Abstract
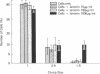
Human and murine tumor cells contain cell surface receptors for the basement membrane glycoprotein laminin. Since a biologic role for the receptor had not previously been demonstrated, we explored the possibility that the laminin receptor may be involved in hematogenous metastases formation. Preincubation of metastatic murine melanoma cells with syngeneic whole laminin followed by tail vein injection increased tumor cell retention in the lung and strongly stimulated metastases formation. The domain of the laminin molecule responsible for stimulating metastases was identified. Laminin is a cross-shaped molecule with three short arms and one long arm. All arms have globular end regions. Purified protease-derived fragments of laminin were prepared which (a) lacked only the long arm of the molecule (alpha fragment) or, (b) lacked both the long arm and the globular end regions of the short arms (C1 fragment). Both types of fragments contained the laminin receptor binding region. The fragments had opposite effects on metastases. The alpha fragment stimulated metastases formation to the same extent as whole laminin. In contrast, the C1 fragment greatly reduced or abolished metastases formation in a dose-dependent manner. The C1 fragment also inhibited tumor cell attachment to whole amnion basement membrane in vitro. We conclude that intact globular end regions on the short arms (but not the long arm) of the cell surface receptor-bound laminin molecule are necessary for stimulating metastases by the intravenous route.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Engel J., Odermatt E., Engel A., Madri J. A., Furthmayr H., Rohde H., Timpl R. Shapes, domain organizations and flexibility of laminin and fibronectin, two multifunctional proteins of the extracellular matrix. J Mol Biol. 1981 Jul 25;150(1):97–120. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(81)90326-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fidler I. J. Metastasis: quantitative analysis of distribution and fate of tumor emboli labeled with 125 I-5-iodo-2'-deoxyuridine. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1970 Oct;45(4):773–782. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hart I. R., Fidler I. J. Role of organ selectivity in the determination of metastatic patterns of B16 melanoma. Cancer Res. 1980 Jul;40(7):2281–2287. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liotta L. A., DeLisi C. Method for quantitating tumor cell removal and tumor cell-invasive capacity in experimental metastases. Cancer Res. 1977 Nov;37(11):4003–4008. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liotta L. A., Saidel M. G., Kleinerman J. The significance of hematogenous tumor cell clumps in the metastatic process. Cancer Res. 1976 Mar;36(3):889–894. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malinoff H. L., Wicha M. S. Isolation of a cell surface receptor protein for laminin from murine fibrosarcoma cells. J Cell Biol. 1983 May;96(5):1475–1479. doi: 10.1083/jcb.96.5.1475. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nicolson G. L., Poste G. The cancer cell: dynamic aspects and modifications in cell-surface organization (first of two parts). N Engl J Med. 1976 Jul 22;295(4):197–203. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197607222950405. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poste G., Nicolson G. L. Experimental systems for analysis of the surface properties of metastatic tumor cells. Biomembranes. 1983;11:341–364. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rao C. N., Goldstein I. J., Liotta L. A. Lectin-binding domains on laminin. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1983 Nov;227(1):118–124. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(83)90354-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rao C. N., Margulies I. M., Goldfarb R. H., Madri J. A., Woodley D. T., Liotta L. A. Differential proteolytic susceptibility of laminin alpha and beta subunits. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1982 Nov;219(1):65–70. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(82)90134-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rao C. N., Margulies I. M., Tralka T. S., Terranova V. P., Madri J. A., Liotta L. A. Isolation of a subunit of laminin and its role in molecular structure and tumor cell attachment. J Biol Chem. 1982 Aug 25;257(16):9740–9744. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rao N. C., Barsky S. H., Terranova V. P., Liotta L. A. Isolation of a tumor cell laminin receptor. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1983 Mar 29;111(3):804–808. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(83)91370-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Russo R. G., Foltz C. M., Liotta L. A. New invasion assay using endothelial cells grown on native human basement membrane. Clin Exp Metastasis. 1983 Apr-Jun;1(2):115–127. doi: 10.1007/BF00121491. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Terranova V. P., Liotta L. A., Russo R. G., Martin G. R. Role of laminin in the attachment and metastasis of murine tumor cells. Cancer Res. 1982 Jun;42(6):2265–2269. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Terranova V. P., Rao C. N., Kalebic T., Margulies I. M., Liotta L. A. Laminin receptor on human breast carcinoma cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jan;80(2):444–448. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.2.444. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Varani J., Lovett E. J., 3rd, McCoy J. P., Jr, Shibata S., Maddox D. E., Goldstein I. J., Wicha M. Differential expression of a lamininlike substance by high- and low-metastatic tumor cells. Am J Pathol. 1983 Apr;111(1):27–34. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]