Abstract
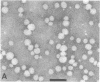
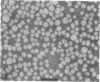
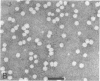
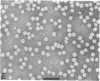
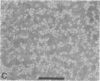
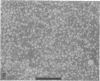
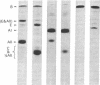
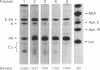
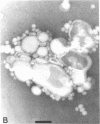
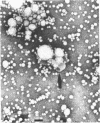
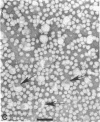
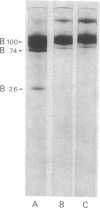
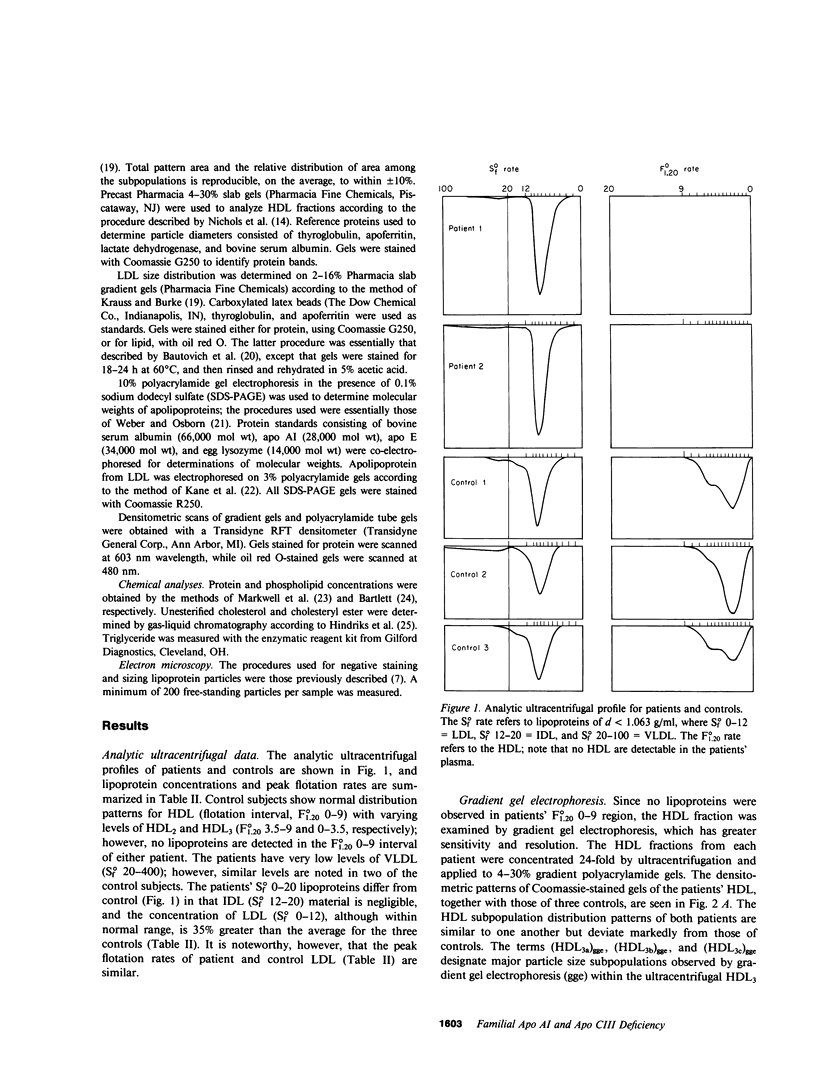
Lipoprotein classes isolated from the plasma of two patients with apolipoprotein AI (apo AI) and apolipoprotein CIII (apo CIII) deficiency were characterized and compared with those of healthy, age- and sex-matched controls. The plasma triglyceride values for patients 1 and 2 were 31 and 51 mg/dl, respectively, and their cholesterol values were 130 and 122 mg/dl, respectively; the patients, however, had no measurable high density lipoprotein (HDL)-cholesterol. Analytic ultracentrifugation showed that patients' S degrees f 0-20 lipoproteins possess a single peak with S degrees f rates of 7.4 and 7.6 for patients 1 and 2, respectively, which is similar to that of the controls. The concentration of low density lipoprotein (LDL) (S degrees f 0-12) particles, although within normal range (331 and 343 mg/dl for patients 1 and 2, respectively), was 35% greater than that of controls. Intermediate density lipoproteins (IDL) and very low density lipoproteins (VLDL) (S degrees f 20-400) were extremely low in the patients. HDL in the patients had a calculated mass of 15.4 and 11.8 mg/dl for patients 1 and 2, respectively. No HDL could be detected by analytic ultracentrifugation, but polyacrylamide gradient gel electrophoresis (gge) revealed that patients possessed two major HDL subclasses: (HDL2b)gge at 11.0 nm and (HDL3b)gge at 7.8 nm. The major peak in the controls, (HDL3a)gge, was lacking in the patients. Gradient gel analysis of LDL indicated that patients' LDL possessed two peaks: a major one at 27 nm and a minor one at 26 nm. The electron microscopic structure of patients' lipoprotein fractions was indistinguishable from controls. Patients' HDL were spherical and contained a cholesteryl ester core, which suggests that lecithin/cholesterol acyltransferase was functional in the absence of apo AI. The effects of postprandial lipemia (100-g fat meal) were studied in patient 1. The major changes were the appearance of a 33-nm particle in the LDL density region of 1.036-1.041 g/ml and the presence of discoidal particles (12% of total particles) in the HDL region. The latter suggests that transformation of discs to spheres may be delayed in the patient. The simultaneous deficiency of apo AI and apo CIII suggests a dual defect in lipoprotein metabolism: one in triglyceride-rich lipoproteins and the other in HDL. The absence of apo CIII may result in accelerated catabolism of triglyceride-rich particles and an increased rate of LDL formation. Additionally, absence of apo CIII would favor rapid uptake of apo E-containing remnants by liver and peripheral cells. Excess cellular cholesterol would not be removed by the reverse cholesterol transport mechanism since HDL levels are exceedingly low and thus premature atherosclerosis occurs.
Full text
PDF

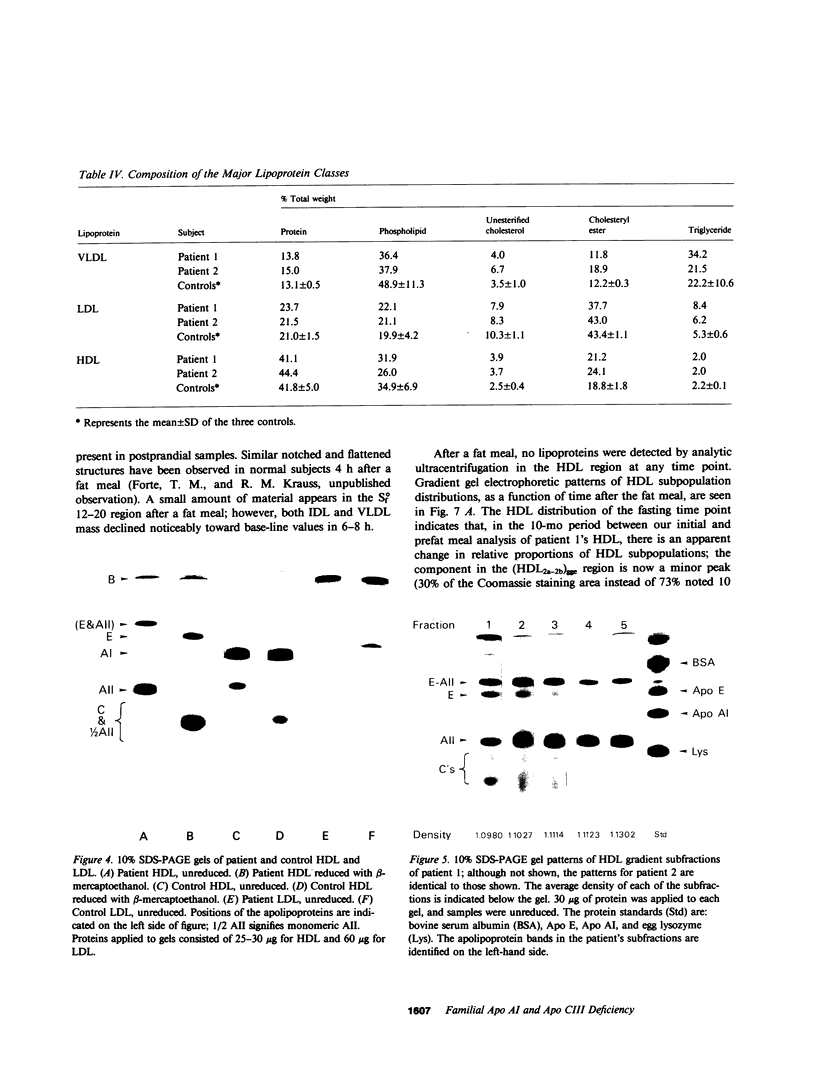
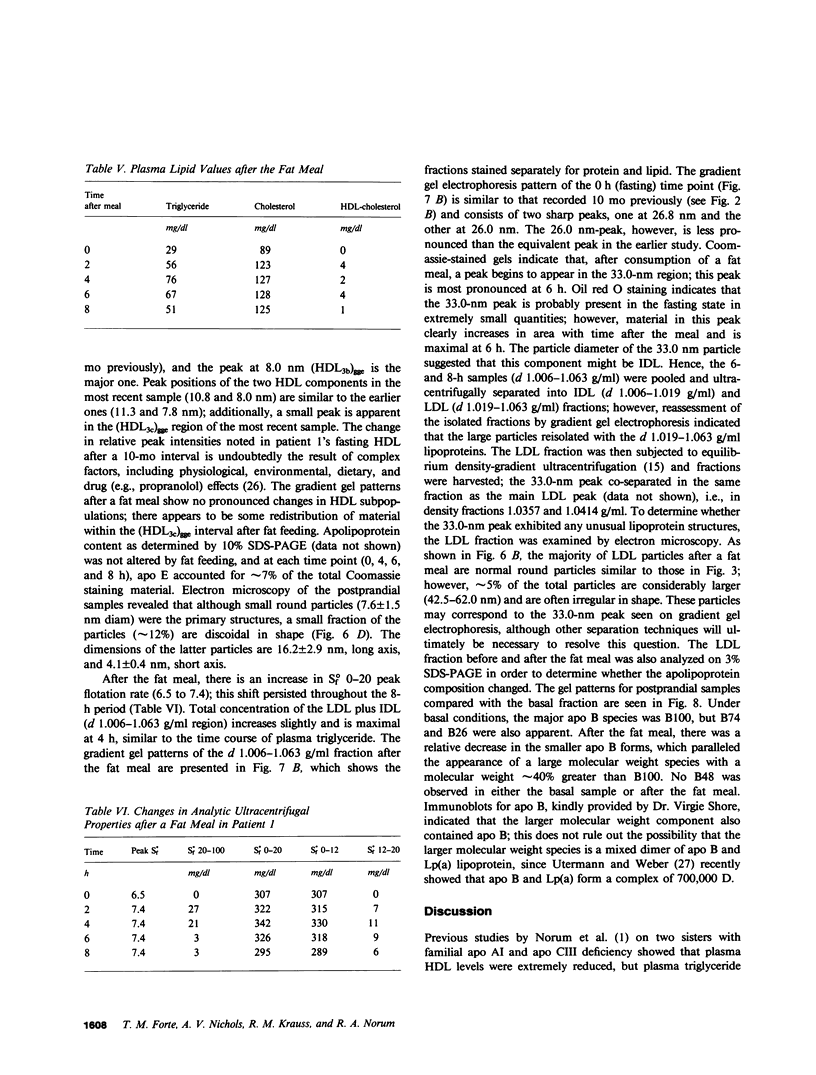
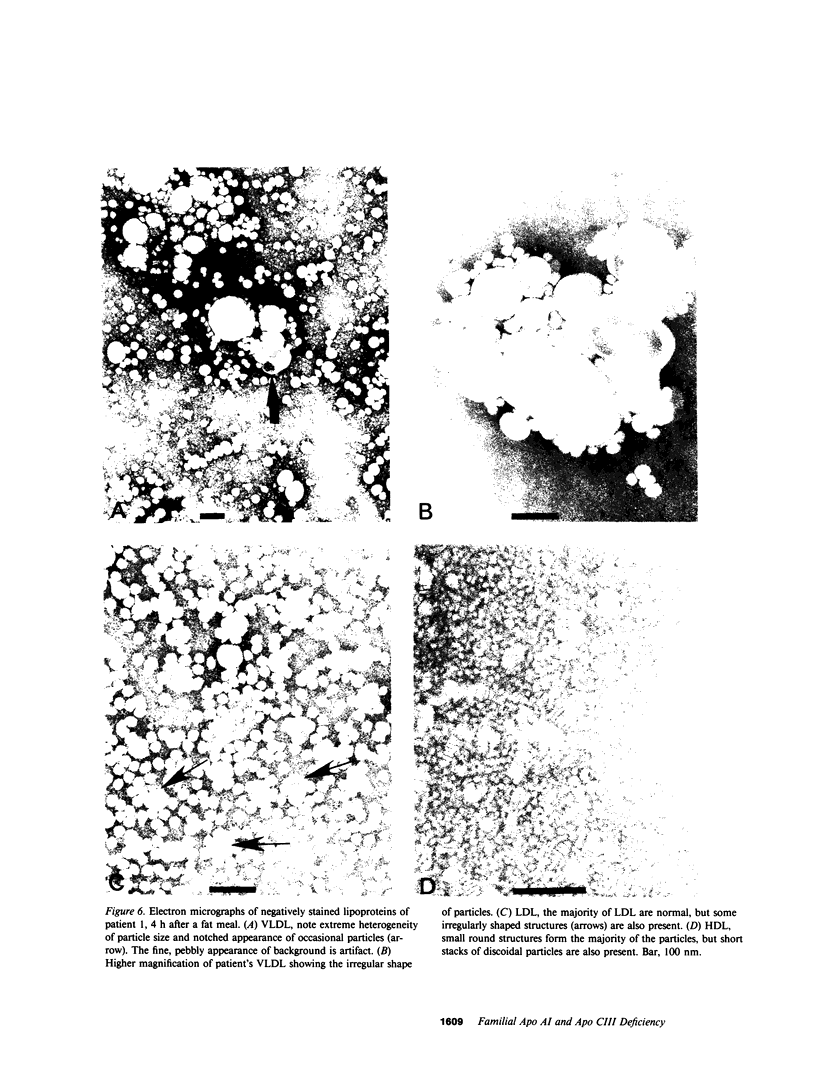
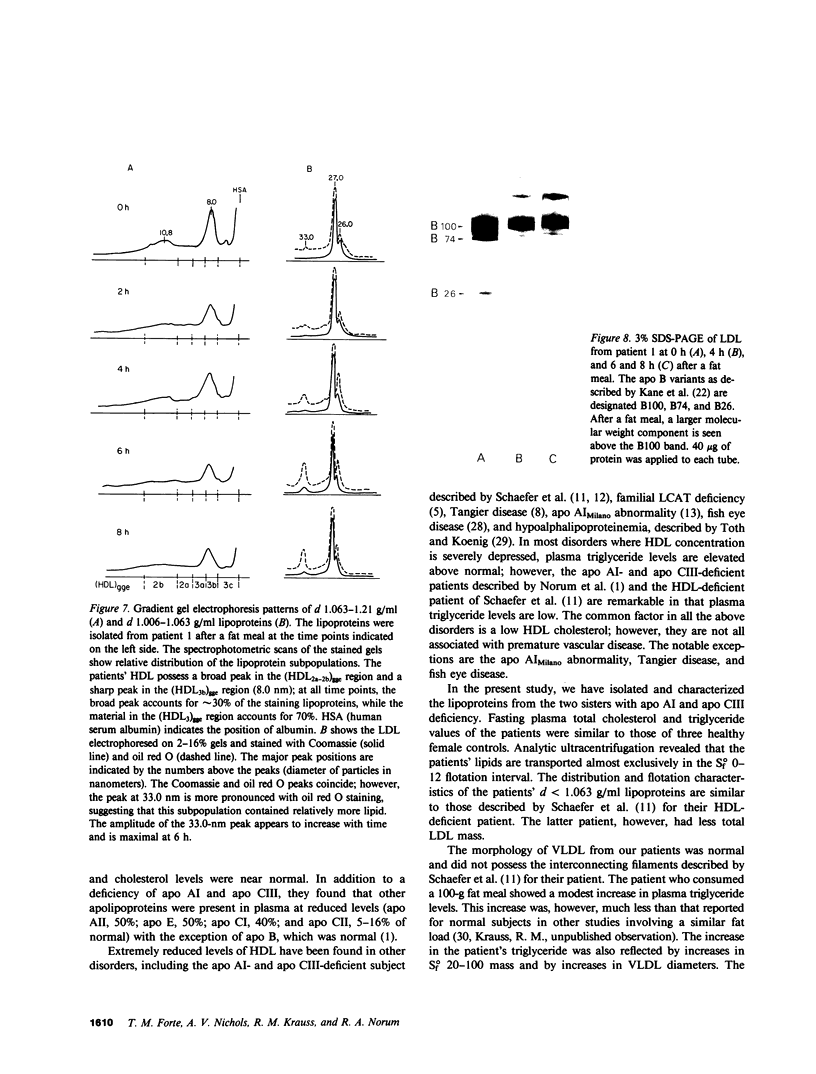



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anderson D. W., Nichols A. V., Forte T. M., Lindgren F. T. Particle distribution of human serum high density lipoproteins. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1977 Jul 22;493(1):55–68. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(77)90259-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Assmann G., Herbert P. N., Fredrickson D. S., Forte T. Isolation and characterization of an abnormal high density lipoprotein in Tangier Diesase. J Clin Invest. 1977 Jul;60(1):242–252. doi: 10.1172/JCI108761. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BARTLETT G. R. Phosphorus assay in column chromatography. J Biol Chem. 1959 Mar;234(3):466–468. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bautovich G. J., Dash M. J., Hensley W. J., Turtle J. R. Gradient gel electrophoresis of human plasma lipoproteins. Clin Chem. 1973 Apr;19(4):415–418. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blanchette-Mackie E. J., Scow R. O. Effects of lipoprotein lipase on the structure of chylomicrons. J Cell Biol. 1973 Sep;58(3):689–708. doi: 10.1083/jcb.58.3.689. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown W. V., Baginsky M. L. Inhibition of lipoprotein lipase by an apoprotein of human very low density lipoprotein. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1972 Jan 31;46(2):375–382. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(72)80149-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carlson L. A. Fish eye disease: a new familial condition with massive corneal opacities and dyslipoproteinaemia. Eur J Clin Invest. 1982 Feb;12(1):41–53. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2362.1982.tb00938.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chajek T., Eisenberg S. Very low density lipoprotein. Metabolism of phospholipids, cholesterol, and apolipoprotein C in the isolated perfused rat heart. J Clin Invest. 1978 Jun;61(6):1654–1665. doi: 10.1172/JCI109086. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheung M. C., Albers J. J. Distribution of cholesterol and apolipoprotein A-I and A-II in human high density lipoprotein subfractions separated by CsCl equilibrium gradient centrifugation: evidence for HDL subpopulations with differing A-I/A-II molar ratios. J Lipid Res. 1979 Feb;20(2):200–207. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis P. A., Forte T. M., Nichols A. V., Blum C. B. Umbilical cord blood lipoproteins. Isolation and characterization of high density lipoproteins. Arteriosclerosis. 1983 Jul-Aug;3(4):357–365. doi: 10.1161/01.atv.3.4.357. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deckelbaum R. J., Eisenberg S., Oschry Y., Cooper M., Blum C. Abnormal high density lipoproteins of abetalipoproteinemia: relevance to normal HDL metabolism. J Lipid Res. 1982 Dec;23(9):1274–1282. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forte T. M., Carlson L. A. Electron microscopic structure of serum lipoproteins from patients with fish eye disease. Arteriosclerosis. 1984 Mar-Apr;4(2):130–137. doi: 10.1161/01.atv.4.2.130. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forte T. M., Krauss R. M., Lindgren F. T., Nichols A. V. Changes in plasma lipoprotein distribution and formation of two unusual particles after heparin-induced lipolysis in hypertriglyceridemic subjects. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Nov;76(11):5934–5938. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.11.5934. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forte T., Norum K. R., Glomset J. A., Nichols A. V. Plasma lipoproteins in familial lecithin: cholesterol acyltransferase deficiency: structure of low and high density lipoproteins as revealed by elctron microscopy. J Clin Invest. 1971 May;50(5):1141–1148. doi: 10.1172/JCI106586. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Franceschini G., Sirtori C. R., Capurso A., 2nd, Weisgraber K. H., Mahley R. W. A-IMilano apoprotein. Decreased high density lipoprotein cholesterol levels with significant lipoprotein modifications and without clinical atherosclerosis in an Italian family. J Clin Invest. 1980 Nov;66(5):892–900. doi: 10.1172/JCI109956. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glomset J. A., Applegate K., Forte T., King W. C., Mitchell C. D., Norum K. R., Gjone E. Abnormalities in lipoproteins of d < 1.006 g/ml in familial lecithin:cholesterol acyltransferase deficiency. J Lipid Res. 1980 Nov;21(8):1116–1127. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glomset J. A., Norum K. R. The metabolic role of lecithin: cholesterol acyltransferase: perspectives form pathology. Adv Lipid Res. 1973;11:1–65. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heinen R. J., Herbert P. N., Fredrickson D. S. Properties of the plasma very low and low density lipoproteins in Tangier disease. J Clin Invest. 1978 Jan;61(1):120–132. doi: 10.1172/JCI108910. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hindriks F. R., Wolthers B. G., Groen A. The determination of total cholesterol in serum by gas-liquid chromatography compared with two other methods. Clin Chim Acta. 1977 Feb 1;74(3):207–215. doi: 10.1016/0009-8981(77)90287-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Innerarity T. L., Mahley R. W., Weisgraber K. H., Bersot T. P. Apoprotein (E--A-II) complex of human plasma lipoproteins. II. Receptor binding activity of a high density lipoprotein subfraction modulated by the apo(E--A-II) complex. J Biol Chem. 1978 Sep 10;253(17):6289–6295. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kane J. P., Hardman D. A., Paulus H. E. Heterogeneity of apolipoprotein B: isolation of a new species from human chylomicrons. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 May;77(5):2465–2469. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.5.2465. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karathanasis S. K., McPherson J., Zannis V. I., Breslow J. L. Linkage of human apolipoproteins A-I and C-III genes. 1983 Jul 28-Aug 3Nature. 304(5924):371–373. doi: 10.1038/304371a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karathanasis S. K., Norum R. A., Zannis V. I., Breslow J. L. An inherited polymorphism in the human apolipoprotein A-I gene locus related to the development of atherosclerosis. Nature. 1983 Feb 24;301(5902):718–720. doi: 10.1038/301718a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krauss R. M., Burke D. J. Identification of multiple subclasses of plasma low density lipoproteins in normal humans. J Lipid Res. 1982 Jan;23(1):97–104. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krauss R. M., Lindgren F. T., Ray R. M. Interrelationships among subgroups of serum lipoproteins in normal human subjects. Clin Chim Acta. 1980 Jul 1;104(3):275–290. doi: 10.1016/0009-8981(80)90385-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krauss R. M. Regulation of high density lipoprotein levels. Med Clin North Am. 1982 Mar;66(2):403–430. doi: 10.1016/s0025-7125(16)31427-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Markwell M. A., Haas S. M., Bieber L. L., Tolbert N. E. A modification of the Lowry procedure to simplify protein determination in membrane and lipoprotein samples. Anal Biochem. 1978 Jun 15;87(1):206–210. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(78)90586-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Norum R. A., Lakier J. B., Goldstein S., Angel A., Goldberg R. B., Block W. D., Noffze D. K., Dolphin P. J., Edelglass J., Bogorad D. D. Familial deficiency of apolipoproteins A-I and C-III and precocious coronary-artery disease. N Engl J Med. 1982 Jun 24;306(25):1513–1519. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198206243062503. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patsch J. R., Karlin J. B., Scott L. W., Smith L. C., Gotto A. M., Jr Inverse relationship between blood levels of high density lipoprotein subfraction 2 and magnitude of postprandial lipemia. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Mar;80(5):1449–1453. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.5.1449. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schaefer E. J. Clinical, biochemical, and genetic features in familial disorders of high density lipoprotein deficiency. Arteriosclerosis. 1984 Jul-Aug;4(4):303–322. doi: 10.1161/01.atv.4.4.303. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schaefer E. J., Heaton W. H., Wetzel M. G., Brewer H. B., Jr Plasma apolipoprotein A-1 absence associated with a marked reduction of high density lipoproteins and premature coronary artery disease. Arteriosclerosis. 1982 Jan-Feb;2(1):16–26. doi: 10.1161/01.atv.2.1.16. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmitz G., Assmann G. Isolation of human serum HDL1 by zonal ultracentrifugation. J Lipid Res. 1982 Aug;23(6):903–910. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
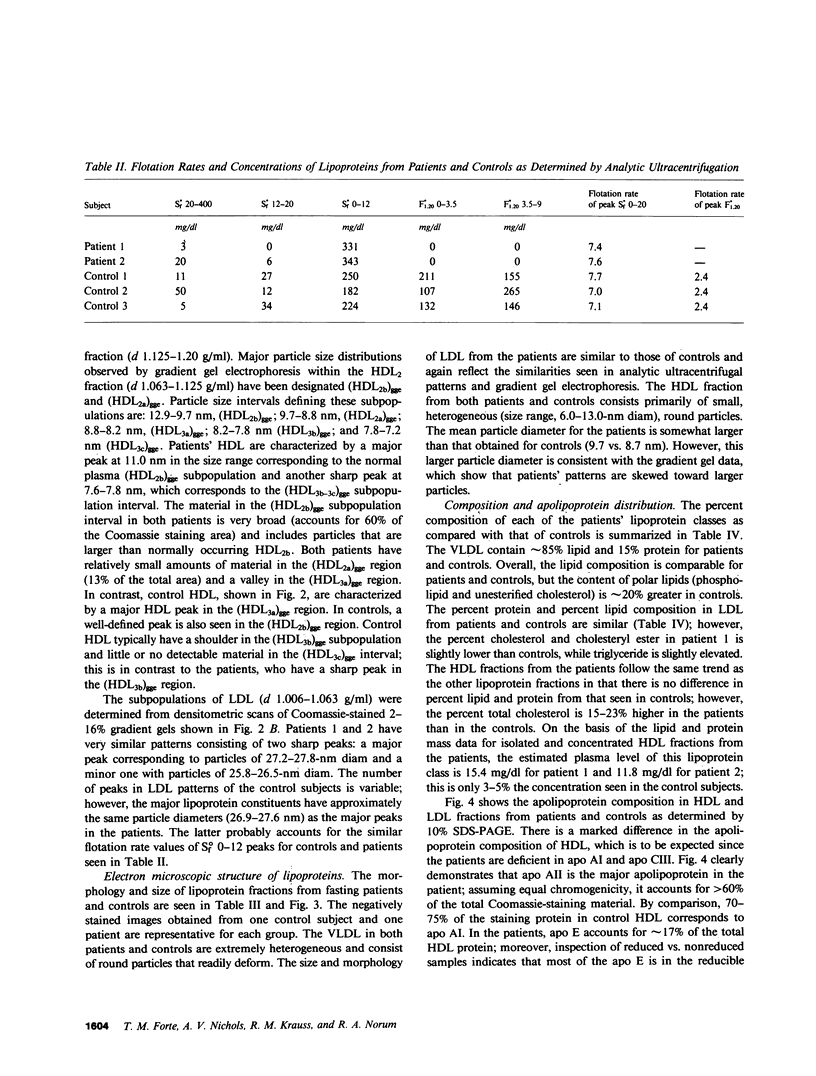
- Shelburne F., Hanks J., Meyers W., Quarfordt S. Effect of apoproteins on hepatic uptake of triglyceride emulsions in the rat. J Clin Invest. 1980 Mar;65(3):652–658. doi: 10.1172/JCI109710. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shen M. M., Krauss R. M., Lindgren F. T., Forte T. M. Heterogeneity of serum low density lipoproteins in normal human subjects. J Lipid Res. 1981 Feb;22(2):236–244. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Soutar A. K., Garner C. W., Baker H. N., Sparrow J. T., Jackson R. L., Gotto A. M., Smith L. C. Effect of the human plasma apolipoproteins and phosphatidylcholine acyl donor on the activity of lecithin: cholesterol acyltransferase. Biochemistry. 1975 Jul 15;14(14):3057–3064. doi: 10.1021/bi00685a003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Soutar A. K., Knight B. L., Myant N. B. The characterization of lipoproteins in the high density fraction obtained from patients with familial lecithin:cholesterol acyltransferase deficiency and their interaction with cultured human fibroblasts. J Lipid Res. 1982 Mar;23(3):380–390. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tall A. R., Small D. M. Body cholesterol removal: role of plasma high-density lipoproteins. Adv Lipid Res. 1980;17:1–51. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Toth L., Koenig W. Hypoalpha-hyperbeta-lipoproteinemia in a patient with coronary artery disease and occlusive peripheral arterial disease. Atherosclerosis. 1982 Mar;42(1):121–124. doi: 10.1016/0021-9150(82)90132-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Utermann G., Weber W. Protein composition of Lp(a) lipoprotein from human plasma. FEBS Lett. 1983 Apr 18;154(2):357–361. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(83)80182-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weber K., Osborn M. The reliability of molecular weight determinations by dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. J Biol Chem. 1969 Aug 25;244(16):4406–4412. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weisgraber K. H., Mahley R. W. Subfractionation of human high density lipoproteins by heparin-Sepharose affinity chromatography. J Lipid Res. 1980 Mar;21(3):316–325. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Windler E., Chao Y., Havel R. J. Regulation of the hepatic uptake of triglyceride-rich lipoproteins in the rat. Opposing effects of homologous apolipoprotein E and individual C apoproteins. J Biol Chem. 1980 Sep 10;255(17):8303–8307. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]