Abstract
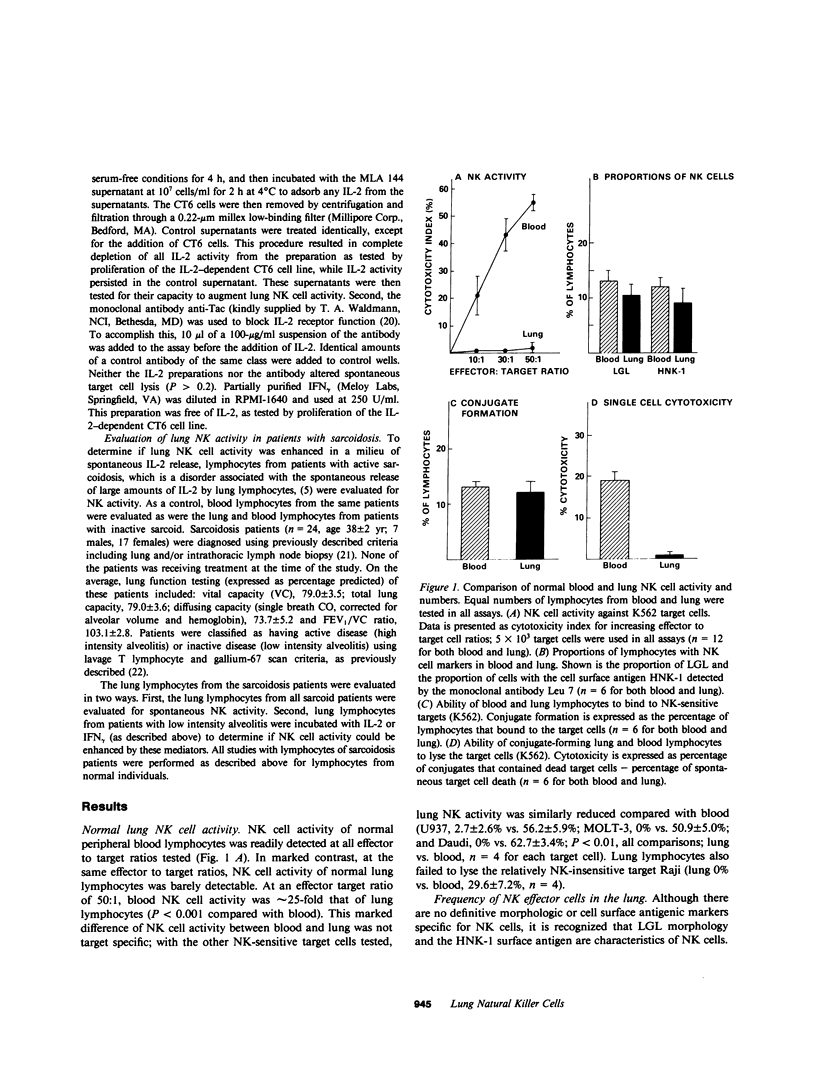
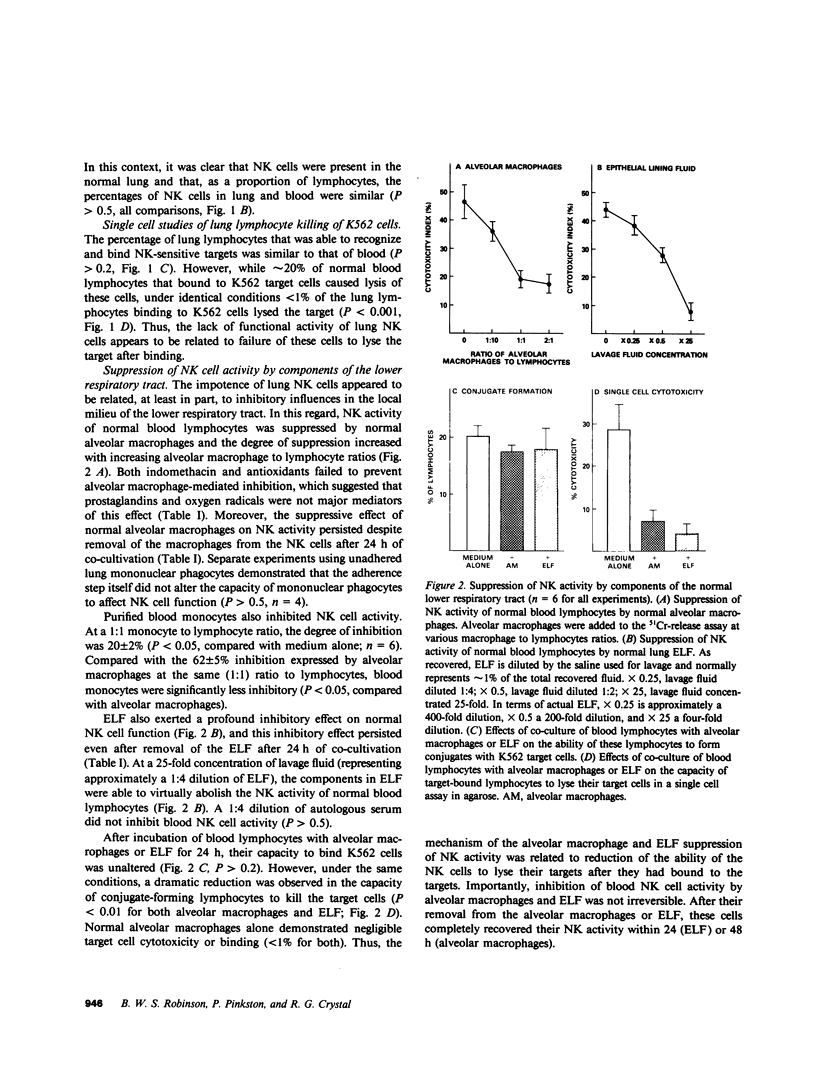
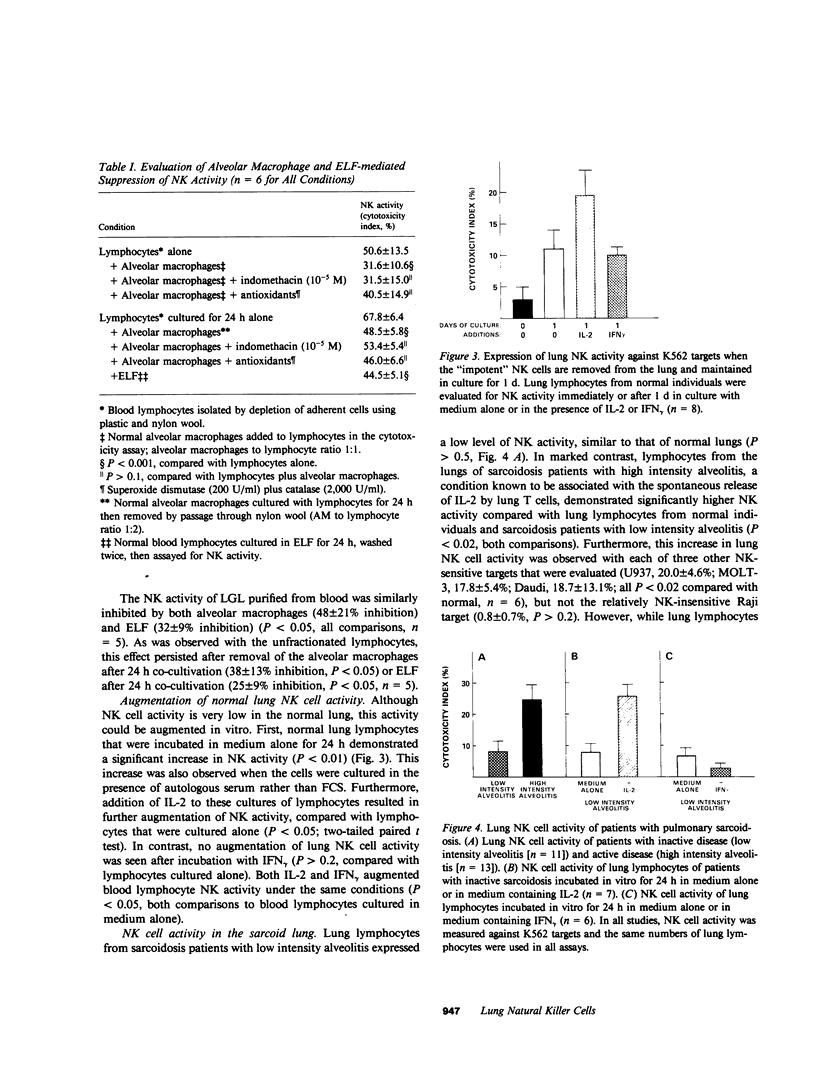
The lung is affected by disorders in which natural killer (NK) cells are thought to play an important defensive role. This study, however, demonstrated that normal lung lymphocytes actually express very little NK cell activity (P less than 0.001 compared with blood lymphocytes). This was true independent of the NK-sensitive target used (K562, U937, MOLT-3, or Daudi). This lack of lung lymphocyte NK activity occurred even though the proportions of lymphocytes in the normal lower respiratory tract with the morphology (large granular lymphocytes) and surface antigen markers of NK cells were similar to that of blood (P greater than 0.5). Although normal lung lymphocytes bound to known NK-sensitive targets, they did not lyse these cells (P less than 0.001 compared with blood), which suggested that the lack of lung NK cell activity resulted from a relative inability of lung NK cells to destroy their targets. While the mechanisms of this functional impotence of lung NK cells are not clear, normal human alveolar macrophages and lower respiratory tract epithelial lining fluid exerted a profound suppressive effect on blood NK cell activity (P less than 0.001 for both) by inhibiting their ability to lyse target cells after binding (P less than 0.001). Though impotent initially, when incubated for 24 h in medium alone, normal lung lymphocytes demonstrated markedly enhanced NK activity (P less than 0.02), which suggested that lung NK cells do have the potential to express NK activity. Interleukin-2 (IL-2) further augmented this effect (P less than 0.05), but gamma interferon did not (P greater than 0.2). Consistent with this observation, lung lymphocytes from patients with active sarcoidosis, a disease in which lung lymphocytes are spontaneously releasing IL-2, did express NK cell activity (P less than 0.01). These studies suggest that although NK cells are present in the normal lung, they are functionally inactive, due, at least in part, to local inhibitory influences. In the presence of IL-2, however, lung NK cell activity is expressed, which suggests that lung NK cell activity can be modulated.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abo T., Balch C. M. A differentiation antigen of human NK and K cells identified by a monoclonal antibody (HNK-1). J Immunol. 1981 Sep;127(3):1024–1029. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Abo T., Miller C. A., Balch C. M., Cooper M. D. Interleukin 2 receptor expression by activated HNK-1+ granular lymphocytes: a requirement for their proliferation. J Immunol. 1983 Oct;131(4):1822–1826. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bonavida B., Bradley T. P., Grimm E. A. Frequency determination of killer cells by a single-cell cytotoxic assay. Methods Enzymol. 1983;93:270–280. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(83)93049-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bordignon C., Villa F., Allavena P., Introna M., Biondi A., Avallone R., Mantovani A. Inhibition of natural killer activity by human bronchoalveolar macrophages. J Immunol. 1982 Aug;129(2):587–591. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bordignon C., Villa F., Vecchi A., Giavazzi R., Introna M., Avallone R., Mantovani A. Natural cytotoxic activity in human lungs. Clin Exp Immunol. 1982 Feb;47(2):437–444. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Depper J. M., Leonard W. J., Robb R. J., Waldmann T. A., Greene W. C. Blockade of the interleukin-2 receptor by anti-Tac antibody: inhibition of human lymphocyte activation. J Immunol. 1983 Aug;131(2):690–696. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Domzig W., Stadler B. M., Herberman R. B. Interleukin 2 dependence of human natural killer (NK) cell activity. J Immunol. 1983 Apr;130(4):1970–1973. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gadek J. E., Fells G. A., Zimmerman R. L., Rennard S. I., Crystal R. G. Antielastases of the human alveolar structures. Implications for the protease-antiprotease theory of emphysema. J Clin Invest. 1981 Oct;68(4):889–898. doi: 10.1172/JCI110344. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hefeneider S. H., Conlon P. J., Henney C. S., Gillis S. In vivo interleukin 2 administration augments the generation of alloreactive cytolytic T lymphocytes and resident natural killer cells. J Immunol. 1983 Jan;130(1):222–227. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henderson L. E., Hewetson J. F., Hopkins R. F., 3rd, Sowder R. C., Neubauer R. H., Rabin H. A rapid, large scale purification procedure for gibbon interleukin 2. J Immunol. 1983 Aug;131(2):810–815. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henney C. S., Kuribayashi K., Kern D. E., Gillis S. Interleukin-2 augments natural killer cell activity. Nature. 1981 May 28;291(5813):335–338. doi: 10.1038/291335a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herberman R. B. Natural killer (NK) cells and their possible roles in resistance against disease. Clin Immunol Rev. 1981;1(1):1–65. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoidal J. R., Fox R. B., LeMarbe P. A., Perri R., Repine J. E. Altered oxidative metabolic responses in vitro of alveolar macrophages from asymptomatic cigarette smokers. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1981 Jan;123(1):85–89. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1981.123.1.85. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hooks J. J., Moutsopoulos H. M., Geis S. A., Stahl N. I., Decker J. L., Notkins A. L. Immune interferon in the circulation of patients with autoimmune disease. N Engl J Med. 1979 Jul 5;301(1):5–8. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197907053010102. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hudig D., Haverty T., Fulcher C., Redelman D., Mendelsohn J. Inhibition of human natural cytotoxicity by macromolecular antiproteases. J Immunol. 1981 Apr;126(4):1569–1574. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunninghake G. W., Crystal R. G. Pulmonary sarcoidosis: a disorder mediated by excess helper T-lymphocyte activity at sites of disease activity. N Engl J Med. 1981 Aug 20;305(8):429–434. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198108203050804. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunninghake G. W., Gadek J. E., Kawanami O., Ferrans V. J., Crystal R. G. Inflammatory and immune processes in the human lung in health and disease: evaluation by bronchoalveolar lavage. Am J Pathol. 1979 Oct;97(1):149–206. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson H. M., Farrar W. L. The role of a gamma interferon-like lymphokine in the activation of T cells for expression of interleukin 2 receptors. Cell Immunol. 1983 Jan;75(1):154–159. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(83)90314-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keogh B. A., Hunninghake G. W., Line B. R., Crystal R. G. The alveolitis of pulmonary sarcoidosis. Evaluation of natural history and alveolitis-dependent changes in lung function. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1983 Aug;128(2):256–265. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1983.128.2.256. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koren H. S., Anderson S. J., Fischer D. G., Copeland C. S., Jensen P. J. Regulation of human natural killing. I. The role of monocytes, interferon, and prostaglandins. J Immunol. 1981 Nov;127(5):2007–2013. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Linker-Israeli M., Bakke A. C., Kitridou R. C., Gendler S., Gillis S., Horwitz D. A. Defective production of interleukin 1 and interleukin 2 in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE). J Immunol. 1983 Jun;130(6):2651–2655. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NIH conference. Pulmonary sarcoidosis: a disease characterized and perpetuated by activated lung T-lymphocytes. Ann Intern Med. 1981 Jan;94(1):73–94. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-94-1-73. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neighbour P. A., Grayzel A. I., Miller A. E. Endogenous and interferon-augmented natural killer cell activity of human peripheral blood mononuclear cells in vitro. Studies of patients with multiple sclerosis, systemic lupus erythematosus or rheumatoid arthritis. Clin Exp Immunol. 1982 Jul;49(1):11–21. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pick E., Keisari Y. A simple colorimetric method for the measurement of hydrogen peroxide produced by cells in culture. J Immunol Methods. 1980;38(1-2):161–170. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(80)90340-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pinkston P., Bitterman P. B., Crystal R. G. Spontaneous release of interleukin-2 by lung T lymphocytes in active pulmonary sarcoidosis. N Engl J Med. 1983 Apr 7;308(14):793–800. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198304073081401. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rabin H., Hopkins R. F., 3rd, Ruscetti F. W., Neubauer R. H., Brown R. L., Kawakami T. G. Spontaneous release of a factor with properties of T cell growth factor from a continuous line of primate tumor T cells. J Immunol. 1981 Nov;127(5):1852–1856. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reynolds C. W., Timonen T., Herberman R. B. Natural killer (NK) cell activity in the rat. I. Isolation and characterization of the effector cells. J Immunol. 1981 Jul;127(1):282–287. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roder J. C., Ahrlund-Richter L., Jondal M. Target-effector interaction in the human and murine natural killer system: specificity and xenogeneic reactivity of the solubilized natural killer-target structure complex and its loss in a somatic cell hybrid. J Exp Med. 1979 Sep 19;150(3):471–481. doi: 10.1084/jem.150.3.471. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roder J. C., Pross H. F. The biology of the human natural killer cell. J Clin Immunol. 1982 Oct;2(4):249–263. doi: 10.1007/BF00915064. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rook A. H., Masur H., Lane H. C., Frederick W., Kasahara T., Macher A. M., Djeu J. Y., Manischewitz J. F., Jackson L., Fauci A. S. Interleukin-2 enhances the depressed natural killer and cytomegalovirus-specific cytotoxic activities of lymphocytes from patients with the acquired immune deficiency syndrome. J Clin Invest. 1983 Jul;72(1):398–403. doi: 10.1172/JCI110981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rubin P., Pross H. F., Roder J. C. Studies of human natural killer cells. II. Analysis at the single cell level. J Immunol. 1982 Jun;128(6):2553–2558. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seaman W. E., Gindhart T. D., Blackman M. A., Dalal B., Talal N., Werb Z. Suppression of natural killing in vitro by monocytes and polymorphonuclear leukocytes: requirement for reactive metabolites of oxygen. J Clin Invest. 1982 Apr;69(4):876–888. doi: 10.1172/JCI110527. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Si L., Whiteside T. L. Tissue distribution of human NK cells studied with anti-Leu-7 monoclonal antibody. J Immunol. 1983 May;130(5):2149–2155. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sulica A., Gherman M., Galatiuc C., Manciulea M., Herberman R. B. Inhibition of human natural killer cell activity by cytophilic immunoglobulin G. J Immunol. 1982 Mar;128(3):1031–1036. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Timonen T., Ortaldo J. R., Herberman R. B. Characteristics of human large granular lymphocytes and relationship to natural killer and K cells. J Exp Med. 1981 Mar 1;153(3):569–582. doi: 10.1084/jem.153.3.569. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Timonen T., Saksela E. Isolation of human NK cells by density gradient centrifugation. J Immunol Methods. 1980;36(3-4):285–291. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(80)90133-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ullberg M., Jondal M. Recycling and target binding capacity of human natural killer cells. J Exp Med. 1981 Mar 1;153(3):615–628. doi: 10.1084/jem.153.3.615. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- West W. H., Cannon G. B., Kay H. D., Bonnard G. D., Herberman R. B. Natural cytotoxic reactivity of human lymphocytes against a myeloid cell line: characterization of effector cells. J Immunol. 1977 Jan;118(1):355–361. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]