Abstract
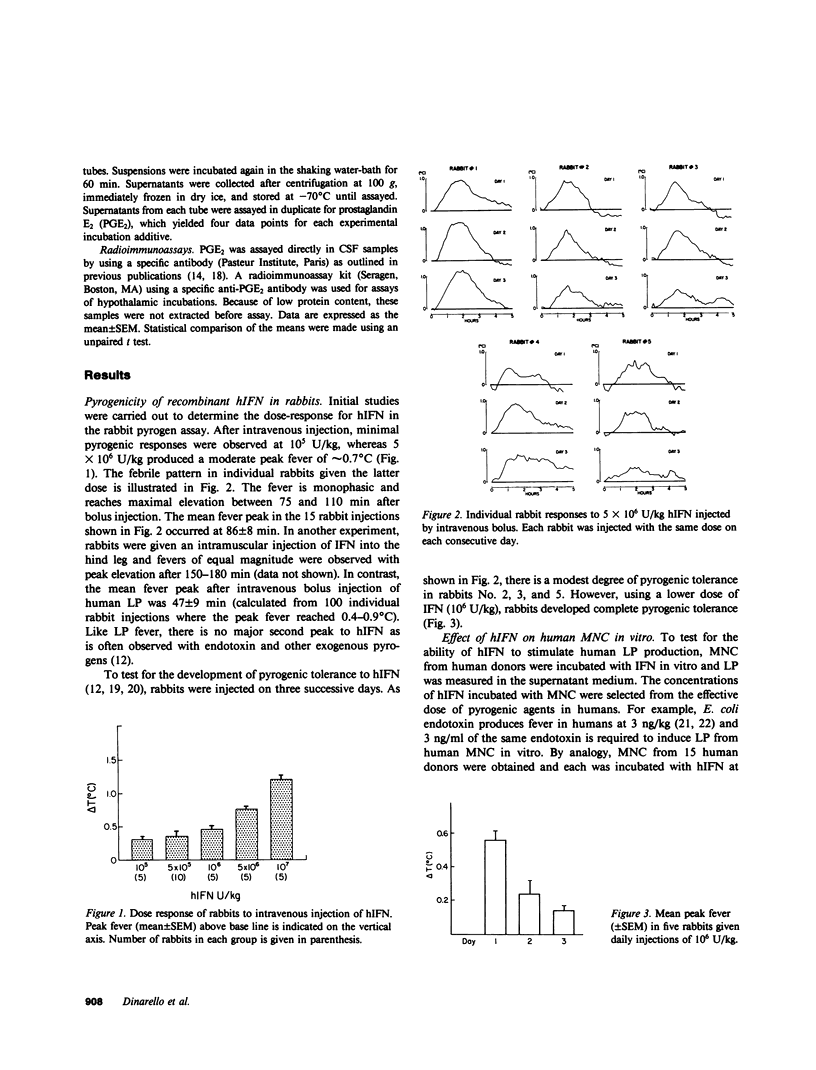
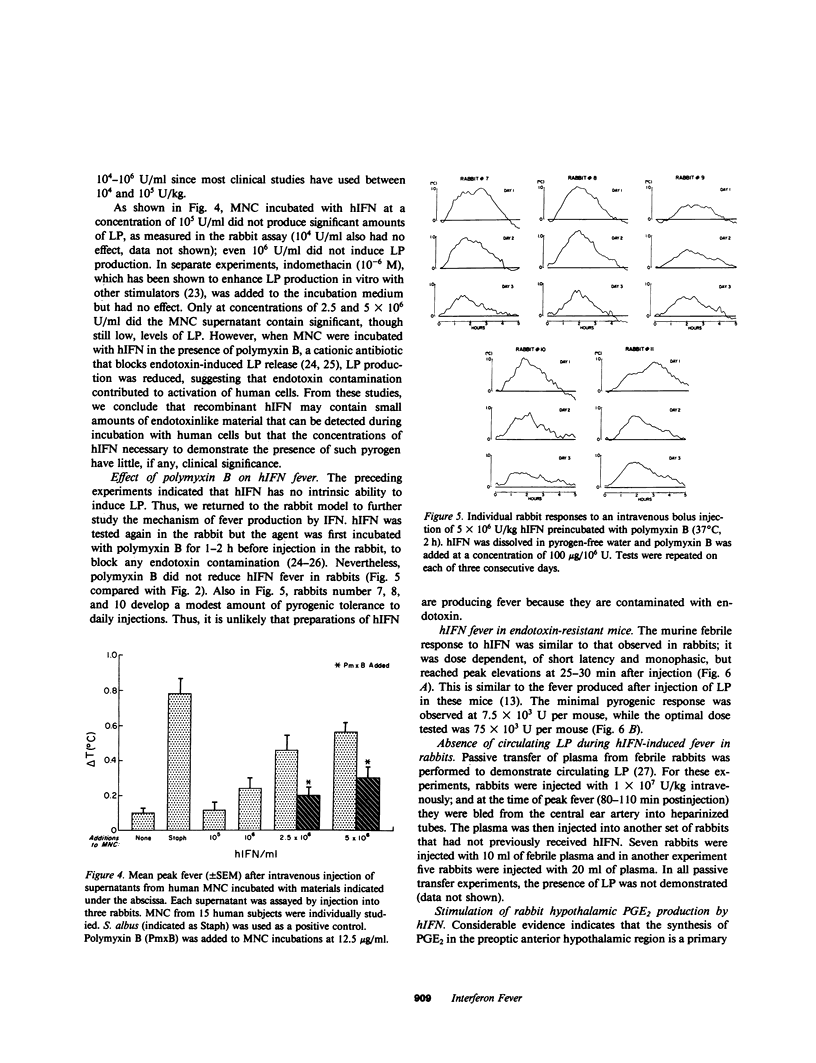
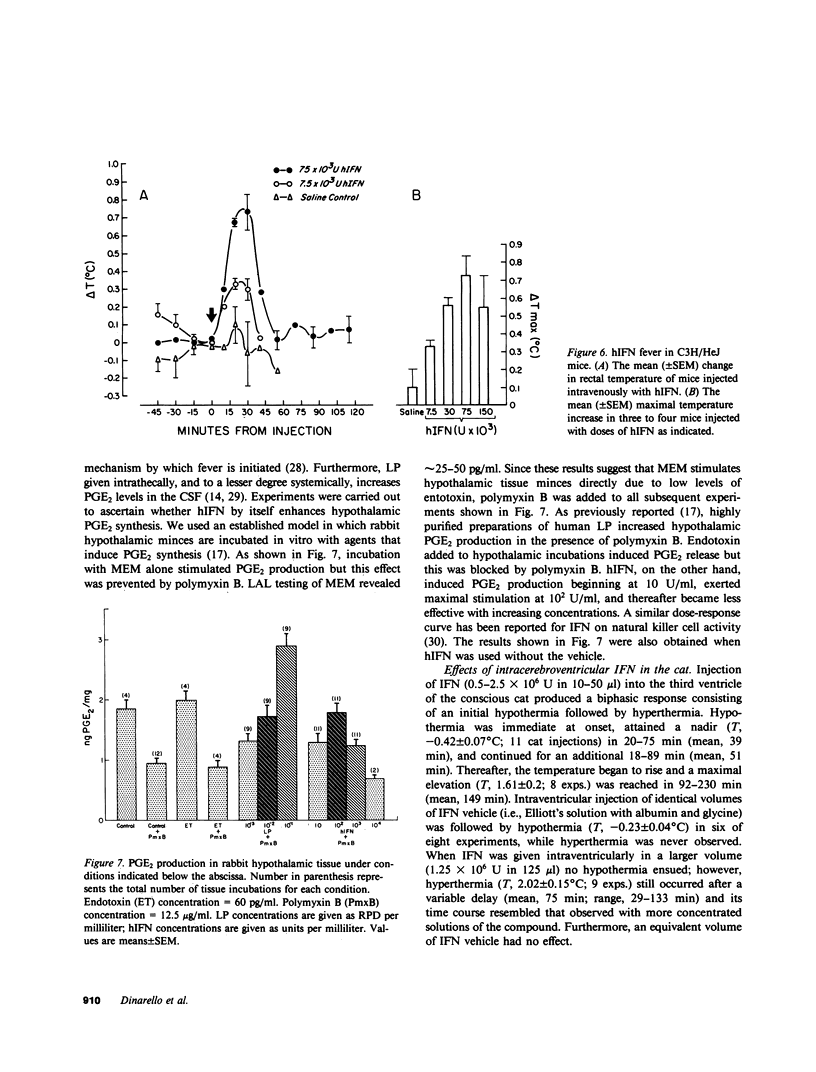
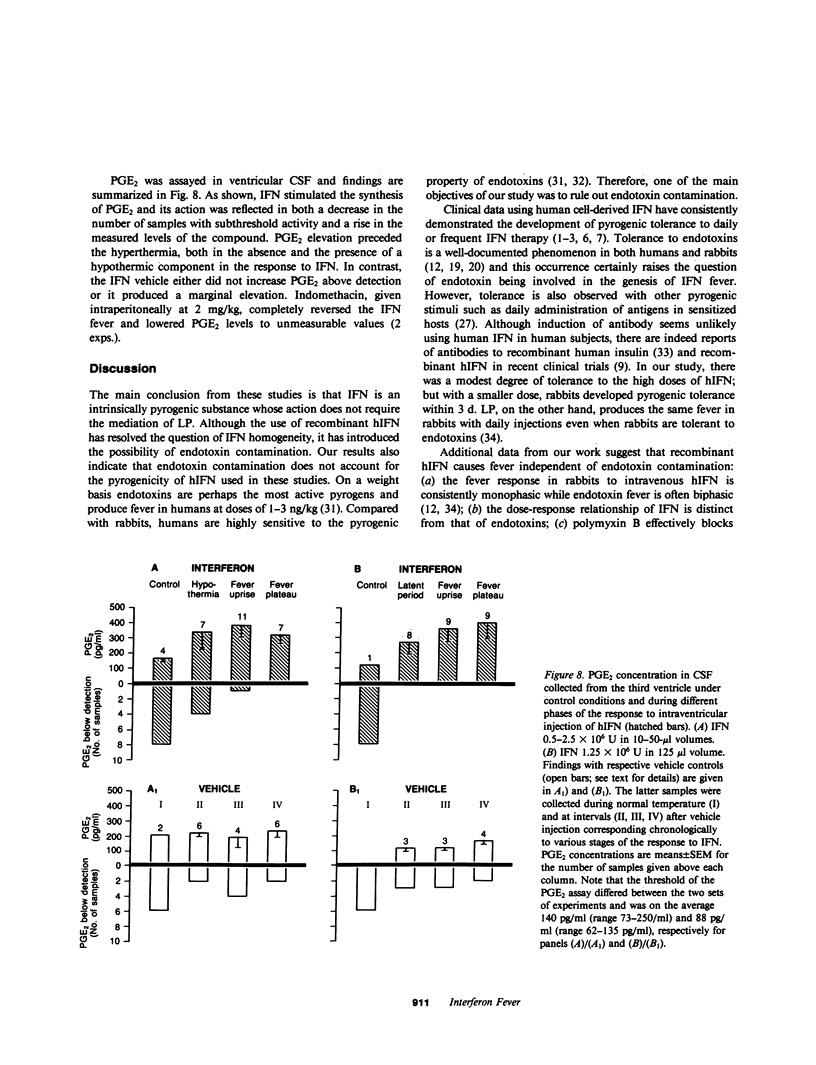
Since the early trials using human interferon (hIFN) derived from blood leukocytes or cell lines, fever has been a prominent component of IFN therapy. Human protein impurities might account for the fever to cell-derived hIFN, but recombinant hIFN, free of extraneous human proteins, has produced fever in nearly all recipients during clinical trials. Our present studies were carried out to determine the mechanisms of fever due to recombinant hIFN currently being used in humans. Because recombinant hIFN is produced in Escherichia coli, in these experiments we considered contaminating endotoxin as the cause of fever. Polymyxin B, which blocks endotoxin, had no effect on the pyrogenicity of hIFN in rabbits. In addition, hIFN injected into an endotoxin-resistant strain of mice produced fever. The pyrogenicity of hIFN does not appear to involve production of leukocytic pyrogen (LP), since no circulating LP was detected in rabbits during IFN fever. Furthermore, human mononuclear cells incubated with hIFN in vitro at 10(4)-10(6) U/ml did not release LP. However, hIFN stimulated prostaglandin E2 (PGE2) release from rabbit hypothalamic tissue in vitro. Intracerebroventricular injection of hIFN into the awake cat also produced fever and a rise in PGE2 levels in the cerebrospinal fluid; both effects were reversed by treatment with indomethacin. We conclude that the fever of recombinant hIFN is not due to endotoxin but that hIFN is intrinsically pyrogenic by inducing PGE2 in the hypothalamus.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ATKINS E. Pathogenesis of fever. Physiol Rev. 1960 Jul;40:580–646. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1960.40.3.580. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arenzana-Seisdedos F., Virelizier J. L. Interferons as macrophage-activating factors. II. Enhanced secretion of interleukin 1 by lipopolysaccharide-stimulated human monocytes. Eur J Immunol. 1983 Jun;13(6):437–440. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830130602. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baracos V., Rodemann H. P., Dinarello C. A., Goldberg A. L. Stimulation of muscle protein degradation and prostaglandin E2 release by leukocytic pyrogen (interleukin-1). A mechanism for the increased degradation of muscle proteins during fever. N Engl J Med. 1983 Mar 10;308(10):553–558. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198303103081002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bernheim H. A., Block L. H., Atkins E. Fever: pathogenesis, pathophysiology, and purpose. Ann Intern Med. 1979 Aug;91(2):261–270. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-91-2-261. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bernheim H. A., Gilbert T. M., Stitt J. T. Prostaglandin E levels in third ventricular cerebrospinal fluid of rabbits during fever and changes in body temperature. J Physiol. 1980 Apr;301:69–78. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1980.sp013189. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Billiau A., Heine J. W., Van Damme J., Heremans H., De Somer P. Tolerability of pure fibroblast interferon in man. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1980;350:374–375. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1980.tb20637.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Billiau A. Pharmacokinetic and pharmacological aspects of interferon therapy in man. Acta Microbiol Acad Sci Hung. 1981;28(3):257–262. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bocci V. U. Possible causes of fever after interferon administration. Biomedicine. 1980 Dec;32(4):159–162. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Borg H., Lundgren E., Hollenberg M. D., Veale W. L., Tan Y. H., McPherson A. Human interferon for clinical trials: removal of pyrogen by a simple two-step procedure. Can J Physiol Pharmacol. 1981 Aug;59(8):890–892. doi: 10.1139/y81-134. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coceani F., Bishai I., Dinarello C. A., Fitzpatrick F. A. Prostaglandin E2 and thromboxane B2 in cerebrospinal fluid of afebrile and febrile cat. Am J Physiol. 1983 Jun;244(6):R785–R793. doi: 10.1152/ajpregu.1983.244.6.R785. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dey P. K., Feldberg W., Gupta K. P., Wendlandt S. Lipid A fever in cats. J Physiol. 1975 Dec;253(1):103–119. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1975.sp011182. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dinarello C. A., Bernheim H. A. Ability of human leukocytic pyrogen to stimulate brain prostaglandin synthesis in vitro. J Neurochem. 1981 Sep;37(3):702–708. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1982.tb12544.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dinarello C. A. Demonstration of a human pyrogen-inducing factor during mixed leukocyte reactions. J Exp Med. 1981 May 1;153(5):1215–1224. doi: 10.1084/jem.153.5.1215. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dinarello C. A., Goldin N. P., Wolff S. M. Demonstration and characterization of two distinct human leukocytic pyrogens. J Exp Med. 1974 Jun 1;139(6):1369–1381. doi: 10.1084/jem.139.6.1369. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dinarello C. A., Renfer L., Wolff S. M. Human leukocytic pyrogen: purification and development of a radioimmunoassay. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Oct;74(10):4624–4627. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.10.4624. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dinarello C. A., Rosenwasser L. J., Wolff S. M. Demonstration of a circulating suppressor factor of thymocyte proliferation during endotoxin fever in humans. J Immunol. 1981 Dec;127(6):2517–2519. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dinarello C. A., Wolff S. M. Molecular basis of fever in humans. Am J Med. 1982 May;72(5):799–819. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(82)90548-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dray F., Charbonnel B., Maclouf J. Radioimmunoassay of prostaglandins Falpha, E1 and E2 in human plasma. Eur J Clin Invest. 1975 Jul 29;5(4):311–318. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2362.1975.tb00459.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duff G. W., Atkins E. The detection of endotoxin by in vitro production of endogenous pyrogen: comparison with limulus amebocyte lysate gelation. J Immunol Methods. 1982 Aug 13;52(3):323–331. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(82)90004-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duff G. W., Atkins E. The inhibitory effect of polymyxin B on endotoxin-induced endogenous pyrogen production. J Immunol Methods. 1982 Aug 13;52(3):333–340. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(82)90005-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duff G. W., Durum S. K. The pyrogenic and mitogenic actions of interleukin-1 are related. Nature. 1983 Aug 4;304(5925):449–451. doi: 10.1038/304449a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dunnick J. K., Galasso G. J. Clinical trials with exogenous interferon: summary of a meeting. J Infect Dis. 1979 Jan;139(1):109–123. doi: 10.1093/infdis/139.1.109. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dunnick J. K., Galasso G. J. From the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases. Update on clinical trials with exogenous interferon. J Infect Dis. 1980 Aug;142(2):293–299. doi: 10.1093/infdis/142.2.293. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elin R. J., Wolff S. M., McAdam K. P., Chedid L., Audibert F., Bernard C., Oberling F. Properties of reference Escherichia coli endotoxin and its phthalylated derivative in humans. J Infect Dis. 1981 Oct;144(4):329–336. doi: 10.1093/infdis/144.4.329. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fireman P., Fineberg S. E., Galloway J. A. Development of IgE antibodies to human (recombinant DNA), porcine, and bovine insulins in diabetic subjects. Diabetes Care. 1982 Nov-Dec;5 (Suppl 2):119–125. doi: 10.2337/diacare.5.2.s119. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fitzpatrick F. A., Stringfellow D. A. Virus and interferon effects on cellular prostaglandin biosynthesis. J Immunol. 1980 Jul;125(1):431–437. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fontana A., Kristensen F., Dubs R., Gemsa D., Weber E. Production of prostaglandin E and an interleukin-1 like factor by cultured astrocytes and C6 glioma cells. J Immunol. 1982 Dec;129(6):2413–2419. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greisman S. E., Hornick R. B. Comparative pyrogenic reactivity of rabbit and man to bacterial endotoxin. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1969 Sep;131(4):1154–1158. doi: 10.3181/00379727-131-34059. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gutterman J. U., Fine S., Quesada J., Horning S. J., Levine J. F., Alexanian R., Bernhardt L., Kramer M., Spiegel H., Colburn W. Recombinant leukocyte A interferon: pharmacokinetics, single-dose tolerance, and biologic effects in cancer patients. Ann Intern Med. 1982 May;96(5):549–556. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-96-5-549. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ingimarsson S., Cantell K., Strander H. Side effects of long-term treatment with human leukocyte interferon. J Infect Dis. 1979 Oct;140(4):560–563. doi: 10.1093/infdis/140.4.560. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kohl S. Stimulation of human natural killer cytotoxicity and protection of mice from infection due to herpes simplex virus by recombinant human leukocyte interferon. J Infect Dis. 1983 Mar;147(3):484–488. doi: 10.1093/infdis/147.3.484. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parant M., Riveau G., Parant F., Dinarello C. A., Wolff S. M., Chedid L. Effect of indomethacin on increased resistance to bacterial infection and on febrile responses induced by muramyl dipeptide. J Infect Dis. 1980 Nov;142(5):708–715. doi: 10.1093/infdis/142.5.708. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prange H., Wismann H. Intrathecal use of interferon in encephalitis. N Engl J Med. 1981 Nov 19;305(21):1283–1284. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198111193052113. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rietschel E. T., Schade U., Jensen M., Wollenweber H. W., Lüderitz O., Greisman S. G. Bacterial endotoxins: chemical structure, biological activity and role in septicaemia. Scand J Infect Dis Suppl. 1982;31:8–21. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WOLFF S. M., MULHOLLAND J. H., WARD S. B. QUANTITATIVE ASPECTS OF THE PYROGENIC RESPONSE OF RABBITS TO ENDOTOXIN. J Lab Clin Med. 1965 Feb;65:268–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WOLFF S. M., RUBENSTEIN M., MULHOLLAND J. H., ALLING D. W. COMPARISON OF HEMATOLOGIC AND FEBRILE RESPONSE TO ENDOTOXIN IN MAN. Blood. 1965 Aug;26:190–201. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watson J., Largen M., McAdam K. P. Genetic control of endotoxic responses in mice. J Exp Med. 1978 Jan 1;147(1):39–49. doi: 10.1084/jem.147.1.39. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Miert A. S., van Duin C. T. Further studies on the antipyretic action of polymyxin B in pyrogen-induced fever. Arzneimittelforschung. 1978;28(12):2246–2251. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


