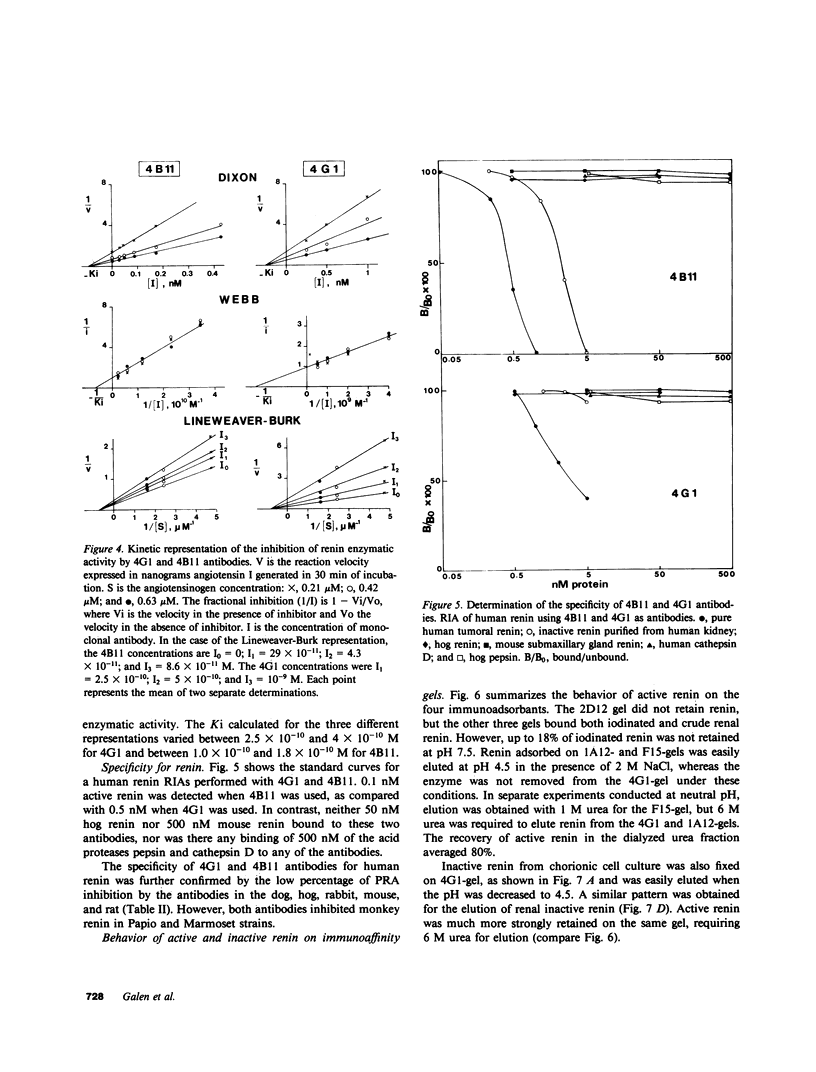
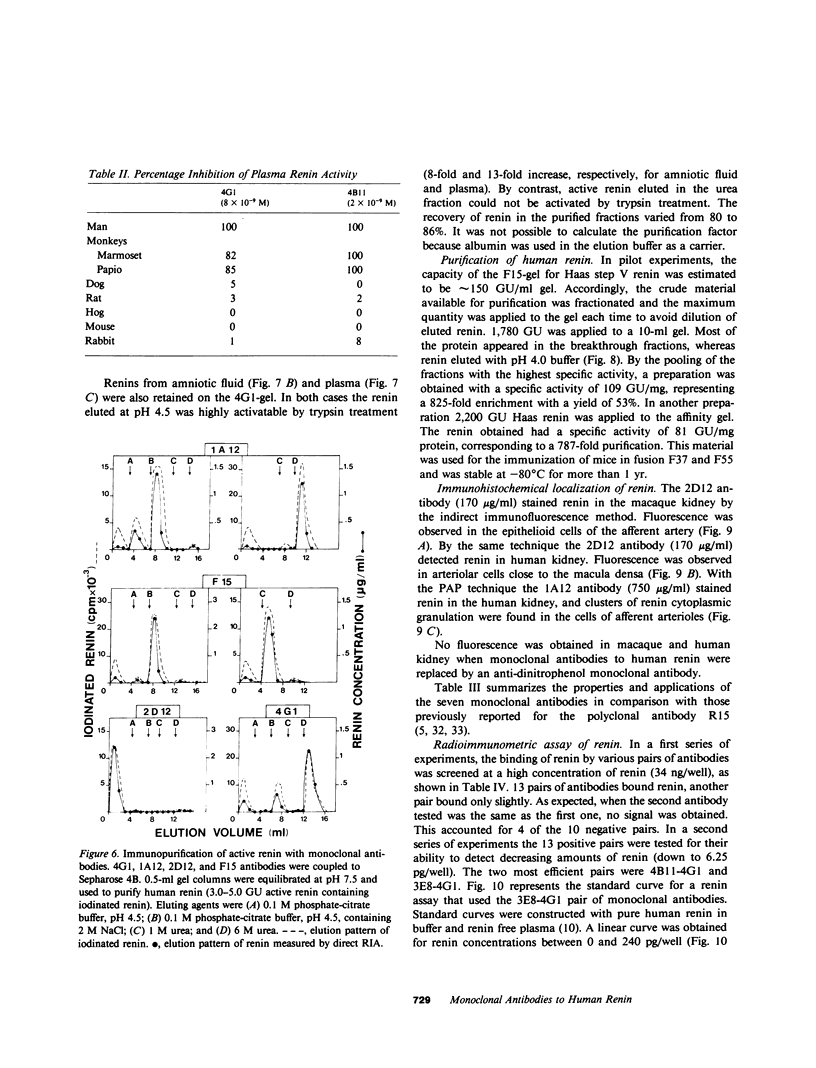
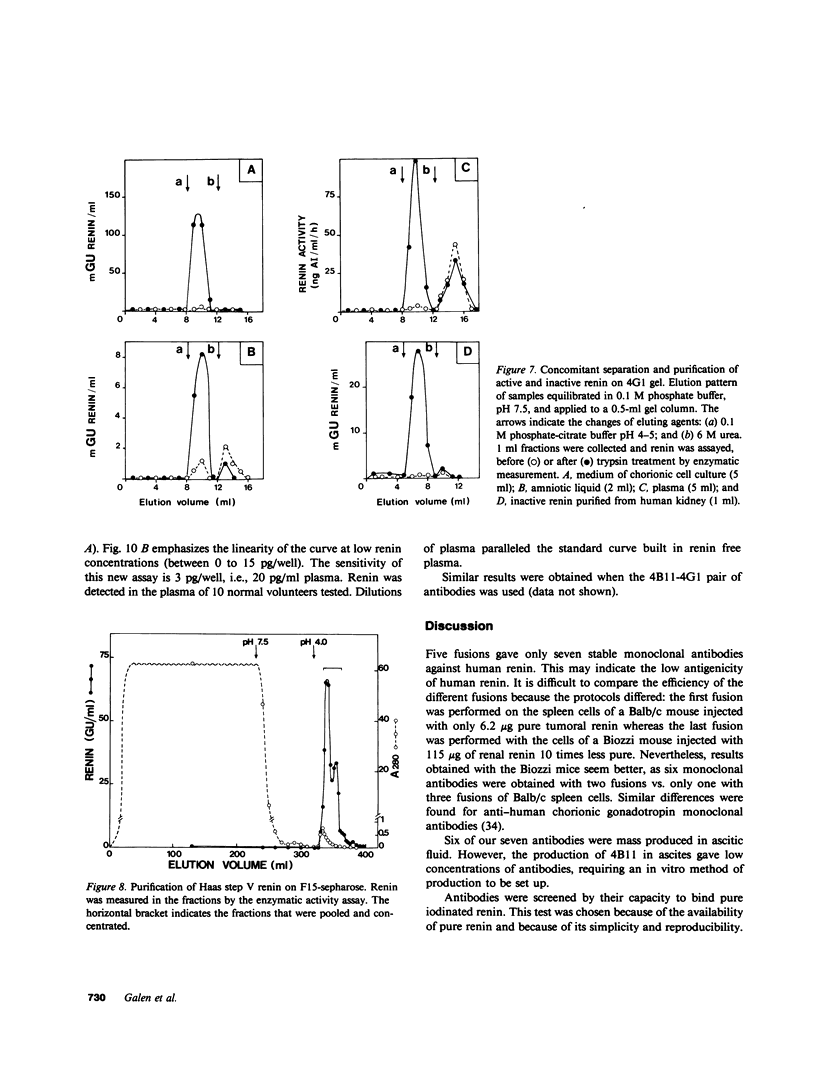
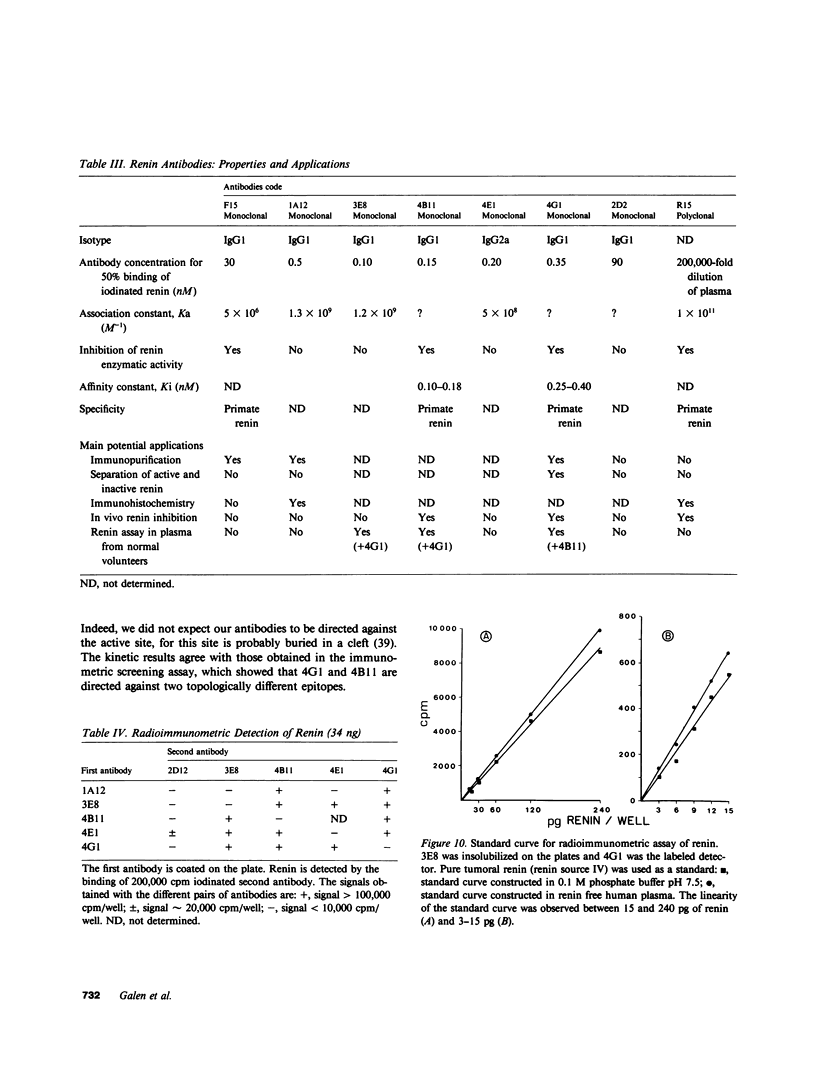
Abstract
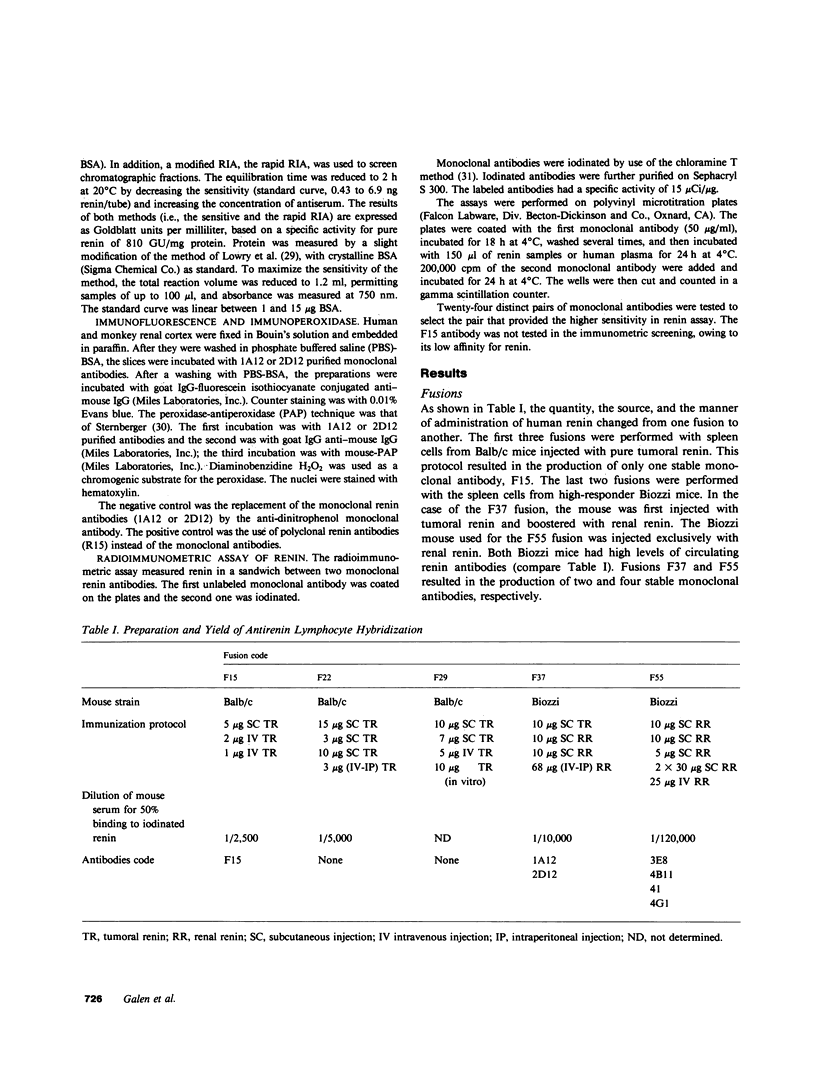
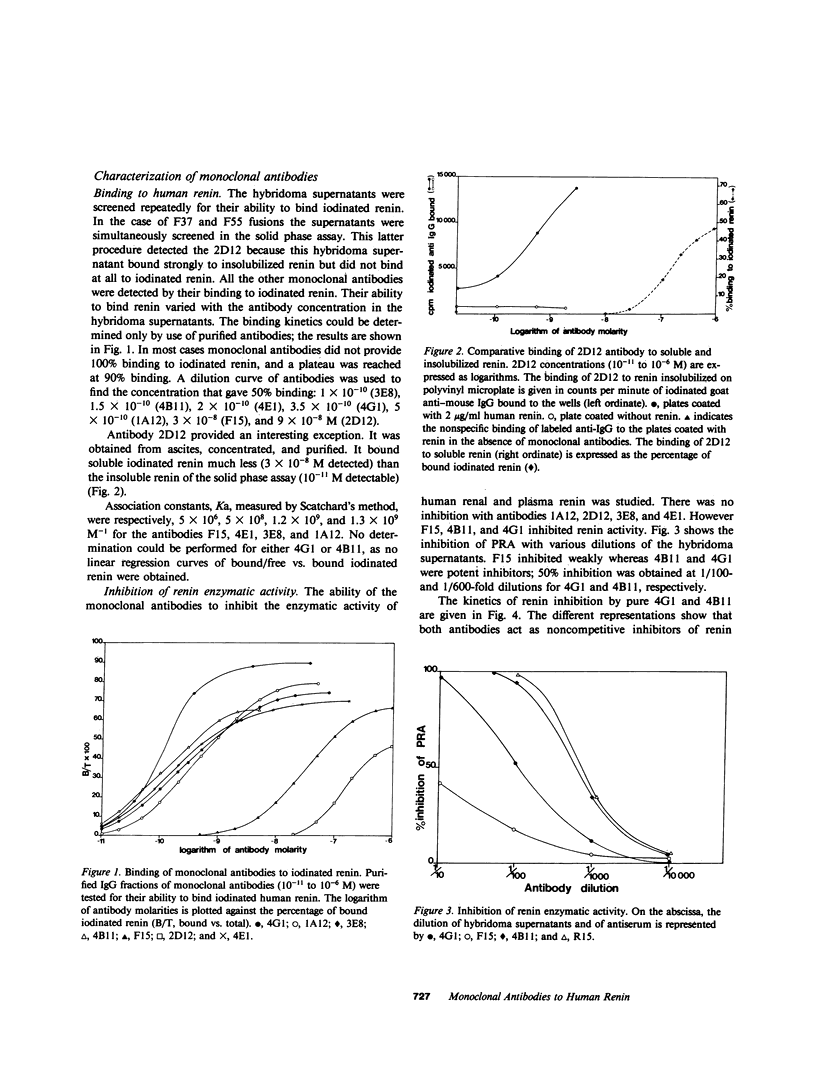
Monoclonal antibodies directed against human renin were obtained by the fusing of myeloma cells with spleen cells from Balb/c or high-responder Biozzi mice injected with pure tumoral or highly purified renal renin. These procedures resulted in the production of seven stable monoclonal antibodies to human renin. Antibodies in the hybridoma culture medium were screened by binding to pure iodinated renin or insolubilized renin in a solid phase assay. The concentration of purified antibodies that provided a 50% binding to iodinated renin varied from 1 X 10(-10) to 1 X 10(-7) M. Two monoclonal antibodies were found to be potent inhibitors of renin enzymatic activity in vitro, behaving as noncompetitive inhibitors (Ki, 1 to 4 X 10(-10) M). They were specific for primate renin. Three monoclonal antibodies provided suitable immunoadsorbants for renin purification. One of these immunoadsorbants was used for large-scale purification of the renal enzyme, resulting in an 825-fold renin enrichment in a single step. Two antibodies were able to distinguish between active and inactive renin and enabled concomitant separation and purification of the two enzyme forms in various biological fluids. Monoclonal antibodies also stained human and monkey renal renin when indirect immunofluorescence and peroxidase-antiperoxidase techniques were used. A highly sensitive radioimmunometric assay of renin was constructed with two monoclonal antibodies. The sensitivity of this improved assay should permit the detection of renin in normal human plasma. Monoclonal antibodies have been shown to be superior to polyclonal antibodies in the following areas: the separation of active from inactive renin, the purification of renin from biological fluids, and the setting up of a direct assay of plasma renin.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Acker G. M., Galen F. X., Devaux C., Foote S., Papernik E., Pesty A., Menard J., Corvol P. Human chorionic cells in primary culture: a model for renin biosynthesis. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1982 Nov;55(5):902–909. doi: 10.1210/jcem-55-5-902. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Amat D., Camilleri J. P., Phat V. N., Bariety J., Corvol P., Menard J. Renin localization in segmental renal hypoplasia. Immunohistochemical demonstration in two cases. Virchows Arch A Pathol Anat Histol. 1981;390(2):193–204. doi: 10.1007/BF02215984. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Atlas S. A., Sealey J. E., Hesson T. E., Kaplan A. P., Ménard J., Corvol P., Laragh J. H. Biochemical similarity of partially purified inactive renins from human plasma and kidney. Hypertension. 1982 May-Jun;4(3 Pt 2):86–95. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barrett A. J. Cathepsin D. Purification of isoenzymes from human and chicken liver. Biochem J. 1970 Apr;117(3):601–607. doi: 10.1042/bj1170601. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blundell T., Sibanda B. L., Pearl L. Three-dimensional structure, specificity and catalytic mechanism of renin. Nature. 1983 Jul 21;304(5923):273–275. doi: 10.1038/304273a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boumsell L., Bernard A. High efficiency of Biozzi's high responder mouse strain in the generation of antibody secreting hybridomas. J Immunol Methods. 1980;38(3-4):225–229. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(80)90270-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Camilleri J. P., Phat V. N., Bariety J., Corvol P., Menard J. Use of a specific antiserum for renin detection in human kidney. J Histochem Cytochem. 1980 Dec;28(12):1343–1346. doi: 10.1177/28.12.7014714. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang J. J., Kisaragi M., Okamoto H., Inagami T. Isolation and activation of inactive renin from human kidney and plasma. Plasma and renal inactive renins have different molecular weights. Hypertension. 1981 Sep-Oct;3(5):509–515. doi: 10.1161/01.hyp.3.5.509. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen S., Taylor J. M., Murakami K., Michelakis A. M., Inagami T. Isolation and characterization of renin-like enzymes from mouse submaxillary glands. Biochemistry. 1972 Nov 7;11(23):4286–4293. doi: 10.1021/bi00773a015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Corvol P., Devaux C., Ito T., Sicard P., Ducloux J., Menard J. Large scale purification of hog renin. Physicochemical characterization. Circ Res. 1977 Nov;41(5):616–622. doi: 10.1161/01.res.41.5.616. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dzau V. J., Devine D., Mudgett-Hunter M., Kopelman R. I., Barger A. C., Haber E. Antibodies as specific renin inhibitors: studies with polyclonal and monoclonal antibodies and Fab fragments. Clin Exp Hypertens A. 1983;5(7-8):1207–1220. doi: 10.3109/10641968309048852. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ey P. L., Prowse S. J., Jenkin C. R. Isolation of pure IgG1, IgG2a and IgG2b immunoglobulins from mouse serum using protein A-sepharose. Immunochemistry. 1978 Jul;15(7):429–436. doi: 10.1016/0161-5890(78)90070-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Faraggiana T., Gresik E., Tanaka T., Inagami T., Lupo A. Immunohistochemical localization of renin in the human kidney. J Histochem Cytochem. 1982 May;30(5):459–465. doi: 10.1177/30.5.7042817. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GREENWOOD F. C., HUNTER W. M., GLOVER J. S. THE PREPARATION OF I-131-LABELLED HUMAN GROWTH HORMONE OF HIGH SPECIFIC RADIOACTIVITY. Biochem J. 1963 Oct;89:114–123. doi: 10.1042/bj0890114. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galen F. X., Devaux C., Guyenne T., Menard J., Corvol P. Multiple forms of human renin. Purification and characterization. J Biol Chem. 1979 Jun 10;254(11):4848–4855. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galen F. X., Guyenne T. T., Devaux C., Auzan C., Corvol P., Menard J. Direct radioimmunoassay of human renin. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1979 Jun;48(6):1041–1043. doi: 10.1210/jcem-48-6-1041. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guyene T. T., Galen F. X., Devaux C., Corvol P., Menard J. Direct radioimmunoassay of human renin: comparison with renin activity in plasma and amniotic fluid. Hypertension. 1980 Jul-Aug;2(4):465–470. doi: 10.1161/01.hyp.2.4.465. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haas E., Goldblatt H., Gipson E. C., Lewis L. Extraction, purification, and assay of human renin free of angiotensinase. Circ Res. 1966 Oct;19(4):739–749. doi: 10.1161/01.res.19.4.739. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henderson P. J. A linear equation that describes the steady-state kinetics of enzymes and subcellular particles interacting with tightly bound inhibitors. Biochem J. 1972 Apr;127(2):321–333. doi: 10.1042/bj1270321. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inagami T., Okamoto H., Ohtsuki K., Shimamoto K., Chao J., Margolius H. S. Human plasma inactive renin: purification and activation by proteases. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1982 Oct;55(4):619–627. doi: 10.1210/jcem-55-4-619. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leckie B. J. Inactive renin: an attempt at a perspective. Clin Sci (Lond) 1981 Feb;60(2):119–130. doi: 10.1042/cs0600119. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luben R. A., Mohler M. A. In vitro immunization as an adjunct to the production of hybridomas producing antibodies against the lymphokine osteoclast activating factor. Mol Immunol. 1980 May;17(5):635–639. doi: 10.1016/0161-5890(80)90161-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- March S. C., Parikh I., Cuatrecasas P. A simplified method for cyanogen bromide activation of agarose for affinity chromatography. Anal Biochem. 1974 Jul;60(1):149–152. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(74)90139-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Menard J., Catt K. J. Measurement of renin activity, concentration and substrate in rat plasma by radioimmunoassay of angiotensin I. Endocrinology. 1972 Feb;90(2):422–430. doi: 10.1210/endo-90-2-422. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michel J. B., Wood J., Hofbauer K., Corvol P., Menard J. Blood pressure effects of renin inhibition by human renin antiserum in normotensive marmosets. Am J Physiol. 1984 Mar;246(3 Pt 2):F309–F316. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1984.246.3.F309. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mumby M. C., Martins T. J., Chang M. L., Beavo J. A. Identification of cGMP-stimulated cyclic nucleotide phosphodiesterase in lung tissue with monoclonal antibodies. J Biol Chem. 1982 Nov 25;257(22):13283–13290. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murakami K., Inagami T. Isolation of pure and stable renin from hog kidney. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1975 Feb 3;62(3):757–763. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(75)90464-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pau B., Simon D., Galen F. X., Devaux C., Soubrier F., Ménard J., Corvol P. A monoclonal antibody for immunopurification of human renin. Clin Sci (Lond) 1981 Dec;61 (Suppl 7):239s–240s. doi: 10.1042/cs061239s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Phat V. N., Camilleri J. P., Bariety J., Galtier M., Baviera E., Corvol P., Menard J. Immunohistochemical characterization of renin-containing cells in the human juxtaglomerular apparatus during embryonal and fetal development. Lab Invest. 1981 Nov;45(5):387–390. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simon D., Galen F. X., Devaux C., Soubrier F., Pau B., Menard J., Corvol P. Monoclonal antibody against human renin. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1981 Aug;53(2):453–455. doi: 10.1210/jcem-53-2-453. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Slater E. E., Strout H. V., Jr Pure human renin. Identification and characterization and of two major molecular weight forms. J Biol Chem. 1981 Aug 10;256(15):8164–8171. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Soubrier F., Devaux C., Galen F. X., Skinner S. L., Aurell M., Genest J., Menard J., Corvol P. Biochemical and immunological characterization of ectopic tumoral renin. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1982 Jan;54(1):139–144. doi: 10.1210/jcem-54-1-139. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sternberger L. A., Hardy P. H., Jr, Cuculis J. J., Meyer H. G. The unlabeled antibody enzyme method of immunohistochemistry: preparation and properties of soluble antigen-antibody complex (horseradish peroxidase-antihorseradish peroxidase) and its use in identification of spirochetes. J Histochem Cytochem. 1970 May;18(5):315–333. doi: 10.1177/18.5.315. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanaka S., Hu S. Z., Wang T. S., Korn D. Preparation and preliminary characterization of monoclonal antibodies against human DNA polymerase alpha. J Biol Chem. 1982 Jul 25;257(14):8386–8390. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yokosawa H., Holladay L. A., Inagami T., Haas E., Murakami K. Human renal renin. Complete purification and characterization. J Biol Chem. 1980 Apr 25;255(8):3498–3502. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yokosawa H., Yokosawa N., Inagami T. Specific antibody to human renal renin and its cross-reactivity with inactive human plasma prorenin. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1980 Sep;164(4):466–470. doi: 10.3181/00379727-164-40897. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]