Abstract
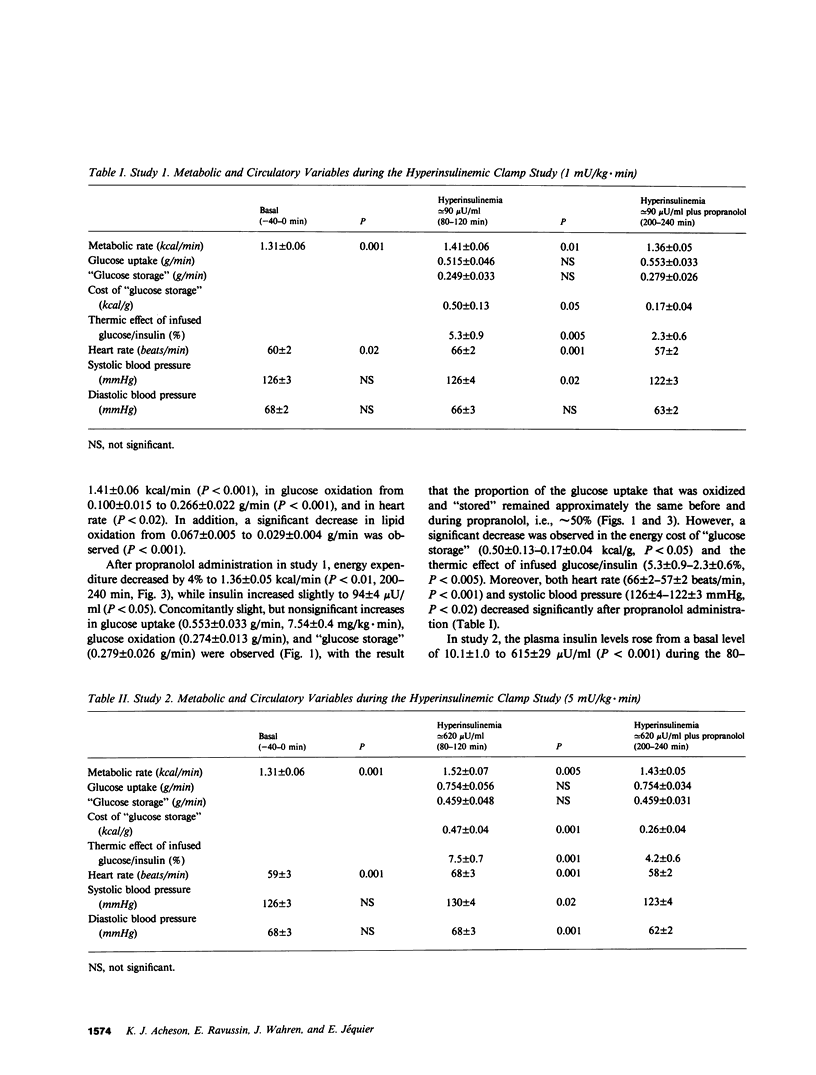
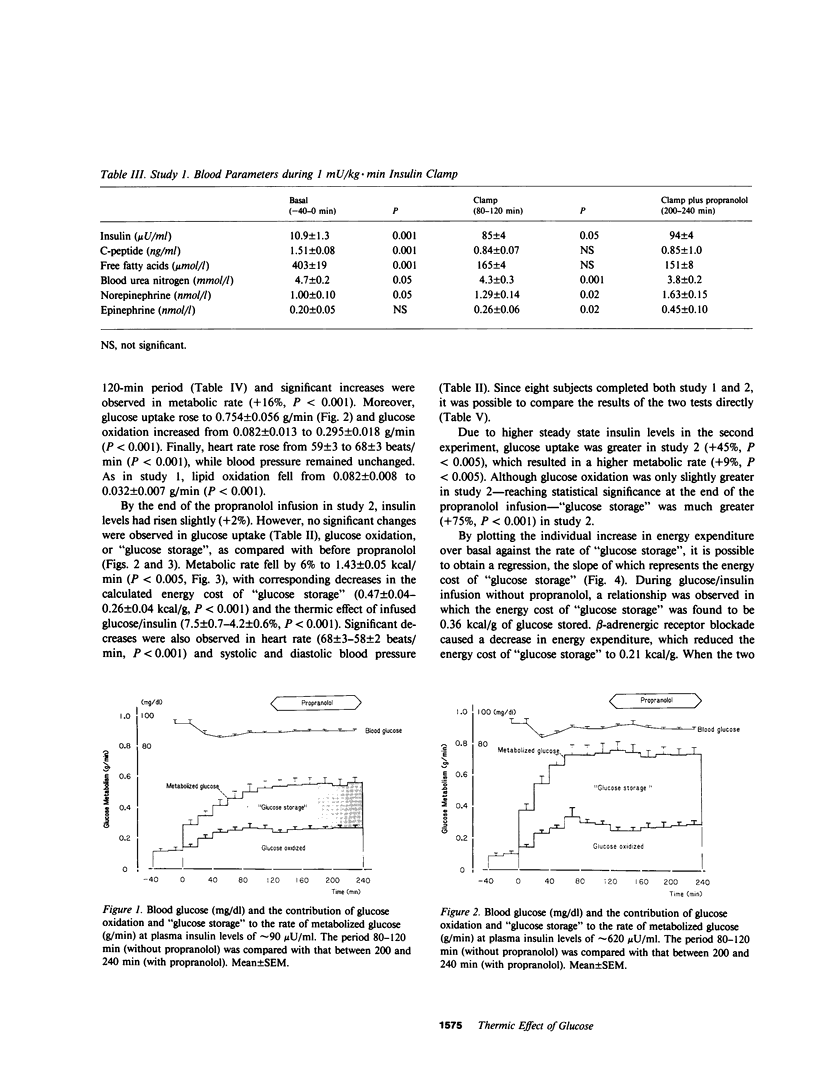
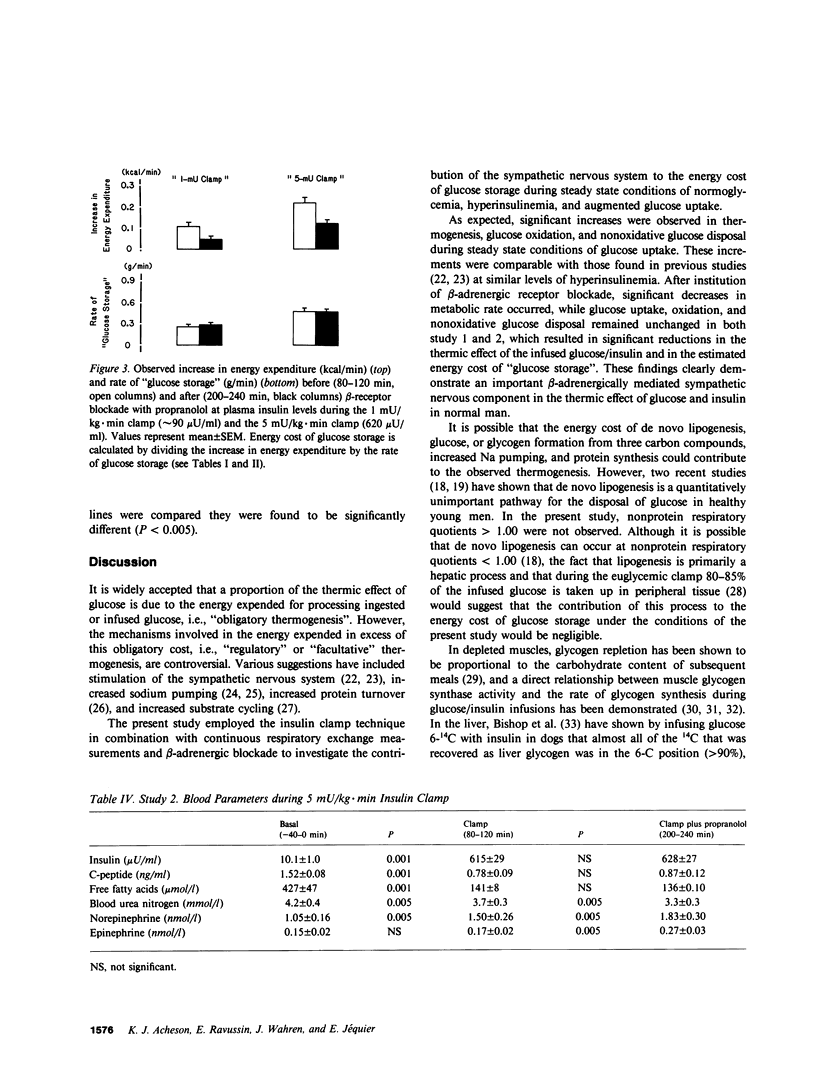
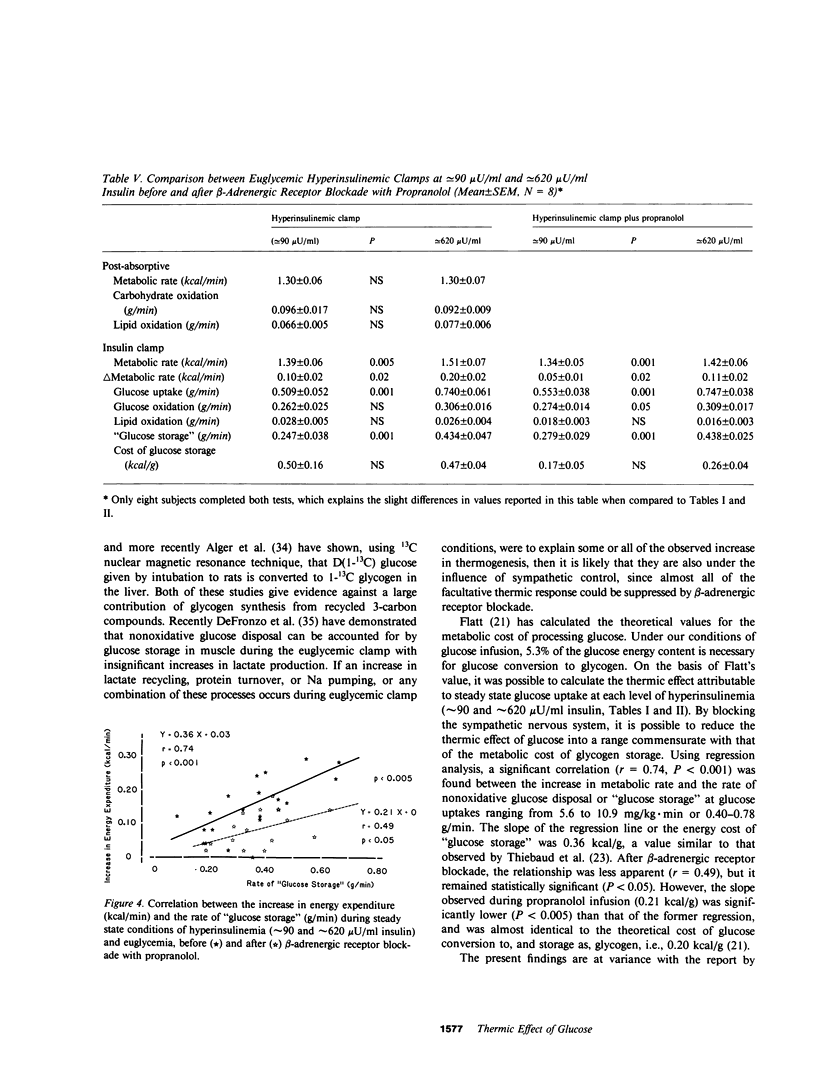
The contribution of the sympathetic nervous system to the thermic effect of intravenously infused glucose and insulin was studied in 10 healthy young men before and after beta-adrenergic receptor blockade with propranolol during conditions of normoglycemia (90 mg/dl) at two levels of hyperinsulinemia (approximately 90 microU/ml and approximately 620 microU/ml). During steady state conditions of glucose uptake (0.515 +/- 0.046 and 0.754 +/- 0.056 g/min), significant increases were observed in energy expenditure (0.10 +/- 0.02 kcal/min, P less than 0.001, and 0.21 +/- 0.02 kcal/min, P less than 0.01, respectively). Similarly, glucose oxidation increased from 0.100 +/- 0.015 to 0.266 +/- 0.022 g/min (P less than 0.001) at approximately microU/ml insulin and from 0.082 +/- 0.013 to 0.295 +/- 0.018 g/min (P less than 0.001) at approximately 620 microU/ml insulin. Concomitantly, the rate of nonoxidative glucose disposal or "glucose storage" was 0.249 +/- 0.033 and 0.459 +/- 0.048 g/min, respectively. At this time the thermic effect of infused glucose/insulin was 5.3 +/- 0.9 and 7.5 +/- 0.7%, and the energy cost of "glucose storage" was 0.50 +/- 0.16 kcal/g and 0.47 +/- 0.04 kcal/g at the two different levels of glucose uptake. After beta-adrenergic receptor blockade with propranolol, glucose uptake, oxidation, and "storage" were unchanged in both studies, but significant decreases in energy expenditure were observed (1.41 +/- 0.06-1.36 +/- 0.05 kcal/min, P less than 0.01 at approximately 90 microU/ml insulin, and 1.52 +/- 0.07-1.43 +/- 0.05 kcal/min, P less than 0.005 at approximately 620 microU/ml insulin) causing significant falls in both the estimated thermic effect of infused glucose/insulin and the energy cost of "glucose storage". Regression analysis of the results from both studies indicated a mean energy cost for "glucose storage" of 0.36 kcal/g (r = 0.74, P less than 0.001), which fell significantly (P less than 0.005) to 0.21 kcal/g (r = 0.49, P less than 0.05) during beta-adrenergic receptor blockade with propranolol. The latter is in close agreement with that calculated on theoretical grounds for the metabolic cost of glucose storage as glycogen, i.e., obligatory thermogenesis. It is concluded that beta-adrenergically mediated sympathetic nervous activity is responsible for almost the entire rise in energy expenditure in excess of the obligatory requirements for processing and storing glucose during conditions of normoglycemia and hyperinsulinemia in healthy man, and that the energy cost of "glucose storage" is not different at normal (approximately 90 microU/ml) and supraphysiological (approximately 620 microU/ml) plasma insulin concentrations.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ANAND B. K., CHHINA G. S., SHARMA K. N., DUA S., SINGH B. ACTIVITY OF SINGLE NEURONS IN THE HYPOTHALAMIC FEEDING CENTERS: EFFECT OF GLUCOSE. Am J Physiol. 1964 Nov;207:1146–1154. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1964.207.5.1146. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Acheson K. J., Flatt J. P., Jéquier E. Glycogen synthesis versus lipogenesis after a 500 gram carbohydrate meal in man. Metabolism. 1982 Dec;31(12):1234–1240. doi: 10.1016/0026-0495(82)90010-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Acheson K. J., Schutz Y., Bessard T., Ravussin E., Jéquier E., Flatt J. P. Nutritional influences on lipogenesis and thermogenesis after a carbohydrate meal. Am J Physiol. 1984 Jan;246(1 Pt 1):E62–E70. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.1984.246.1.E62. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Acheson K., Jéquier E., Wahren J. Influence of beta-adrenergic blockade on glucose-induced thermogenesis in man. J Clin Invest. 1983 Sep;72(3):981–986. doi: 10.1172/JCI111070. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alger J. R., Sillerud L. O., Behar K. L., Gillies R. J., Shulman R. G., Gordon R. E., Shae D., Hanley P. E. In vivo carbon-13 nuclear magnetic resonance studies of mammals. Science. 1981 Nov 6;214(4521):660–662. doi: 10.1126/science.7292005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BISHOP J. S., STEELE R., ALTSZULER N., DUNN A., BJERKNES C., DEBODO R. C. EFFECTS OF INSULIN ON LIVER GLYCOGEN SYNTHESIS AND BREAKDOWN IN THE DOG. Am J Physiol. 1965 Feb;208:307–316. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1965.208.2.307. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bogardus C., Lillioja S., Stone K., Mott D. Correlation between muscle glycogen synthase activity and in vivo insulin action in man. J Clin Invest. 1984 Apr;73(4):1185–1190. doi: 10.1172/JCI111304. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bogardus C., Thuillez P., Ravussin E., Vasquez B., Narimiga M., Azhar S. Effect of muscle glycogen depletion on in vivo insulin action in man. J Clin Invest. 1983 Nov;72(5):1605–1610. doi: 10.1172/JCI111119. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bray G. A., York D. A. Hypothalamic and genetic obesity in experimental animals: an autonomic and endocrine hypothesis. Physiol Rev. 1979 Jul;59(3):719–809. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1979.59.3.719. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DOLE V. P., MEINERTZ H. Microdetermination of long-chain fatty acids in plasma and tissues. J Biol Chem. 1960 Sep;235:2595–2599. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeFronzo R. A., Alvestrand A., Smith D., Hendler R., Hendler E., Wahren J. Insulin resistance in uremia. J Clin Invest. 1981 Feb;67(2):563–568. doi: 10.1172/JCI110067. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeFronzo R. A., Jacot E., Jequier E., Maeder E., Wahren J., Felber J. P. The effect of insulin on the disposal of intravenous glucose. Results from indirect calorimetry and hepatic and femoral venous catheterization. Diabetes. 1981 Dec;30(12):1000–1007. doi: 10.2337/diab.30.12.1000. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeFronzo R. A., Thorin D., Felber J. P., Simonson D. C., Thiebaud D., Jequier E., Golay A. Effect of beta and alpha adrenergic blockade on glucose-induced thermogenesis in man. J Clin Invest. 1984 Mar;73(3):633–639. doi: 10.1172/JCI111253. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeFronzo R. A., Tobin J. D., Andres R. Glucose clamp technique: a method for quantifying insulin secretion and resistance. Am J Physiol. 1979 Sep;237(3):E214–E223. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.1979.237.3.E214. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deibert D. C., DeFronzo R. A. Epinephrine-induced insulin resistance in man. J Clin Invest. 1980 Mar;65(3):717–721. doi: 10.1172/JCI109718. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doberne L., Greenfield M. S., Schulz B., Reaven G. M. Enhanced glucose utilization during prolonged glucose clamp studies. Diabetes. 1981 Oct;30(10):829–835. doi: 10.2337/diab.30.10.829. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guernsey D. L., Stevens E. D. The cell membrane sodium pump as a mechanism for increasing thermogenesis during cold acclimation in rats. Science. 1977 May 20;196(4292):908–910. doi: 10.1126/science.860125. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hallman H., Farnebo L. O., Hamberger B., Johnsson G. A sensitive method for the determination of plasma catecholamines using liquid chromatography with electrochemical detection. Life Sci. 1978 Sep 11;23(10):1049–1052. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(78)90665-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heindel J. J., Cushman S. W., Jeanrenaud B. Cell-associated fatty acid levels and energy-requiring processes in mouse adipocytes. Am J Physiol. 1974 Jan;226(1):16–24. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1974.226.1.16. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herbert V., Lau K. S., Gottlieb C. W., Bleicher S. J. Coated charcoal immunoassay of insulin. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1965 Oct;25(10):1375–1384. doi: 10.1210/jcem-25-10-1375. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hervey G. R., Tobin G. Luxuskonsumption, diet-induced thermogenesis and brown fat: a critical review. Clin Sci (Lond) 1983 Jan;64(1):7–18. doi: 10.1042/cs0640007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hjemdahl P., Daleskog M., Kahan T. Determination of plasma catecholamines by high performance liquid chromatography with electrochemical detection: comparison with a radioenzymatic method. Life Sci. 1979 Jul 9;25(2):131–138. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(79)90384-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jung R. T., Shetty P. S., James W. P., Barrand M. A., Callingham B. A. Reduced thermogenesis in obesity. Nature. 1979 May 24;279(5711):322–323. doi: 10.1038/279322a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kolterman O. G., Insel J., Saekow M., Olefsky J. M. Mechanisms of insulin resistance in human obesity: evidence for receptor and postreceptor defects. J Clin Invest. 1980 Jun;65(6):1272–1284. doi: 10.1172/JCI109790. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MARSH W. H., FINGERHUT B., MILLER H. AUTOMATED AND MANUAL DIRECT METHODS FOR THE DETERMINATION OF BLOOD UREA. Clin Chem. 1965 Jun;11:624–627. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller B. G., Otto W. R., Grimble R. F., York D. A., Taylor T. G. The relationship between protein turnover and energy balance in lean and genetically obese (ob/ob) mice. Br J Nutr. 1979 Sep;42(2):185–199. doi: 10.1079/bjn19790106. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morgan J. B., York D. A., Wasilewska A., Portman J. A study of the thermic responses to a meal and to a sympathomimetic drug (ephedrine) in relation to energy balance in man. Br J Nutr. 1982 Jan;47(1):21–32. doi: 10.1079/bjn19820005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Newsholme E. A., Crabtree B. Substrate cycles in metabolic regulation and in heat generation. Biochem Soc Symp. 1976;(41):61–109. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Piehl K. Time course for refilling of glycogen stores in human muscle fibres following exercise-induced glycogen depletion. Acta Physiol Scand. 1974 Feb;90(2):297–302. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1974.tb05592.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ravussin E., Bogardus C. Thermogenic response to insulin and glucose infusions in man: a model to evaluate the different components of the thermic effect of carbohydrate. Life Sci. 1982 Nov 1;31(18):2011–2018. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(82)90040-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ravussin E., Pahud P., Dörner A., Arnaud M. J., Jéquier E. Substrate utilization during prolonged exercise preceded by ingestion of 13C-glucose in glycogen depleted and control subjects. Pflugers Arch. 1979 Nov;382(3):197–202. doi: 10.1007/BF00583702. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rothwell N. J., Stock M. J. A role for brown adipose tissue in diet-induced thermogenesis. Nature. 1979 Sep 6;281(5726):31–35. doi: 10.1038/281031a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rothwell N. J., Stock M. J. A role for insulin in the diet-induced thermogenesis of cafeteria-fed rats. Metabolism. 1981 Jul;30(7):673–678. doi: 10.1016/0026-0495(81)90082-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rowe J. W., Young J. B., Minaker K. L., Stevens A. L., Pallotta J., Landsberg L. Effect of insulin and glucose infusions on sympathetic nervous system activity in normal man. Diabetes. 1981 Mar;30(3):219–225. doi: 10.2337/diab.30.3.219. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thiebaud D., Schutz Y., Acheson K., Jacot E., DeFronzo R. A., Felber J. P., Jequier E. Energy cost of glucose storage in human subjects during glucose-insulin infusions. Am J Physiol. 1983 Mar;244(3):E216–E221. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.1983.244.3.E216. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trayhurn P., James W. P. Thermoregulation and non-shivering thermogenesis in the genetically obese (ob/ob) mouse. Pflugers Arch. 1978 Feb 22;373(2):189–193. doi: 10.1007/BF00584859. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Welle S., Campbell R. G. Stimulation of thermogenesis by carbohydrate overfeeding. Evidence against sympathetic nervous system mediation. J Clin Invest. 1983 Apr;71(4):916–925. doi: 10.1172/JCI110846. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Welle S., Lilavivat U., Campbell R. G. Thermic effect of feeding in man: increased plasma norepinephrine levels following glucose but not protein or fat consumption. Metabolism. 1981 Oct;30(10):953–958. doi: 10.1016/0026-0495(81)90092-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]