Abstract
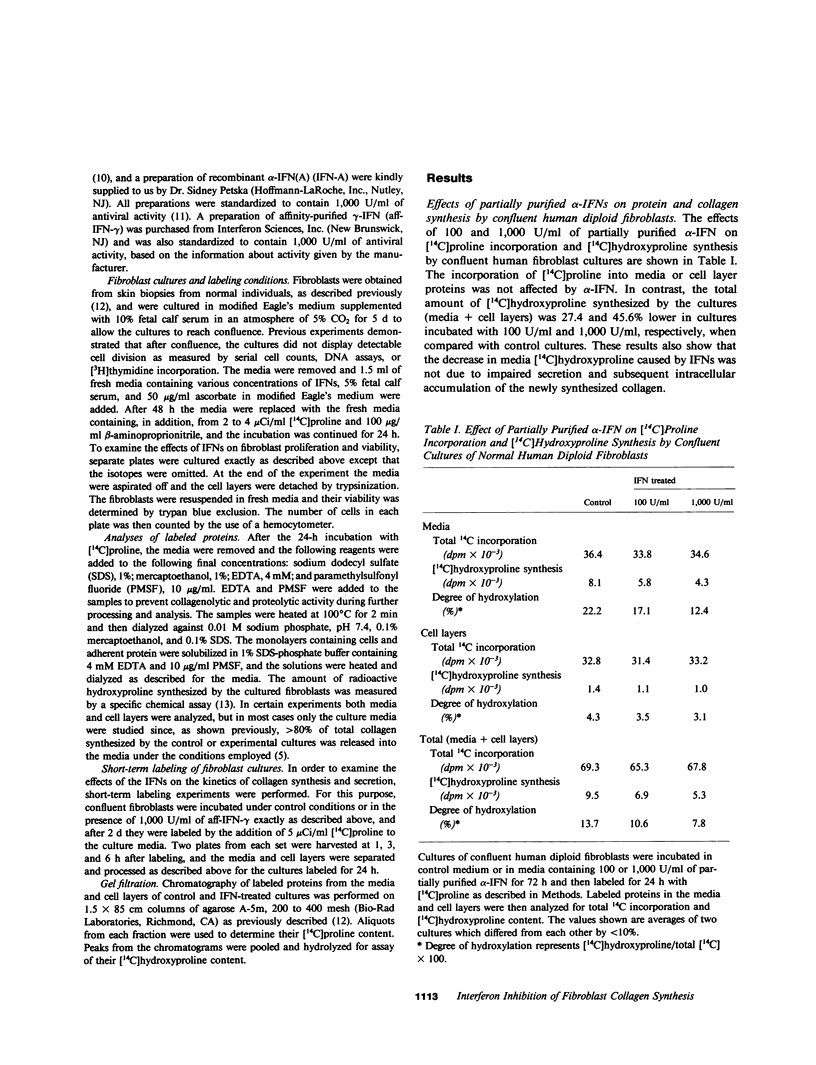
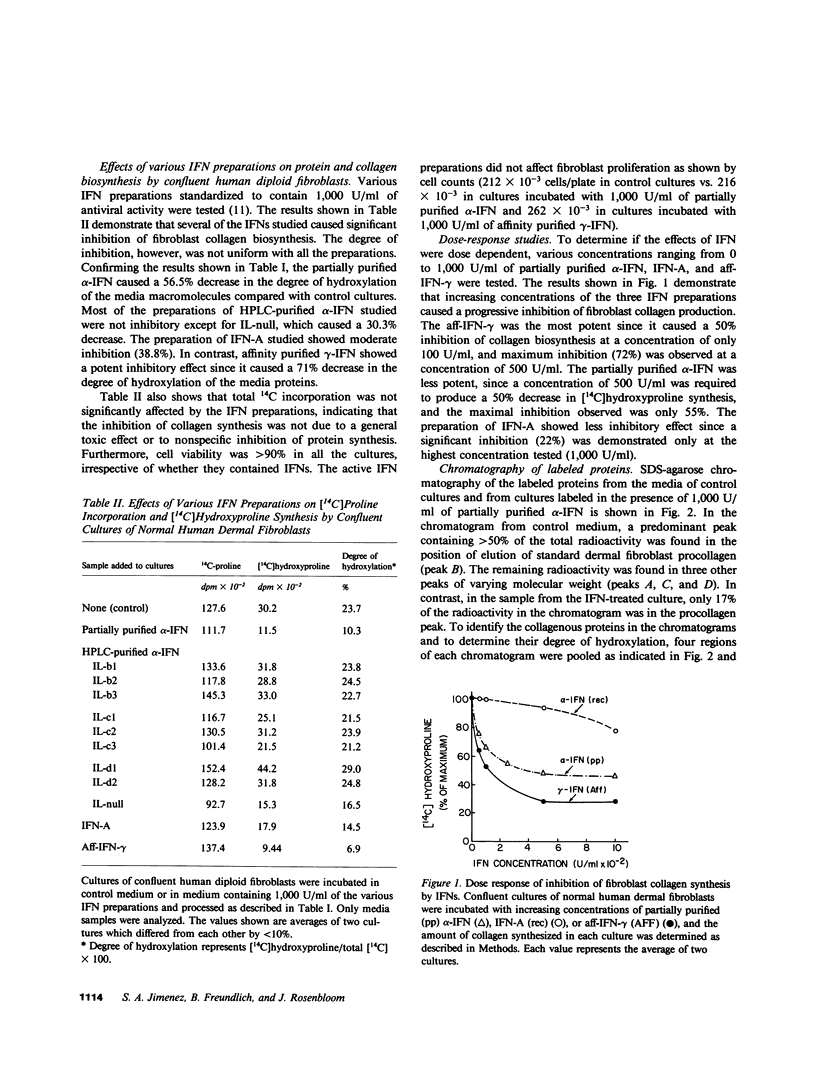
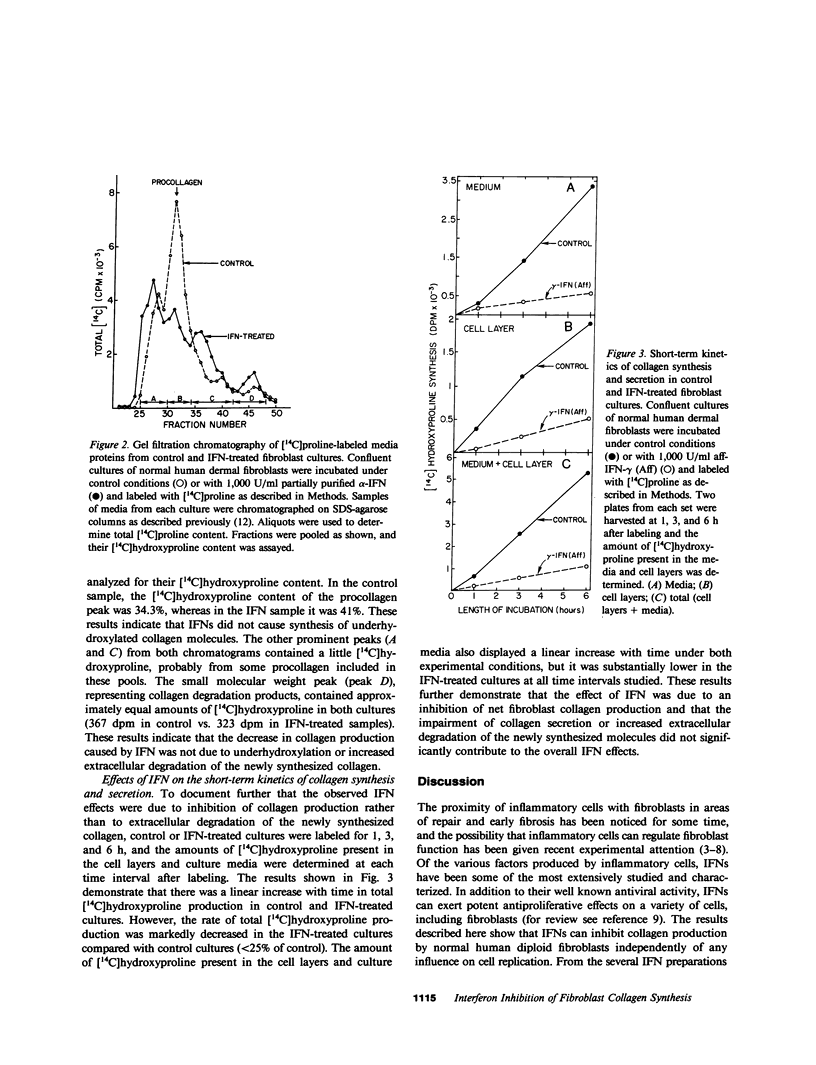
The effects of alpha- and gamma-interferons (IFNs) on collagen production by confluent human diploid fibroblasts in culture were examined. It was found that partially purified alpha-IFNs and affinity purified gamma-IFNs caused greater than 50% inhibition of collagen synthesis by these cells independently of their effect on cell proliferation. Recombinant alpha-IFNs showed a similar effect (38.8% inhibition), indicating that collagen synthesis inhibition was a constitutive property of IFNs. Collagen synthesis inhibition by IFNs was concentration dependent. Gel filtration chromatography of the newly synthesized proteins from the media of fibroblasts incubated with partially purified alpha-IFNs demonstrated a selective depression of molecules eluting in the region of procollagen. No detectable increase in collagen degradation products or underhydroxylation of procollagen was observed. Short-term kinetic studies further demonstrated that the major effect of IFNs was due to a net decrease in fibroblast collagen production rather than to impairment of secretion or increased extracellular degradation of the newly synthesized molecules. These results indicate that alpha- and gamma-IFNs are potent inhibitors of human fibroblast collagen production and suggest that they may play an important role in the regulation of normal and pathologic fibrogenesis.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Hart P. H., Powell L. W., Cooksley W. G., Halliday J. W. Mononuclear cell factors that inhibit fibroblast collagen synthesis. I. In vitro conditions determining their production and expression. Scand J Immunol. 1983 Jul;18(1):41–49. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.1983.tb00834.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hibbs M. S., Postlethwaite A. E., Mainardi C. L., Seyer J. M., Kang A. H. Alterations in collagen production in mixed mononuclear leukocyte-fibroblast cultures. J Exp Med. 1983 Jan 1;157(1):47–59. doi: 10.1084/jem.157.1.47. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hobbs D. S., Pestka S. Purification and characterization of interferons from a continuous myeloblastic cell line. J Biol Chem. 1982 Apr 25;257(8):4071–4076. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jimenez S. A., McArthur W., Rosenbloom J. Inhibition of collagen synthesis by mononuclear cell supernates. J Exp Med. 1979 Dec 1;150(6):1421–1431. doi: 10.1084/jem.150.6.1421. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson R. L., Ziff M. Lymphokine stimulation of collagen accumulation. J Clin Invest. 1976 Jul;58(1):240–252. doi: 10.1172/JCI108455. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Juva K., Prockop D. J. Modified procedure for the assay of H-3-or C-14-labeled hydroxyproline. Anal Biochem. 1966 Apr;15(1):77–83. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(66)90249-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LeRoy E. C. Increased collagen synthesis by scleroderma skin fibroblasts in vitro: a possible defect in the regulation or activation of the scleroderma fibroblast. J Clin Invest. 1974 Oct;54(4):880–889. doi: 10.1172/JCI107827. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nielson E. G., Phillips S. M., Jimenez S. Lymphokine modulation of fibroblast proliferation. J Immunol. 1982 Mar;128(3):1484–1486. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rubinstein S., Familletti P. C., Pestka S. Convenient assay for interferons. J Virol. 1981 Feb;37(2):755–758. doi: 10.1128/jvi.37.2.755-758.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wahl S. M., Wahl L. M., McCarthy J. B. Lymphocyte-mediated activation of fibroblast proliferation and collagen production. J Immunol. 1978 Sep;121(3):942–946. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



