Abstract
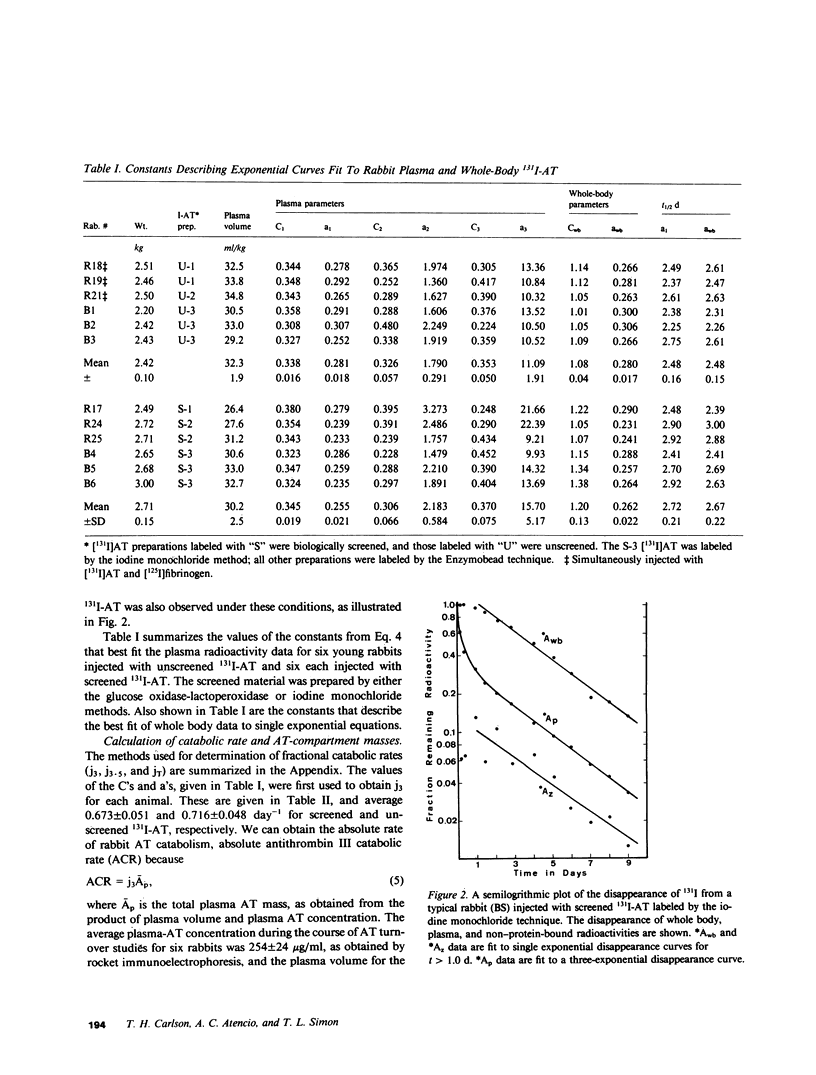
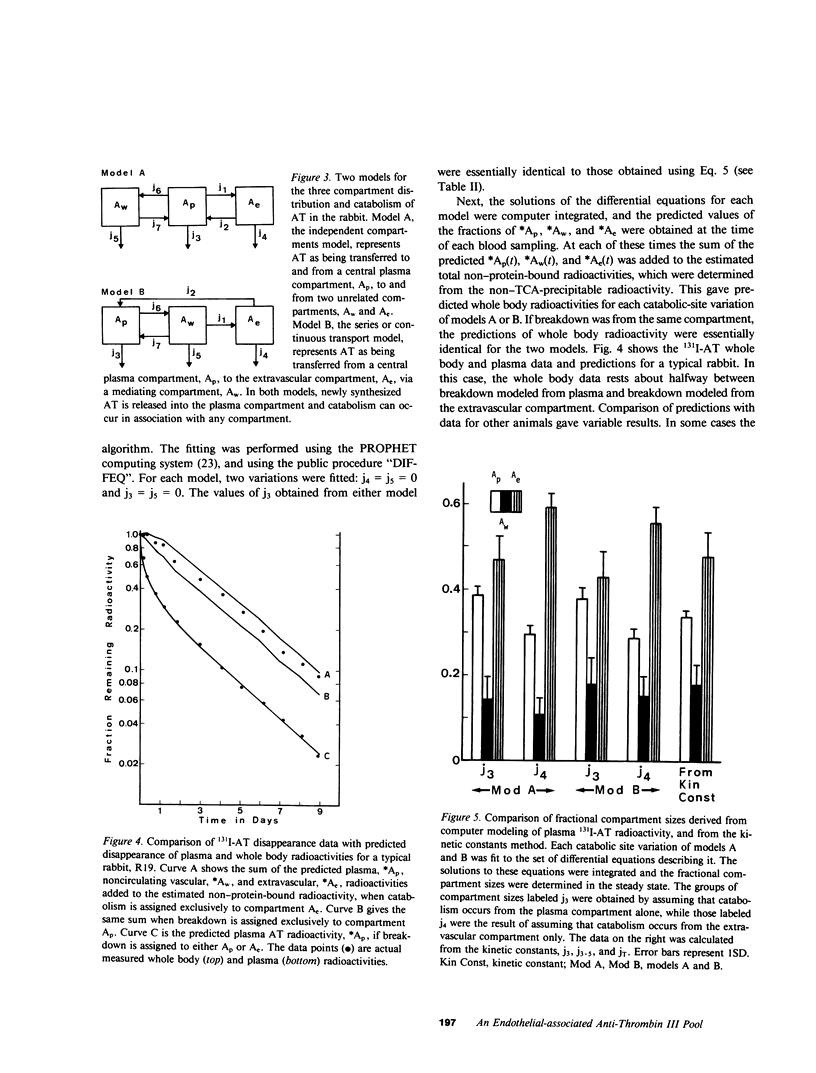
Rabbit antithrombin III (AT), purified by heparin-agarose, was labeled with iodine-131 by either the glucose oxidase-lactoperoxidase or iodine monochloride techniques. When intravenously injected, the disappearance of the 131I-AT from plasma was characterized by rapid initial decreases, and three-exponential equations were required for best fit of the plasma disappearance curves. This rapid 131I-AT removal was not caused by denaturation, as shown by comparison with results obtained when 131I-AT was biologically screened (injected into a first rabbit, and then transferred 16 h later in whole plasma to a second for kinetic evaluation) before injection. Thus, the same rapid initial loss of plasma 131I-AT was observed with screened preparations, and the plasma fractional catabolic rates of 0.716 +/- 0.048 and 0.673 +/- 0.051 day-1 for unscreened and screened 131I-AT were not significantly different. These results support the hypothesis that a vascular-endothelial AT compartment is present in rabbit. The fractions of the total-body AT in the plasma, the vascular-endothelial and the extravascular compartments were 0.337 +/- 0.031, 0.178 +/- 0.056, and 0.485 +/- 0.069, respectively. Two three-compartment kinetic models are discussed. The first pictures AT as distributing independently between plasma and two other compartments, and the second sees AT as first passing to the vascular-endothelial compartment, and then directly into the extravascular compartment. The plasma 131I-AT kinetic data was consistent with both models, but the sizes of the vascular-endothelial compartments were best predicted by the second. If AT catabolism was assigned to the plasma, both models generally underpredicted the whole-body radioactivities, while assignment of breakdown to the extravascular compartment generally resulted in overpredictions. This suggests that AT catabolism occurs from both plasma and extravascular compartments.
Full text
PDF






Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abildgaard U. Binding of thrombin to antithrombin III. Scand J Clin Lab Invest. 1969 Aug;24(1):23–27. doi: 10.3109/00365516909080127. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Abildgaard U., Lie M., Odegård O. R. Antithrombin (heparin cofactor) assay with "new" chromogenic substrates (S-2238 and Chromozym TH). Thromb Res. 1977 Oct;11(4):549–553. doi: 10.1016/0049-3848(77)90208-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ambruso D. R., Leonard B. D., Bies R. D., Jacobson L., Hathaway W. E., Reeve E. B. Antithrombin III deficiency: decreased synthesis of a biochemically normal molecule. Blood. 1982 Jul;60(1):78–83. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Atencio A. C., Joiner K., Reeve E. B. Experimental and control systems studies of plasma fibrinogen regulation in rabbits. Am J Physiol. 1969 Apr;216(4):764–772. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1969.216.4.764. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Busch C., Owen W. G. Identification in vitro of an endothelial cell surface cofactor for antithrombin III. Parallel studies with isolated perfused rat hearts and microcarrier cultures of bovine endothelium. J Clin Invest. 1982 Mar;69(3):726–729. doi: 10.1172/JCI110502. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carlson T. H., Atencio A. C. Isolation and partial characterization of two distinct types of antithrombin III from rabbit. Thromb Res. 1982 Jul 1;27(1):23–34. doi: 10.1016/0049-3848(82)90274-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chan V., Lai C. L., Chan T. K. Metabolism of antithrombin III in cirrhosis and carcinoma of the liver. Clin Sci (Lond) 1981 Jun;60(6):681–688. doi: 10.1042/cs0600681. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collen D., Schetz J., de Cock F., Holmer E., Verstraete M. Metabolism of antithrombin III (heparin cofactor) in man: effects of venous thrombosis and of heparin administration. Eur J Clin Invest. 1977 Feb;7(1):27–35. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2362.1977.tb01566.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collen D., Tytgat G., Claeys H., Verstraete M., Wallén P. Metabolism of plasminogen in healthy subjects: effect of tranexamic acid. J Clin Invest. 1972 Jun;51(6):1310–1318. doi: 10.1172/JCI106927. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collen D., de Cock F., Verstraete M. Quantitation of thrombin-antithrombin III complexes in human blood. Eur J Clin Invest. 1977 Oct;7(5):407–411. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2362.1977.tb01627.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- EGEBERG O. INHERITED ANTITHROMBIN DEFICIENCY CAUSING THROMBOPHILIA. Thromb Diath Haemorrh. 1965 Jun 15;13:516–530. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FRANKS J. J., REEVE E. B. Errors in volume measurement from absorption losses of albumin-I131. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1956 Nov;93(2):299–302. doi: 10.3181/00379727-93-22737. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldstein J. L., Anderson R. G., Brown M. S. Coated pits, coated vesicles, and receptor-mediated endocytosis. Nature. 1979 Jun 21;279(5715):679–685. doi: 10.1038/279679a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kobayashi N., Takeda Y. Effects of a large dose of oestradiol on antithrombin III metabolism in male and female dogs. Eur J Clin Invest. 1977 Oct;7(5):373–381. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2362.1977.tb01622.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koj A., Regoeczi E. Effect of experimental inflammation on the synthesis and distribution of antithrombin III and alpha1-antitrypsin in rabbits. Br J Exp Pathol. 1978 Oct;59(5):473–481. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lollar P., Owen W. G. Clearance of thrombin from circulation in rabbits by high-affinity binding sites on endothelium. Possible role in the inactivation of thrombin by antithrombin III. J Clin Invest. 1980 Dec;66(6):1222–1230. doi: 10.1172/JCI109973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MATTHEWS C. M. The theory of tracer experiments with 131I-labelled plasma proteins. Phys Med Biol. 1957 Jul;2(1):36–53. doi: 10.1088/0031-9155/2/1/305. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- REEVE E. B., BAILEY H. R. Mathematical models describing the distribution of I-131-albumin in man. J Lab Clin Med. 1962 Dec;60:923–943. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- REEVE E. B., ROBERTS J. E. The kinetics of the distribution and breakdown of 1131-albumin in the rabbit. Observations on several mathematical descriptions. J Gen Physiol. 1959 Nov;43:415–444. doi: 10.1085/jgp.43.2.415. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raub W. F. The PROPHET system and resource sharing. Fed Proc. 1974 Dec;33(12):2390–2392. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reeve E. B., Leonard B., Carlson T. Kinetic studies in vivo of antithrombin III. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1981;370:680–694. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1981.tb29775.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reeve E. B., Leonard B., Wentland S. H., Damus P. Studies with 131I-labelled antithrombin III in dogs. Thromb Res. 1980 Nov 15;20(4):375–389. doi: 10.1016/0049-3848(80)90277-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Renkin E. M. Transport of proteins by diffusion, bulk flow and vesicular mechanisms. Physiologist. 1980 Feb;23(1):57–61. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenberg J. S., McKenna P. W., Rosenberg R. D. Inhibition of human factor IXa by human antithrombin. J Biol Chem. 1975 Dec 10;250(23):8883–8888. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenberg R. D. Chemistry of the hemostatic mechanism and its relationship to the action of heparin. Fed Proc. 1977 Jan;36(1):10–18. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- STERLING K. The turnover rate of serum albumin in man as measured by I131-tagged albumin. J Clin Invest. 1951 Nov;30(11):1228–1237. doi: 10.1172/JCI102542. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takeda Y. Studies of the effects of heparin, Coumadin, and vitamin K on prothrombin metabolism and distribution in calves with the use of iodine-125-prothrombin. Characterization of the prothrombin system. J Lab Clin Med. 1970 Mar;75(3):355–381. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yin E. T., Wessler S., Stoll P. J. Biological properties of the naturally occurring plasma inhibitor to activated factor X. J Biol Chem. 1971 Jun 10;246(11):3703–3711. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ZIZZA F., CAMPBELL T. J., REEVE E. B. The nature and rates of excretion of radioactive breakdown products of I131-albumin in the rabbit. J Gen Physiol. 1959 Nov;43:397–413. doi: 10.1085/jgp.43.2.397. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



