Abstract
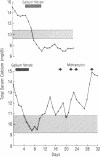
Approximately two-thirds of patients who receive the anticancer drug gallium nitrate develop mild hypocalcemia. To evaluate the mechanism of drug-induced hypocalcemia, we tested the effects of gallium nitrate upon in vitro release of 45Ca++ from explanted fetal rat bones. The drug significantly inhibited 45Ca++ release in response to stimulation with both parathyroid hormone and a lymphokine preparation with osteoclast activating factor activity. The inhibitory effects on bone resorption were both time- and dose-dependent. Later, in a pilot study, we treated 10 patients who had cancer-related hypercalcemia with gallium nitrate administered by continuous infusion. All patients responded by a reduction of total serum calcium to normal or subnormal concentrations (13.8 +/- 1.05 mg/dl, mean +/- SD pretreatment, to 8.03 +/- 1.03 mg/dl, mean posttreatment nadir). Our results indicate that gallium nitrate effectively treats cancer-related hypercalcemia and that it probably acts by inhibiting calcium release from bone.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anghileri L. J. Studies on the accumulation mechanisms of radioisotopes used in tumor diagnostic. Strahlentherapie. 1971 Oct;142(4):456–462. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bockman R. S., Repo M. A. Lymphokine-mediated bone resorption requires endogenous prostaglandin synthesis. J Exp Med. 1981 Aug 1;154(2):529–534. doi: 10.1084/jem.154.2.529. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krakoff I. H., Newman R. A., Goldberg R. S. Clinical toxicologic and pharmacologic studies of gallium nitrate. Cancer. 1979 Nov;44(5):1722–1727. doi: 10.1002/1097-0142(197911)44:5<1722::aid-cncr2820440528>3.0.co;2-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leyland-Jones B., Bhalla R. B., Farag F., Williams L., Coonley C. J., Warrell R. P., Jr Administration of gallium nitrate by continuous infusion: lack of chronic nephrotoxicity confirmed by studies of enzymuria and beta 2-microglobulinuria. Cancer Treat Rep. 1983 Oct;67(10):941–942. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Minkin C. Inhibition of parathyroid hormone stimulated bone resorption in vitro by the antibiotic mithramycin. Calcif Tissue Res. 1973 Dec 31;13(4):249–257. doi: 10.1007/BF02015415. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- OWEN J. A., IGGO B., SCANDRETT F. J., STEWART C. P. The determination of creatinine in plasma or serum, and in urine; a critical examination. Biochem J. 1954 Nov;58(3):426–437. doi: 10.1042/bj0580426. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Payne R. B., Carver M. E., Morgan D. B. Interpretation of serum total calcium: effects of adjustment for albumin concentration on frequency of abnormal values and on detection of change in the individual. J Clin Pathol. 1979 Jan;32(1):56–60. doi: 10.1136/jcp.32.1.56. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stewart A. F., Horst R., Deftos L. J., Cadman E. C., Lang R., Broadus A. E. Biochemical evaluation of patients with cancer-associated hypercalcemia: evidence for humoral and nonhumoral groups. N Engl J Med. 1980 Dec 11;303(24):1377–1383. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198012113032401. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Warrell R. P., Jr, Coonley C. J., Straus D. J., Young C. W. Treatment of patients with advanced malignant lymphoma using gallium nitrate administered as a seven-day continuous infusion. Cancer. 1983 Jun 1;51(11):1982–1987. doi: 10.1002/1097-0142(19830601)51:11<1982::aid-cncr2820511104>3.0.co;2-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]