Abstract
Identification of diabetes-associated T-cell autoantigens is important for understanding the immunopathology of diabetes and developing improved therapeutic strategies. We have used a genetic approach to move toward identifying the autoantigen recognized by a diabetogenic islet-specific T-cell clone from a nonobese diabetic (NOD) mouse. The unique antigen recognition pattern of this clone was utilized to map the gene encoding the antigen (or its expression) by genetic linkage analysis. In vitro analysis of T-cell proliferation by this clone showed that the capacity of the islets to stimulate T cells segregates as a single codominant gene in BALB/cByJ x (BALB/cByJ x NOD/Bdc) backcross mice. This phenotype was tightly linked to two microsatellites in the telomeric region of mouse chromosome 6.
Full text
PDF
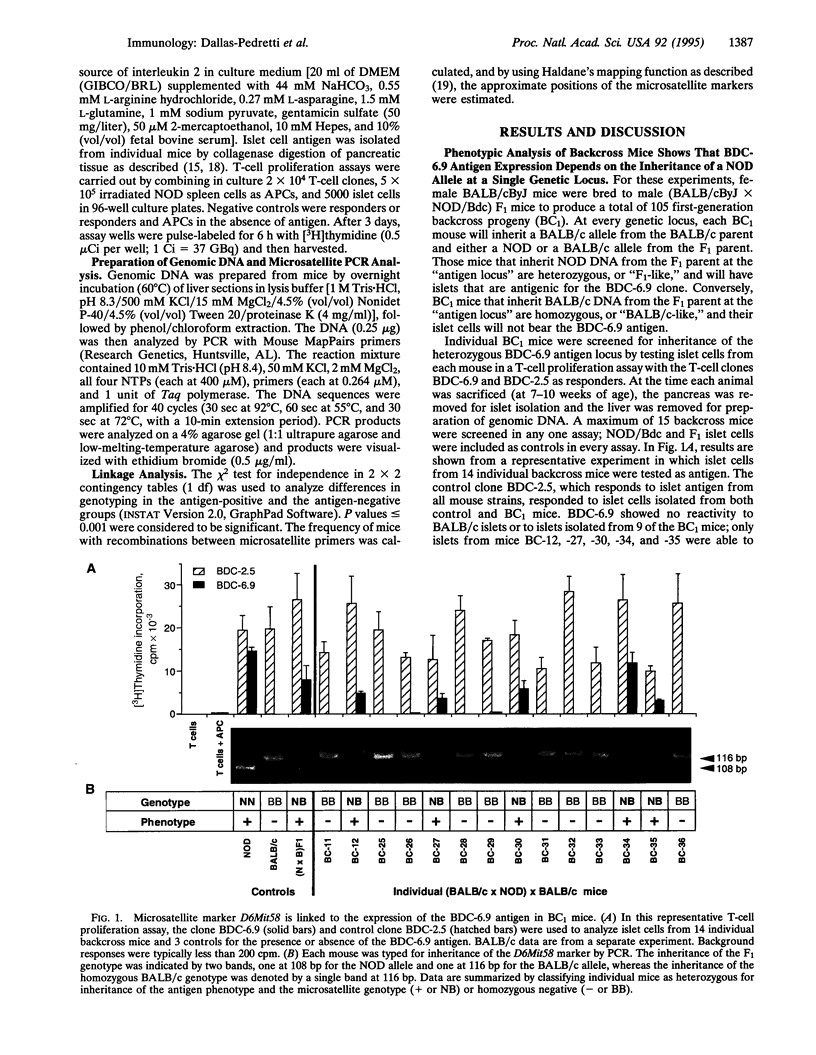
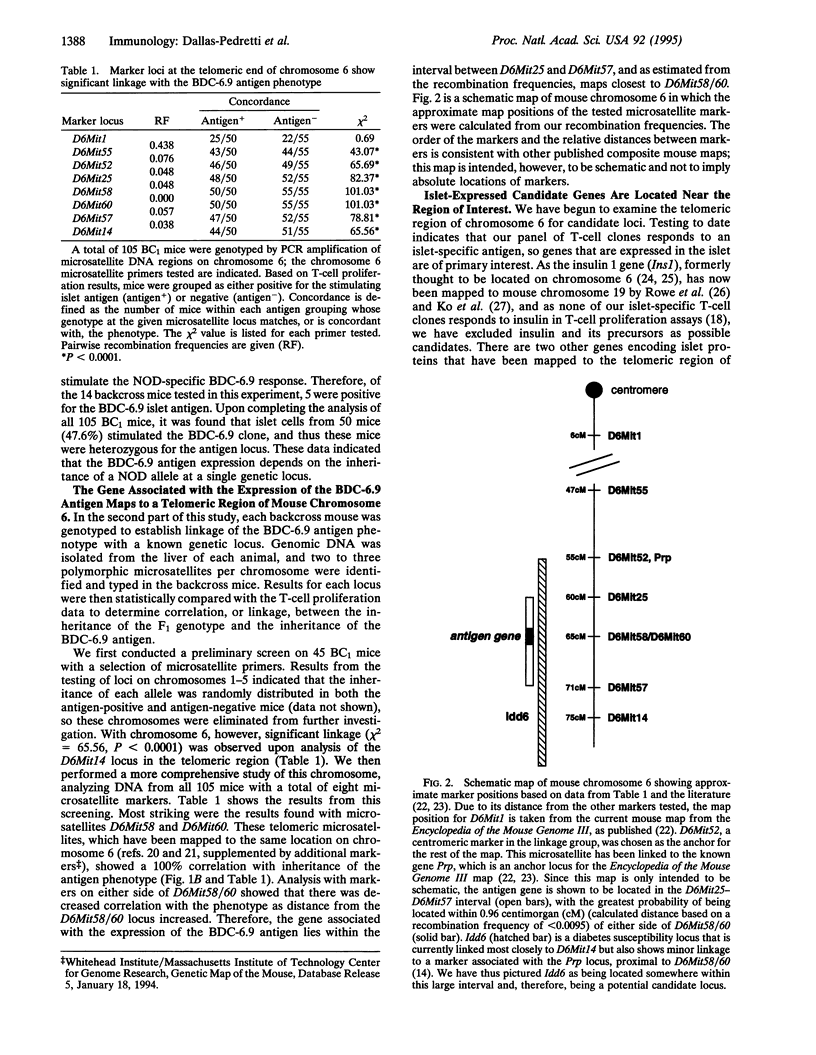


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Atkinson M. A., Maclaren N. K., Luchetta R. Insulitis and diabetes in NOD mice reduced by prophylactic insulin therapy. Diabetes. 1990 Aug;39(8):933–937. doi: 10.2337/diab.39.8.933. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bergman B., Haskins K. Islet-specific T-cell clones from the NOD mouse respond to beta-granule antigen. Diabetes. 1994 Feb;43(2):197–203. doi: 10.2337/diab.43.2.197. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Britton-Davidian J., Ruiz Bustos A., Thaler L., Topal M. Lactate dehydrogenase polymorphism in Mus musculus L. and Mus spretus Lataste. Experientia. 1978 Sep 15;34(9):1144–1145. doi: 10.1007/BF01922920. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Christianson S. W., Shultz L. D., Leiter E. H. Adoptive transfer of diabetes into immunodeficient NOD-scid/scid mice. Relative contributions of CD4+ and CD8+ T-cells from diabetic versus prediabetic NOD.NON-Thy-1a donors. Diabetes. 1993 Jan;42(1):44–55. doi: 10.2337/diab.42.1.44. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Copeland N. G., Gilbert D. J., Jenkins N. A., Nadeau J. H., Eppig J. T., Maltais L. J., Miller J. C., Dietrich W. F., Steen R. G., Lincoln S. E. Genome maps IV 1993. Wall chart. Science. 1993 Oct 1;262(5130):67–82. doi: 10.1126/science.8211131. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cornall R. J., Aitman T. J., Hearne C. M., Todd J. A. The generation of a library of PCR-analyzed microsatellite variants for genetic mapping of the mouse genome. Genomics. 1991 Aug;10(4):874–881. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(91)90175-e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dietrich W., Katz H., Lincoln S. E., Shin H. S., Friedman J., Dracopoli N. C., Lander E. S. A genetic map of the mouse suitable for typing intraspecific crosses. Genetics. 1992 Jun;131(2):423–447. doi: 10.1093/genetics/131.2.423. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elias D., Markovits D., Reshef T., van der Zee R., Cohen I. R. Induction and therapy of autoimmune diabetes in the non-obese diabetic (NOD/Lt) mouse by a 65-kDa heat shock protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Feb;87(4):1576–1580. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.4.1576. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ghosh S., Palmer S. M., Rodrigues N. R., Cordell H. J., Hearne C. M., Cornall R. J., Prins J. B., McShane P., Lathrop G. M., Peterson L. B. Polygenic control of autoimmune diabetes in nonobese diabetic mice. Nat Genet. 1993 Aug;4(4):404–409. doi: 10.1038/ng0893-404. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorus F. K., Sodoyez J. C., Pipeleers D. G., Keymeulen B., Foriers A., Van Schravendijk C. F. Detection of autoantibodies against islet amyloid polypeptide in human serum. Lack of association with type 1 (insulin-dependent) diabetes mellitus, or with conditions favouring amyloid deposition in islets. The Belgian Diabetes Registry. Diabetologia. 1992 Nov;35(11):1080–1086. doi: 10.1007/BF02221685. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamaguchi K., Gaskins H. R., Leiter E. H. NIT-1, a pancreatic beta-cell line established from a transgenic NOD/Lt mouse. Diabetes. 1991 Jul;40(7):842–849. doi: 10.2337/diab.40.7.842. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haskins K., McDuffie M. Acceleration of diabetes in young NOD mice with a CD4+ islet-specific T cell clone. Science. 1990 Sep 21;249(4975):1433–1436. doi: 10.1126/science.2205920. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haskins K., Portas M., Bergman B., Lafferty K., Bradley B. Pancreatic islet-specific T-cell clones from nonobese diabetic mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Oct;86(20):8000–8004. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.20.8000. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haskins K., Portas M., Bradley B., Wegmann D., Lafferty K. T-lymphocyte clone specific for pancreatic islet antigen. Diabetes. 1988 Oct;37(10):1444–1448. doi: 10.2337/diab.37.10.1444. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hattori M., Buse J. B., Jackson R. A., Glimcher L., Dorf M. E., Minami M., Makino S., Moriwaki K., Kuzuya H., Imura H. The NOD mouse: recessive diabetogenic gene in the major histocompatibility complex. Science. 1986 Feb 14;231(4739):733–735. doi: 10.1126/science.3003909. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hearne C. M., McAleer M. A., Love J. M., Aitman T. J., Cornall R. J., Ghosh S., Knight A. M., Prins J. B., Todd J. A. Additional microsatellite markers for mouse genome mapping. Mamm Genome. 1991;1(4):273–282. doi: 10.1007/BF00352339. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaufman D. L., Clare-Salzler M., Tian J., Forsthuber T., Ting G. S., Robinson P., Atkinson M. A., Sercarz E. E., Tobin A. J., Lehmann P. V. Spontaneous loss of T-cell tolerance to glutamic acid decarboxylase in murine insulin-dependent diabetes. Nature. 1993 Nov 4;366(6450):69–72. doi: 10.1038/366069a0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Khlebodarova T. M., Serov O. L. A new locus regulating the expression of the Ldh-2 gene in mouse liver. Biochem Genet. 1980 Oct;18(9-10):1027–1039. doi: 10.1007/BF00500133. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ko M. S., Wang X., Horton J. H., Hagen M. D., Takahashi N., Maezaki Y., Nadeau J. H. Genetic mapping of 40 cDNA clones on the mouse genome by PCR. Mamm Genome. 1994 Jun;5(6):349–355. doi: 10.1007/BF00356553. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lathrop G. M., Lalouel J. M., Julier C., Ott J. Strategies for multilocus linkage analysis in humans. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Jun;81(11):3443–3446. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.11.3443. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Love J. M., Knight A. M., McAleer M. A., Todd J. A. Towards construction of a high resolution map of the mouse genome using PCR-analysed microsatellites. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Jul 25;18(14):4123–4130. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.14.4123. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moore K. J., Elliott R. W. Encyclopedia of the mouse genome III. October 1993. Mouse chromosome 6. Mamm Genome. 1993;4(Spec No):S88–109. doi: 10.1007/BF00360832. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishi M., Chan S. J., Nagamatsu S., Bell G. I., Steiner D. F. Conservation of the sequence of islet amyloid polypeptide in five mammals is consistent with its putative role as an islet hormone. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Aug;86(15):5738–5742. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.15.5738. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Brien T. D., Butler A. E., Roche P. C., Johnson K. H., Butler P. C. Islet amyloid polypeptide in human insulinomas. Evidence for intracellular amyloidogenesis. Diabetes. 1994 Feb;43(2):329–336. doi: 10.2337/diab.43.2.329. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peters G., Placzek M., Brookes S., Kozak C., Smith R., Dickson C. Characterization, chromosome assignment, and segregation analysis of endogenous proviral units of mouse mammary tumor virus. J Virol. 1986 Sep;59(3):535–544. doi: 10.1128/jvi.59.3.535-544.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peterson J. D., Pike B., McDuffie M., Haskins K. Islet-specific T cell clones transfer diabetes to nonobese diabetic (NOD) F1 mice. J Immunol. 1994 Sep 15;153(6):2800–2806. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prochazka M., Leiter E. H., Serreze D. V., Coleman D. L. Three recessive loci required for insulin-dependent diabetes in nonobese diabetic mice. Science. 1987 Jul 17;237(4812):286–289. doi: 10.1126/science.2885918. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rowe L. B., Nadeau J. H., Turner R., Frankel W. N., Letts V. A., Eppig J. T., Ko M. S., Thurston S. J., Birkenmeier E. H. Maps from two interspecific backcross DNA panels available as a community genetic mapping resource. Mamm Genome. 1994 May;5(5):253–274. doi: 10.1007/BF00389540. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tisch R., Yang X. D., Singer S. M., Liblau R. S., Fugger L., McDevitt H. O. Immune response to glutamic acid decarboxylase correlates with insulitis in non-obese diabetic mice. Nature. 1993 Nov 4;366(6450):72–75. doi: 10.1038/366072a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wegmann D. R., Norbury-Glaser M., Daniel D. Insulin-specific T cells are a predominant component of islet infiltrates in pre-diabetic NOD mice. Eur J Immunol. 1994 Aug;24(8):1853–1857. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830240820. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Westermark P., Engström U., Johnson K. H., Westermark G. T., Betsholtz C. Islet amyloid polypeptide: pinpointing amino acid residues linked to amyloid fibril formation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Jul;87(13):5036–5040. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.13.5036. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wicker L. S., Miller B. J., Coker L. Z., McNally S. E., Scott S., Mullen Y., Appel M. C. Genetic control of diabetes and insulitis in the nonobese diabetic (NOD) mouse. J Exp Med. 1987 Jun 1;165(6):1639–1654. doi: 10.1084/jem.165.6.1639. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]