Abstract
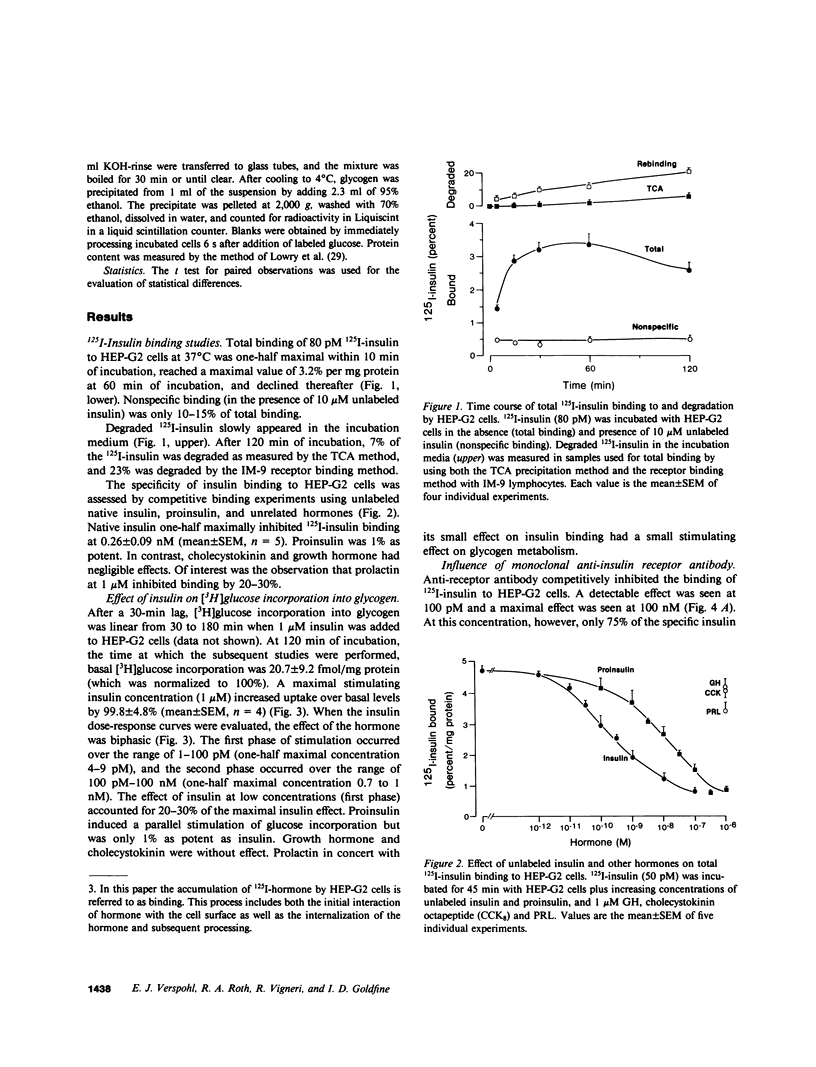
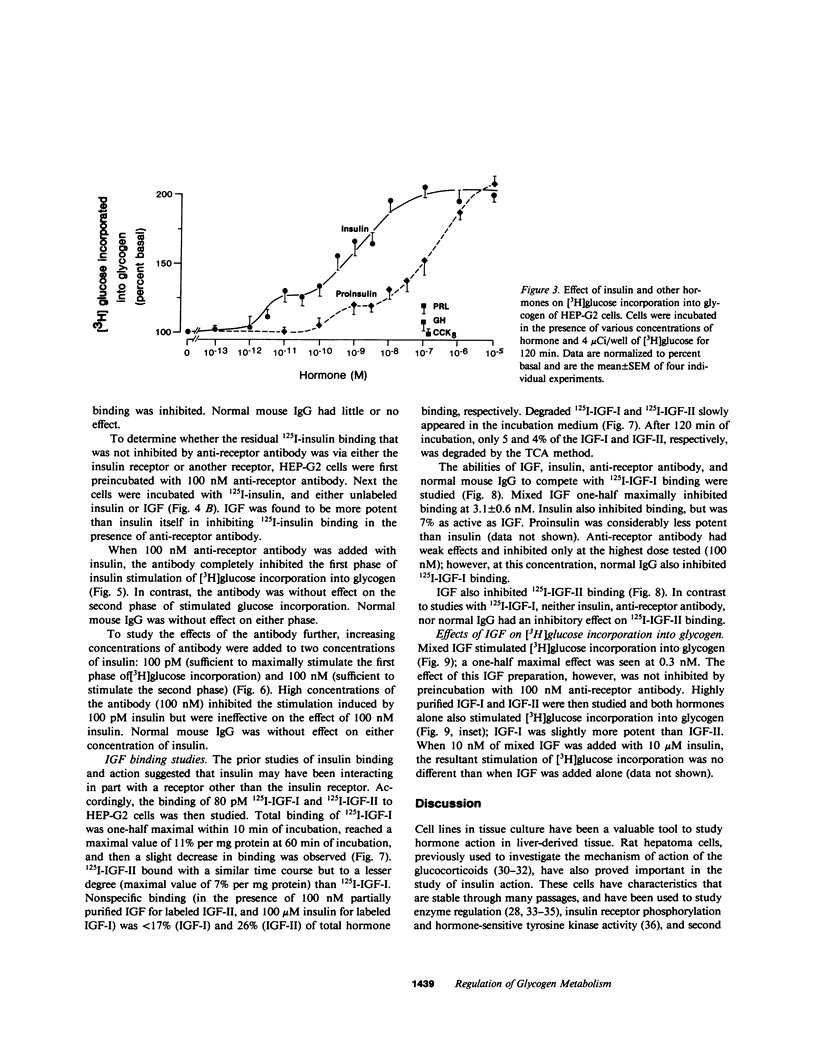
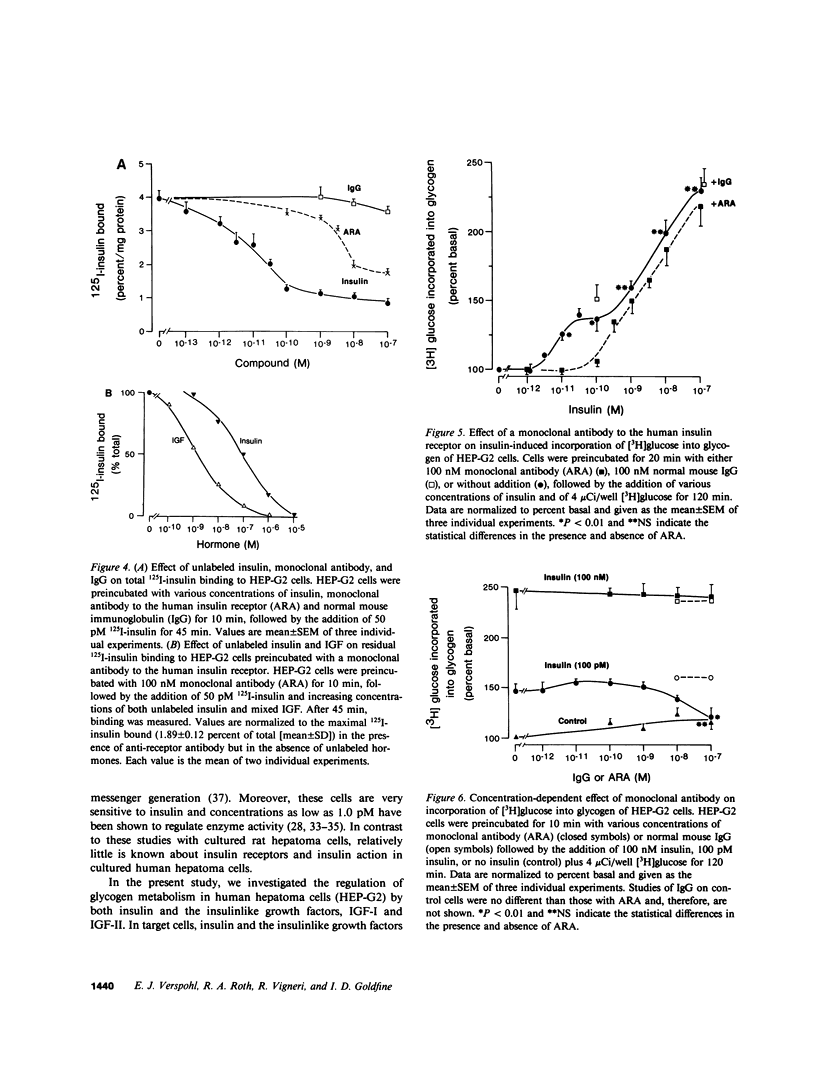
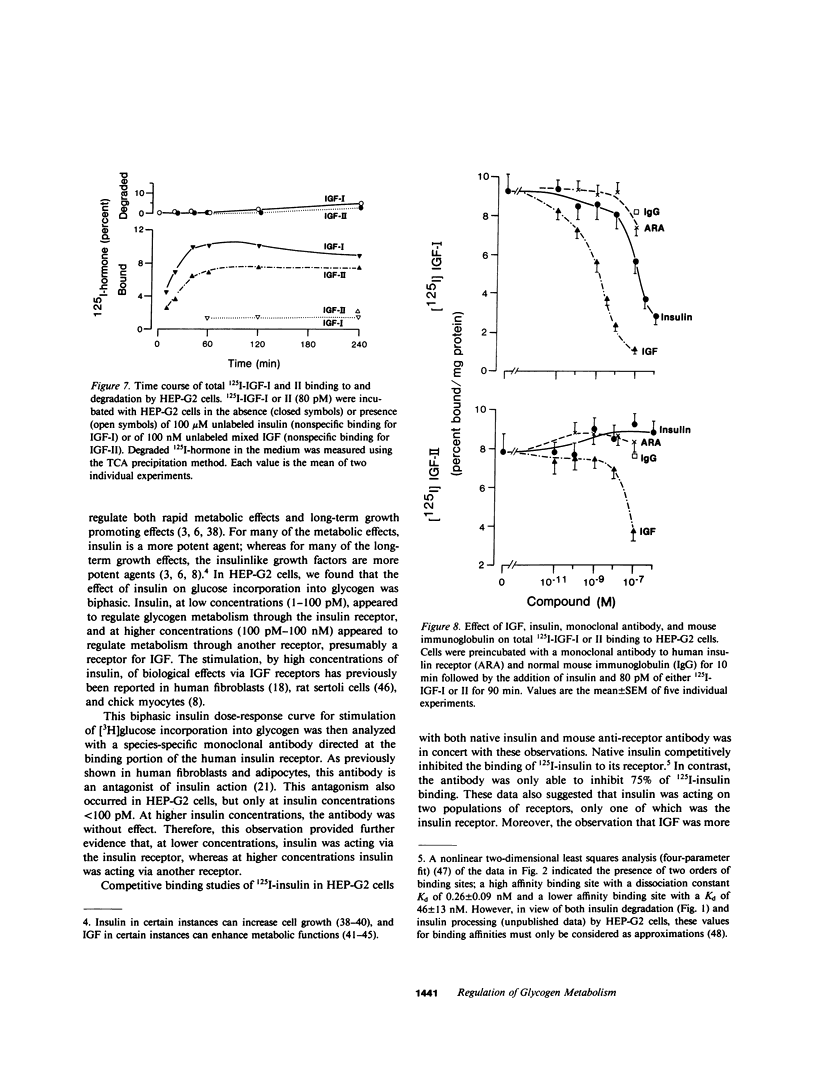
Insulin and the insulinlike growth factors (IGF-I and IGF-II) are members of a family of hormones that regulate the metabolism and growth of many tissues. Cultured HEP-G2 cells (a minimal deviation human hepatoma) have insulin receptors and respond to insulin by increasing their glycogen metabolism. In the present study with HEP-G2 cells, we used 125I-labeled insulin, IGF-I, and IGF-II to identify distinct receptors for each hormone by competition-inhibition studies. Unlabeled insulin was able to inhibit 125I-IGF-I binding but not 125I-IGF-II binding. A mouse monoclonal antibody to the human insulin receptor that inhibits insulin binding and blocks insulin action inhibited 75% of 125I-insulin binding, but inhibited neither 125I-IGF-I nor 125I-IGF-II binding. When glycogen metabolism was studied, insulin stimulated [3H]glucose incorporation into glycogen in a biphasic manner; one phase that was 20-30% of the maximal response occurred over 1-100 pM, and the other phase occurred over 100 pM-100 nM. The anti-receptor monoclonal antibody inhibited the first phase of insulin stimulation but not the second. Both IGF-I and IGF-II stimulated [3H]glucose incorporation over the range of 10 pM-10 nM; IGF-I was three to fivefold more potent. The monoclonal antibody, however, was without effect on IGF regulation of glycogen metabolism. Therefore, these studies indicate that insulin as well as the IGFs at physiological concentrations regulate glycogen metabolism in HEP-G2 cells. Moreover, this regulation of glycogen metabolism is mediated by both the insulin receptor and the IGF receptors.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Beck J. S., Goren H. J. Simulation of association curves and 'Scatchard' plots of binding reactions where ligand and receptor are degraded or internalized. J Recept Res. 1983;3(5):561–577. doi: 10.3109/10799898309041948. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berhanu P., Olefsky J. M. Effects of insulin and insulin-like agents on the glucose transport system of cultured human fibroblasts. Diabetes. 1981 Jun;30(6):523–529. doi: 10.2337/diab.30.6.523. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blundell T. L., Bedarkar S., Rinderknecht E., Humbel R. E. Insulin-like growth factor: a model for tertiary structure accounting for immunoreactivity and receptor binding. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Jan;75(1):180–184. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.1.180. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Borland K., Mita M., Oppenheimer C. L., Blinderman L. A., Massague J., Hall P. F., Czech M. P. The actions of insulin-like growth factors I and II on cultured Sertoli cells. Endocrinology. 1984 Jan;114(1):240–246. doi: 10.1210/endo-114-1-240. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(76)90527-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ciechanover A., Schwartz A. L., Lodish H. F. The asialoglycoprotein receptor internalizes and recycles independently of the transferrin and insulin receptors. Cell. 1983 Jan;32(1):267–275. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90517-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crettaz M., Kahn C. R. Analysis of insulin action using differentiated and dedifferentiated hepatoma cells. Endocrinology. 1983 Oct;113(4):1201–1209. doi: 10.1210/endo-113-4-1201. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Czech M. P., Massague J. Subunit structure and dynamics of the insulin receptor. Fed Proc. 1982 Sep;41(11):2719–2723. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freychet P., Kahn R., Roth J., Neville D. M., Jr Insulin interactions with liver plasma membranes. Independence of binding of the hormone and its degradation. J Biol Chem. 1972 Jun 25;247(12):3953–3961. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldfine I. D., Smith G. J. Binding of insulin to isolated nuclei. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 May;73(5):1427–1431. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.5.1427. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hofmann C., Marsh J. W., Miller B., Steiner D. F. Cultured hepatoma cells as a model system for studying insulin processing and biologic responsiveness. Diabetes. 1980 Nov;29(11):865–874. doi: 10.2337/diab.29.11.865. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iwamoto Y., Wong K. Y., Goldfine I. D. Insulin action in cultured HTC and H35 rat hepatoma cells: receptor binding and hormone sensitivity. Endocrinology. 1981 Jan;108(1):44–51. doi: 10.1210/endo-108-1-44. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jonas H. A., Baxter R. C., Harrison L. C. Structural differences between insulin and somatomedin-C/insulin-like growth factor-1 receptors revealed by autoantibodies to the insulin receptor. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1982 Nov 30;109(2):463–470. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(82)91744-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kasuga M., Karlsson F. A., Kahn C. R. Insulin stimulates the phosphorylation of the 95,000-dalton subunit of its own receptor. Science. 1982 Jan 8;215(4529):185–187. doi: 10.1126/science.7031900. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kasuga M., Van Obberghen E., Nissley S. P., Rechler M. M. Demonstration of two subtypes of insulin-like growth factor receptors by affinity cross-linking. J Biol Chem. 1981 Jun 10;256(11):5305–5308. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- King G. L., Kahn C. R., Rechler M. M., Nissley S. P. Direct demonstration of separate receptors for growth and metabolic activities of insulin and multiplication-stimulating activity (an insulinlike growth factor) using antibodies to the insulin receptor. J Clin Invest. 1980 Jul;66(1):130–140. doi: 10.1172/JCI109826. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knight A. B., Rechler M. M., Romanus J. A., Van Obberghen-Schilling E. E., Nissley S. P. Stimulation of glucose incorporation and amino acid transport by insulin and an insulin-like growth factor in fibroblasts with defective insulin receptors cultured from a patient with leprechaunism. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Apr;78(4):2554–2558. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.4.2554. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knowles B. B., Howe C. C., Aden D. P. Human hepatocellular carcinoma cell lines secrete the major plasma proteins and hepatitis B surface antigen. Science. 1980 Jul 25;209(4455):497–499. doi: 10.1126/science.6248960. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koontz J. W., Iwahashi M. Insulin as a potent, specific growth factor in a rat hepatoma cell line. Science. 1981 Feb 27;211(4485):947–949. doi: 10.1126/science.7008195. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kull F. C., Jr, Jacobs S., Su Y. F., Svoboda M. E., Van Wyk J. J., Cuatrecasas P. Monoclonal antibodies to receptors for insulin and somatomedin-C. J Biol Chem. 1983 May 25;258(10):6561–6566. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Massagué J., Blinderman L. A., Czech M. P. The high affinity insulin receptor mediates growth stimulation in rat hepatoma cells. J Biol Chem. 1982 Dec 10;257(23):13958–13963. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Massagué J., Czech M. P. Role of disulfides in the subunit structure of the insulin receptor. Reduction of class I disulfides does not impair transmembrane signalling. J Biol Chem. 1982 Jun 25;257(12):6729–6738. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Massagué J., Czech M. P. The subunit structures of two distinct receptors for insulin-like growth factors I and II and their relationship to the insulin receptor. J Biol Chem. 1982 May 10;257(9):5038–5045. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parker J. C., Kiechle F. L., Jarett L. Partial purification from hepatoma cells of an intracellular substance which mediates the effects of insulin on pyruvate dehydrogenase and low Km cyclic AMP phosphodiesterase. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1982 Apr 15;215(1):339–344. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(82)90312-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poggi C., Le Marchand-Brustel Y., Zapf J., Froesch E. R., Freychet P. Effects and binding of insulin-like growth factor I in the isolated soleus muscle of lean and obese mice: comparison with insulin. Endocrinology. 1979 Sep;105(3):723–730. doi: 10.1210/endo-105-3-723. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rechler M. M., Podskalny J. M., Nissley S. P. Characterization of the binding of multiplication-stimulating activity to a receptor for growth polypeptides in chick embryo fibroblasts. J Biol Chem. 1977 Jun 10;252(11):3898–3910. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rechler M. M., Zapf J., Nissley S. P., Froesch E. R., Moses A. C., Podskalny J. M., Schilling E. E., Humbel R. E. Interactions of insulin-like growth factors I and II and multiplication-stimulating activity with receptors and serum carrier proteins. Endocrinology. 1980 Nov;107(5):1451–1459. doi: 10.1210/endo-107-5-1451. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rinderknecht E., Humbel R. E. Primary structure of human insulin-like growth factor II. FEBS Lett. 1978 May 15;89(2):283–286. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(78)80237-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rinderknecht E., Humbel R. E. The amino acid sequence of human insulin-like growth factor I and its structural homology with proinsulin. J Biol Chem. 1978 Apr 25;253(8):2769–2776. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roth R. A., Cassell D. J., Wong K. Y., Maddux B. A., Goldfine I. D. Monoclonal antibodies to the human insulin receptor block insulin binding and inhibit insulin action. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Dec;79(23):7312–7316. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.23.7312. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roth R. A., Maddux B., Wong K. Y., Styne D. M., Van Vliet G., Humbel R. E., Goldfine I. D. Interactions of a monoclonal antibody to the insulin receptor with receptors for insulin-like growth factors. Endocrinology. 1983 May;112(5):1865–1867. doi: 10.1210/endo-112-5-1865. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rousseau G. G., Baxter J. D., Higgins S. J., Tomkins G. M. Steroid-induced nuclear binding of glucocorticoid receptors in intact hepatoma cells. J Mol Biol. 1973 Sep 25;79(3):539–554. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(73)90405-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmid C., Steiner T., Froesch E. R. Insulin-like growth factors stimulate synthesis of nucleic acids and glycogen in cultured calvaria cells. Calcif Tissue Int. 1983 Jul;35(4-5):578–585. doi: 10.1007/BF02405097. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmid C., Steiner T., Froesch E. R. Preferential enhancement of myoblast differentiation by insulin-like growth factors (IGF I and IGF II) in primary cultures of chicken embryonic cells. FEBS Lett. 1983 Sep 5;161(1):117–121. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(83)80742-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stuart C. A., Pietrzyk R., Siu A. K., Furlanetto R. W. Size discrepancy between somatomedin-C and insulin receptors. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1984 Jan;58(1):1–5. doi: 10.1210/jcem-58-1-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson E. B., Aviv D., Lippman M. E. Variants of HTC cells with low tyrosine aminotransferinase inducibility and apparently normal glucorticoid receptors. Endocrinology. 1977 Feb;100(2):406–419. doi: 10.1210/endo-100-2-406. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson E. B., Granner D. K., Gelehrter T., Erickson J., Hager G. L. Unlinked control of multiple glucocorticoid-induced processes in HTC cells. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 1979 Sep;15(3):135–150. doi: 10.1016/0303-7207(79)90034-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wicks W. D., Barnett C. A., McKibbin J. B. Interaction between hormones and cyclic AMP in regulating specific hepatic enzyme synthesis. Fed Proc. 1974 Apr;33(4):1105–1111. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams J. A., Bailey A., Humbel R., Goldfine I. D. Insulinlike growth factors bind to specific receptors in isolated pancreatic acini. Am J Physiol. 1984 Jan;246(1 Pt 1):G96–G99. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.1984.246.1.G96. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zapf J., Rinderknecht E., Humbel R. E., Froesch E. R. Nonsuppressible insulin-like activity (NSILA) from human serum: recent accomplishments and their physiologic implications. Metabolism. 1978 Dec;27(12):1803–1828. doi: 10.1016/0026-0495(78)90267-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zapf J., Schoenle E., Froesch E. R. Insulin-like growth factors I and II: some biological actions and receptor binding characteristics of two purified constituents of nonsuppressible insulin-like activity of human serum. Eur J Biochem. 1978 Jun 15;87(2):285–296. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1978.tb12377.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zapf J., Walter H., Froesch E. R. Radioimmunological determination of insulinlike growth factors I and II in normal subjects and in patients with growth disorders and extrapancreatic tumor hypoglycemia. J Clin Invest. 1981 Nov;68(5):1321–1330. doi: 10.1172/JCI110379. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



