Abstract
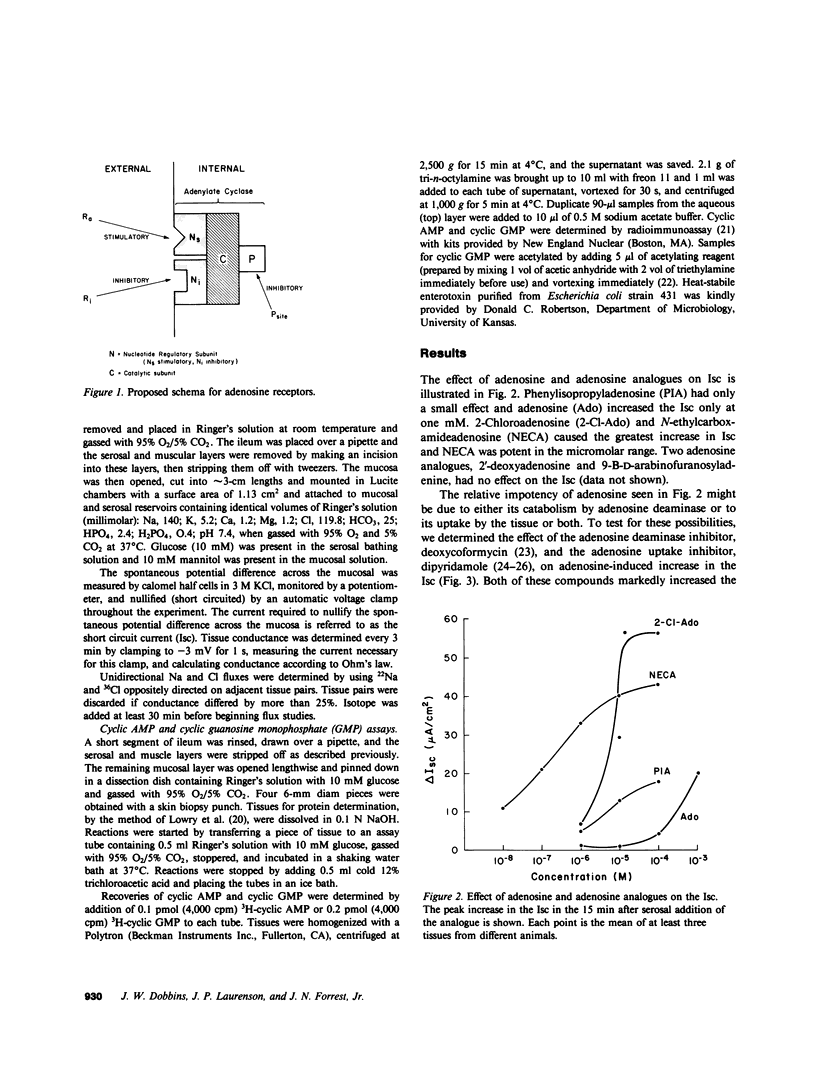
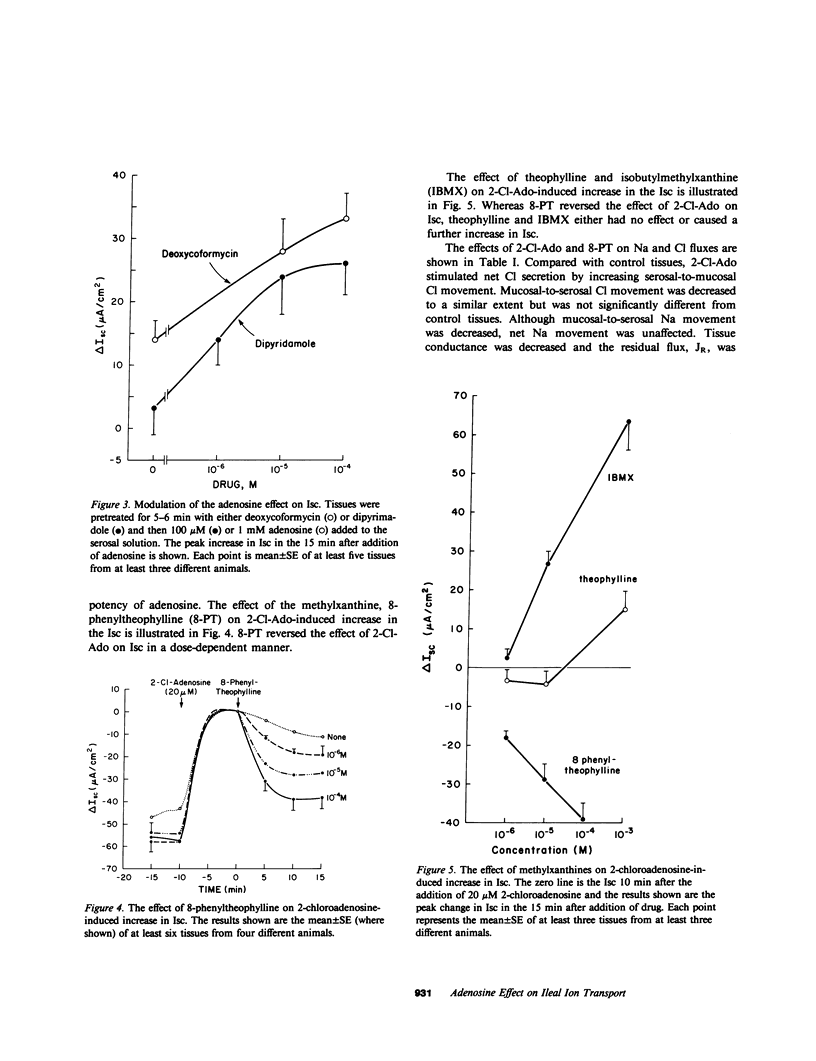
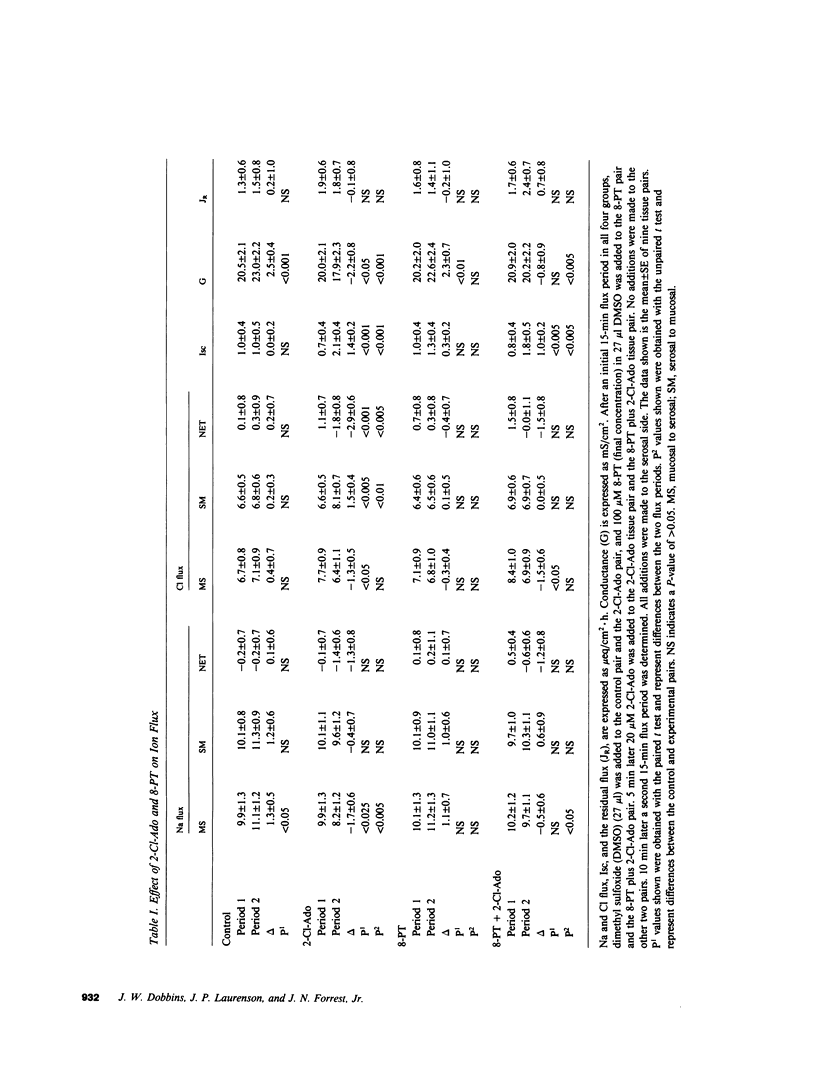
Adenosine receptors that modulate adenylate cyclase activity have been identified recently in a number of tissues. The purpose of these investigations was to determine the effect of adenosine on ion transport in rabbit ileum in vitro. Adenosine and some of its analogues were found to increase the short circuit current (Isc) and the order of potency was N-ethylcarboxamide-adenosine greater than or equal to 2-chloroadenosine greater than phenylisopropyladenosine greater than adenosine. Purine-intact adenosine analogues had no effect on Isc. The effect of adenosine on Isc was enhanced by deoxycoformycin, an adenosine deaminase inhibitor, and by dipyridamole, an adenosine uptake inhibitor. The increase in Isc induced by 2-chloroadenosine was partially reversed in a dose-dependent manner by 8-phenyltheophylline but not by theophylline or isobutylmethylxanthine. 2-Chloroadenosine increased cyclic AMP content, and stimulated net Cl secretion; these effects were partially blocked by 8-phenyltheophylline. These results suggest that there is an adenosine receptor on rabbit ileal mucosal cells that stimulates adenylate cyclase, which results in secondary active Cl secretion.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arch J. R., Newsholme E. A. The control of the metabolism and the hormonal role of adenosine. Essays Biochem. 1978;14:82–123. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bender A. S., Wu P. H., Phillis J. W. The characterization of [3H] adenosine uptake into rat cerebral cortical synaptosomes. J Neurochem. 1980 Sep;35(3):629–640. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1980.tb03702.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daly J. W. Adenosine receptors: targets for future drugs. J Med Chem. 1982 Mar;25(3):197–207. doi: 10.1021/jm00345a001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daly J. W., Bruns R. F., Snyder S. H. Adenosine receptors in the central nervous system: relationship to the central actions of methylxanthines. Life Sci. 1981 May 11;28(19):2083–2097. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(81)90614-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Field M. Ion transport in rabbit ileal mucosa. II. Effects of cyclic 3', 5'-AMP. Am J Physiol. 1971 Oct;221(4):992–997. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1971.221.4.992. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fox I. H., Kelley W. N. The role of adenosine and 2'-deoxyadenosine in mammalian cells. Annu Rev Biochem. 1978;47:655–686. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.47.070178.003255. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frizzell R. A., Field M., Schultz S. G. Sodium-coupled chloride transport by epithelial tissues. Am J Physiol. 1979 Jan;236(1):F1–F8. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1979.236.1.F1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerencser G. A., Armstrong W. M. Sodium transfer in bullfrog small intestine. Stimulation by exogenous ATP. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1972 Feb 11;255(2):663–674. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(72)90169-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harper J. F., Brooker G. Femtomole sensitive radioimmunoassay for cyclic AMP and cyclic GMP after 2'0 acetylation by acetic anhydride in aqueous solution. J Cyclic Nucleotide Res. 1975;1(4):207–218. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haslam R. J., Rosson G. M. Effects of adenosine on levels of adenosine cyclic 3',5'-monophosphate in human blood platelets in relation to adenosine incorporation and platelet aggregation. Mol Pharmacol. 1975 Sep;11(5):528–544. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kohn P. G., Newey H., Smyth D. H. The effect of adenosine triphosphate on the transmural potential in rat small intestine. J Physiol. 1970 May;208(1):203–220. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1970.sp009114. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Korman L. Y., Lemp G. F., Jackson M. J., Gardner J. D. Mechanism of action of ATP on intestinal epithelial cells. Cyclic AMP-mediated stimulation of active ion transport. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1982 Sep 13;721(1):47–54. doi: 10.1016/0167-4889(82)90022-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Londos C., Cooper D. M., Wolff J. Subclasses of external adenosine receptors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 May;77(5):2551–2554. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.5.2551. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Londos C., Wolff J. Two distinct adenosine-sensitive sites on adenylate cyclase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5482–5486. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5482. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olsson R. A., Davis C. J., Khouri E. M., Patterson R. E. Evidence for an adenosine receptor on the surface of dog coronary myocytes. Circ Res. 1976 Jul;39(1):93–98. doi: 10.1161/01.res.39.1.93. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olsson R. A., Snow J. A., Gentry M. K., Frick G. P. Adenosine uptake by canine heart. Circ Res. 1972 Nov;31(5):767–778. doi: 10.1161/01.res.31.5.767. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paterson A. R., Lau E. Y., Dahlig E., Cass C. E. A common basis for inhibition of nucleoside transport by dipyridamole and nitrobenzylthioinosine? Mol Pharmacol. 1980 Jul;18(1):40–44. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pichard A. L., Hanoune J., Kaplan J. C. Human brain and platelet cyclic adenosine 3',5'-monophosphate phosphodiesterases: different response to drugs. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1972 Aug 18;279(1):217–220. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(72)90258-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Plunkett W., Alexander L., Chubb S., Loo T. L. Comparison of the activity of 2'-deoxycoformycin and erythro-9-(2-hydroxy-3-nonyl)adenine in vivo. Biochem Pharmacol. 1979;28(2):201–206. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(79)90504-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schrader J., Nees S., Gerlach E. Evidence for a cell surface adenosine receptor on coronary myocytes and atrial muscle cells. Studies with an adenosine derivative of high molecular weight. Pflugers Arch. 1977 Jul 19;369(3):251–257. doi: 10.1007/BF00582192. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smellie F. W., Davis C. W., Daly J. W., Wells J. N. Alkylxanthines: inhibition of adenosine-elicited accumulation of cyclic AMP in brain slices and of brain phosphodiesterase activity. Life Sci. 1979 Jun 25;24(26):2475–2482. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(79)90458-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spinowitz B. S., Zadunaisky J. A. Action of adenosine on chloride active transport of isolated frog cornea. Am J Physiol. 1979 Aug;237(2):F121–F127. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1979.237.2.F121. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steiner A. L., Parker C. W., Kipnis D. M. Radioimmunoassay for cyclic nucleotides. I. Preparation of antibodies and iodinated cyclic nucleotides. J Biol Chem. 1972 Feb 25;247(4):1106–1113. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Turnheim K., Plank B., Kolassa N. Inhibition of adenosine uptake in human erythrocytes by adenosine-5'-carboxamides, xylosyladenine, dipyridamole, hexobendine, and p-nitrobenzylthioguanosine. Biochem Pharmacol. 1978;27(18):2191–2197. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(78)90076-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolff J., Cook G. H. Activation of steroidogenesis and adenylate cyclase by adenosine in adrenal and Leydig tumor cells. J Biol Chem. 1977 Jan 25;252(2):687–693. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Calker D., Müller M., Hamprecht B. Adenosine regulates via two different types of receptors, the accumulation of cyclic AMP in cultured brain cells. J Neurochem. 1979 Nov;33(5):999–1005. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1979.tb05236.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



