Abstract
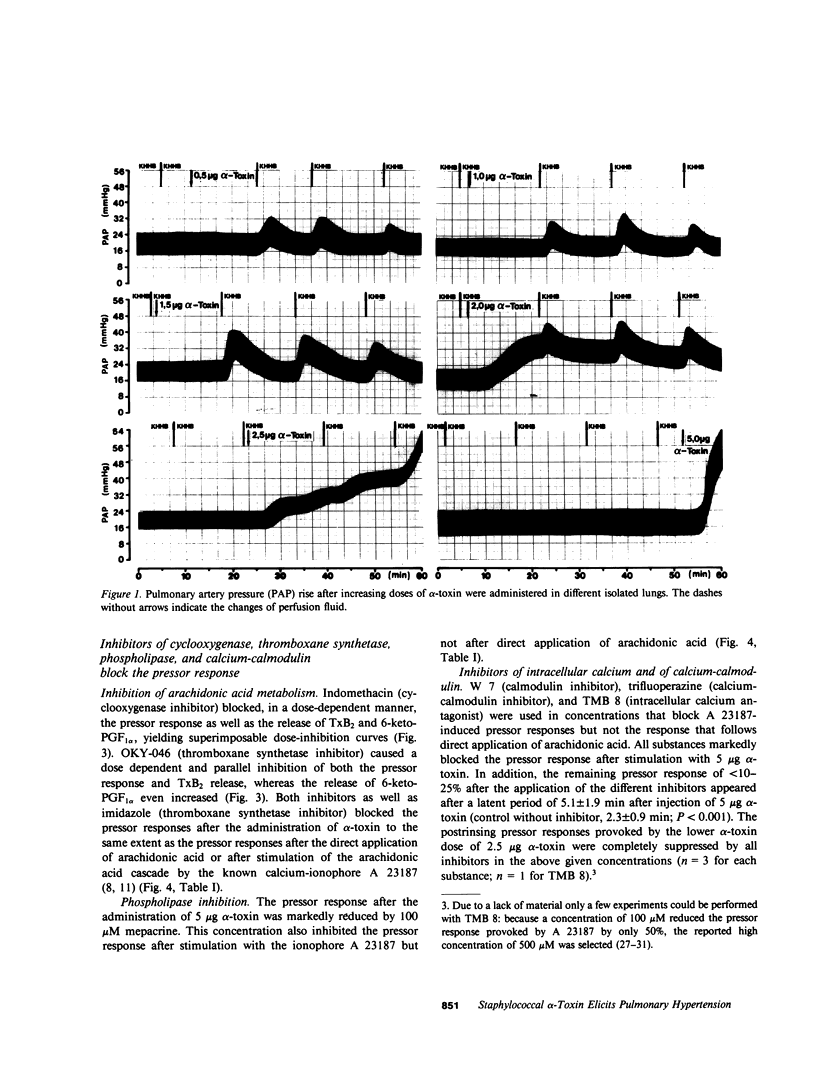
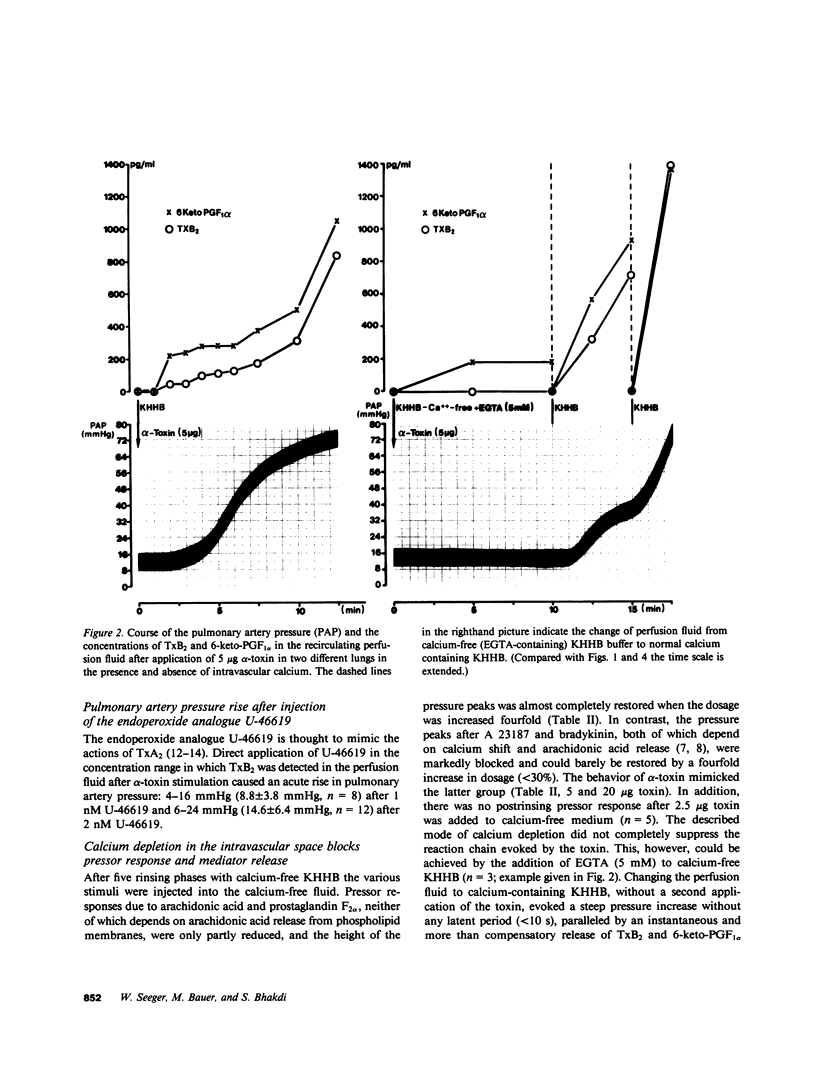
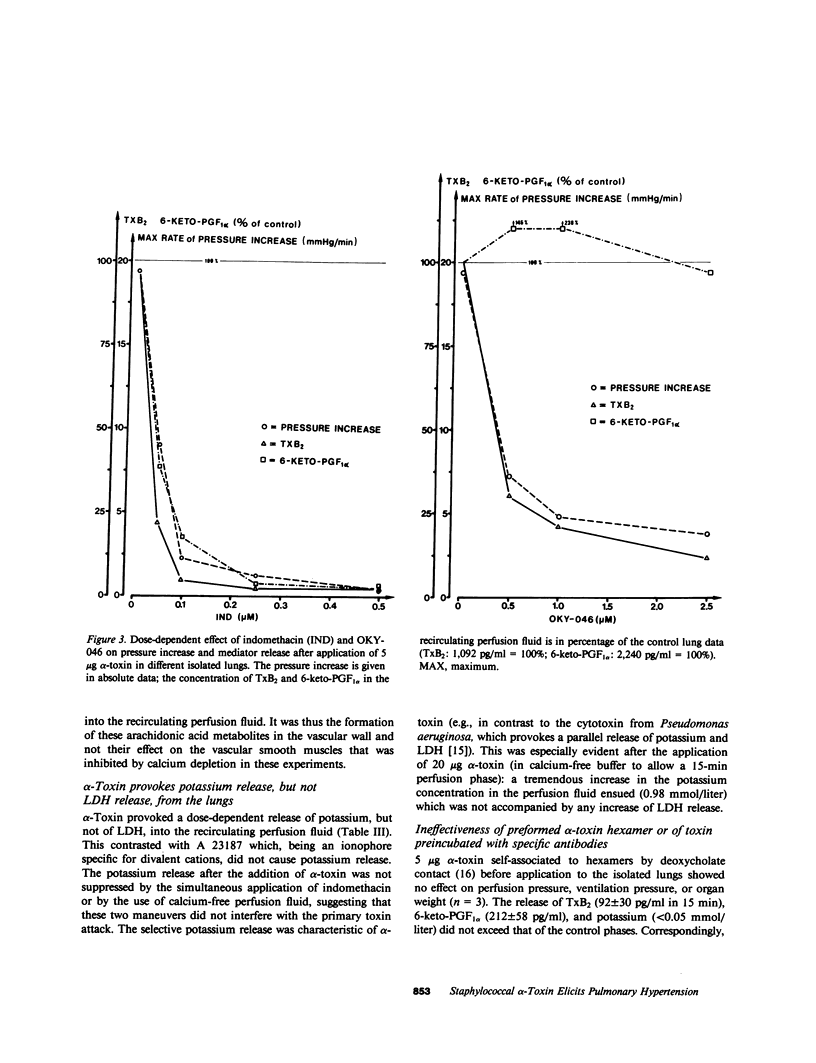
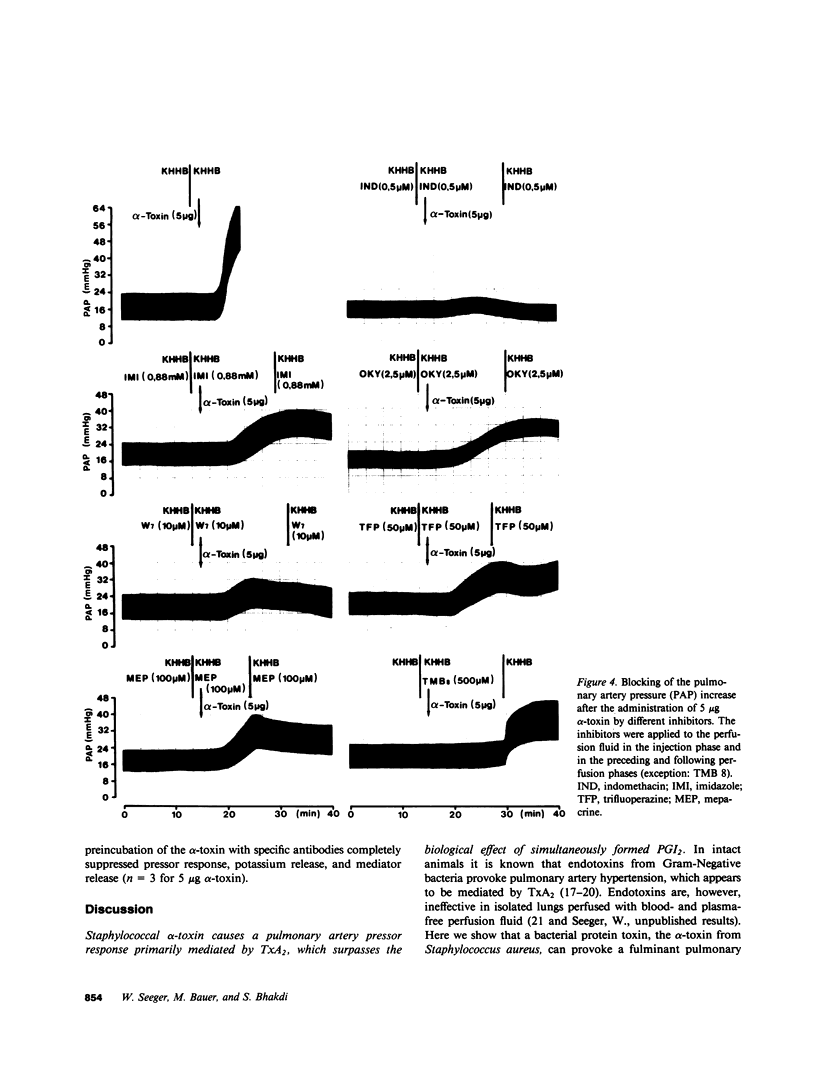
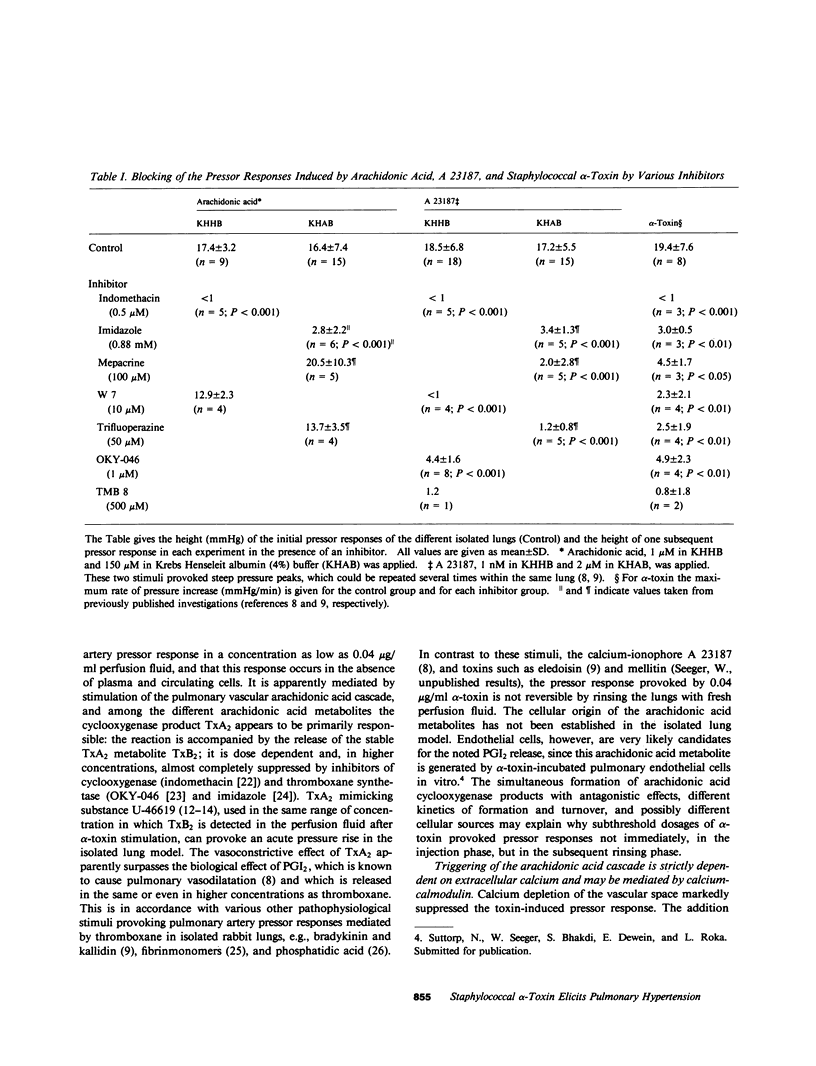
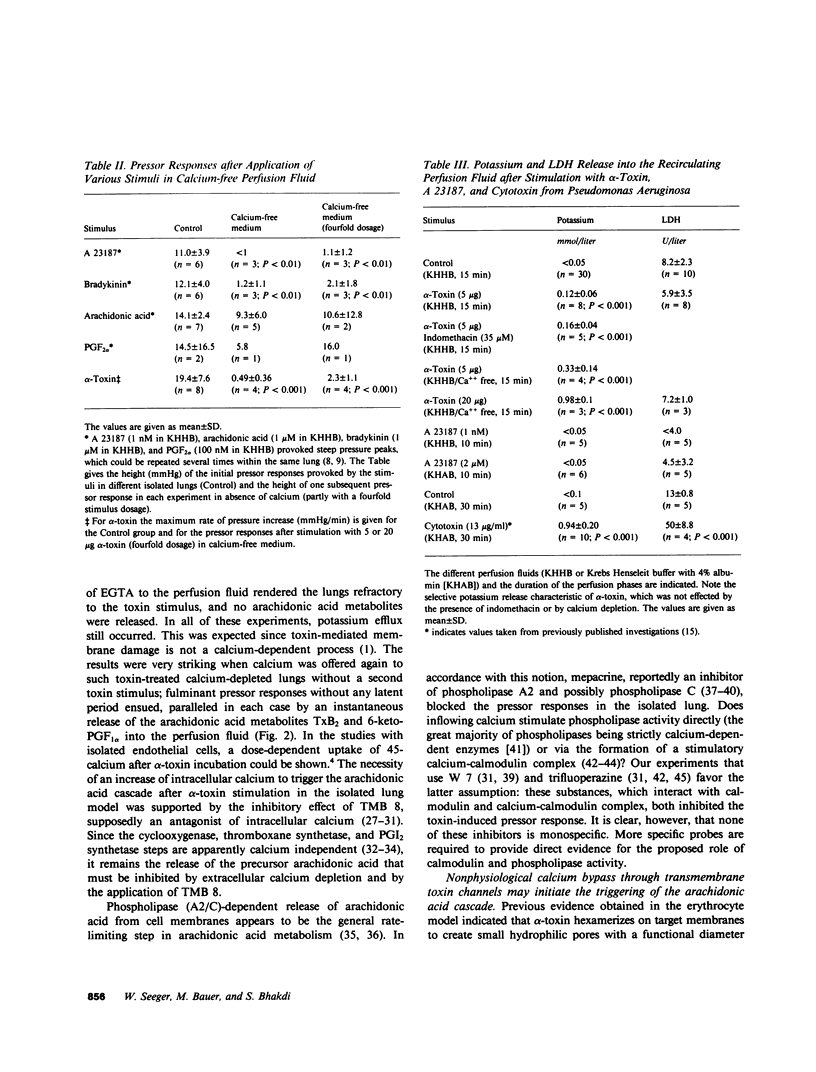
Staphylococcal alpha-toxin is known to damage mammalian cell membranes. Studies of erythrocytes indicate that the native toxin generates a discrete transmembrane channel with an effective diameter of 2-3 nm. (Füssle, R., S. Bhakdi, A. Szeigoleit, J. Tranum-Jensen, T. Kranz, and H.J. Wellensiek. 1981. J. Cell Biol. 91:83-94.) In isolated rabbit lungs, perfused with recirculating blood- and plasma-free perfusion fluid, the mediation of a toxin-provoked vascular pressor response by the triggering of the arachidonic acid cascade and its dependence on extracellular calcium were investigated. Dose-dependent pulmonary artery pressor responses were elicited by the injection of 0.5-5 micrograms staphylococcal alpha-toxin into the pulmonary artery. The pressor responses were completely abolished by preincubation of the toxin with neutralizing antibodies or by preformation of alpha-toxin hexamers in vitro. They were accompanied by the release of the arachidonic acid metabolites thromboxane B2 and 6-keto-prostaglandin F1 alpha (stable metabolites of thromboxane A2 and prostaglandin I2, respectively) into the perfusion fluid. They were blocked by inhibitors of thromboxane synthetase, cyclooxygenase, and phospholipase, as well as by substances that interfere with calcium-calmodulin function. alpha-Toxin induced selective release of potassium, but not lactatedehydrogenase into the medium. Calcium depletion of the intravascular space did not suppress the toxin-dependent potassium release but did abrogate the pressor response and the release of the arachidonic acid metabolites. When calcium was reintroduced into the circulation without the application of a second toxin stimulus, marked pressor responses paralleled by the release of arachidonic acid metabolites occurred. The conclusion drawn from these studies is that staphylococcal alpha-toxin provokes pulmonary vascular hypertension which is apparently mediated by thromboxane A2 formation, which surpasses the biological effect of the simultaneously formed prostaglandin I2. The triggering of the arachidonic acid cascade is strictly dependent on extracellular calcium and may be mediated by a nonphysiological calcium bypass through transmembrane toxin channels with subsequent stimulation of phospholipase activity.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bhakdi S., Füssle R., Tranum-Jensen J. Staphylococcal alpha-toxin: oligomerization of hydrophilic monomers to form amphiphilic hexamers induced through contact with deoxycholate detergent micelles. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Sep;78(9):5475–5479. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.9.5475. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blackwell G. J., Flower R. J., Nijkamp F. P., Vane J. R. Phospholipase A2 activity of guinea-pig isolated perfused lungs: stimulation, and inhibition by anti-inflammatory steroids. Br J Pharmacol. 1978 Jan;62(1):79–89. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1978.tb07009.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Charo I. F., Feinman R. D., Detwiler T. C. Inhibition of platelet secretion by an antagonist of intracellular calcium. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1976 Oct 18;72(4):1462–1467. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(76)80178-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheung W. Y. Calmodulin plays a pivotal role in cellular regulation. Science. 1980 Jan 4;207(4426):19–27. doi: 10.1126/science.6243188. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Demling R. H., Smith M., Gunther R., Flynn J. T., Gee M. H. Pulmonary injury and prostaglandin production during endotoxemia in conscious sheep. Am J Physiol. 1981 Mar;240(3):H348–H353. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.1981.240.3.H348. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flower R. J., Blackwell G. J. The importance of phospholipase-A2 in prostaglandin biosynthesis. Biochem Pharmacol. 1976 Feb 1;25(3):285–291. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(76)90216-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Füssle R., Bhakdi S., Sziegoleit A., Tranum-Jensen J., Kranz T., Wellensiek H. J. On the mechanism of membrane damage by Staphylococcus aureus alpha-toxin. J Cell Biol. 1981 Oct;91(1):83–94. doi: 10.1083/jcb.91.1.83. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hiraku S., Wakitani K., Katsube N., Kawasaki A., Tsuboshima M., Naito J., Ujiie A., Komatsu H., Iizuka K. Pharmacological studies on OKY-1581: a selective thromboxane synthetase inhibitor. Adv Prostaglandin Thromboxane Leukot Res. 1983;11:241–244. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kayama N., Sakaguchi K., Kaneko S., Kubota T., Fukuzawa T., Kawamura S., Yoshimoto T., Yamamoto S. Inhibition of platelet aggregation by 1-alkylimidazole derivatives, thromboxane A synthetase inhibitors. Prostaglandins. 1981 Apr;21(4):543–554. doi: 10.1016/0090-6980(81)90003-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klee C. B., Crouch T. H., Richman P. G. Calmodulin. Annu Rev Biochem. 1980;49:489–515. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.49.070180.002421. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knapp H. R., Oelz O., Roberts L. J., Sweetman B. J., Oates J. A., Reed P. W. Ionophores stimulate prostaglandin and thromboxane biosynthesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Oct;74(10):4251–4255. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.10.4251. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Majerus P. W., Prescott S. M., Hofmann S. L., Neufeld E. J., Wilson D. B. Uptake and release of arachidonate by platelets. Adv Prostaglandin Thromboxane Leukot Res. 1983;11:45–52. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moncada S., Needleman P., Bunting S., Vane J. R. Prostaglandin endoperoxide and thromboxane generating systems and their selective inhibition. Prostaglandins. 1976 Sep;12(3):323–335. doi: 10.1016/0090-6980(76)90014-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moncada S., Needleman P., Bunting S., Vane J. R. Prostaglandin endoperoxide and thromboxane generating systems and their selective inhibition. Prostaglandins. 1976 Sep;12(3):323–335. doi: 10.1016/0090-6980(76)90014-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Needleman P., Raz A., Ferrendelli J. A., Minkes M. Application of imidazole as a selective inhibitor thromboxane synthetase in human platelets. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Apr;74(4):1716–1720. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.4.1716. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rittenhouse-Simmons S., Deykin D. The activation by Ca2+ of platelet phospholipase A2. Effects of dibutyryl cyclic adenosine monophosphate and 8-(N,N-diethylamino)-octyl-3,4,5-trimethoxybenzoate. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1978 Nov 1;543(4):409–422. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(78)90296-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rittenhouse-Simmons S. Production of diglyceride from phosphatidylinositol in activated human platelets. J Clin Invest. 1979 Apr;63(4):580–587. doi: 10.1172/JCI109339. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rogolsky M. Nonenteric toxins of Staphylococcus aureus. Microbiol Rev. 1979 Sep;43(3):320–360. doi: 10.1128/mr.43.3.320-360.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Samuelsson B., Goldyne M., Granström E., Hamberg M., Hammarström S., Malmsten C. Prostaglandins and thromboxanes. Annu Rev Biochem. 1978;47:997–1029. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.47.070178.005025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seeger W., Wolf H. R., Neuhof H., Roka L. Release and oxygenation of arachidonic acid: nonspecific triggering and pathophysiological consequences in isolated rabbit lungs. Adv Prostaglandin Thromboxane Leukot Res. 1983;12:99–105. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seeger W., Wolf H., Stähler G., Neuhof H., Róka L. Increased pulmonary vascular resistance and permeability due to arachidonate metabolism in isolated rabbit lungs. Prostaglandins. 1982 Feb;23(2):157–173. doi: 10.1016/0090-6980(82)90043-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shaw J. O. Effects of extracellular Ca2+ and the intracellular Ca2+ antagonist 8-(n,n-diethylamino)octyl-3,4,5-trimethoxybenzoate on rabbit platelet conversion of arachidonic acid into thromboxane. Prostaglandins. 1981 Apr;21(4):571–579. doi: 10.1016/0090-6980(81)90005-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith R. J., Iden S. S. Phorbol myristate acetate-induced release of granule enzymes from human neutrophils: inhibition by the calcium antagonist, 8-(N,N-diethylamino)-octyl 3,4,5-trimethoxybenzoate hydrochloride. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1979 Nov 14;91(1):263–271. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(79)90612-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smolen J. E., Korchak H. M., Weissmann G. The roles of extracellular and intracellular calcium in lysosomal enzyme release and superoxide anion generation by human neutrophils. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1981 Nov 5;677(3-4):512–520. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(81)90267-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van der Ouderaa F. J., Buytenhek M., Nugteren D. H., Van Dorp D. A. Purification and characterisation of prostaglandin endoperoxide synthetase from sheep vesicular glands. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1977 May 25;487(2):315–331. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(77)90008-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vargaftig B. B., Hai N. D. Selective inhibition by mepacrine of the release of "rabbit aorta contracting substance" evoked by the administration of bradykinin. J Pharm Pharmacol. 1972 Feb;24(2):159–161. doi: 10.1111/j.2042-7158.1972.tb08953.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watkins W. D., Hüttemeier P. C., Kong D., Peterson M. B. Thromboxane and pulmonary hypertension following E. coli endotoxin infusion in sheep: effect of an imidazole derivative. Prostaglandins. 1982 Mar;23(3):273–285. doi: 10.1016/0090-6980(82)90073-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winn R., Harlan J., Nadir B., Harker L., Hildebrandt J. Thromboxane A2 mediates lung vasoconstriction but not permeability after endotoxin. J Clin Invest. 1983 Sep;72(3):911–918. doi: 10.1172/JCI111062. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wong P. Y., Cheung W. Y. Calmodulin stimulates human platelet phospholipase A2. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1979 Sep 27;90(2):473–480. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(79)91259-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van den Bosch H. Intracellular phospholipases A. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1980 Sep 30;604(2):191–246. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(80)90574-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


