Abstract
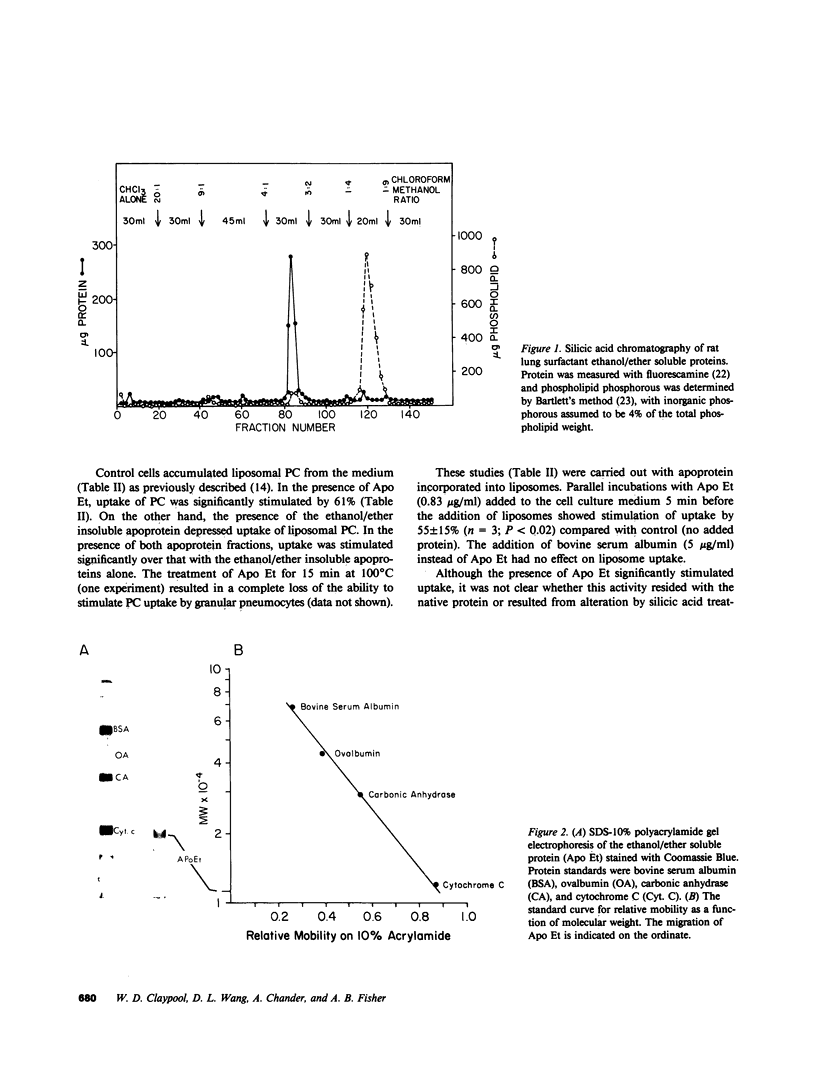
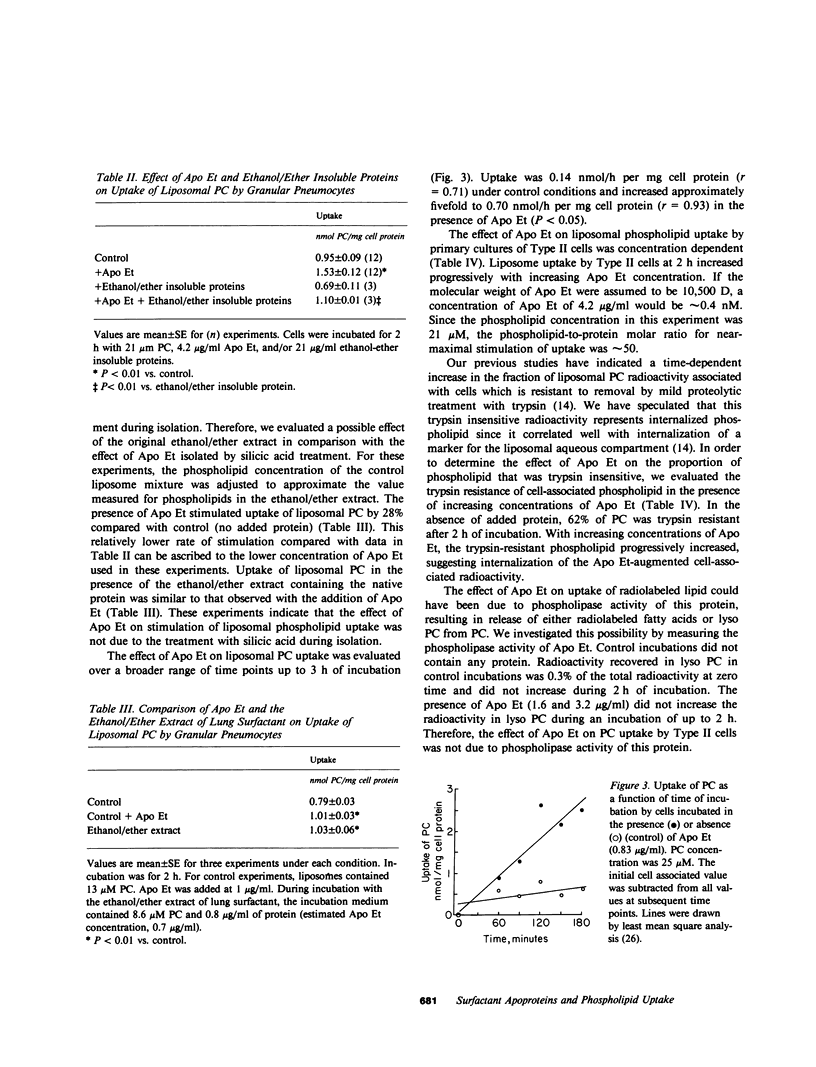
Ethanol/ether soluble apoproteins, comprising 17% of the total recovered surfactant-associated proteins, were isolated from rat lung surfactant and purified by silicic acid chromatography. The protein that eluted in 4:1 chloroform/methanol accounted for greater than 85% of protein in the ethanol/ether soluble fraction and was termed surfactant apoprotein Et (Apo Et). By sodium dodecyl sulfate polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis, this protein had an apparent molecular weight of approximately 10,500. Apo Et was evaluated for its effect on uptake of synthetic phospholipids in liposomal form by isolated granular pneumocytes (Type II alveolar epithelial cells) in primary culture. Liposomes were prepared to approximate the phospholipid composition of the alveolar surfactant, and uptake was measured by the accumulation of the radioactively labeled dipalmitoyl phosphatidyl choline fraction. The uptake of liposomal phosphatidylcholine by cells incubated for 2 h with Apo Et was increased by 61% over control. Most of the cell-associated phospholipid uptake was resistant to treatment with trypsin, suggesting an increased internalization of liposomal material in the presence of Apo Et. The effect of Apo Et on uptake was concentration and time dependent and was not associated with cell damage, phospholipase activity, or detergent properties of the protein. Apo Et had no significant effect on phosphatidylcholine uptake by granular pneumocytes maintained for 7 d in primary culture. Apo Et augmented the uptake of phospholipids by alveolar macrophages although total uptake by these cells was less than that observed with granular pneumocytes. Because Apo Et increases the rate of uptake of surfactant phospholipids by alveolar cells (granular pneumocytes and alveolar macrophages), this protein may represent a physiologically important regulator for clearance of lung surfactant phospholipids.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BARTLETT G. R. Phosphorus assay in column chromatography. J Biol Chem. 1959 Mar;234(3):466–468. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baritussio A. G., Magoon M. W., Goerke J., Clements J. A. Precursor-product relationship between rabbit type II cell lamellar bodies and alveolar surface-active material. Surfactant turnover time. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1981 Dec 23;666(3):382–393. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(81)90297-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(76)90527-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Böhlen P., Stein S., Dairman W., Udenfriend S. Fluorometric assay of proteins in the nanogram range. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1973 Mar;155(1):213–220. doi: 10.1016/s0003-9861(73)80023-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chander A., Claypool W. D., Jr, Strauss J. F., 3rd, Fisher A. B. Uptake of liposomal phosphatidylcholine by granular pneumocytes in primary culture. Am J Physiol. 1983 Nov;245(5 Pt 1):C397–C404. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1983.245.5.C397. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Comroe J. H., Jr Premature science and immature lungs. Part III. The attack on immature lungs. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1977 Sep;116(3):497–518. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1977.116.3.497. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diglio C. A., Kikkawa Y. The type II epithelial cells of the lung. IV. Adaption and behavior of isolated type II cells in culture. Lab Invest. 1977 Dec;37(6):622–631. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farrell P. M., Avery M. E. Hyaline membrane disease. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1975 May;111(5):657–688. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1975.111.5.657. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fisher A. B., Furia L., Berman H. Metabolism of rat granular pneumocytes isolated in primary culture. J Appl Physiol Respir Environ Exerc Physiol. 1980 Oct;49(4):743–750. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1980.49.4.743. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geiger K., Gallagher M. L., Hedley-Whyte J. Cellular distribution and clearance of aerosolized dipalmitoyl lecithin. J Appl Physiol. 1975 Nov;39(5):759–766. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1975.39.5.759. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gluck L. Biochemical development of the lung: clinical aspects of surfactant development, RDS and the intrauterine assessment of lung maturity. Clin Obstet Gynecol. 1971 Sep;14(3):710–721. doi: 10.1097/00003081-197109000-00005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goerke J. Lung surfactant. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1974 Dec 16;344(3-4):241–261. doi: 10.1016/0304-4157(74)90009-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guo L. S., Hamilton R. L., Goerke J., Weinstein J. N., Havel R. J. Interaction of unilamellar liposomes with serum lipoproteins and apolipoproteins. J Lipid Res. 1980 Nov;21(8):993–1003. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HANKS J. H., WALLACE J. H. Determination of cell viability. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1958 May;98(1):188–192. doi: 10.3181/00379727-98-23985. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hallman M., Epstein B. L., Gluck L. Analysis of labeling and clearance of lung surfactant phospholipids in rabbit. Evidence of bidirectional surfactant flux between lamellar bodies and alveolar lavage. J Clin Invest. 1981 Sep;68(3):742–751. doi: 10.1172/JCI110310. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamilton R. L., Jr, Goerke J., Guo L. S., Williams M. C., Havel R. J. Unilamellar liposomes made with the French pressure cell: a simple preparative and semiquantitative technique. J Lipid Res. 1980 Nov;21(8):981–992. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacobs H., Jobe A., Ikegami M., Conaway D. The significance of reutilization of surfactant phosphatidylcholine. J Biol Chem. 1983 Apr 10;258(7):4159–4165. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katyal S. L., Estes L. W., Lombardi B. Method for the isolation of surfactant from homogenates and lavages of lung of adult, newborn, and fetal rats. Lab Invest. 1977 Jun;36(6):585–592. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- King R. J., Gikas E. G., Ruch J., Clements J. A. The radioimmunoassay of pulmonary surface active material in sheep lung. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1974 Sep;110(3):273–281. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1974.110.3.273. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- King R. J., Klass D. J., Gikas E. G., Clements J. A. Isolation of apoproteins from canine surface active material. Am J Physiol. 1973 Apr;224(4):788–795. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1973.224.4.788. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- King R. J., Martin H. Intracellular metabolism of the apoproteins of pulmonary surfactant in rat lung. J Appl Physiol Respir Environ Exerc Physiol. 1980 May;48(5):812–820. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1980.48.5.812. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- King R. J., Martin H., Mitts D., Holmstrom F. M. Metabolism of the apoproteins in pulmonary surfactant. J Appl Physiol Respir Environ Exerc Physiol. 1977 Apr;42(4):483–491. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1977.42.4.483. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- King R. J. The surfactant system of the lung. Fed Proc. 1974 Nov;33(11):2238–2247. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitnick M., DeMarco B., Gibbons J. M. Amniotic fluid phosphatidylglycerol and phosphatidylinositol separated by stepwise-development thin-layer chromatography. Clin Chem. 1980 Feb;26(2):277–281. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Phizackerley P. J., Town M. H., Newman G. E. Hydrophobic proteins of lamellated osmiophilic bodies isolated from pig lung. Biochem J. 1979 Dec 1;183(3):731–736. doi: 10.1042/bj1830731. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weber K., Pringle J. R., Osborn M. Measurement of molecular weights by electrophoresis on SDS-acrylamide gel. Methods Enzymol. 1972;26:3–27. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(72)26003-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams M. C., Benson B. J. Immunocytochemical localization and identification of the major surfactant protein in adult rat lung. J Histochem Cytochem. 1981 Feb;29(2):291–305. doi: 10.1177/29.2.7019304. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]