Abstract
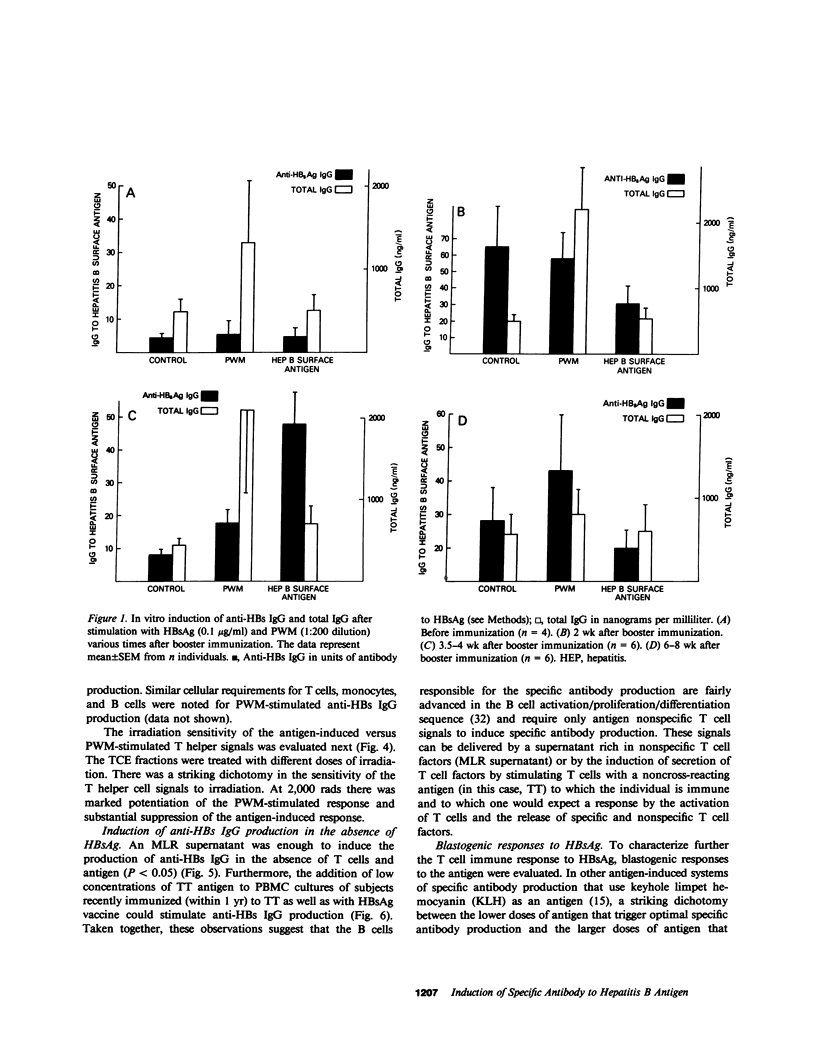
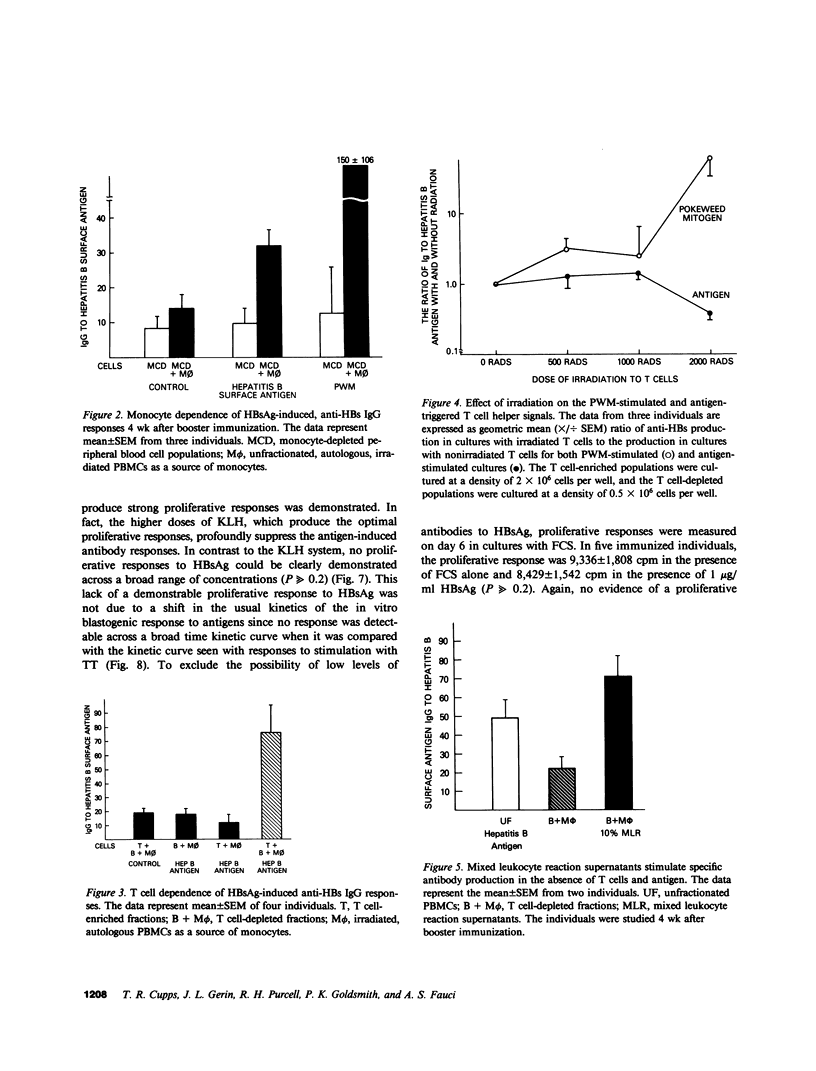
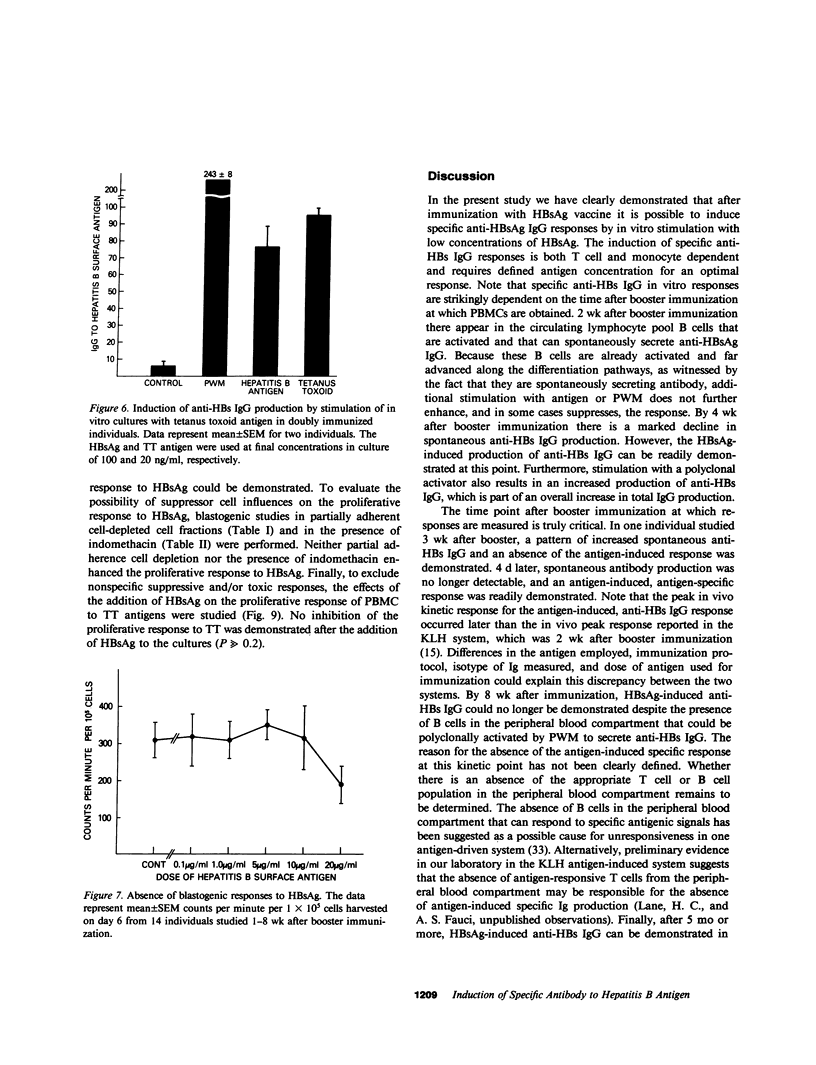
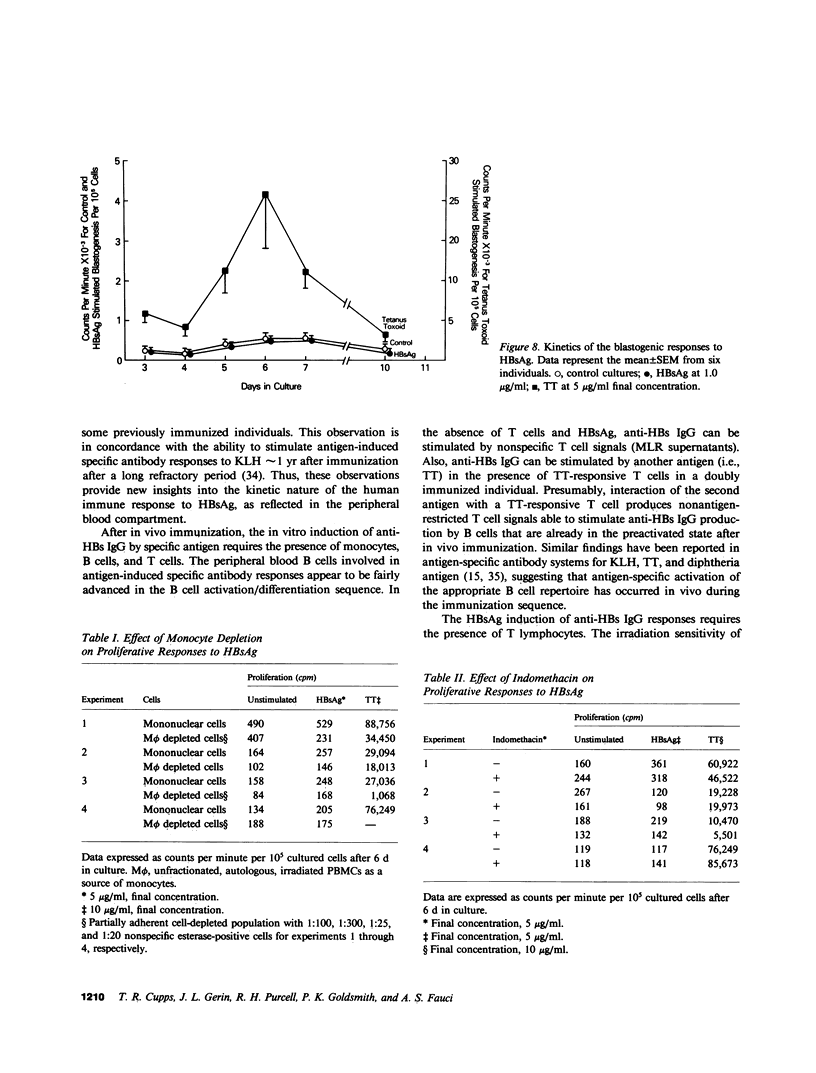
In this report we define the parameters of the human immune response after immunization with hepatitis B vaccine. 2 wk after booster immunization, there is significant spontaneous secretion of antibody to hepatitis B surface antigen (anti-HBs IgG), which is not further augmented by stimulation with antigen or pokeweed mitogen (PWM). By 4 wk there is little spontaneous secretion of specific antibody, and low doses of antigen or PWM produce significant increases in the amount of anti-HBs IgG produced. By 8 wk the peripheral blood mononuclear cells are refractory to stimulation by antigen, but anti-HBs IgG is produced in response to PWM. 0.5 yr or more after the last immunization, some individuals will manifest an antigen-induced specific antibody response. This induction of anti-HBs IgG by hepatitis B surface antigen (HBsAg) is monocyte- and T cell-dependent. Note that there is a dichotomy in the T cell response to HBsAg. The specific antibody response is clearly T cell dependent, but no in vitro T cell proliferative response to HBsAG could be demonstrated in the immunized individuals. Although the precise reason for the absent proliferative response to HBsAg despite well-established humoral immunity has not been determined, there was no evidence to suggest nonspecific suppression by HBsAg or the presence of an adherent suppressor cell population. The ability to evaluate antigen-induced, antigen-specific responses to HBsAg will be useful in defining the unique interaction between the human immune response and this clinically important viral agent.
Full text
PDF





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arvin A. M., Pollard R. B., Rasmussen L. E., Merigan T. C. Selective impairment of lymphocyte reactivity to varicella-zoster virus antigen among untreated patients with lymphoma. J Infect Dis. 1978 May;137(5):531–540. doi: 10.1093/infdis/137.5.531. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bianchi L., Gudat F. Immunopathology of hepatitis B. Prog Liver Dis. 1979;6:371–392. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bolin T. D., Davis A. E., Liddelow A. G. Liver disease and cell-mediated immunity in hepatitis-associated antigen (HAA) carriers. Gut. 1973 May;14(5):365–368. doi: 10.1136/gut.14.5.365. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brzosko W. J., Krawczyński K., Nazarewicz T., Morzycka M., Nowoslawski A. Glomerulonephritis associated with hepatitis-B surface antigen immune complexes in children. Lancet. 1974 Aug 31;2(7879):477–482. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(74)92012-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Böyum A. Isolation of mononuclear cells and granulocytes from human blood. Isolation of monuclear cells by one centrifugation, and of granulocytes by combining centrifugation and sedimentation at 1 g. Scand J Clin Lab Invest Suppl. 1968;97:77–89. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Callard R. E., McCaughan G. W., Babbage J., Souhami R. L. Specific in vitro antibody responses by human blood lymphocytes: apparent nonresponsiveness of PBL is due to a lack of recirculating memory B cells. J Immunol. 1982 Jul;129(1):153–156. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Callard R. E. Specific in vitro antibody response to influenza virus by human blood lymphocytes. Nature. 1979 Dec 13;282(5740):734–736. doi: 10.1038/282734a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chisari F. V., Edgington T. S. Lymphocyte E rosette inhibitory factor: a regulatory serum lipoprotein. J Exp Med. 1975 Nov 1;142(5):1092–1107. doi: 10.1084/jem.142.5.1092. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chisari F. V., Routenberg J. A., Edgington T. S. Mechanisms responsible for defective human T-lymphocyte sheep erythrocyte rosette function associated with hepatitis B virus infections. J Clin Invest. 1976 May;57(5):1227–1238. doi: 10.1172/JCI108391. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dolin R., Murphy B. R., Caplan E. A. Lymphocyte blastogenic responses to influenza virus antigens after influenza infection and vaccination in humans. Infect Immun. 1978 Mar;19(3):867–874. doi: 10.1128/iai.19.3.867-874.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duffy J., Lidsky M. D., Sharp J. T., Davis J. S., Person D. A., Hollinger F. B., Min K. W. Polyarthritis, polyarteritis and hepatitis B. Medicine (Baltimore) 1976 Jan;55(1):19–37. doi: 10.1097/00005792-197601000-00002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dusheiko G. M., Hoofnagle J. H., Cooksley W. G., James S. P., Jones E. A. Synthesis of antibodies to hepatitis B virus by cultured lymphocytes from chronic hepatitis B surface antigen carriers. J Clin Invest. 1983 May;71(5):1104–1113. doi: 10.1172/JCI110860. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ellner J. J. Suppressor adherent cells in human tuberculosis. J Immunol. 1978 Dec;121(6):2573–2579. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Engvall E., Perlmann P. Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay, Elisa. 3. Quantitation of specific antibodies by enzyme-labeled anti-immunoglobulin in antigen-coated tubes. J Immunol. 1972 Jul;109(1):129–135. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Falkoff R. J., Zhu L. P., Fauci A. S. Separate signals for human B cell proliferation and differentiation in response to Staphylococcus aureus: evidence for a two-signal model of B cell activation. J Immunol. 1982 Jul;129(1):97–102. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fauci A. S., Dale D. C. Alternate-day prednisone therapy and human lymphocyte subpopulations. J Clin Invest. 1975 Jan;55(1):22–32. doi: 10.1172/JCI107914. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Francis D. P., Hadler S. C., Thompson S. E., Maynard J. E., Ostrow D. G., Altman N., Braff E. H., O'Malley P., Hawkins D., Judson F. N. The prevention of hepatitis B with vaccine. Report of the centers for disease control multi-center efficacy trial among homosexual men. Ann Intern Med. 1982 Sep;97(3):362–366. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-97-3-362. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerin J. L., Faust R. M., Holland P. V. Biophysical characterization of the adr subtype of hepatitis B antigen and preparation of anti-r sera in rabbits. J Immunol. 1975 Jul;115(1):100–105. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerrard T. L., Fauci A. S. Activation and immunoregulation of antigen-specific human b lymphocyte responses: multifaceted role of the monocyte. J Immunol. 1982 May;128(5):2367–2372. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldsmith P. K. A highly sensitive enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay for human immunoglobulin E: comparison of microtiter plate and disk methodologies. Anal Biochem. 1981 Oct;117(1):53–60. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(81)90690-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodwin J. S., Messner R. P., Bankhurst A. D., Peake G. T., Saiki J. H., Williams R. C., Jr Prostaglandin-producing suppressor cells in Hodgkin's disease. N Engl J Med. 1977 Nov 3;297(18):963–968. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197711032971802. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Imai M., Yanase Y., Nojiri T., Miyakawa Y., Mayumi M. A receptor for polymerized human and chimpanzee albumins on hepatitis B virus particles co-occurring with HBeAg. Gastroenterology. 1979 Feb;76(2):242–247. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kohler P. F., Cronin R. E., Hammond W. S., Olin D., Carr R. I. Chronic membranous glomerulonephritis caused by hepatitis B antigen-antibody immune complexes. Ann Intern Med. 1974 Oct;81(4):448–451. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-81-4-448. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laiwah A. A., Chaudhuri A. K., Anderson J. R. Lymphocyte transformation and leucocyte migration-inhibition by Australia antigen. Clin Exp Immunol. 1973 Sep;15(1):27–34. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lane H. C., Volkman D. J., Whalen G., Fauci A. S. In vitro antigen-induced, antigen-specific antibody production in man. Specific and polyclonal components, kinetics, and cellular requirements. J Exp Med. 1981 Oct 1;154(4):1043–1057. doi: 10.1084/jem.154.4.1043. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lane H. C., Whalen G., Fauci A. S. Antigen-induced human T cell help. Precursor frequency, radiation sensitivity, and allogeneic effects. J Clin Invest. 1983 Aug;72(2):636–647. doi: 10.1172/JCI111013. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levo Y., Gorevic P. D., Kassab H. J., Zucker-Franklin D., Franklin E. C. Association between hepatitis B virus and essential mixed cryoglobulinemia. N Engl J Med. 1977 Jun 30;296(26):1501–1504. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197706302962605. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meyer zum Büschenfelde K. H., Hütteroth T. H., Arnold W., Hopf U. Immunologic liver injury: the role of hepatitis B viral antigens and liver membrane antigens as targets. Prog Liver Dis. 1979;6:407–424. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muraguchi A., Butler J. L., Kehrl J. H., Fauci A. S. Differential sensitivity of human B cell subsets to activation signals delivered by anti-mu antibody and proliferative signals delivered by a monoclonal B cell growth factor. J Exp Med. 1983 Feb 1;157(2):530–546. doi: 10.1084/jem.157.2.530. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neurath A. R., Strick N. Radioimmunoassay for albumin-binding sites associated with HBsAg: correlation of results with the presence of e-antigen in serum. Intervirology. 1979;11(2):128–132. doi: 10.1159/000149024. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ottesen E. A. Modulation of the host response in human schistosomiasis. I. Adherent suppressor cells that inhibit lymphocyte proliferative responses to parasite antigens. J Immunol. 1979 Oct;123(4):1639–1644. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peters M., Fauci A. S. Selective activation of antigen-specific human B cells in recently immunized individuals by nonspecific factors in the absence of antigen. J Immunol. 1983 Feb;130(2):678–680. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peterson L. B., Wilner G. D., Thomas D. W. Proliferating and helper T lymphocytes display distinct fine specificities in response to human fibrinopeptide B. J Immunol. 1983 Jun;130(6):2542–2545. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Piessens W. F., Ratiwayanto S., Tuti S., Palmieri J. H., Piessens P. W., Koiman I., Dennis D. T. Antigen-specific suppressor cells and suppressor factors in human filariasis with Brugia malayi. N Engl J Med. 1980 Apr 10;302(15):833–837. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198004103021503. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sergent J. S., Lockshin M. D., Christian C. L., Gocke D. J. Vasculitis with hepatitis B antigenemia: long-term observation in nine patients. Medicine (Baltimore) 1976 Jan;55(1):1–18. doi: 10.1097/00005792-197601000-00001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sherlock S., Fox R. A., Niazi S. P., Scheuer P. J. Chronic liver disease and primary liver-cell cancer with hepatitis-associated (Australia) antigen in serum. Lancet. 1970 Jun 13;1(7659):1243–1247. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(70)91737-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Souhami R. L., Babbage J., Callard R. E. Specific in vitro antibody response to varicella zoster. Clin Exp Immunol. 1981 Oct;46(1):98–105. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Szmuness W., Stevens C. E., Harley E. J., Zang E. A., Oleszko W. R., William D. C., Sadovsky R., Morrison J. M., Kellner A. Hepatitis B vaccine: demonstration of efficacy in a controlled clinical trial in a high-risk population in the United States. N Engl J Med. 1980 Oct 9;303(15):833–841. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198010093031501. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tong M. J., Wallace A. M., Peters R. L., Reynolds T. B. Lymphocyte stimulation in hepatitis B infections. N Engl J Med. 1975 Aug 14;293(7):318–322. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197508142930702. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Volkman D. J., Allyn S. P., Fauci A. S. Antigen-induced in vitro antibody production in humans: tetanus toxoid-specific antibody synthesis. J Immunol. 1982 Jul;129(1):107–112. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Volkman D. J., Lane H. C., Fauci A. S. Antigen-induced in vitro antibody production in humans: a model for B cell activation and immunoregulation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Apr;78(4):2528–2531. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.4.2528. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wainberg M. A., Israel E. Viral inhibition of lymphocyte mitogenesis. I. Evidence for the nonspecificity of the effect. J Immunol. 1980 Jan;124(1):64–70. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wands J. R., Perrotto J. L., Alpert E., Isselbacher K. J. Cell-mediated immunity in acute and chronic hepatitis. J Clin Invest. 1975 May;55(5):921–929. doi: 10.1172/JCI108021. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Werner C., Klouda P. T., Corréa M. C., Vassalli P., Jeannet M. Isolation of B and T lymphocytes by nylon fiber columns. Tissue Antigens. 1977 Apr;9(4):227–229. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-0039.1977.tb01112.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yarchoan R., Murphy B. R., Strober W., Schneider H. S., Nelson D. L. Specific anti-influenza virus antibody production in vitro by human peripheral blood mononuclear cells. J Immunol. 1981 Dec;127(6):2588–2594. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Gast G. C., Houwen B., Nieweg H. O. Specific lymphocyte stimulation by purified, heat-inactivated hepatitis-B antigen. Br Med J. 1973 Dec 22;4(5894):707–709. doi: 10.1136/bmj.4.5894.707. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



