Abstract
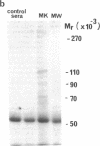
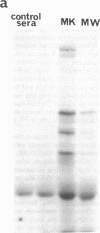
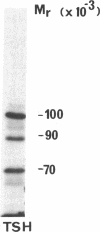
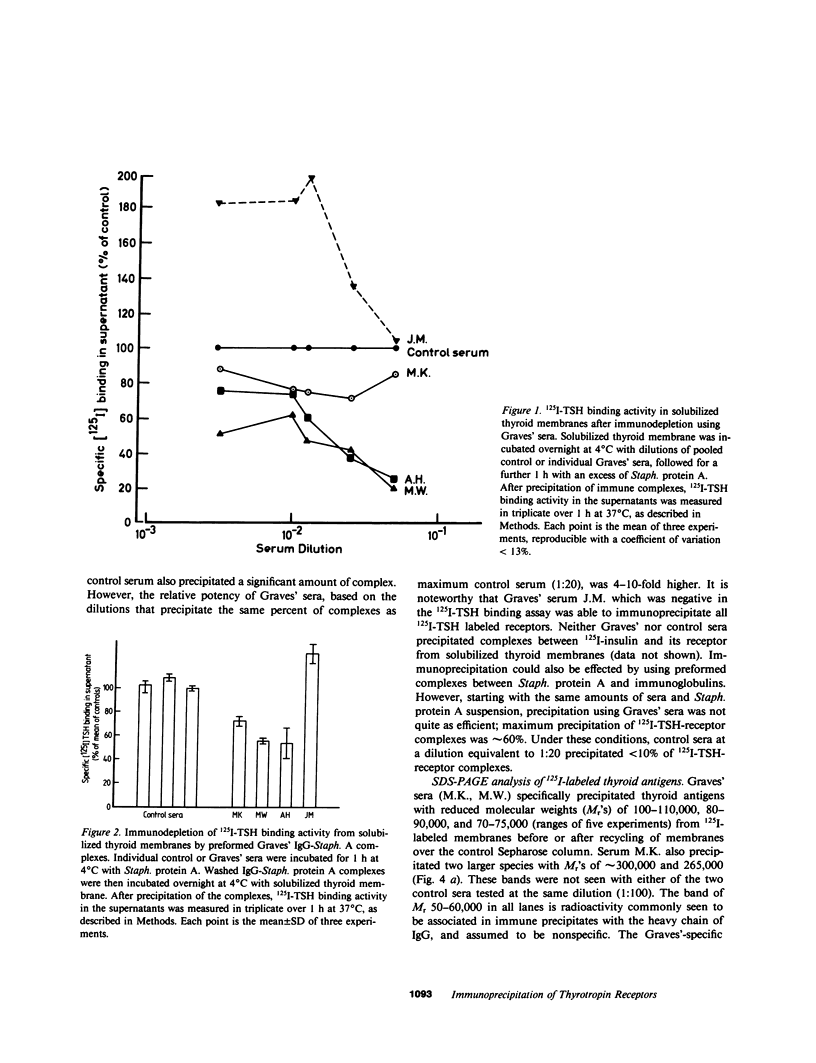
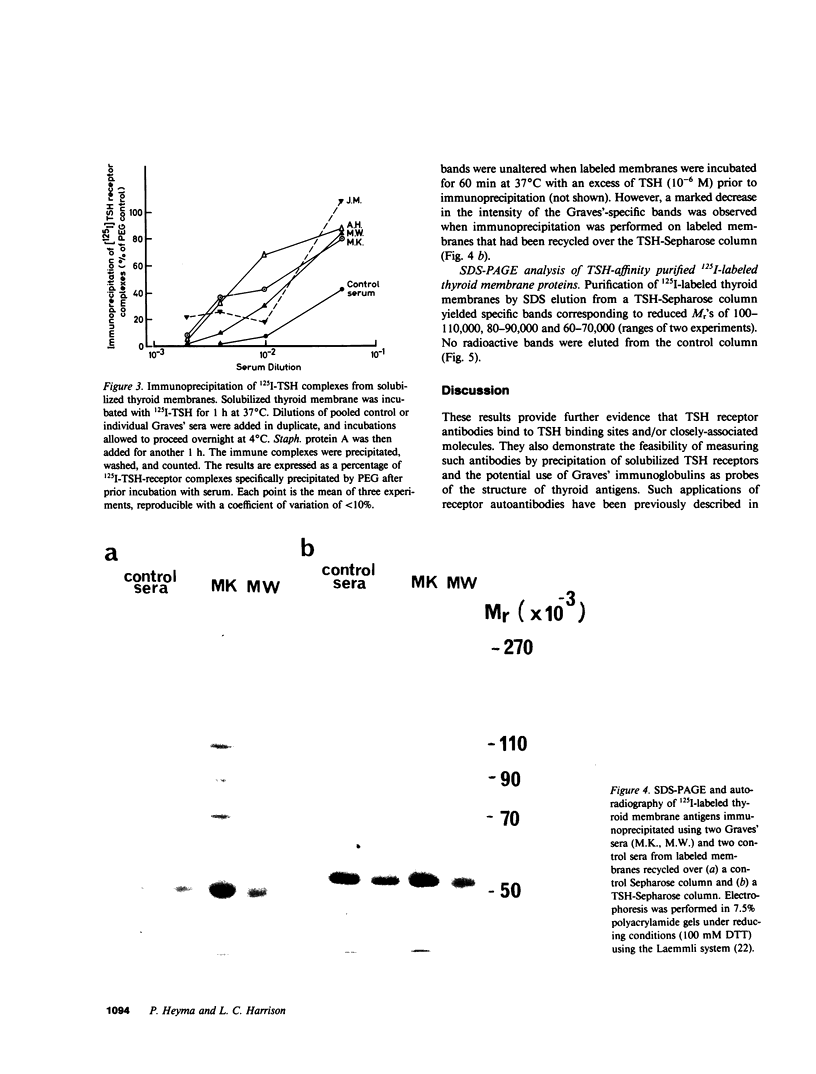
The thyrotropin (TSH) receptor is a putative target for autoantibodies in Graves' hyperthyroidism and therefore, should be capable of being identified, isolated, and structurally characterized by immunological means. To this end, four sera from patients with hyperthyroidism, three of which inhibited the binding of 125I-TSH to Triton-solubilized human thyroid membranes, were used to isolate TSH receptors by immunoprecipitation. To account for an effect of TSH binding or receptor occupancy on the ability of Graves' immunoglobulins to precipitate TSH receptors, two approaches were taken: (a) specific 125I-TSH binding activity was measured after solubilized thyroid membranes had been incubated with Graves' sera followed by precipitation with Staphylococcus protein A ("receptor depletion"); (b) TSH binding sites were labeled with 125I-TSH and the complexes were precipitated using Graves' sera and Staphylococcus protein A ("receptor precipitation"). The three sera which inhibited 125I-TSH binding depleted 125I-TSH binding activity between 30-80%. Preformed complexes between Staphylococcus protein A and immunoglobulins in these sera were also able to deplete 125I-TSH binding activity. However, after receptor depletion, the one serum that did not inhibit 125I-TSH binding was associated with a significant increase in 125I-TSH binding. All four sera specifically precipitated 80-100% of receptors identified by prelabeling with 125I-TSH. The dilutions of sera that precipitated 50% of 125I-TSH-receptor complexes ranged from 1:150-1:20. Complexes were partially precipitated by high concentrations of control sera (1:20), but the relative potency of control sera was at least fourfold less than Graves' sera. Immunoprecipitates of 125I-labeled thyroid membranes were analysed by sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis and autoradiography to reveal Graves'-specific bands of reduced molecular weights of 100-110,000, 80-90,000, and 70-75,000. These bands were similar to those obtained from 125I-labeled thyroid membranes purified by TSH affinity chromatography. Thus, Graves' immunoglobulins: (a) precipitate unoccupied and occupied TSH receptors, (b) in one case, neither inhibit binding nor immunodeplete the unoccupied receptor but immunoprecipitate 125I-TSH-receptor complexes, suggesting that binding of TSH may initiate an interaction between the binding site and a separate immunoreactive molecule, and (c) identify the molecular structure of Graves' autoantigens, putatively, the TSH receptor.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Beall G. N., Chopra I. J., Solomon D. H., Kruger S. R. Serum protein inhibition of thyrotropin binding to human thyroid tissue. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1978 Nov;47(5):967–973. doi: 10.1210/jcem-47-5-967. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(76)90527-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown R. S., Kertiles L. P., Reichlin S. Partial purification and characterization of thyrotropin binding inhibitory immunoglobulins from normal human plasma. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1983 Jan;56(1):156–163. doi: 10.1210/jcem-56-1-156. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Czarnocka B., Nauman J., Adler G., Kiełczyński W. Solubilization and partial characterization of thyroid membrane TSH binding proteins. Acta Endocrinol (Copenh) 1979 Nov;92(3):512–521. doi: 10.1530/acta.0.0920512. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Etienne-Decerf J., Winand R. J. A sensitive technique for determination of thyroid-stimulating immunoglobulin (TSI) in unfractionated serum. Clin Endocrinol (Oxf) 1981 Jan;14(1):83–91. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2265.1981.tb00368.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harrison L. C., Kahn C. R. Autoantibodies to the insulin receptor: clinical significance and experimental applications. Prog Clin Immunol. 1980;4:107–125. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hinds W. E., Takai N., Rapoport B., Filetti S., Clark O. H. Thyroid-stimulating immunoglobulin bioassay using cultured human thyroid cells. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1981 Jun;52(6):1204–1210. doi: 10.1210/jcem-52-6-1204. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hubbard A. L., Cohn Z. A. The enzymatic iodination of the red cell membrane. J Cell Biol. 1972 Nov;55(2):390–405. doi: 10.1083/jcb.55.2.390. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iida Y., Konishi J., Kasagi K., Ikekubo K., Kuma K., Torizuka K. Characterization of triton-solubilized TSH receptors from human thyroid plasma membranes. Acta Endocrinol (Copenh) 1981 Sep;98(1):50–56. doi: 10.1530/acta.0.0980050. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KRISS J. P., PLESHAKOV V., CHIEN J. R. ISOLATION AND IDENTIFICATION OF THE LONG-ACTING THYROID STIMULATOR AND ITS RELATION TO HYPERTHYROIDISM AND CIRCUMSCRIBED PRETIBIAL MYXEDEMA. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1964 Oct;24:1005–1028. doi: 10.1210/jcem-24-10-1005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karlsson F. A., Dahlberg P. A., Wålinder O. Activation of membrane-bound adenylcyclase by thyroid stimulating antibodies. Acta Endocrinol (Copenh) 1981 May;97(1):60–66. doi: 10.1530/acta.0.0970060. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kessler S. W. Rapid isolation of antigens from cells with a staphylococcal protein A-antibody adsorbent: parameters of the interaction of antibody-antigen complexes with protein A. J Immunol. 1975 Dec;115(6):1617–1624. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kleinmann R. E., Braverman L. E., Vagenakis A. G., Butcher R. W., Clark R. B. A new method for measurement of human thyroid-stimulating immunoglobulins. J Lab Clin Med. 1980 Apr;95(4):581–589. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kohn L. D., Valente W. A., Laccetti P., Cohen J. L., Aloj S. M., Grollman E. F. Multicomponent structure of the thyrotropin receptor: relationship to Graves' disease. Life Sci. 1983 Jan 3;32(1-2):15–30. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(83)90170-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koizumi Y., Zakarija M., McKenzie J. M. Solubilization, purification, and partial characterization of thyrotropin receptor from bovine and human thyroid glands. Endocrinology. 1982 Apr;110(4):1381–1391. doi: 10.1210/endo-110-4-1381. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindstrom J. Immunological studies of acetylcholine receptors. J Supramol Struct. 1976;4(3):389–403. doi: 10.1002/jss.400040310. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manley S. W., Bourke J. R., Hawker R. W. The thyrotrophin receptor in guinea-pig thyroid homogenate: interaction with the long-acting thyroid stimulator. J Endocrinol. 1974 Jun;61(3):437–445. doi: 10.1677/joe.0.0610437. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manley S. W., Knight A., Adams D. D. The thyrotrophin receptor. Springer Semin Immunopathol. 1982;5(4):413–431. doi: 10.1007/BF01857428. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKenzie J. M., Zakarija M. A reconsideration of a thyroid-stimulating immunoglobulin as the cause of hyperthyroidism in Graves' disease. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1976 Apr;42(4):778–781. doi: 10.1210/jcem-42-4-778. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKenzie J. M., Zakarija M. Pathogenesis of neonatal Graves' disease. J Endocrinol Invest. 1978 Apr;1(2):183–189. doi: 10.1007/BF03350370. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKenzie J. M., Zakarija M., Sato A. Humoral immunity in Graves' disease. Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1978 Mar;7(1):31–45. doi: 10.1016/s0300-595x(78)80034-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pekonen F., Weintraub B. D. Thyrotropin receptors on bovine thyroid membranes: two types with different affinities and specificities. Endocrinology. 1979 Aug;105(2):352–359. doi: 10.1210/endo-105-2-352. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rickards C., Buckland P., Smith B. R., Hall R. The interaction of Graves' IgG with the thyrotrophin receptor. FEBS Lett. 1981 May 5;127(1):17–21. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(81)80330-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rodbell M. The role of hormone receptors and GTP-regulatory proteins in membrane transduction. Nature. 1980 Mar 6;284(5751):17–22. doi: 10.1038/284017a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shewring G., Smith B. R. An improved radioreceptor assay for TSH receptor antibodies. Clin Endocrinol (Oxf) 1982 Oct;17(4):409–417. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2265.1982.tb01607.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith B. R., Hall R. Thyroid-stimulating immunoglobulins in Graves' disease. Lancet. 1974 Aug 24;2(7878):427–431. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(74)91815-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Valente W. A., Vitti P., Yavin Z., Yavin E., Rotella C. M., Grollman E. F., Toccafondi R. S., Kohn L. D. Monoclonal antibodies to the thyrotropin receptor: stimulating and blocking antibodies derived from the lymphocytes of patients with Graves disease. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Nov;79(21):6680–6684. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.21.6680. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Bruin T. W., van der Heide D. Anti-thyrotrophin receptor antibodies in Graves' disease as demonstrated directly by immunoprecipitation assay. Acta Endocrinol (Copenh) 1983 Jan;102(1):49–56. doi: 10.1530/acta.0.1020049. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]