Abstract
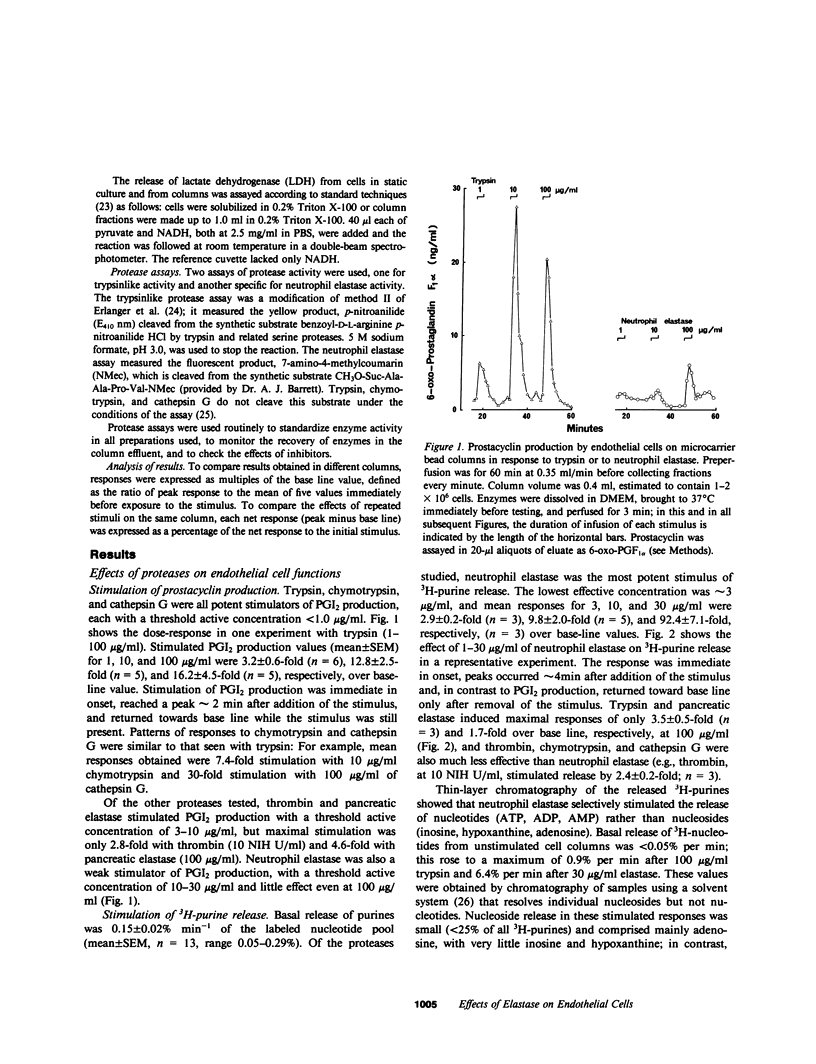
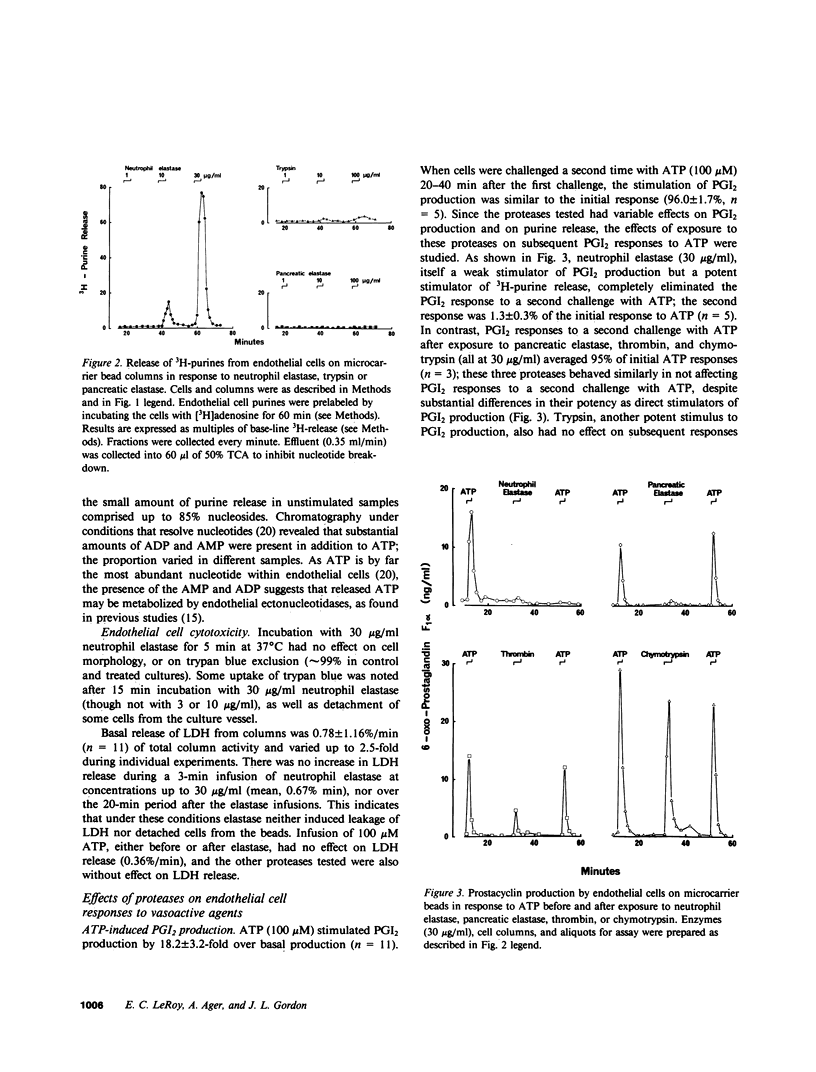
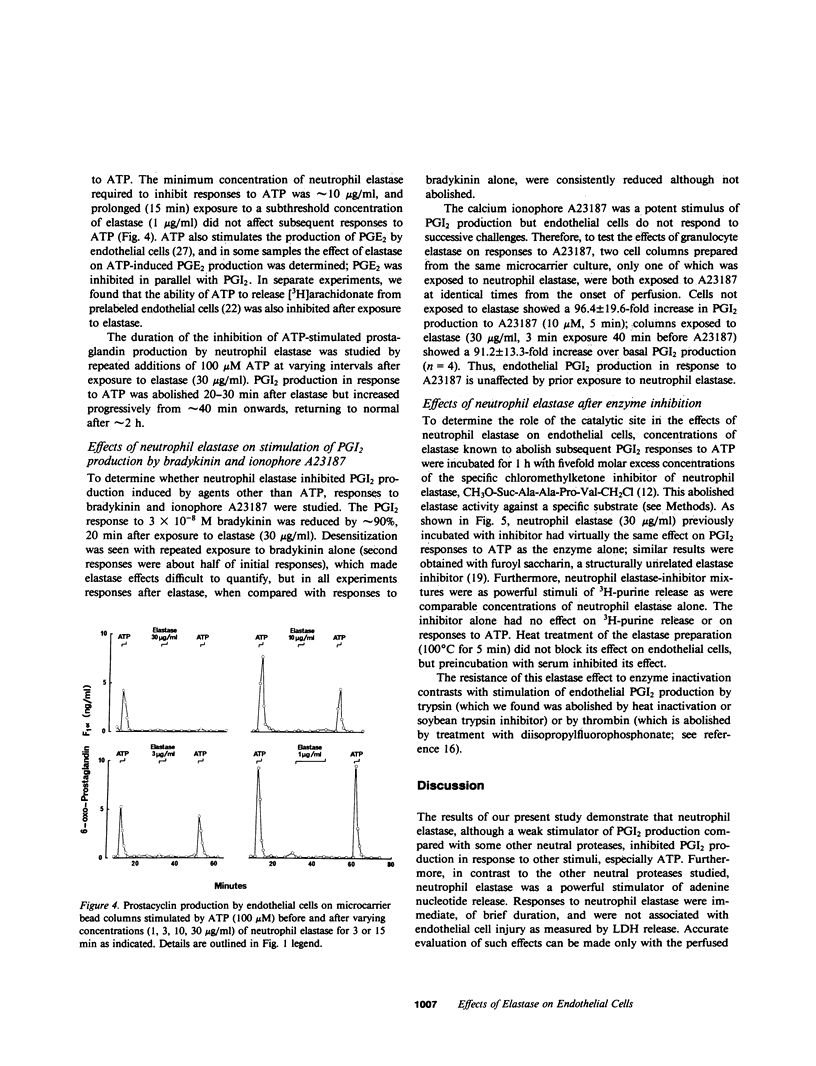
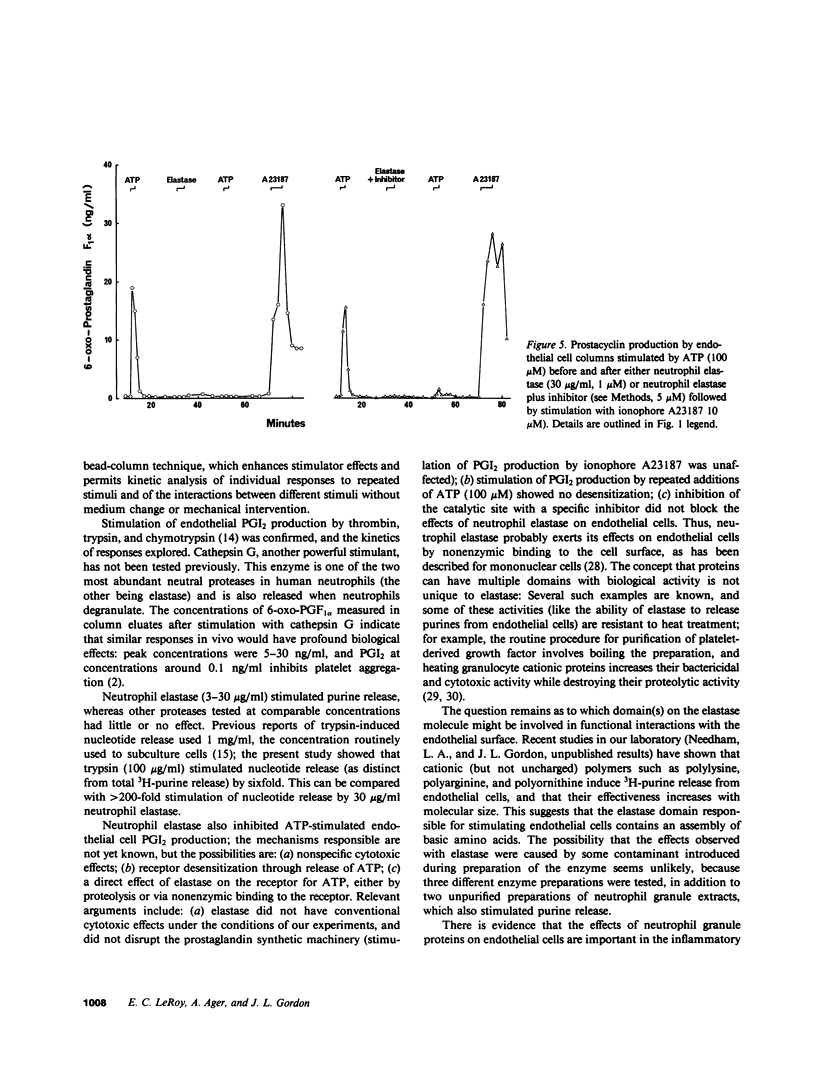
The effects of neutrophil elastase on endothelial prostacyclin (PGI2) production, nucleotide release, and responsiveness to vasoactive agents were compared with the effects of cathepsin G (the other major neutral protease of neutrophils), pancreatic elastase, trypsin, chymotrypsin, and thrombin. PGI2 production by pig aortic endothelial cells cultured on microcarrier beads and perfused in columns was stimulated in a dose-dependent manner by trypsin, chymotrypsin, and cathepsin G (1-100 micrograms/ml for 3 min). Thrombin, while active at low concentrations (0.1-10 National Institutes of Health U/ml), induced smaller responses. Neutrophil and pancreatic elastase had little or no effect on PGI2 production. Dose-dependent, selective release of adenine nucleotides was induced by neutrophil elastase (3-30 micrograms/ml). The other proteases were much less active; for example, trypsin (100 micrograms/ml) induced a response only approximately 5% as great as did 30 micrograms/ml neutrophil elastase. After exposure to 30 micrograms/ml neutrophil elastase, cells did not exhibit the characteristic burst of PGI2 production in response to extracellular ATP; responsiveness gradually returned after 40-120 min. This effect was not seen with the other proteases. Elastase partly inhibited responses to bradykinin and had no effect on PGI2 production that was stimulated by ionophore A23187. There was no evidence of cytotoxicity, as measured by release of lactate dehydrogenase. Neutrophil degranulation can generate concentrations of elastase and cathepsin G comparable with those tested in the present study, and the effects of these enzymes on endothelial function lead us to suggest that they may play a role in vasoregulation and vascular pathology.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ager A., Gordon J. L. Differential effects of hydrogen peroxide on indices of endothelial cell function. J Exp Med. 1984 Feb 1;159(2):592–603. doi: 10.1084/jem.159.2.592. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ager A., Gordon J. L., Moncada S., Pearson J. D., Salmon J. A., Trevethick M. A. Effects of isolation and culture on prostaglandin synthesis by porcine aortic endothelial and smooth muscle cells. J Cell Physiol. 1982 Jan;110(1):9–16. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041100103. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ashe B. M., Clark R. L., Jones H., Zimmerman M. Selective inhibition of human leukocyte elastase and bovine alpha-chymotrypsin by novel heterocycles. J Biol Chem. 1981 Nov 25;256(22):11603–11606. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barrett A. J. Leukocyte elastase. Methods Enzymol. 1981;80(Pt 100):581–588. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(81)80046-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beesley J. E., Pearson J. D., Carleton J. S., Hutchings A., Gordon J. L. Interaction of leukocytes with vascular cells in culture. J Cell Sci. 1978 Oct;33:85–101. doi: 10.1242/jcs.33.1.85. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Campbell E. J. Human leukocyte elastase, cathepsin G, and lactoferrin: family of neutrophil granule glycoproteins that bind to an alveolar macrophage receptor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Nov;79(22):6941–6945. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.22.6941. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Campbell E. J., Senior R. M., McDonald J. A., Cox D. L. Proteolysis by neutrophils. Relative importance of cell-substrate contact and oxidative inactivation of proteinase inhibitors in vitro. J Clin Invest. 1982 Oct;70(4):845–852. doi: 10.1172/JCI110681. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark R. A., Olsson I., Klebanoff S. J. Cytotoxicity for tumor cells of cationic proteins from human neutrophil granules. J Cell Biol. 1976 Sep;70(3):719–723. doi: 10.1083/jcb.70.3.719. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cocks T. M., Angus J. A. Endothelium-dependent relaxation of coronary arteries by noradrenaline and serotonin. Nature. 1983 Oct 13;305(5935):627–630. doi: 10.1038/305627a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Mey J. G., Vanhoutte P. M. Heterogeneous behavior of the canine arterial and venous wall. Importance of the endothelium. Circ Res. 1982 Oct;51(4):439–447. doi: 10.1161/01.res.51.4.439. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Mey J. G., Vanhoutte P. M. Role of the intima in cholinergic and purinergic relaxation of isolated canine femoral arteries. J Physiol. 1981 Jul;316:347–355. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1981.sp013792. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ERLANGER B. F., KOKOWSKY N., COHEN W. The preparation and properties of two new chromogenic substrates of trypsin. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1961 Nov;95:271–278. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(61)90145-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Furchgott R. F., Zawadzki J. V. The obligatory role of endothelial cells in the relaxation of arterial smooth muscle by acetylcholine. Nature. 1980 Nov 27;288(5789):373–376. doi: 10.1038/288373a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gordon J. L., Martin W. Endothelium-dependent relaxation of the pig aorta: relationship to stimulation of 86Rb efflux from isolated endothelial cells. Br J Pharmacol. 1983 Jun;79(2):531–541. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1983.tb11028.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gordon J. L., Martin W. Stimulation of endothelial prostacyclin production plays no role in endothelium-dependent relaxation of the pig aorta. Br J Pharmacol. 1983 Sep;80(1):179–186. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1983.tb11064.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harlan J. M., Killen P. D., Harker L. A., Striker G. E., Wright D. G. Neutrophil-mediated endothelial injury in vitro mechanisms of cell detachment. J Clin Invest. 1981 Dec;68(6):1394–1403. doi: 10.1172/JCI110390. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henson P. M., Larsen G. L., Webster R. O., Mitchell B. C., Goins A. J., Henson J. E. Pulmonary microvascular alterations and injury induced by complement fragments: synergistic effect of complement activation, neutrophil sequestration, and prostaglandins. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1982;384:287–300. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1982.tb21379.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Issekutz A. C., Movat K. W., Movat H. Z. Enhanced vascular permeability and haemorrhage-inducing activity of rabbit C5ades arg: probable role of polymorphonuclear leucocyte lysosomes. Clin Exp Immunol. 1980 Sep;41(3):512–520. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lollar P., Owen W. G. Active-site-dependent, thrombin-induced release of adenine nucleotides from cultured human endothelial cells. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1981;370:51–56. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1981.tb29720.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Needleman P., Minkes M. S., Douglas J. R., Jr Stimulation of prostaglandin biosynthesis by adenine nucleotides. Profile of prostaglandin release by perfused organs. Circ Res. 1974 Apr;34(4):455–460. doi: 10.1161/01.res.34.4.455. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Odeberg H., Olsson I. Antibacterial activity of cationic proteins from human granulocytes. J Clin Invest. 1975 Nov;56(5):1118–1124. doi: 10.1172/JCI108186. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pearson J. D., Carleton J. S., Hutchings A., Gordon J. L. Uptake and metabolism of adenosine by pig aortic endothelial and smooth-muscle cells in culture. Biochem J. 1978 Feb 15;170(2):265–271. doi: 10.1042/bj1700265. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pearson J. D., Carleton J. S., Hutchings A. Prostacyclin release stimulated by thrombin or bradykinin in porcine endothelial cells cultured from aorta and umbilical vein. Thromb Res. 1983 Jan 15;29(2):115–124. doi: 10.1016/0049-3848(83)90133-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pearson J. D., Gordon J. L. Vascular endothelial and smooth muscle cells in culture selectively release adenine nucleotides. Nature. 1979 Oct 4;281(5730):384–386. doi: 10.1038/281384a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pearson J. D., Slakey L. L., Gordon J. L. Stimulation of prostaglandin production through purinoceptors on cultured porcine endothelial cells. Biochem J. 1983 Jul 15;214(1):273–276. doi: 10.1042/bj2140273. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Powers J. C., Gupton B. F., Harley A. D., Nishino N., Whitley R. J. Specificity of porcine pancreatic elastase, human leukocyte elastase and cathepsin G. Inhibition with peptide chloromethyl ketones. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1977 Nov 23;485(1):156–166. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(77)90203-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pull I., McIlwain H. Metabolism of ( 14 C)adenine and derivatives by cerebral tissues, superfused and electrically stimulated. Biochem J. 1972 Feb;126(4):965–973. doi: 10.1042/bj1260965. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saklatvala J., Barrett A. J. Identification of proteinases in rheumatoid synovium. Detection of leukocyte elastase cathepsin G and another serine proteinase. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1980 Sep 9;615(1):167–177. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(80)90020-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartzman M., Raz A. Purinergic vs peptidergic stimulation of lipolysis and prostaglandin generation in the perfused rabbit kidney. Biochem Pharmacol. 1982 Aug 1;31(15):2453–2458. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(82)90053-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WROBLEWSKI F., LADUE J. S. Lactic dehydrogenase activity in blood. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1955 Oct;90(1):210–213. doi: 10.3181/00379727-90-21985. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weksler B. B., Ley C. W., Jaffe E. A. Stimulation of endothelial cell prostacyclin production by thrombin, trypsin, and the ionophore A 23187. J Clin Invest. 1978 Nov;62(5):923–930. doi: 10.1172/JCI109220. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weksler B. B., Marcus A. J., Jaffe E. A. Synthesis of prostaglandin I2 (prostacyclin) by cultured human and bovine endothelial cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Sep;74(9):3922–3926. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.9.3922. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



