Abstract
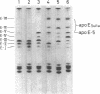
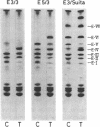
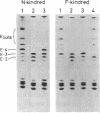
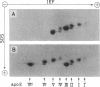
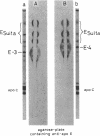
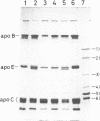
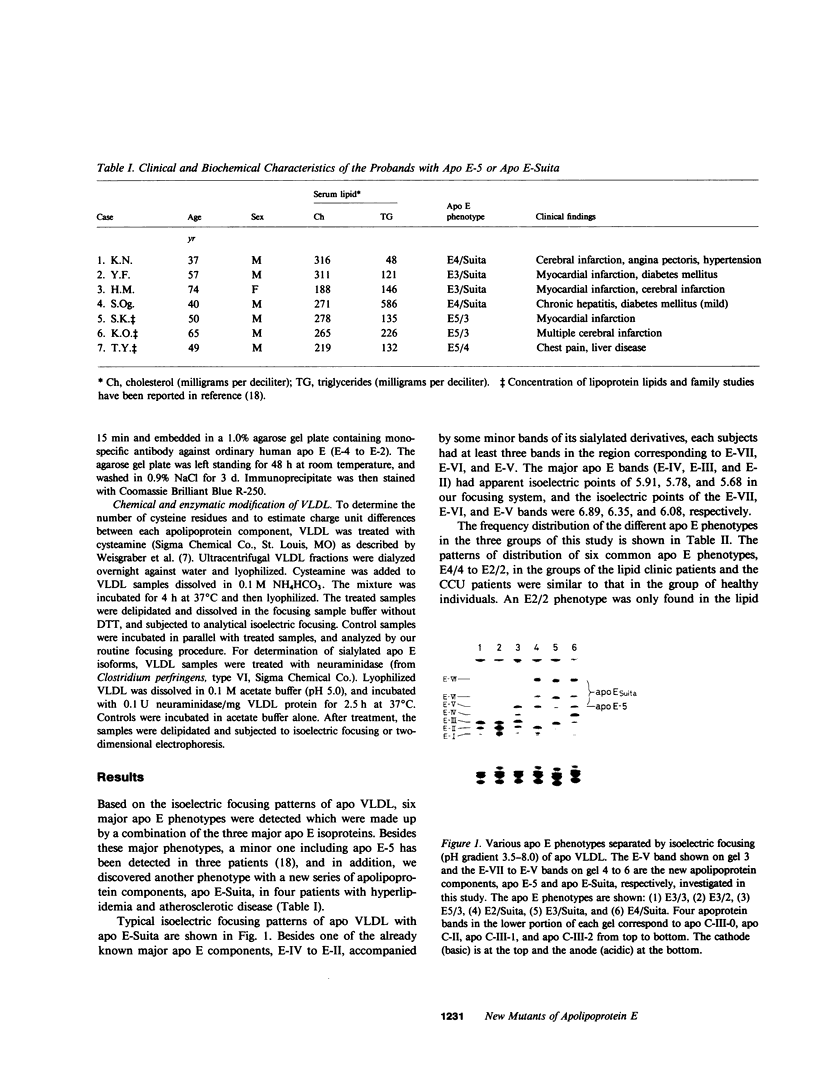
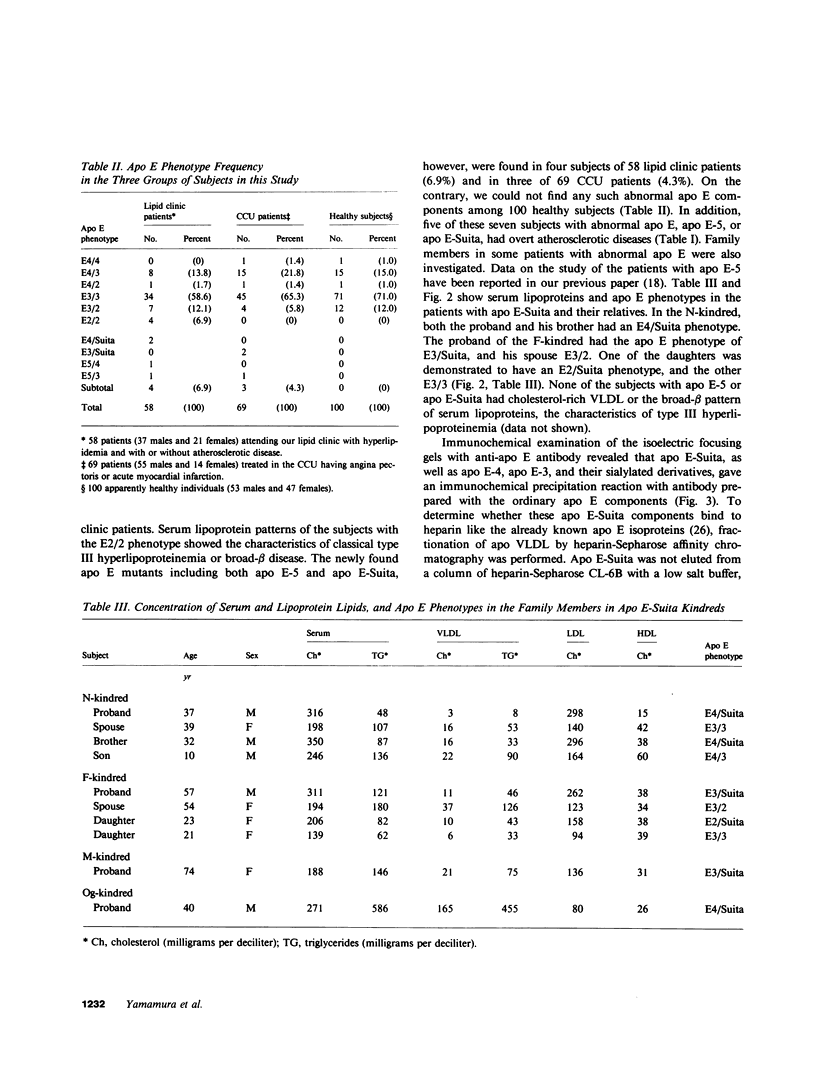
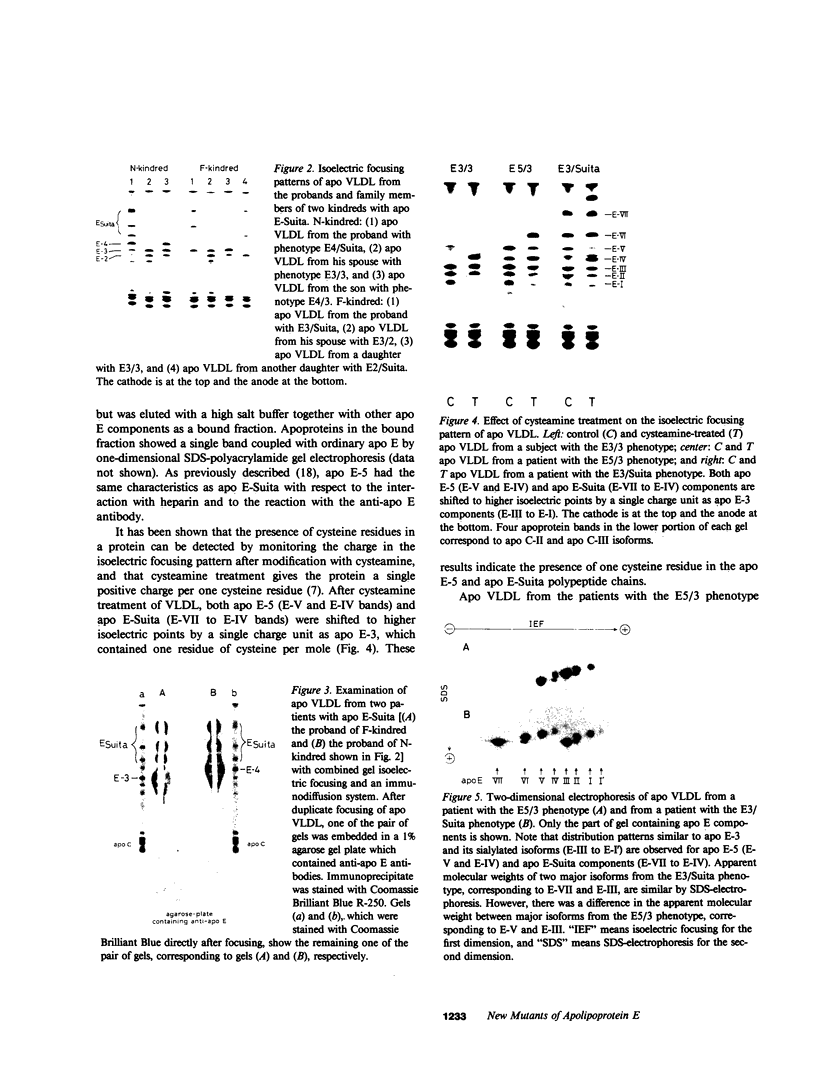
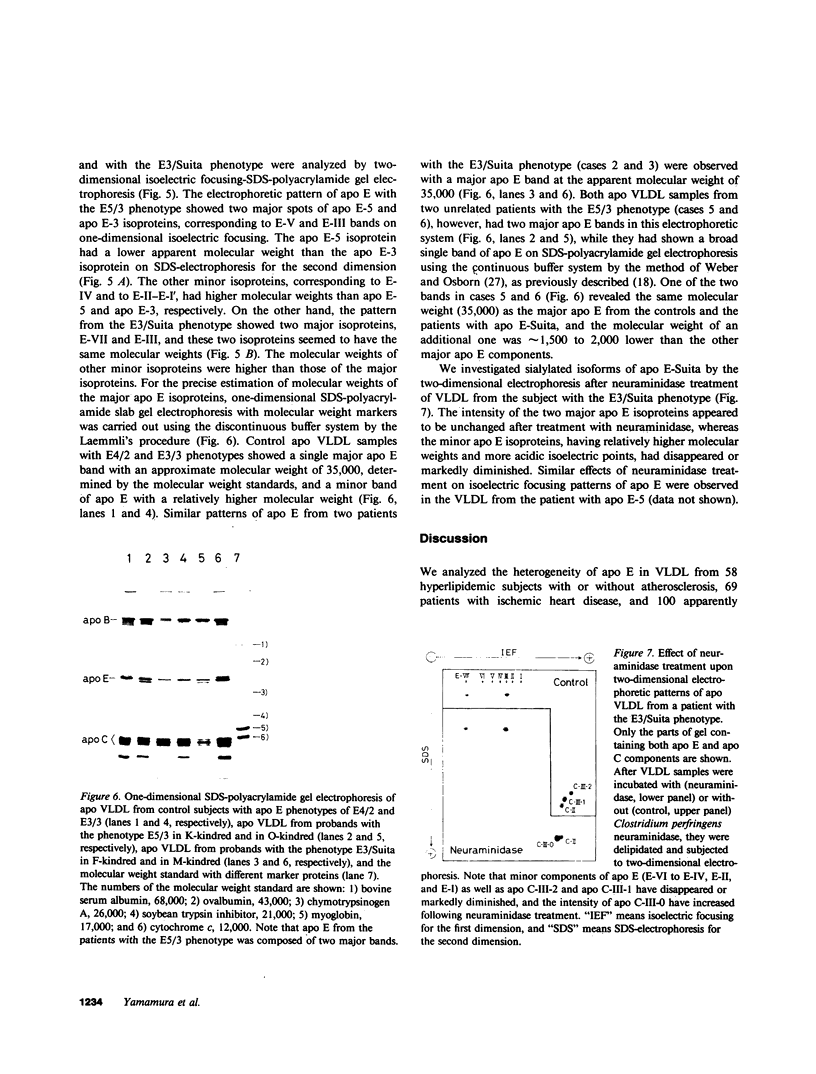
We analyzed the heterogeneity of apo E in very low density lipoprotein from 58 hyperlipidemic subjects with or without atherosclerosis, 69 patients with ischemic heart disease, and 100 apparently healthy individuals. Apo E gene frequencies in the group of healthy individuals were comparable with those in German and American populations. The distribution of six common apo E phenotypes in the groups of hyperlipidemia and ischemic heart disease was similar to that in the healthy group. In addition to the three major isoforms of apolipoprotein E (apo E-4, E-3, and E-2) and the new one (apo E-5) which was recently found in this laboratory, we have discovered an additional series of components, which showed themselves as at least three bands on an isoelectric focusing gel in the region of E-VII through E-V, in four patients with hyperlipidemia and atherosclerosis. The new series of apo E components, named apo E-Suita, was identical with the ordinary apo E in its interaction with heparin-Sepharose gel and with anti-apo E antibody. The most basic component of apo E-Suita (E-VII) was the unsialylated form and other components (E-VI and E-V), the sialylated forms. Family studies revealed that apo E-Suita was determined by inheritance of a new apo E allele located at the same locus as the hitherto known apo E components. Apo E-5 and apo E-Suita isoproteins had isoelectric points more basic than apo E-3, the parent type, by two and four units of charge, respectively. While the apo E-Suita isoprotein had the same molecular weight as ordinary major apo E isoproteins, the molecular weight of the apo E-5 isoprotein was approximately 1,500-2,000 lower than the other apo E isoproteins by sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. The incidence of abnormal apo E components, including apo E-5 and apo E-Suita, was high among patients with hyperlipidemia and ischemic heart disease (7:127), while we could not find such components among 100 healthy individuals. Moreover, five of seven patients with the abnormal apo E had overt atherosclerotic disease. The findings suggest that these kinds of apolipoprotein mutation are closely related to the development of atherosclerosis.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Burstein M., Scholnick H. R. Lipoprotein-polyanion-metal interactions. Adv Lipid Res. 1973;11(0):67–108. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fainaru M., Mahley R. W., Hamilton R. L., Innerarity T. L. Structural and metabolic heterogeneity of beta-very low density lipoproteins from cholesterol-fed dogs and from humans with type III hyperlipoproteinemia. J Lipid Res. 1982 Jul;23(5):702–714. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ghiselli G., Schaefer E. J., Gascon P., Breser H. B., Jr Type III hyperlipoproteinemia associated with apolipoprotein E deficiency. Science. 1981 Dec 11;214(4526):1239–1241. doi: 10.1126/science.6795720. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ghiselli G., Schaefer E. J., Zech L. A., Gregg R. E., Brewer H. B., Jr Increased prevalence of apolipoprotein E4 in type V hyperlipoproteinemia. J Clin Invest. 1982 Aug;70(2):474–477. doi: 10.1172/JCI110638. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gregg R. E., Ghiselli G., Brewer H. B., Jr Apolipoprotein EBethesda: a new variant of apolipoprotein E associated with type III hyperlipoproteinemia. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1983 Nov;57(5):969–974. doi: 10.1210/jcem-57-5-969. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Innerarity T. L., Friedlander E. J., Rall S. C., Jr, Weisgraber K. H., Mahley R. W. The receptor-binding domain of human apolipoprotein E. Binding of apolipoprotein E fragments. J Biol Chem. 1983 Oct 25;258(20):12341–12347. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kashyap M. L., Hynd B. A., Robinson K. A rapid and simple method for measurement of total protein in very low density lipoproteins by the Lowry assay. J Lipid Res. 1980 May;21(4):491–495. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mahley R. W. Atherogenic hyperlipoproteinemia. The cellular and molecular biology of plasma lipoproteins altered by dietary fat and cholesterol. Med Clin North Am. 1982 Mar;66(2):375–402. doi: 10.1016/s0025-7125(16)31426-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Menzel H. J., Kladetzky R. G., Assmann G. Apolipoprotein E polymorphism and coronary artery disease. Arteriosclerosis. 1983 Jul-Aug;3(4):310–315. doi: 10.1161/01.atv.3.4.310. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Farrell P. H. High resolution two-dimensional electrophoresis of proteins. J Biol Chem. 1975 May 25;250(10):4007–4021. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rall S. C., Jr, Weisgraber K. H., Innerarity T. L., Bersot T. P., Mahley R. W., Blum C. B. Identification of a new structural variant of human apolipoprotein E, E2(Lys146 leads to Gln), in a type III hyperlipoproteinemic subject with the E3/2 phenotype. J Clin Invest. 1983 Oct;72(4):1288–1297. doi: 10.1172/JCI111085. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rall S. C., Jr, Weisgraber K. H., Innerarity T. L., Mahley R. W. Structural basis for receptor binding heterogeneity of apolipoprotein E from type III hyperlipoproteinemic subjects. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Aug;79(15):4696–4700. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.15.4696. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rall S. C., Jr, Weisgraber K. H., Mahley R. W. Human apolipoprotein E. The complete amino acid sequence. J Biol Chem. 1982 Apr 25;257(8):4171–4178. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schneider W. J., Kovanen P. T., Brown M. S., Goldstein J. L., Utermann G., Weber W., Havel R. J., Kotite L., Kane J. P., Innerarity T. L. Familial dysbetalipoproteinemia. Abnormal binding of mutant apoprotein E to low density lipoprotein receptors of human fibroblasts and membranes from liver and adrenal of rats, rabbits, and cows. J Clin Invest. 1981 Oct;68(4):1075–1085. doi: 10.1172/JCI110330. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shelburne F. A., Quarfordt S. H. The interaction of heparin with an apoprotein of human very low density lipoprotein. J Clin Invest. 1977 Oct;60(4):944–950. doi: 10.1172/JCI108849. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Utermann G., Hees M., Steinmetz A. Polymorphism of apolipoprotein E and occurrence of dysbetalipoproteinaemia in man. Nature. 1977 Oct 13;269(5629):604–607. doi: 10.1038/269604a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Utermann G., Jaeschke M., Menzel J. Familial hyperlipoproteinemia type III: deficiency of a specific apolipoprotein (apo E-III) in the very-low-density lipoproteins. FEBS Lett. 1975 Aug 15;56(2):352–355. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(75)81125-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Utermann G., Langenbeck U., Beisiegel U., Weber W. Genetics of the apolipoprotein E system in man. Am J Hum Genet. 1980 May;32(3):339–347. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Utermann G., Steinmetz A., Weber W. Genetic control of human apolipoprotein E polymorphism: comparison of one- and two-dimensional techniques of isoprotein analysis. Hum Genet. 1982;60(4):344–351. doi: 10.1007/BF00569216. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Utermann G., Vogelberg K. H., Steinmetz A., Schoenborn W., Pruin N., Jaeschke M., Hees M., Canzler H. Polymorphism of apolipoprotein E. II. Genetics of hyperlipoproteinemia type III. Clin Genet. 1979 Jan;15(1):37–62. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weber K., Osborn M. The reliability of molecular weight determinations by dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. J Biol Chem. 1969 Aug 25;244(16):4406–4412. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weisgraber K. H., Innerarity T. L., Harder K. J., Mahley R. W., Milne R. W., Marcel Y. L., Sparrow J. T. The receptor-binding domain of human apolipoprotein E. Monoclonal antibody inhibition of binding. J Biol Chem. 1983 Oct 25;258(20):12348–12354. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weisgraber K. H., Innerarity T. L., Mahley R. W. Abnormal lipoprotein receptor-binding activity of the human E apoprotein due to cysteine-arginine interchange at a single site. J Biol Chem. 1982 Mar 10;257(5):2518–2521. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weisgraber K. H., Rall S. C., Jr, Mahley R. W. Human E apoprotein heterogeneity. Cysteine-arginine interchanges in the amino acid sequence of the apo-E isoforms. J Biol Chem. 1981 Sep 10;256(17):9077–9083. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamamura T., Sudo H., Ishikawa K., Yamamoto A. Familial type I hyperlipoproteinemia caused by apolipoprotein C-II deficiency. Atherosclerosis. 1979 Sep;34(1):53–65. doi: 10.1016/0021-9150(79)90106-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamamura T., Yamamoto A., Hiramori K., Nambu S. A new isoform of apolipoprotein E--apo E-5--associated with hyperlipidemia and atherosclerosis. Atherosclerosis. 1984 Feb;50(2):159–172. doi: 10.1016/0021-9150(84)90019-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zannis V. I., Breslow J. L. Human very low density lipoprotein apolipoprotein E isoprotein polymorphism is explained by genetic variation and posttranslational modification. Biochemistry. 1981 Feb 17;20(4):1033–1041. doi: 10.1021/bi00507a059. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zannis V. I., Breslow J. L., Utermann G., Mahley R. W., Weisgraber K. H., Havel R. J., Goldstein J. L., Brown M. S., Schonfeld G., Hazzard W. R. Proposed nomenclature of apoE isoproteins, apoE genotypes, and phenotypes. J Lipid Res. 1982 Aug;23(6):911–914. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]