Abstract
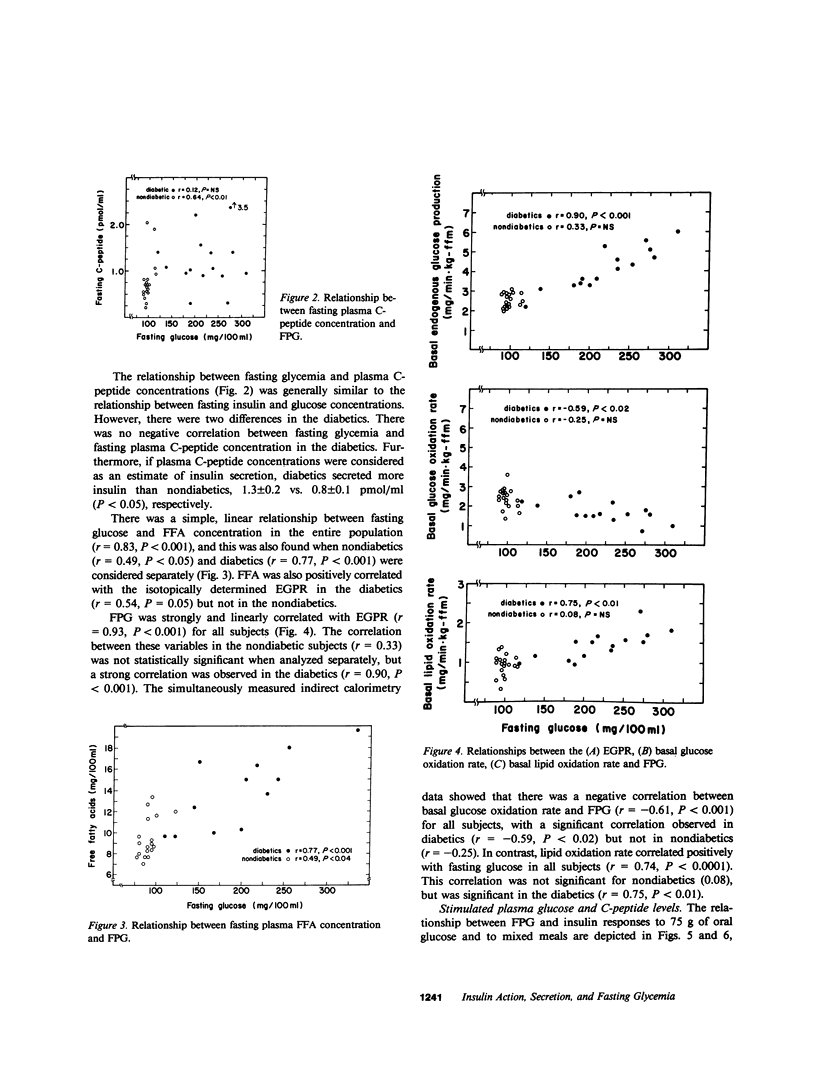
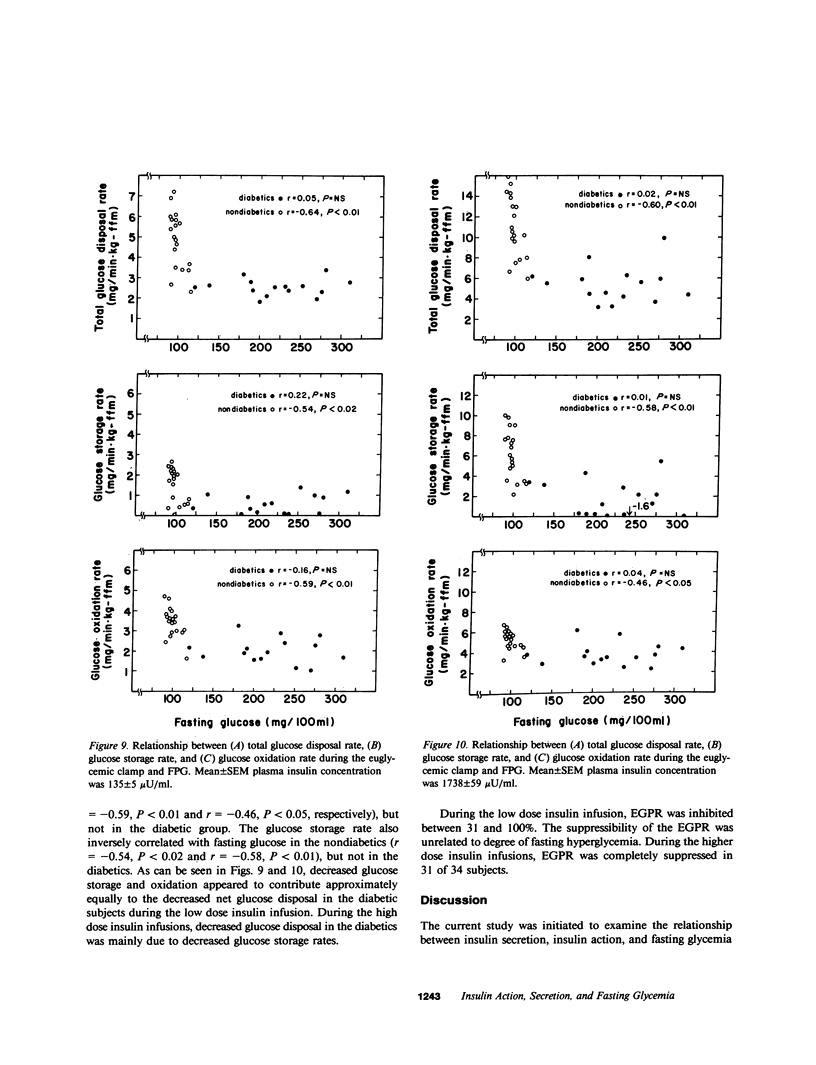
The relationships between insulin secretion, insulin action, and fasting plasma glucose concentration (FPG) were examined in 34 southwest American Indians (19 nondiabetics, 15 noninsulin-dependent diabetics) who had a broad range of FPG (88-310 mg/100 ml). Fasting, glucose-stimulated, and meal-stimulated plasma insulin concentrations were negatively correlated with FPG in diabetics but not in nondiabetics. In contrast, fasting and glucose-stimulated plasma C-peptide concentrations did not decrease with increasing FPG in either group and 24-h urinary C-peptide excretion during a diet of mixed composition was positively correlated with FPG for all subjects (r = 0.36, P less than 0.05). Fasting free fatty acid (FFA) was correlated with FPG in nondiabetics (r = 0.49, P less than 0.05) and diabetics (r = 0.77, P less than 0.001). Fasting FFA was also correlated with the isotopically determined endogenous glucose production rate in the diabetics (r = 0.54, P less than 0.05). Endogenous glucose production was strongly correlated with FPG in the diabetics (r = 0.90, P less than 0.0001), but not in the nondiabetics. Indirect calorimetry showed that FPG was also negatively correlated with basal glucose oxidation rates (r = -0.61, P less than 0.001), but positively with lipid oxidation (r = 0.74, P less than 0.001) in the diabetics. Insulin action was measured as total insulin-mediated glucose disposal, glucose oxidation, and storage rates, using the euglycemic clamp with simultaneous indirect calorimetry at plasma insulin concentrations of 135 +/- 5 and 1738 +/- 59 microU/ml. These parameters of insulin action were significantly, negatively correlated with FPG in the nondiabetics at both insulin concentrations, but not in the diabetics although all the diabetics had markedly decreased insulin action. We conclude that decreased insulin action is present in the noninsulin-dependent diabetics in this population and marked hyperglycemia occurs with the addition of decreased peripheral insulin availability. Decreased peripheral insulin availability leads to increased FFA concentrations and lipid oxidation rates (and probably also increased concentrations of gluconeogenic precursors) that together stimulate gluconeogenesis, hepatic glucose production, and progressive hyperglycemia.
Full text
PDF






Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aronoff S. L., Bennett P. H., Gorden P., Rushforth N., Miller M. Unexplained hyperinsulinemia in normal and "prediabetic" Pima Indians compared with normal Caucasians. An example of racial differences in insulin secretion. Diabetes. 1977 Sep;26(9):827–840. doi: 10.2337/diab.26.9.827. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Best J. D., Judzewitsch R. G., Pfeifer M. A., Beard J. C., Halter J. B., Porte D., Jr The effect of chronic sulfonylurea therapy on hepatic glucose production in non-insulin-dependent diabetes. Diabetes. 1982 Apr;31(4 Pt 1):333–338. doi: 10.2337/diab.31.4.333. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blumenthal S. A. Stimulation of gluconeogenesis by palmitic acid in rat hepatocytes: evidence that this effect can be dissociated from the provision of reducing equivalents. Metabolism. 1983 Oct;32(10):971–976. doi: 10.1016/0026-0495(83)90137-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bogardus C., Lillioja S., Stone K., Mott D. Correlation between muscle glycogen synthase activity and in vivo insulin action in man. J Clin Invest. 1984 Apr;73(4):1185–1190. doi: 10.1172/JCI111304. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeFronzo R. A., Ferrannini E. The pathogenesis of non-insulin-dependent diabetes: an update. Medicine (Baltimore) 1982 May;61(3):125–140. doi: 10.1097/00005792-198205000-00001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeFronzo R. A., Simonson D., Ferrannini E. Hepatic and peripheral insulin resistance: a common feature of type 2 (non-insulin-dependent) and type 1 (insulin-dependent) diabetes mellitus. Diabetologia. 1982 Oct;23(4):313–319. doi: 10.1007/BF00253736. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Faber O. K., Hagen C., Binder C., Markussen J., Naithani V. K., Blix P. M., Kuzuya H., Horwitz D. L., Rubenstein A. H., Rossing N. Kinetics of human connecting peptide in normal and diabetic subjects. J Clin Invest. 1978 Jul;62(1):197–203. doi: 10.1172/JCI109106. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Felig P., Wahren J., Hendler R. Influence of maturity-onset diabetes on splanchnic glucose balance after oral glucose ingestion. Diabetes. 1978 Feb;27(2):121–126. doi: 10.2337/diab.27.2.121. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferrannini E., Barrett E. J., Bevilacqua S., DeFronzo R. A. Effect of fatty acids on glucose production and utilization in man. J Clin Invest. 1983 Nov;72(5):1737–1747. doi: 10.1172/JCI111133. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frank B. H., Beckage M. J., Willey K. A. High-performance liquid chromatographic preparation of single-site carrier-free pancreatic polypeptide hormone radiotracers. J Chromatogr. 1983 Aug 26;266:239–248. doi: 10.1016/s0021-9673(01)90897-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frost D. P., Srivastava M. C., Jones R. H., Nabarro J. D., Sonksen P. H. The kinetics of insulin metabolism in diabetes mellitus. Postgrad Med J. 1973 Dec;49(Suppl):949–954. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hagenfeldt L. Metabolism of free fatty acids and ketone bodies during exercise in normal and diabetic man. Diabetes. 1979 Jan;28 (Suppl 1):66–70. doi: 10.2337/diab.28.1.s66. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heding L. G. Radioimmunological determination of human C-peptide in serum. Diabetologia. 1975 Dec;11(6):541–548. doi: 10.1007/BF01222104. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herbert V., Lau K. S., Gottlieb C. W., Bleicher S. J. Coated charcoal immunoassay of insulin. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1965 Oct;25(10):1375–1384. doi: 10.1210/jcem-25-10-1375. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howard B. V., Savage P. J., Nagulesparan M., Bennion L. J., Unger R. H., Bennett P. H. Evidence for marked sensitivity to the antilipolytic action of insulin in obese maturity-onset diabetics. Metabolism. 1979 Jul;28(7):744–750. doi: 10.1016/0026-0495(79)90180-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karnieli E., Hissin P. J., Simpson I. A., Salans L. B., Cushman S. W. A possible mechanism of insulin resistance in the rat adipose cell in streptozotocin-induced diabetes mellitus. Depletion of intracellular glucose transport systems. J Clin Invest. 1981 Sep;68(3):811–814. doi: 10.1172/JCI110318. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kobayashi M., Olefsky J. M. Effects of streptozotocin-induced diabetes on insulin binding, glucose transport, and intracellular glucose metabolism in isolated rat adipocytes. Diabetes. 1979 Feb;28(2):87–95. doi: 10.2337/diab.28.2.87. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kolterman O. G., Gray R. S., Griffin J., Burstein P., Insel J., Scarlett J. A., Olefsky J. M. Receptor and postreceptor defects contribute to the insulin resistance in noninsulin-dependent diabetes mellitus. J Clin Invest. 1981 Oct;68(4):957–969. doi: 10.1172/JCI110350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu G., Coulston A., Chen Y. D., Reaven G. M. Does day-long absolute hypoinsulinemia characterize the patient with non-insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus? Metabolism. 1983 Aug;32(8):754–756. doi: 10.1016/0026-0495(83)90104-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGuire E. A., Tobin J. D., Berman M., Andres R. Kinetics of native insulin in diabetic, obese, and aged men. Diabetes. 1979 Feb;28(2):110–120. doi: 10.2337/diab.28.2.110. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Navalesi R., Pilo A., Ferrannini E. Kinetic analysis of plasma insulin disappearance in nonketotic diabetic patients and in normal subjects. A tracer study with 125I-insulin. J Clin Invest. 1978 Jan;61(1):197–208. doi: 10.1172/JCI108918. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orskov H., Christensen N. J. Plasma disappearance rate of injected human insulin in juvenile diabetic, maturity-onset diabetic and nondiabetic subjects. Diabetes. 1969 Oct;18(10):653–659. doi: 10.2337/diab.18.10.653. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palumbo P. J., Taylor W. F., Molnar G. D., Tauxe W. N. Disappearance of bovine insulin from plasma in diabetic and normal subjects. Metabolism. 1972 Sep;21(9):787–798. doi: 10.1016/0026-0495(72)90001-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RANDLE P. J., GARLAND P. B., HALES C. N., NEWSHOLME E. A. The glucose fatty-acid cycle. Its role in insulin sensitivity and the metabolic disturbances of diabetes mellitus. Lancet. 1963 Apr 13;1(7285):785–789. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(63)91500-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reaven G. M., Bernstein R., Davis B., Olefsky J. M. Nonketotic diabetes mellitus: insulin deficiency or insulin resistance? Am J Med. 1976 Jan;60(1):80–88. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(76)90536-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reaven G. M. Insulin resistance in noninsulin-dependent diabetes mellitus. Does it exist and can it be measured? Am J Med. 1983 Jan 17;74(1A):3–17. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(83)90650-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reaven G. M. Insulin-independent diabetes mellitus: metabolic characteristics. Metabolism. 1980 May;29(5):445–454. doi: 10.1016/0026-0495(80)90170-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reaven G. M., Sageman W. S., Swenson R. S. Development of insulin resistance in normal dogs following alloxan-induced insulin deficiency. Diabetologia. 1977 Sep;13(5):459–462. doi: 10.1007/BF01234496. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reaven G., Miller R. Study of the relationship between glucose and insulin responses to an oral glucose load in man. Diabetes. 1968 Sep;17(9):560–569. doi: 10.2337/diab.17.9.560. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruderman N. B., Toews C. J., Shafrir E. Role of free fatty acids in glucose homeostasis. Arch Intern Med. 1969 Mar;123(3):299–313. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- STEELE R. Influences of glucose loading and of injected insulin on hepatic glucose output. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1959 Sep 25;82:420–430. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1959.tb44923.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Savage P. J., Dippe S. E., Bennett P. H., Gorden P., Roth J., Rushforth N. B., Miller M. Hyperinsulinemia and hypoinsulinemai. Insulin responses to oral carbohydrate over a wide spectrum of glucose tolerance. Diabetes. 1975 Apr;24(4):362–368. doi: 10.2337/diab.24.4.362. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stimmler L. Disappearance of immunoreactive insulin in normal and adult-onset diabetic subjects. Diabetes. 1967 Sep;16(9):652–655. doi: 10.2337/diab.16.9.652. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ward W. K., Halter J. B., Beard J. C., Porte D., Jr Adaptation of B and A cell function during prolonged glucose infusion in human subjects. Am J Physiol. 1984 May;246(5 Pt 1):E405–E411. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.1984.246.5.E405. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- YALOW R. S., BERSON S. A. Immunoassay of endogenous plasma insulin in man. J Clin Invest. 1960 Jul;39:1157–1175. doi: 10.1172/JCI104130. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



