Abstract
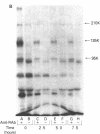
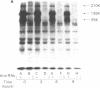
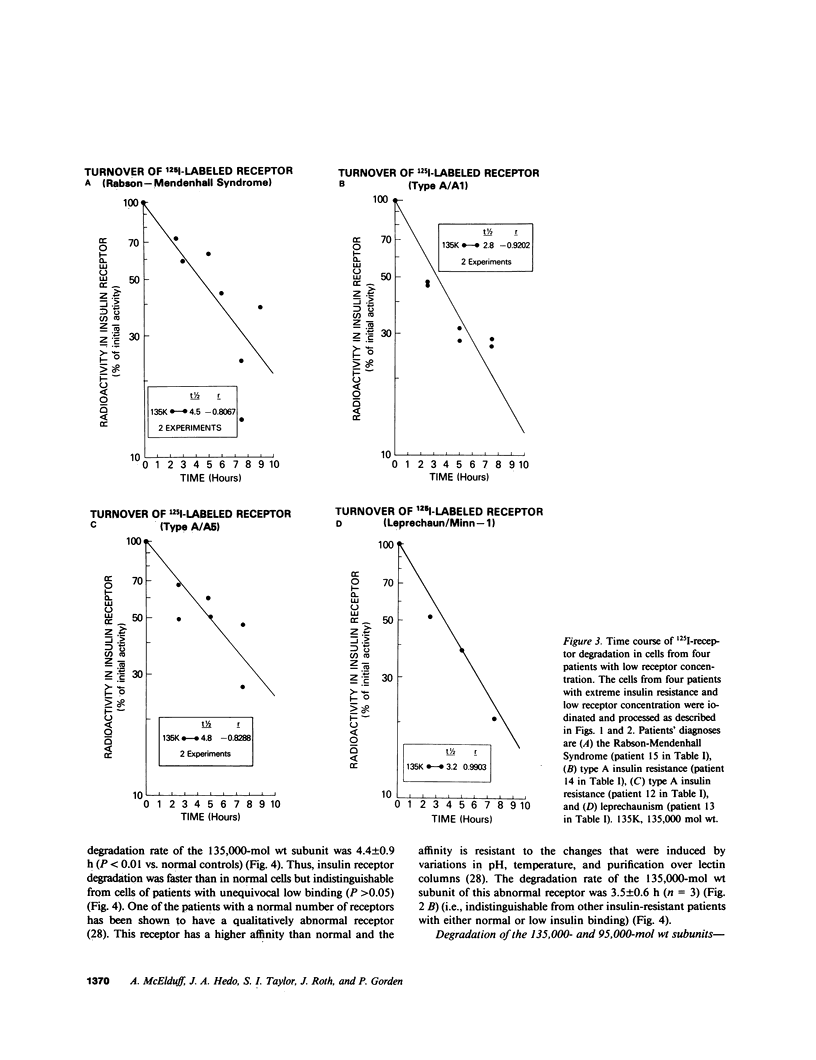
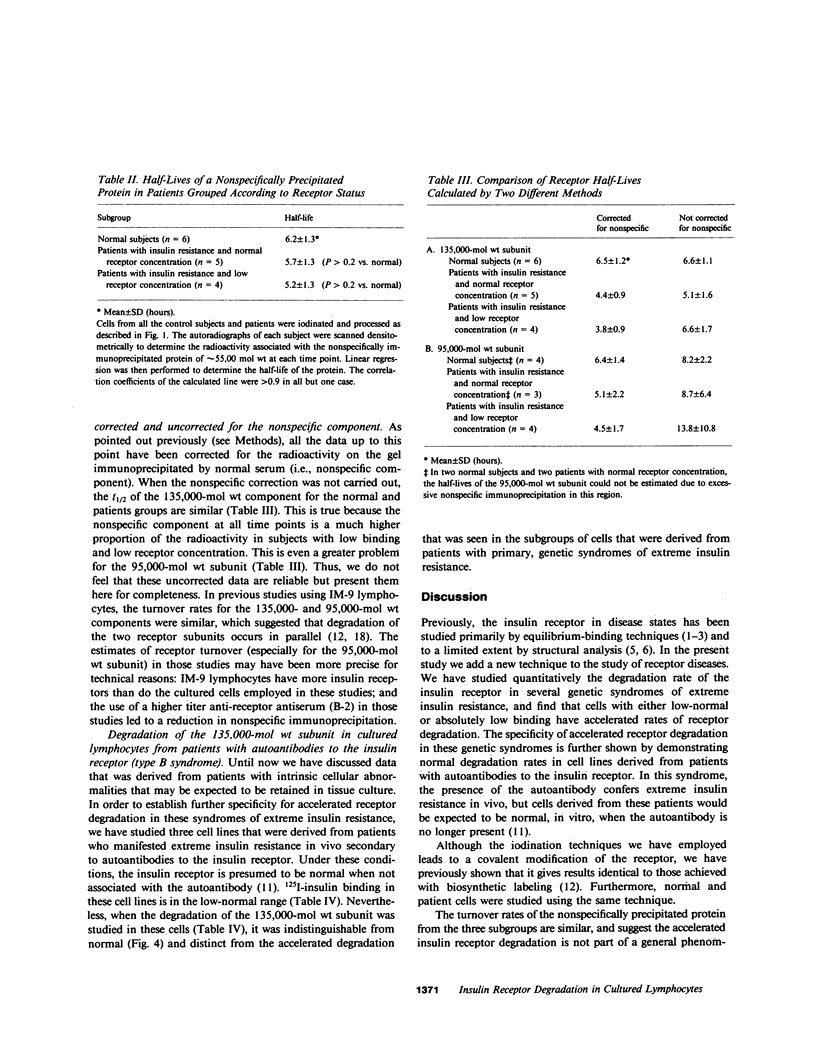
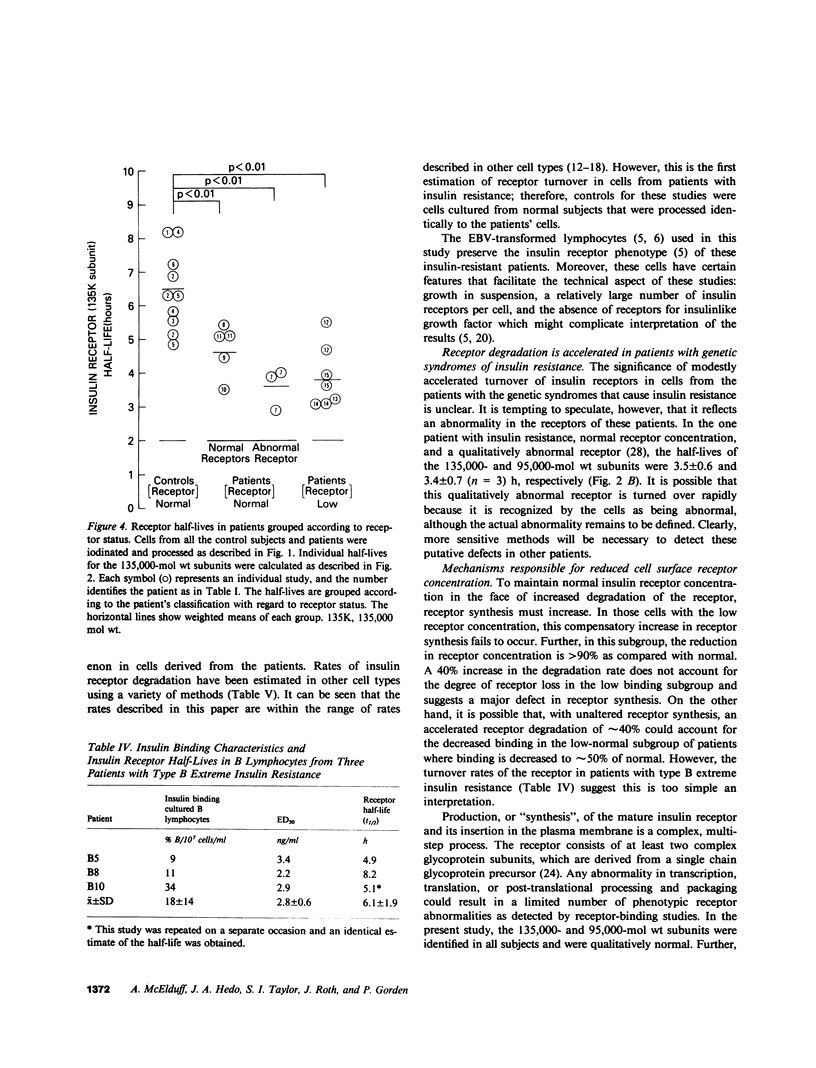
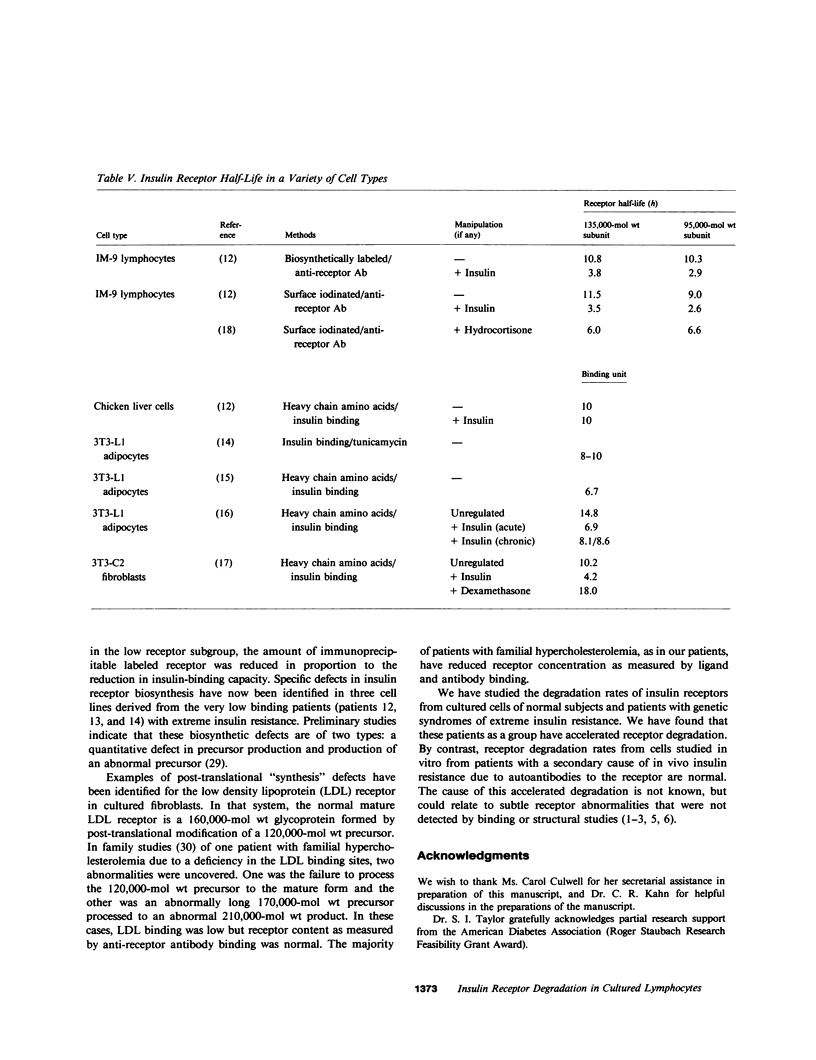
Previous studies of the insulin receptor in disease states have utilized primarily techniques of equilibrium binding and, to a limited extent structural, analysis. Though techniques have been developed to study receptor degradation in normal cells, they have not been applied to disease states. In the present study we have examined insulin receptor degradation rate in B lymphocytes that were obtained from peripheral blood of normal subjects and patients with several syndromes of extreme insulin resistance. B lymphocytes were established in culture from each patient's peripheral cells by transformation with Epstein-Barr virus. The insulin receptors were surface labeled using Na125I/lactoperoxidase and the cells were returned to incubate in growth media. After varying periods of incubation, aliquots of cells were solubilized and the cell content of labeled receptor subunits were measured by immunoprecipitation with anti-receptor antibodies and NaDodSO4/polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. The fall in 125I-insulin receptor content approximated a single exponential and was quantitated as receptor subunit half-life (t1/2). In cell lines from four patients in whom the number of insulin receptors was reduced by greater than 90%, the rate of receptor loss was greater than normal (t1/2 equals 3.8 +/- 0.9 h vs. 6.5 +/- 1.2 h; mean +/- SD, P less than 0.01). However, a similar acceleration in receptor degradation was seen in cells from five patients with extreme insulin resistance but low-normal insulin receptor concentration (t1/2 equals 4.4 +/- 0.9 h). This group included cells from one patient with a qualitatively abnormal receptor. Thus, all the patients with genetic syndromes of insulin resistance had accelerated receptor degradation, regardless of their receptor concentration. By contrast, insulin receptors on cultured lymphocytes that were obtained from patients with extreme insulin resistance secondary to autoantibodies to the insulin receptor had normal receptor degradation (t1/2 equals 6.1 +/- 1.9 h). We conclude that (a) accelerated insulin receptor degradation is an additional feature of cells from patients with genetic forms of insulin resistance; (b) that accelerated insulin receptor degradation may explain the low-normal receptor concentrations that were seen in some patients with extreme insulin resistance; and (c) that accelerated degradation does not explain the decreased receptor concentration in patients with very low insulin receptor binding and, therefore, by inference, a defect in receptor synthesis must be present in this subgroup.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Crettaz M., Jeanrenaud B. Postreceptor alterations in the states of insulin resistance. Metabolism. 1980 May;29(5):467–473. doi: 10.1016/0026-0495(80)90172-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ey P. L., Prowse S. J., Jenkin C. R. Isolation of pure IgG1, IgG2a and IgG2b immunoglobulins from mouse serum using protein A-sepharose. Immunochemistry. 1978 Jul;15(7):429–436. doi: 10.1016/0161-5890(78)90070-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fantus I. G., Saviolakis G. A., Hedo J. A., Gorden P. Mechanism of glucocorticoid-induced increase in insulin receptors of cultured human lymphocytes. J Biol Chem. 1982 Jul 25;257(14):8277–8283. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hedo J. A., Kahn C. R., Hayashi M., Yamada K. M., Kasuga M. Biosynthesis and glycosylation of the insulin receptor. Evidence for a single polypeptide precursor of the two major subunits. J Biol Chem. 1983 Aug 25;258(16):10020–10026. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hedo J. A., Kasuga M., Van Obberghen E., Roth J., Kahn C. R. Direct demonstration of glycosylation of insulin receptor subunits by biosynthetic and external labeling: evidence for heterogeneity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Aug;78(8):4791–4795. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.8.4791. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hurley J. N., Fu S. M., Kunkel H. G., McKenna G., Scharff M. D. Lymphoblastoid cell lines from patients with chronic lymphocytic leukemia: identification of tumor origin by idiotypic analysis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Nov;75(11):5706–5710. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.11.5706. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kahn C. R., Flier J. S., Bar R. S., Archer J. A., Gorden P., Martin M. M., Roth J. The syndromes of insulin resistance and acanthosis nigricans. Insulin-receptor disorders in man. N Engl J Med. 1976 Apr 1;294(14):739–745. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197604012941401. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kahn C. R., Podskalny J. M. Demonstration of a primary (? genetic) defect in insulin receptors in fibroblasts from a patient with the syndrome of insulin resistance and acanthosis nigricans type A. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1980 Jun;50(6):1139–1141. doi: 10.1210/jcem-50-6-1139. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kahn C. R. Role of insulin receptors in insulin-resistant states. Metabolism. 1980 May;29(5):455–466. doi: 10.1016/0026-0495(80)90171-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kasuga M., Kahn C. R., Hedo J. A., Van Obberghen E., Yamada K. M. Insulin-induced receptor loss in cultured human lymphocytes is due to accelerated receptor degradation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Nov;78(11):6917–6921. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.11.6917. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knutson V. P., Ronnett G. V., Lane M. D. Control of insulin receptor level in 3T3 cells: effect of insulin-induced down-regulation and dexamethasone-induced up-regulation on rate of receptor inactivation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 May;79(9):2822–2826. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.9.2822. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krupp M., Lane M. D. On the mechanism of ligand-induced down-regulation of insulin receptor level in the liver cell. J Biol Chem. 1981 Feb 25;256(4):1689–1694. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muggeo M., Kahn C. R., Bar R. S., Rechler M., Flier J. S., Roth J. The underlying insulin receptor in patients with antireceptor autoantibodies: demonstration of normal binding and immunological properties. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1979 Jul;49(1):110–119. doi: 10.1210/jcem-49-1-110. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Podskalny J. M., Kahn C. R. Cell culture studies on patients with extreme insulin resistance. I. Receptor defects on cultured fibroblasts. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1982 Feb;54(2):261–268. doi: 10.1210/jcem-54-2-261. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reed B. C., Kaufmann S. H., Mackall J. C., Student A. K., Lane M. D. Alterations in insulin binding accompanying differentiation of 3T3-L1 preadipocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Nov;74(11):4876–4880. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.11.4876. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ronnett G. V., Knutson V. P., Lane M. D. Insulin-induced down-regulation of insulin receptors in 3T3-L1 adipocytes. Altered rate of receptor inactivation. J Biol Chem. 1982 Apr 25;257(8):4285–4291. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosen O. M., Chia G. H., Fung C., Rubin C. S. Tunicamycin-mediated depletion of insulin receptors in 3T3-L1 adipocytes. J Cell Physiol. 1979 Apr;99(1):37–42. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1040990106. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roth J., Kahn C. R., Lesniak M. A., Gorden P., De Meyts P., Megyesi K., Neville D. M., Jr, Gavin J. R., 3rd, Soll A. H., Freychet P. Receptors for insulin, NSILA-s, and growth hormone: applications to disease states in man. Recent Prog Horm Res. 1975;31:95–139. doi: 10.1016/b978-0-12-571131-9.50007-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schilling E. E., Rechler M. M., Grunfeld C., Rosenberg A. M. Primary defect of insulin receptors in skin fibroblasts cultured from an infant with leprechaunism and insulin resistance. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Nov;76(11):5877–5881. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.11.5877. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor S. I., Dons R. F., Hernandez E., Roth J., Gorden P. Insulin resistance associated with androgen excess in women with autoantibodies to the insulin receptor. Ann Intern Med. 1982 Dec;97(6):851–855. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-97-6-851. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor S. I., Hedo J. A., Underhill L. H., Kasuga M., Elders M. J., Roth J. Extreme insulin resistance in association with abnormally high binding affinity of insulin receptors from a patient with leprechaunism: evidence for a defect intrinsic to the receptor. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1982 Dec;55(6):1108–1113. doi: 10.1210/jcem-55-6-1108. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor S. I., Leventhal S. Defect in cooperativity in insulin receptors from a patient with a congenital form of extreme insulin resistance. J Clin Invest. 1983 Jun;71(6):1676–1685. doi: 10.1172/JCI110922. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor S. I., Samuels B., Roth J., Kasuga M., Hedo J. A., Gorden P., Brasel D. E., Pokora T., Engel R. R. Decreased insulin binding in cultured lymphocytes from two patients with extreme insulin resistance. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1982 May;54(5):919–930. doi: 10.1210/jcem-54-5-919. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor S. I., Underhill L. H., Hedo J. A., Roth J., Rios M. S., Blizzard R. M. Decreased insulin binding to cultured cells from a patient with the Rabson-Mendenhall syndrome: dichotomy between studies with cultured lymphocytes and cultured fibroblasts. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1983 Apr;56(4):856–861. doi: 10.1210/jcem-56-4-856. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tolleshaug H., Goldstein J. L., Schneider W. J., Brown M. S. Posttranslational processing of the LDL receptor and its genetic disruption in familial hypercholesterolemia. Cell. 1982 Oct;30(3):715–724. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90276-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wachslicht-Rodbard H., Muggeo M., Kahn C. R., Saviolakis G. A., Harrison L. C., Flier J. S. Heterogeneity of the insulin-receptor interaction in lipoatropic diabetes. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1981 Mar;52(3):416–425. doi: 10.1210/jcem-52-3-416. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yip C. C., Yeung C. W., Moule M. L. Photoaffinity labeling of insulin receptor of rat adiopocyte plasma membrane. J Biol Chem. 1978 Mar 25;253(6):1743–1745. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]