Abstract
Leukemia inhibitory factor (LIF) has recently been associated with septic shock in humans. In this study we sought to determine, in mice, the role of LIF in septic shock. During sublethal endotoxemia, serum LIF levels, as determined by radio-receptor competition assay, peaked at 2 h and were low (3 ng/ml), whereas in lethal Escherichia coli septic shock serum LIF levels rose progressively (> 30 ng/ml) in the premorbid phase coincident with the development of tissue injury. Single i.v. injections of high doses (up to 50 micrograms per mouse) of recombinant murine LIF had no obvious acute detrimental effects, whereas continued i.p. administration (30 micrograms per mouse per day) for 3-4 days induced a fatal catabolic state without evidence of preceding hemodynamic collapse or shock. Simultaneous or subsequent administration of high doses of LIF had no effect on mortality from sublethal and lethal E. coli septic shock, whereas prior administration conferred significant protection against lethality (P << 0.001 by log-rank test), an effect that was dose and interval dependent. This protective effect resembled endotoxin tolerance and was characterized by suppression of E. coli-induced serum tumor necrosis factor concentration (P < 0.05), reduction in the number of viable bacteria (P < 0.05), and prevention of sepsis-induced tissue injury. These observations suggest that systemic LIF production is part of the host response to both endotoxin and sepsis-induced tissue injury.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aggarwal B. B., Kohr W. J., Hass P. E., Moffat B., Spencer S. A., Henzel W. J., Bringman T. S., Nedwin G. E., Goeddel D. V., Harkins R. N. Human tumor necrosis factor. Production, purification, and characterization. J Biol Chem. 1985 Feb 25;260(4):2345–2354. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alexander H. R., Doherty G. M., Fraker D. L., Block M. I., Swedenborg J. E., Norton J. A. Human recombinant interleukin-1 alpha protection against the lethality of endotoxin and experimental sepsis in mice. J Surg Res. 1991 May;50(5):421–424. doi: 10.1016/0022-4804(91)90018-h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alexander H. R., Sheppard B. C., Jensen J. C., Langstein H. N., Buresh C. M., Venzon D., Walker E. C., Fraker D. L., Stovroff M. C., Norton J. A. Treatment with recombinant human tumor necrosis factor-alpha protects rats against the lethality, hypotension, and hypothermia of gram-negative sepsis. J Clin Invest. 1991 Jul;88(1):34–39. doi: 10.1172/JCI115298. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alexander H. R., Wong G. G., Doherty G. M., Venzon D. J., Fraker D. L., Norton J. A. Differentiation factor/leukemia inhibitory factor protection against lethal endotoxemia in mice: synergistic effect with interleukin 1 and tumor necrosis factor. J Exp Med. 1992 Apr 1;175(4):1139–1142. doi: 10.1084/jem.175.4.1139. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beutler B., Krochin N., Milsark I. W., Luedke C., Cerami A. Control of cachectin (tumor necrosis factor) synthesis: mechanisms of endotoxin resistance. Science. 1986 May 23;232(4753):977–980. doi: 10.1126/science.3754653. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Block M. I., Berg M., McNamara M. J., Norton J. A., Fraker D. L., Alexander H. R. Passive immunization of mice against D factor blocks lethality and cytokine release during endotoxemia. J Exp Med. 1993 Sep 1;178(3):1085–1090. doi: 10.1084/jem.178.3.1085. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
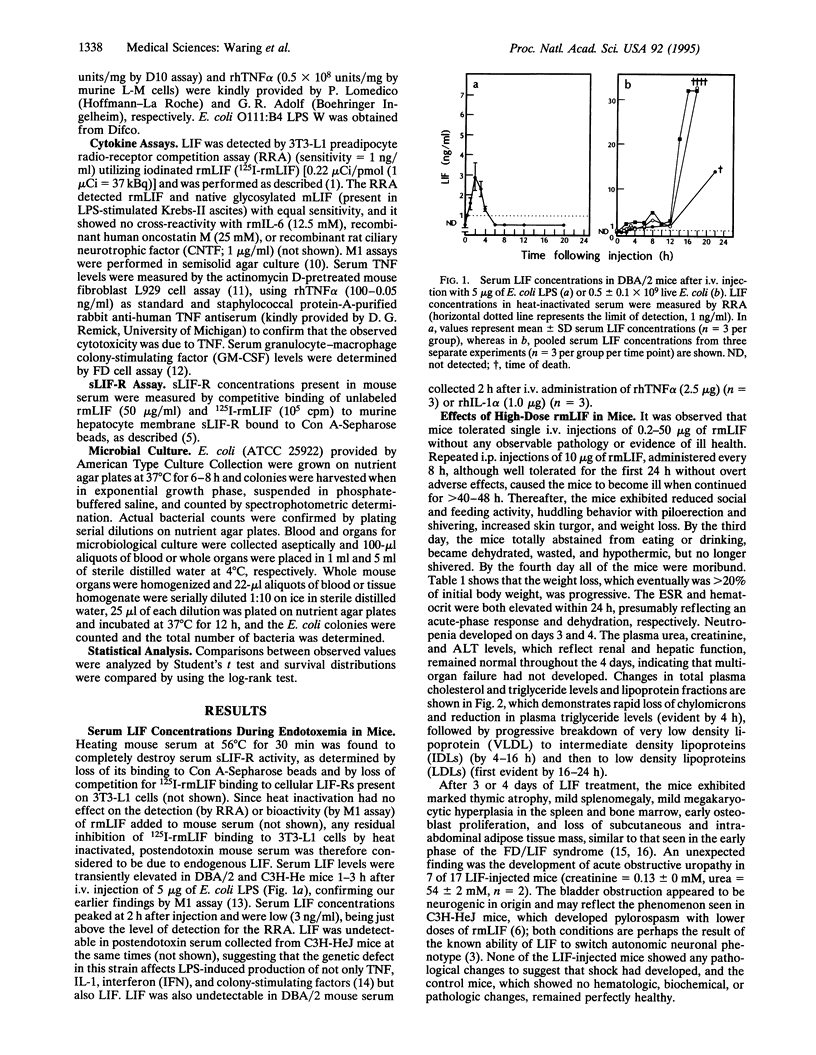
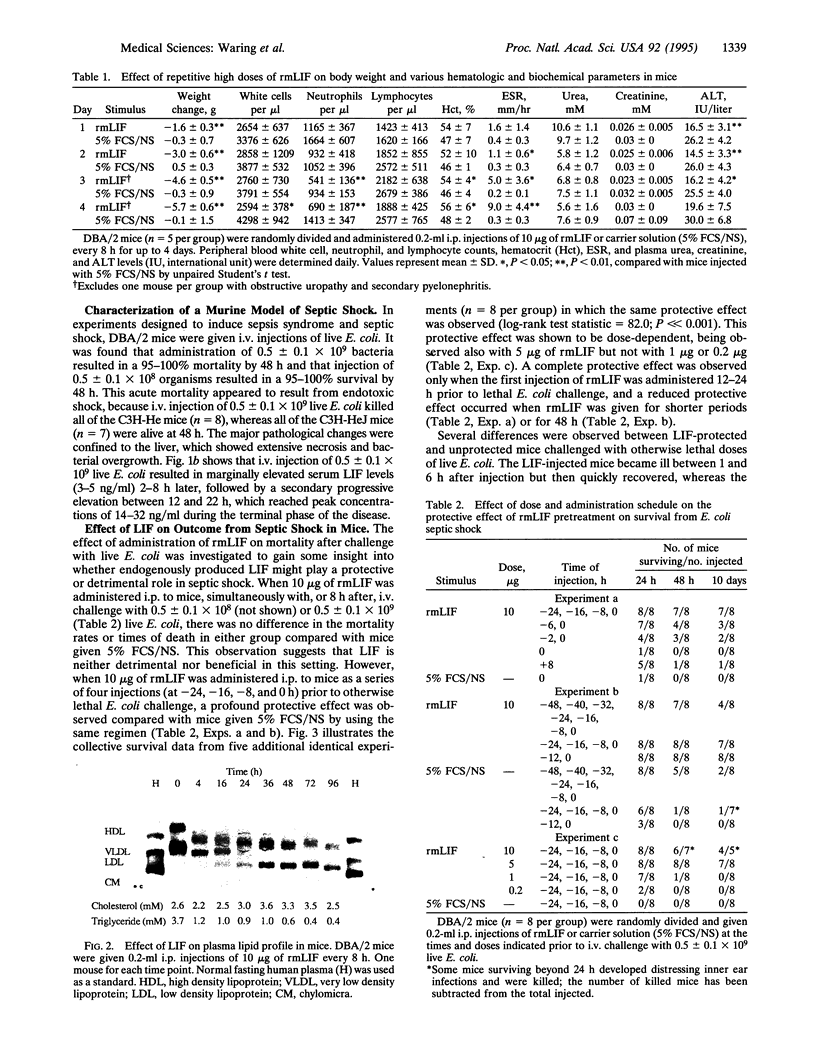
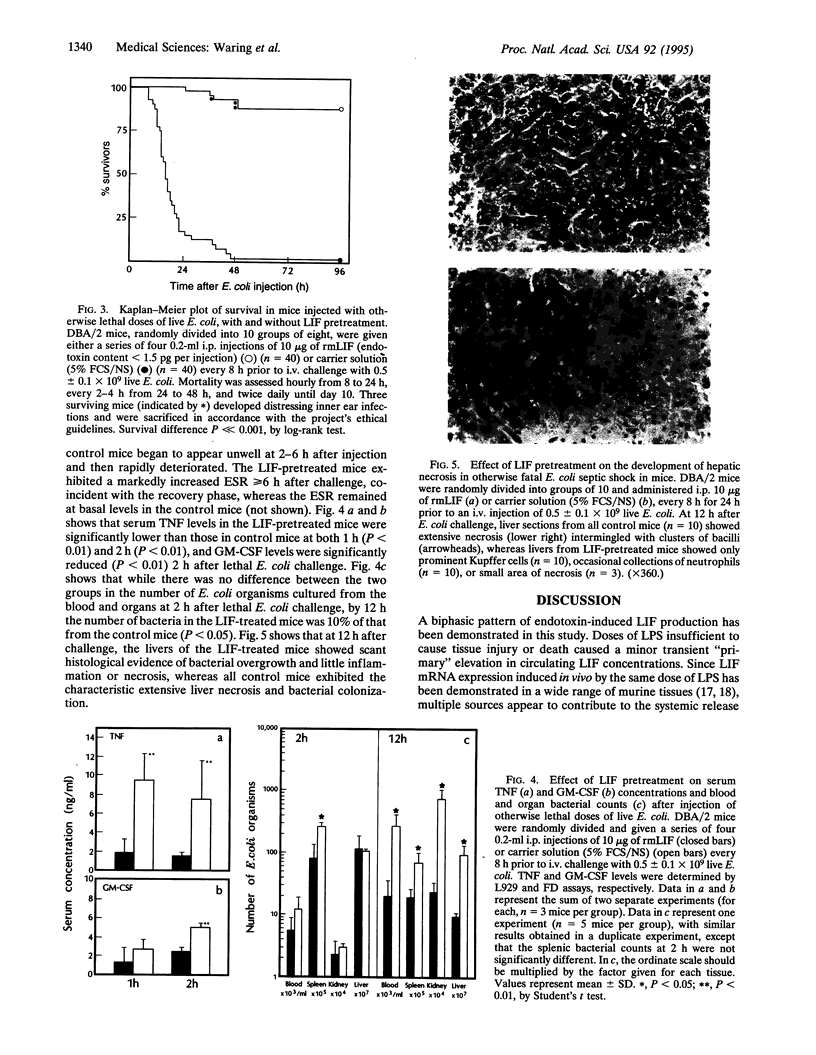
- Bone R. C. The pathogenesis of sepsis. Ann Intern Med. 1991 Sep 15;115(6):457–469. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-115-6-457. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown M. A., Metcalf D., Gough N. M. Leukaemia inhibitory factor and interleukin 6 are expressed at very low levels in the normal adult mouse and are induced by inflammation. Cytokine. 1994 May;6(3):300–309. doi: 10.1016/1043-4666(94)90027-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bucolo G., David H. Quantitative determination of serum triglycerides by the use of enzymes. Clin Chem. 1973 May;19(5):476–482. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greisman S. E., Young E. J., Carozza F. A., Jr Mechanisms of endotoxin tolerance. V. Specificity of the early and late phases of pyrogenic tolerance. J Immunol. 1969 Dec;103(6):1223–1236. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gérard C., Bruyns C., Marchant A., Abramowicz D., Vandenabeele P., Delvaux A., Fiers W., Goldman M., Velu T. Interleukin 10 reduces the release of tumor necrosis factor and prevents lethality in experimental endotoxemia. J Exp Med. 1993 Feb 1;177(2):547–550. doi: 10.1084/jem.177.2.547. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Görgen I., Hartung T., Leist M., Niehörster M., Tiegs G., Uhlig S., Weitzel F., Wendel A. Granulocyte colony-stimulating factor treatment protects rodents against lipopolysaccharide-induced toxicity via suppression of systemic tumor necrosis factor-alpha. J Immunol. 1992 Aug 1;149(3):918–924. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Layton M. J., Cross B. A., Metcalf D., Ward L. D., Simpson R. J., Nicola N. A. A major binding protein for leukemia inhibitory factor in normal mouse serum: identification as a soluble form of the cellular receptor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Sep 15;89(18):8616–8620. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.18.8616. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Metcalf D., Begley C. G., Williamson D. J., Nice E. C., De Lamarter J., Mermod J. J., Thatcher D., Schmidt A. Hemopoietic responses in mice injected with purified recombinant murine GM-CSF. Exp Hematol. 1987 Jan;15(1):1–9. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Metcalf D., Gearing D. P. A myelosclerotic syndrome in mice engrafted with cells producing high levels of leukemia inhibitory factor (LIF). Leukemia. 1989 Dec;3(12):847–852. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Metcalf D., Gearing D. P. Fatal syndrome in mice engrafted with cells producing high levels of the leukemia inhibitory factor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Aug;86(15):5948–5952. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.15.5948. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Metcalf D., Hilton D. J., Nicola N. A. Clonal analysis of the actions of the murine leukemia inhibitory factor on leukemic and normal murine hemopoietic cells. Leukemia. 1988 Apr;2(4):216–221. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Metcalf D., Nicola N. A., Gearing D. P. Effects of injected leukemia inhibitory factor on hematopoietic and other tissues in mice. Blood. 1990 Jul 1;76(1):50–56. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Noble R. P. Electrophoretic separation of plasma lipoproteins in agarose gel. J Lipid Res. 1968 Nov;9(6):693–700. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roeschlau P., Bernt E., Gruber W. Enzymatic determination of total cholesterol in serum. Z Klin Chem Klin Biochem. 1974 May;12(5):226–226. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tzung S. P., Mahl T. C., Lance P., Andersen V., Cohen S. A. Interferon-alpha prevents endotoxin-induced mortality in mice. Eur J Immunol. 1992 Dec;22(12):3097–3101. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830221211. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wallach D., Holtmann H., Engelmann H., Nophar Y. Sensitization and desensitization to lethal effects of tumor necrosis factor and IL-1. J Immunol. 1988 May 1;140(9):2994–2999. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waring P. M., Waring L. J., Metcalf D. Circulating leukemia inhibitory factor levels correlate with disease severity in meningococcemia. J Infect Dis. 1994 Nov;170(5):1224–1228. doi: 10.1093/infdis/170.5.1224. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waring P., Wycherley K., Cary D., Nicola N., Metcalf D. Leukemia inhibitory factor levels are elevated in septic shock and various inflammatory body fluids. J Clin Invest. 1992 Nov;90(5):2031–2037. doi: 10.1172/JCI116083. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ziegler-Heitbrock H. W., Blumenstein M., Käfferlein E., Kieper D., Petersmann I., Endres S., Flegel W. A., Northoff H., Riethmüller G., Haas J. G. In vitro desensitization to lipopolysaccharide suppresses tumour necrosis factor, interleukin-1 and interleukin-6 gene expression in a similar fashion. Immunology. 1992 Feb;75(2):264–268. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]