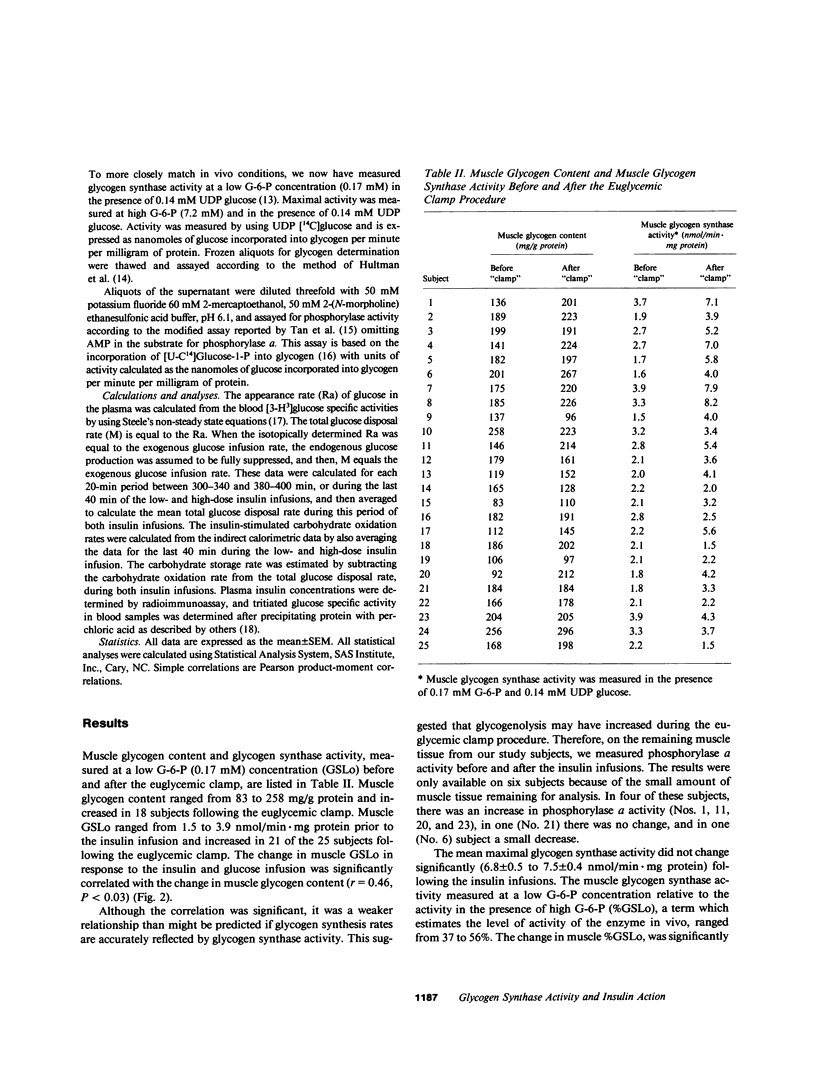
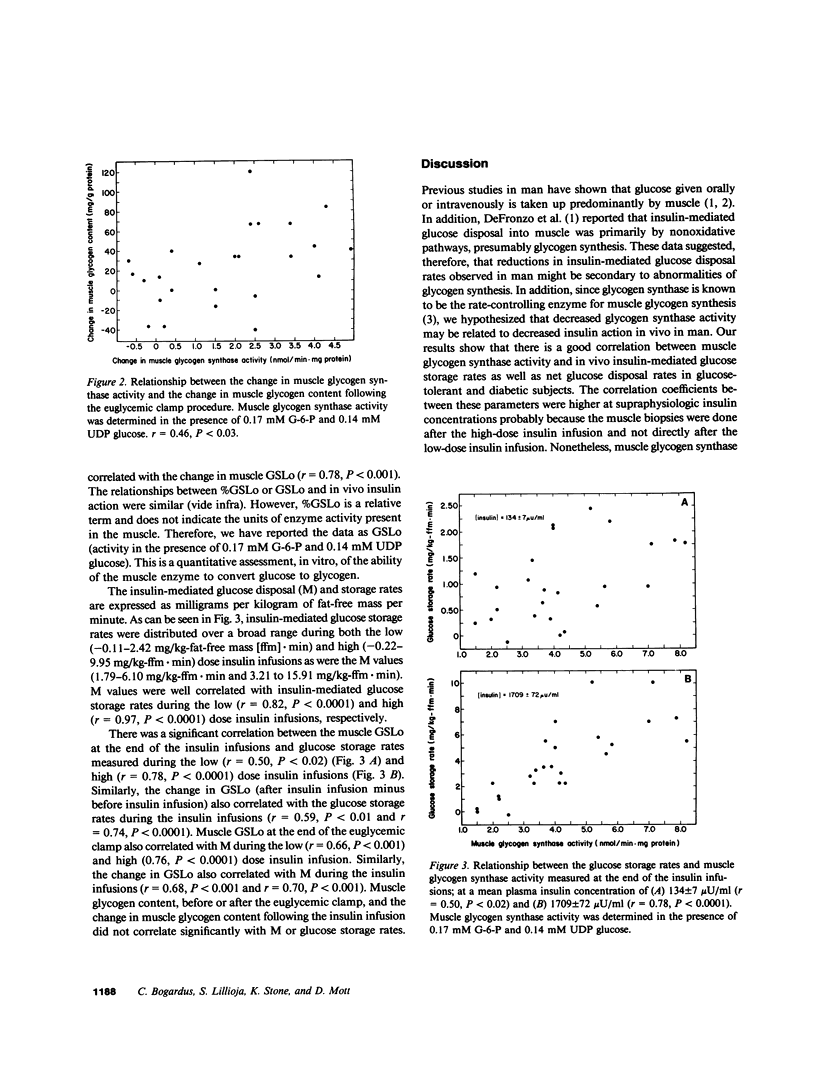
We have studied the relationship between in vivo insulin-mediated glucose disposal rates, muscle glycogen content, and muscle glycogen synthase activity in 25 southwest American Indians with normal glucose tolerance and with varying degrees of glucose intolerance. Insulin-mediated glucose disposal (M) was measured by using the hyperinsulinemic euglycemic clamp technique at plasma insulin concentrations of 134 +/- 7 and 1709 +/- 72 microU/ml, with simultaneous indirect calorimetry to assess glucose oxidation and storage rates. Muscle glycogen content and glycogen synthase activity were measured in percutaneous muscle biopsy samples obtained from the vastus lateralis muscle before and after the euglycemic clamp procedure. The results showed that muscle glycogen synthase activity at the end of the euglycemic clamp was well correlated with insulin-mediated glucose storage rates at both low (r = 0.50, P less than 0.02) and high (r = 0.78, P less than 0.0001) insulin concentrations; and also correlated with M (r = 0.66, P less than 0.001 and r = 0.76, P less than 0.0001). Similar correlations were observed between the change in muscle glycogen synthase activity and glucose storage rates and M. The change in muscle glycogen synthase activity correlated with the change in muscle glycogen content (r = 0.46, P less than 0.03) measured before and after the insulin infusions. The change in muscle glycogen content did not correlate with glucose storage rates or M. The data suggest the possible importance of glycogen synthesis in muscle in determining in vivo insulin-mediated glucose disposal rates in man.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Best J. D., Judzewitsch R. G., Pfeifer M. A., Beard J. C., Halter J. B., Porte D., Jr The effect of chronic sulfonylurea therapy on hepatic glucose production in non-insulin-dependent diabetes. Diabetes. 1982 Apr;31(4 Pt 1):333–338. doi: 10.2337/diab.31.4.333. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bogardus C., Thuillez P., Ravussin E., Vasquez B., Narimiga M., Azhar S. Effect of muscle glycogen depletion on in vivo insulin action in man. J Clin Invest. 1983 Nov;72(5):1605–1610. doi: 10.1172/JCI111119. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeFronzo R. A. Insulin secretion, insulin resistance, and obesity. Int J Obes. 1982;6 (Suppl 1):73–82. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeFronzo R. A., Jacot E., Jequier E., Maeder E., Wahren J., Felber J. P. The effect of insulin on the disposal of intravenous glucose. Results from indirect calorimetry and hepatic and femoral venous catheterization. Diabetes. 1981 Dec;30(12):1000–1007. doi: 10.2337/diab.30.12.1000. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilboe D. P., Larson K. L., Nuttall F. Q. Radioactive method for the assay of glycogen phosphorylases. Anal Biochem. 1972 May;47(1):20–27. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(72)90274-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldstein D. E., Curnow R. T. Impaired glycogen synthase activating system in human diabetic polymorphonuclear leukocytes. Diabetes. 1980 Mar;29(3):217–220. doi: 10.2337/diab.29.3.217. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guinovart J. J., Salavert A., Massagué J., Ciudad C. J., Salsas E., Itarte E. Glycogen synthase: a new activity ratio assay expressing a high sensitivity to the phosphorylation state. FEBS Lett. 1979 Oct 15;106(2):284–288. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(79)80515-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katz L. D., Glickman M. G., Rapoport S., Ferrannini E., DeFronzo R. A. Splanchnic and peripheral disposal of oral glucose in man. Diabetes. 1983 Jul;32(7):675–679. doi: 10.2337/diab.32.7.675. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kolterman O. G., Insel J., Saekow M., Olefsky J. M. Mechanisms of insulin resistance in human obesity: evidence for receptor and postreceptor defects. J Clin Invest. 1980 Jun;65(6):1272–1284. doi: 10.1172/JCI109790. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kroll J. Lysis of 131-I-labelled plasma clots in human subcutaneous tissue in vivo. Scand J Clin Lab Invest. 1967;19(1):1–3. doi: 10.3109/00365516709093475. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LELOIR L. F., OLAVARRIA J. M., GOLDEMBERG S. H., CARMINATTI H. Biosynthesis of glycogen from uridine diphosphate glucose. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1959 Apr;81(2):508–520. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(59)90232-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nuttall F. Q., Barbosa J., Gannon M. C. The glycogen synthase system in skeletal muscle of normal humans and patients with myotonic dystrophy: effect of glucose and insulin administration. Metabolism. 1974 Jun;23(6):561–568. doi: 10.1016/0026-0495(74)90084-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nuttall F. Q., Gannon M. C., Larner J. Oral glucose effect on glycogen synthetase and phosphorylase in heart. Muscle and liver. Physiol Chem Phys. 1972;4(6):497–415. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rizza R. A., Mandarino L. J., Gerich J. E. Dose-response characteristics for effects of insulin on production and utilization of glucose in man. Am J Physiol. 1981 Jun;240(6):E630–E639. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.1981.240.6.E630. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- STEELE R. Influences of glucose loading and of injected insulin on hepatic glucose output. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1959 Sep 25;82:420–430. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1959.tb44923.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tan A. W., Nuttall F. Q. Characteristics of the dephosphorylated form of phosphorylase purified from rat liver and measurement of its activity in crude liver preparations. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1975 Nov 20;410(1):45–60. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(75)90206-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



