Abstract
Renin is present in vascular smooth muscle cells and has been shown to coexist with angiotensins I (AI) and II (AII) in many cell types. Accordingly, we postulated that the renin-angiotensin system controls vascular tone, not by the action of circulating renal renin but rather, by the local generation of angiotensin by vascular renin. Isolated rat hindquarters were perfused in vitro with Krebs-Henseleit buffer containing 7% albumin, and flow-adjusted to obtain a perfusion pressure of approximately 90 mmHg. Infusion of 4.8 nmol X min-1 for 5 min of AII or AI markedly increased perfusion pressure. An identical dose of the synthetic tetradecaptide of renin substrate (TDCP-RS) increased pressure similarly to AI. The pressure increase evoked by TDCP-RS was markedly decreased by captopril and by two different peptides that inhibit renin. Renin activity in the perfusate, incubated with semipurified rat renin substrate, was 21 +/- 3 pg AI X ml-1 X h-1 (mean +/- SEM) at 15 min of perfusion and 47 +/- 4 pg AI X ml-1 X h-1 at 45 min (n = 9; P less than 0.01). When TDCP-RS was infused at 4.8 nmol X min-1 for 5 min in the presence of captopril, AI in the perfusate increased linearly at a rate of 16.5 pmol X min-1 for 10 min (n = 5). The results indicate that TDCP-RS constricted the vasculature by its conversion to AII and suggest that AII was generated from a two-step hydrolysis of TDCP-RS by renin and converting enzyme. The data thus suggest that the renin-angiotensin system controls vascular tone by the local generation of AII by renin and converting enzyme in the vasculature.
Full text
PDF
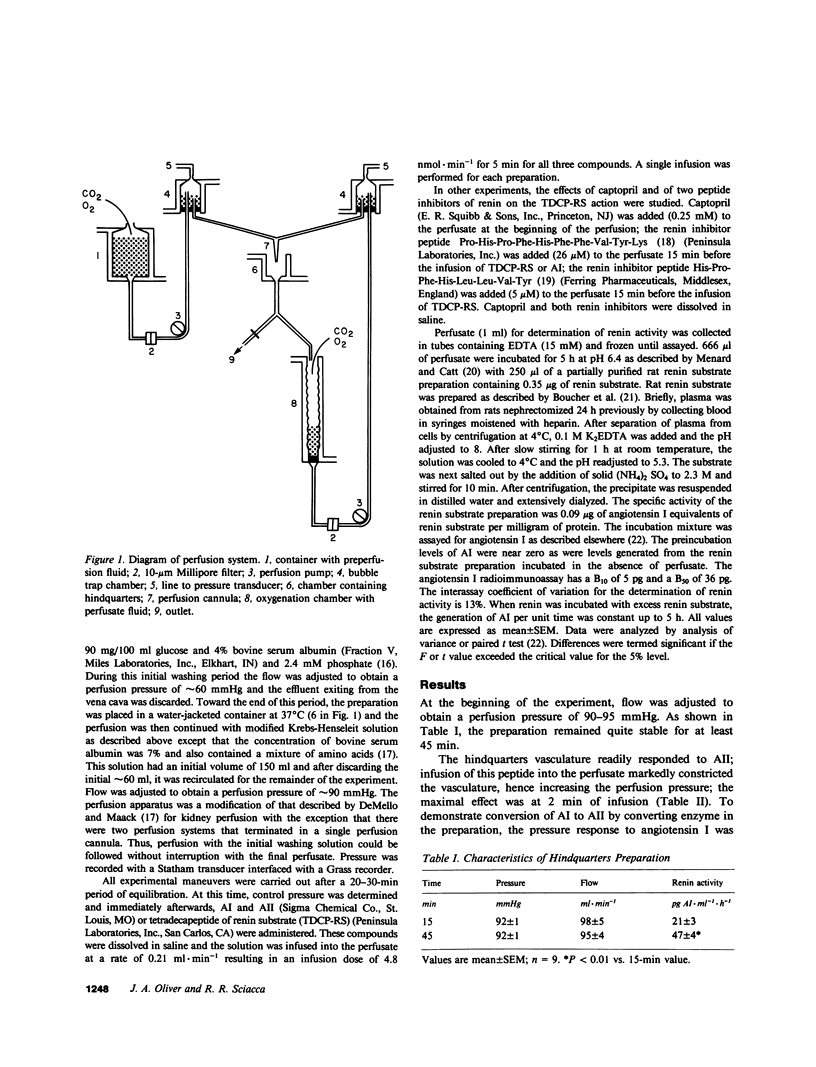
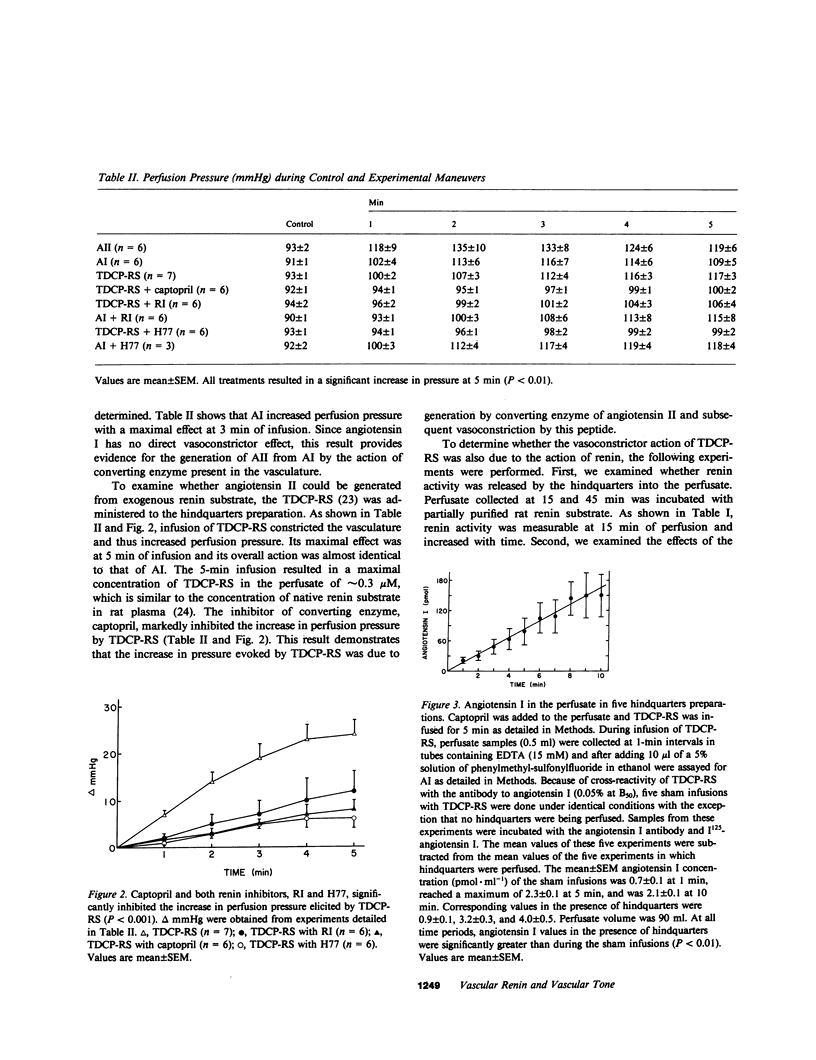


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Antonaccio M. J., Cushman D. W. Drugs inhibiting the renin - angiotensin system. Fed Proc. 1981 Jun;40(8):2275–2284. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bailie M. D., Rector F. C., Jr, Seldin D. W. Angiotensin II in arterial and renal venous plasma and renal lymph in the dog. J Clin Invest. 1971 Jan;50(1):119–126. doi: 10.1172/JCI106465. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boucher R., Ménard J., Genest J. A micromethod for measurement of renin in the plasma and kidney of rats. Can J Physiol Pharmacol. 1967 Sep;45(5):881–890. doi: 10.1139/y67-103. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bouhnik J., Clauser E., Gardes J., Corvol P., Menard J. Direct radioimmunoassay of rat angiotensinogen and its application to rats in various endocrine states. Clin Sci (Lond) 1982 Apr;62(4):355–360. doi: 10.1042/cs0620355. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown C. A., Zusman R. M., Haber E. Identification of an angiotensin receptor in rabbit renomedullary interstitial cells in tissue culture. Correlation with prostaglandin biosynthesis. Circ Res. 1980 Jun;46(6):802–807. doi: 10.1161/01.res.46.6.802. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burton J., Cody R. J., Jr, Herd J. A., Haber E. Specific inhibition of renin by an angiotensinogen analog: studies in sodium depletion and renin-dependent hypertension. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Sep;77(9):5476–5479. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.9.5476. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Campanile C. P., Crane J. K., Peach M. J., Garrison J. C. The hepatic angiotensin II receptor. I. Characterization of the membrane-binding site and correlation with physiological response in hepatocytes. J Biol Chem. 1982 May 10;257(9):4951–4958. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Celio M. R., Inagami T. Angiotensin II immunoreactivity coexists with renin in the juxtaglomerular granular cells of the kidney. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Jun;78(6):3897–3900. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.6.3897. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Mello G., Maack T. Nephron function of the isolated perfused rat kidney. Am J Physiol. 1976 Dec;231(6):1699–1707. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1976.231.6.1699. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dorer F. E., Kahn J. R., Lentz K. E., Levine M., Skeggs L. T. Formation of angiotensin II from tetradecapeptide renin substrate by angiotensin-converting enzyme. Biochem Pharmacol. 1975 May 15;24(10):1137–1139. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(75)90207-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Douglas J., Saltman S., Fredlund P., Kondo T., Catt K. J. Receptor binding of angiotensin II and antagonists. Correlation with aldosterone production by isolated canine adrenal glomerulosa cells. Circ Res. 1976 Jun;38(6 Suppl 2):108–112. doi: 10.1161/01.res.38.6.108. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dávalos M., Frega N. S., Saker B., Leaf A. Effect of exogenous and endogenous angiotensin II in the isolated perfused rat kidney. Am J Physiol. 1978 Dec;235(6):F605–F610. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1978.235.6.F605. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Figueiredo A. F., Takii Y., Tsuji H., Kato K., Inagami T. Rat kidney renin and cathepsin D: purification and comparison of properties. Biochemistry. 1983 Nov 22;22(24):5476–5481. doi: 10.1021/bi00293a004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GOULD A. B., SKEGGS L. T., Jr, KAHN J. R. THE PRESENCE OF RENIN ACTIVITY IN BLOOD VESSEL WALLS. J Exp Med. 1964 Mar 1;119:389–399. doi: 10.1084/jem.119.3.389. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ganten D., Hayduk K., Brecht H. M., Boucher R., Genest J. Evidence of renin release or production in splanchnic territory. Nature. 1970 May 9;226(5245):551–552. doi: 10.1038/226551a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gardes J., Bouhnik J., Clauser E., Corvol P., Menard J. Role of angiotensinogen in blood pressure homeostasis. Hypertension. 1982 Mar-Apr;4(2):185–189. doi: 10.1161/01.hyp.4.2.185. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gunther S., Alexander R. W., Atkinson W. J., Gimbrone M. A., Jr Functional angiotensin II receptors in cultured vascular smooth muscle cells. J Cell Biol. 1982 Feb;92(2):289–298. doi: 10.1083/jcb.92.2.289. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hackenthal E., Hackenthal R., Hilgenfeldt U. Isorenin, pseudorenin, cathepsin D and renin. A comparative enzymatic study of angiotensin-forming enzymes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1978 Feb 10;522(2):574–588. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(78)90089-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inagami T., Clemens D. L., Hirose S., Okamura T., Naruse K., Takii Y., Yokosawa H. Brain renin. Clin Exp Hypertens A. 1982;4(4-5):607–622. doi: 10.3109/10641968209061602. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LEVER A. F., PEART W. S. Renin and angiotensin-like activity in renal lymph. J Physiol. 1962 Mar;160:548–563. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1962.sp006865. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Man in 't Veld A. J., Schicht I. M., Derkx F. H., de Bruyn J. H., Schalekamp M. A. Effects of an angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitor (captopril) on blood pressure in anephric subjects. Br Med J. 1980 Feb 2;280(6210):288–290. doi: 10.1136/bmj.280.6210.288. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Menard J., Catt K. J. Measurement of renin activity, concentration and substrate in rat plasma by radioimmunoassay of angiotensin I. Endocrinology. 1972 Feb;90(2):422–430. doi: 10.1210/endo-90-2-422. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michelakis A. M., Yoshida H., Menzie J., Murakami K., Inagami T. A radioimmunoassay for the direct measurement of renin in mice and its application to submaxillary gland and kidney studies. Endocrinology. 1974 Apr;94(4):1101–1105. doi: 10.1210/endo-94-4-1101. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morgan T., Davis J. M. Renin secretion at the individual nephron level. Pflugers Arch. 1975 Aug 29;359(1-2):23–31. doi: 10.1007/BF00581275. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Naruse M., Inagami T. Markedly elevated specific renin levels in the adrenal in genetically hypertensive rats. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 May;79(10):3295–3299. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.10.3295. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okamura T., Clemens D. L., Inagami T. Renin, angiotensins, and angiotensin-converting enzyme in neuroblastoma cells: evidence for intracellular formation of angiotensins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Nov;78(11):6940–6943. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.11.6940. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oliver J. A., Cannon P. J. The effect of altered sodium balance upon renal vascular reactivity to angiotensin II and norepinephrine in the dog. Mechanism of variation in angiotensin responses. J Clin Invest. 1978 Mar;61(3):610–623. doi: 10.1172/JCI108972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oliver J. A., Pinto J., Sciacca R. R., Cannon P. J. Basal norepinephrine overflow into the renal vein: effect of renal nerve stimulation. Am J Physiol. 1980 Oct;239(4):F371–F377. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1980.239.4.F371. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poisner A. M., Wood G. W., Poisner R., Inagami T. Renin and inactive renin in human amnion at term pregnancy. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1982 Jan;169(1):4–6. doi: 10.3181/00379727-169-41298. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poulsen K., Haber E., Burton J. On the specificity of human renin. Studies with peptide inhibitors. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1976 Dec 8;452(2):533–537. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(76)90205-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Re R., Fallon J. T., Dzau V., Quay S. C., Haber E. Renin synthesis by canine aortic smooth muscle cells in culture. Life Sci. 1982 Jan 4;30(1):99–106. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(82)90641-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reilly C. F., Tewksbury D. A., Schechter N. M., Travis J. Rapid conversion of angiotensin I to angiotensin II by neutrophil and mast cell proteinases. J Biol Chem. 1982 Aug 10;257(15):8619–8622. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rightsel W. A., Okamura T., Inagami T., Pitcock J. A., Takii Y., Brooks B., Brown P., Muirhead E. E. Juxtaglomerular cells grown as monolayer cell culture contain renin, angiotensin I-converting enzyme, and angiotensin I and II/III. Circ Res. 1982 Jun;50(6):822–829. doi: 10.1161/01.res.50.6.822. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SKEGGS L. T., Jr, KAHN J. R., LENTZ K., SHUMWAY N. P. The preparation, purification, and amino acid sequence of a polypeptide renin substrate. J Exp Med. 1957 Sep 1;106(3):439–453. doi: 10.1084/jem.106.3.439. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swales J. D., Thurston H. Generation of angiotensin II at peripheral vascular level: studies using angiotensin II antisera. Clin Sci Mol Med. 1973 Nov;45(5):691–700. doi: 10.1042/cs0450691. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Szelke M., Leckie B. J., Tree M., Brown A., Grant J., Hallett A., Hughes M., Jones D. M., Lever A. F. H-77: a potent new renin inhibitor. In vitro and in vivo studies. Hypertension. 1982 May-Jun;4(3 Pt 2):59–69. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thurston H., Swales J. D., Bing R. F., Hurst B. C., Marks E. S. Vascular renin-like activity and blood pressure maintenance in the rat. Studies of the effect of changes in sodium balance, hypertension and nephrectomy. Hypertension. 1979 Nov-Dec;1(6):643–649. doi: 10.1161/01.hyp.1.6.643. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watkins L., Jr, Burton J. A., Haber E., Cant J. R., Smith F. W., Barger A. C. The renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system in congestive failure in conscious dogs. J Clin Invest. 1976 Jun;57(6):1606–1617. doi: 10.1172/JCI108431. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



