Abstract
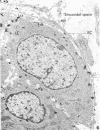
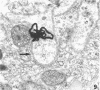
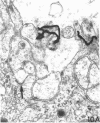
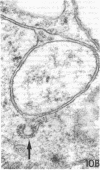
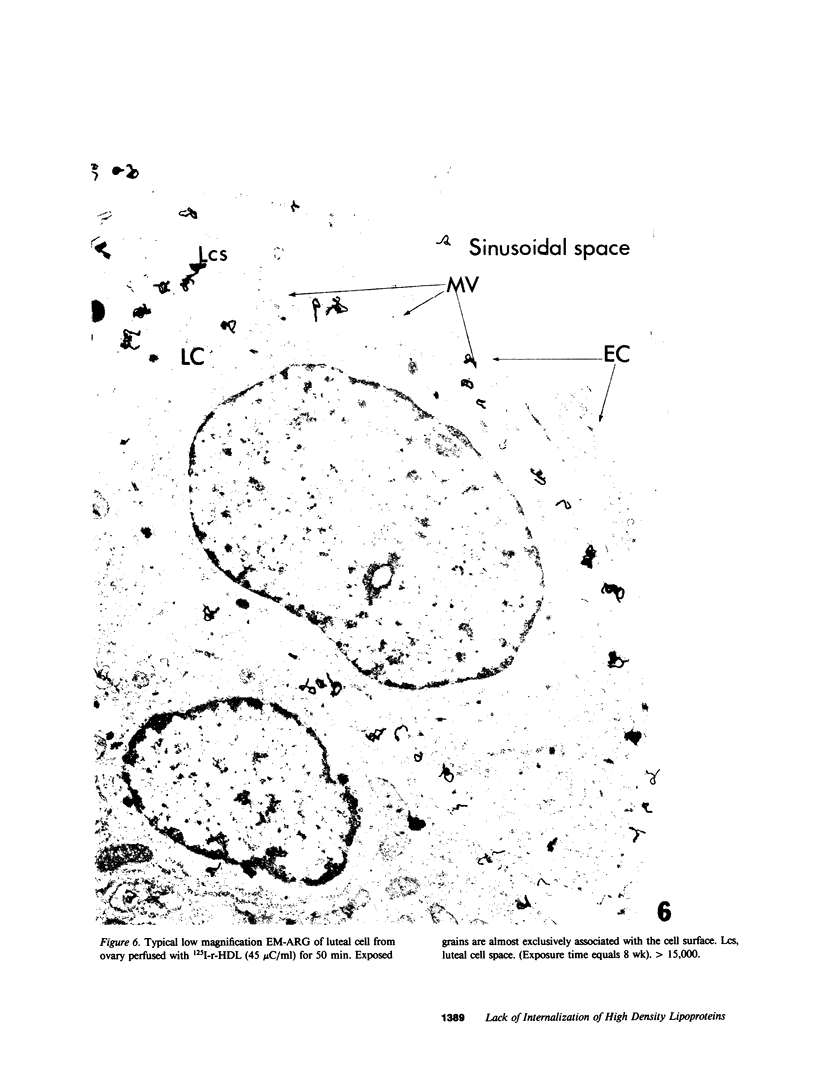
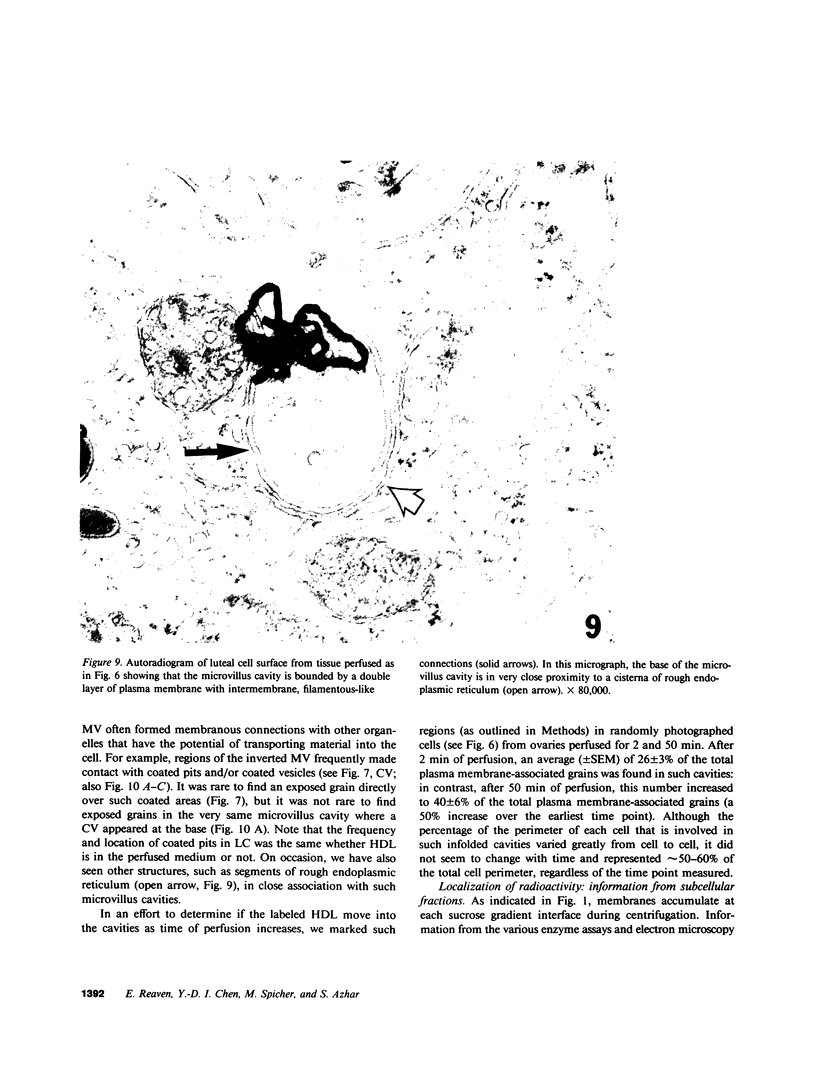
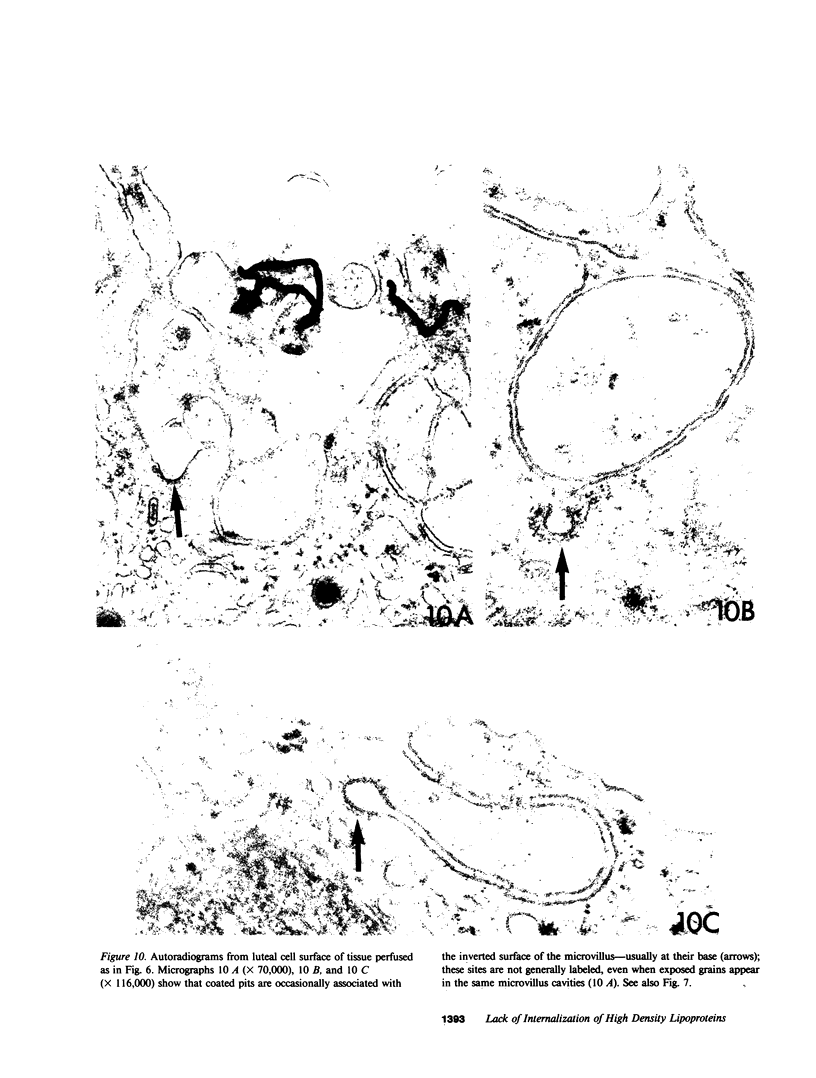
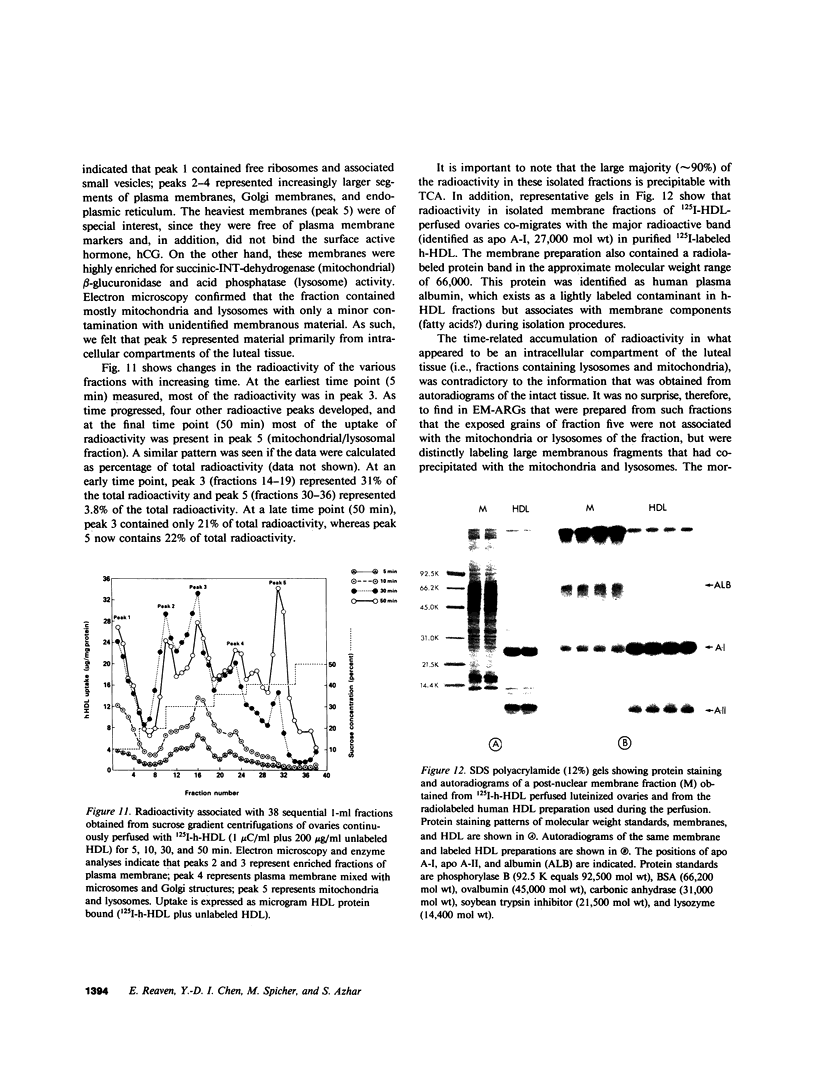
Although it is clear that high density lipoproteins (HDL) can support steroidogenesis in several rat cell systems, questions still arise as to how HDL are processed by cells. In particular, it is not yet clear whether HDL are internalized by a pathway similar to that used for low density lipoproteins. This issue was examined in the present study using the luteinized ovaries of hormone-primed immature rats in an in situ perfusion system. Ovaries were perfused for 2-120 min with 125I-labeled human or rat HDL and processed for autoradiographic studies at the light and electron microscopic level, or homogenized and used for isolation of subcellular membranes. The results show that the luteal cells of this tissue bind both human and rat HDL with great specificity. Moreover, the intact HDL particle does not appear to be internalized by the luteal cell during the period of perfusion: i.e., the protein moiety of the labeled HDL remains associated with the plasma membrane at all times. Evidence from the autoradiographs suggest, however, that with time, an increasing proportion of the plasma membrane-bound protein is associated with inverted microvilli, which are embedded within the cytoplasm and make close contact with structures of the interior of the cell. We speculate that HDL-cholesterol may be transferred at such sites.
Full text
PDF


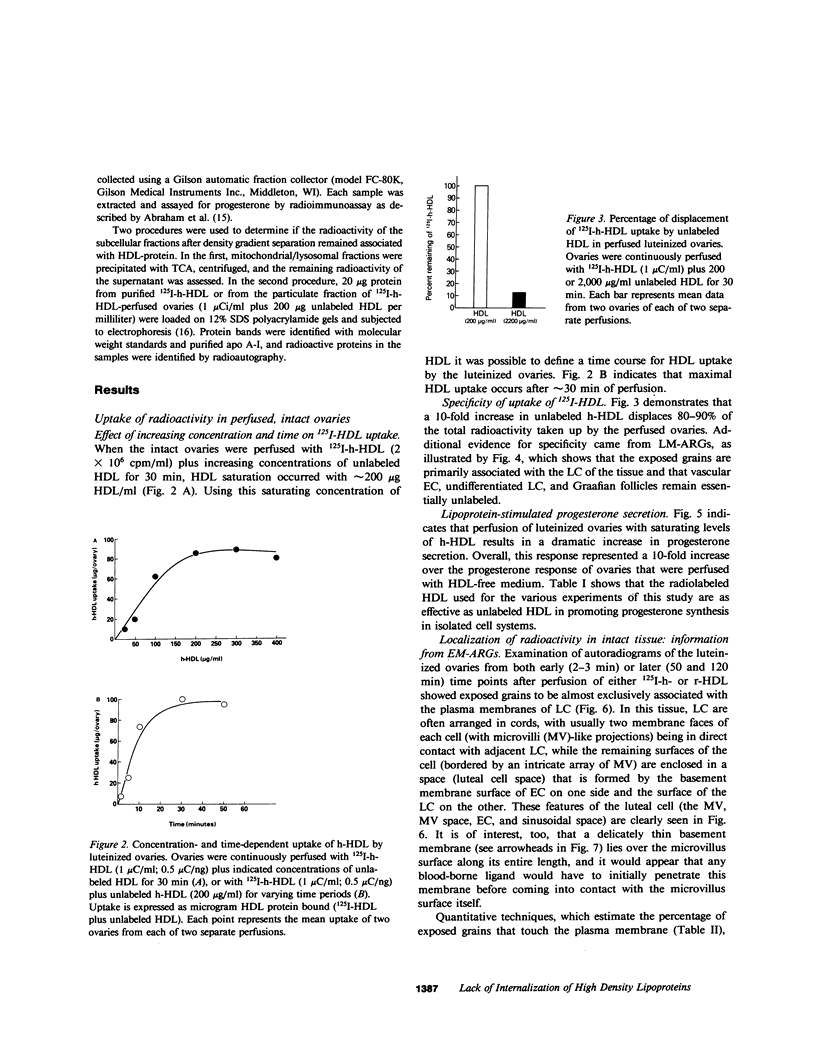
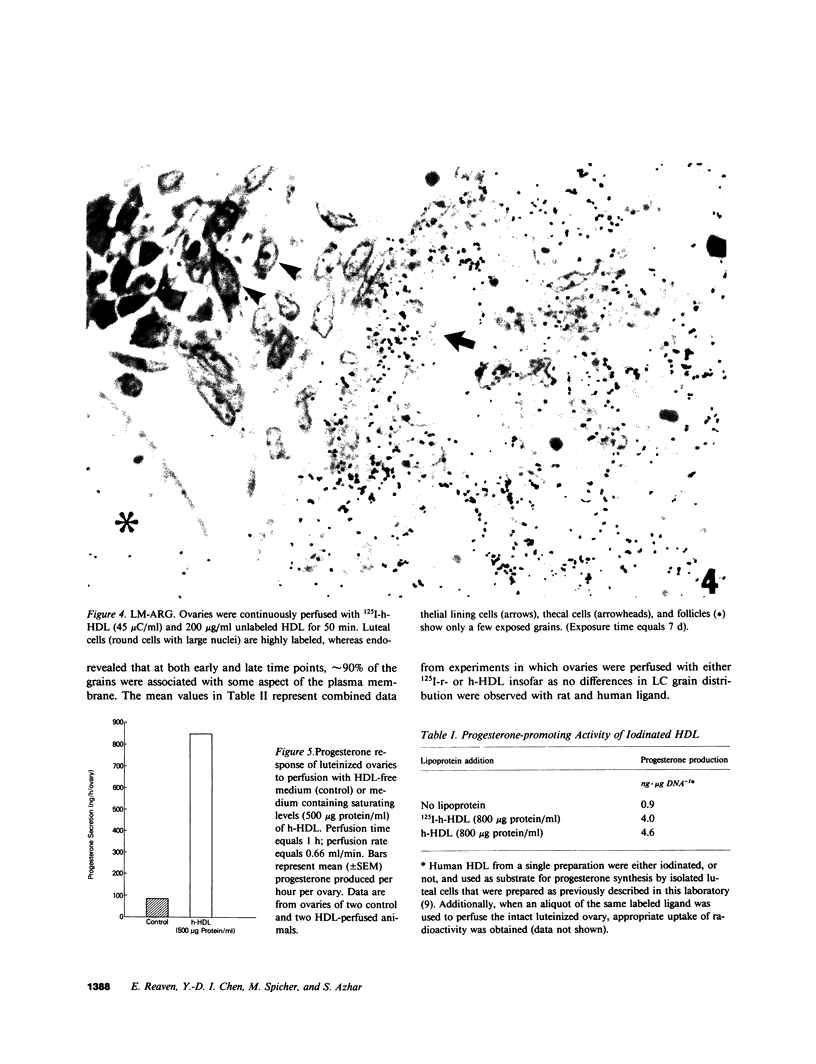





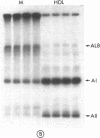
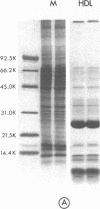
Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Azhar S., Chen Y. D., Reaven G. M. Stimulation of lipoprotein receptors and role of lipoprotein and cellular cholesterol during gonadotropin-induced desensitization of steroidogenic response in luteinized rat ovary. J Biol Chem. 1983 Mar 25;258(6):3735–3740. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Azhar S., Hwang S. F., Reaven E. P. Effect of antimicrotubule agents on terminal glycosyltransferases and other enzymes associated with rat liver subcellular fractions. Biochem J. 1983 Jun 15;212(3):721–731. doi: 10.1042/bj2120721. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Azhar S., Reaven E. Effect of antimicrotubule agents on microtubules and steroidogenesis in luteal cells. Am J Physiol. 1982 Nov;243(5):E380–E386. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.1982.243.5.E380. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chapman M. J. Animal lipoproteins: chemistry, structure, and comparative aspects. J Lipid Res. 1980 Sep;21(7):789–853. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen Y. D., Kraemer F. B., Reaven G. M. Identification of specific high density lipoprotein-binding sites in rat testis and regulation of binding by human chorionic gonadotropin. J Biol Chem. 1980 Oct 10;255(19):9162–9167. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edelstein C., Lim C. T., Scanu A. M. On the subunit structure of the protein of human serum high density lipoprotein. I. A study of its major polypeptide component (Sephadex, fraction 3). J Biol Chem. 1972 Sep 25;247(18):5842–5849. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gwynne J. T., Strauss J. F., 3rd The role of lipoproteins in steroidogenesis and cholesterol metabolism in steroidogenic glands. Endocr Rev. 1982 Summer;3(3):299–329. doi: 10.1210/edrv-3-3-299. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jansen H., De Greef W. J. Heparin-releasable lipase activity of rat adrenals, ovaries and testes. Biochem J. 1981 Jun 15;196(3):739–745. doi: 10.1042/bj1960739. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paavola L. G., Strauss J. F., 3rd Uptake of lipoproteins by in situ perfused rat ovaries: identification of binding sites for high density lipoproteins. J Cell Biol. 1983 Sep;97(3):593–606. doi: 10.1083/jcb.97.3.593. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reaven E. P., Reaven G. M. Evidence that microtubules play a permissive role in hepatocyte very low density lipoprotein secretion. J Cell Biol. 1980 Jan;84(1):28–39. doi: 10.1083/jcb.84.1.28. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reaven E., Azhar S. Effect of various hepatic membrane fractions on microtubule assembly-with special emphasis on the role of membrane phospholipids. J Cell Biol. 1981 May;89(2):300–308. doi: 10.1083/jcb.89.2.300. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rothblat G. H., Arbogast L. Y., Ray E. K. Stimulation of esterified cholesterol accumulation in tissue culture cells exposed to high density lipoproteins enriched in free cholesterol. J Lipid Res. 1978 Mar;19(3):350–358. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tan C. H., Robinson J. The superovulated rat: its use as a model in studies on the acute steroidogenic effects of luteinizing hormone. Endocrinology. 1977 Aug;101(2):396–402. doi: 10.1210/endo-101-2-396. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]