Abstract
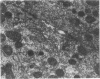
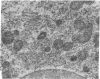
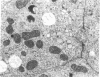
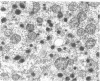
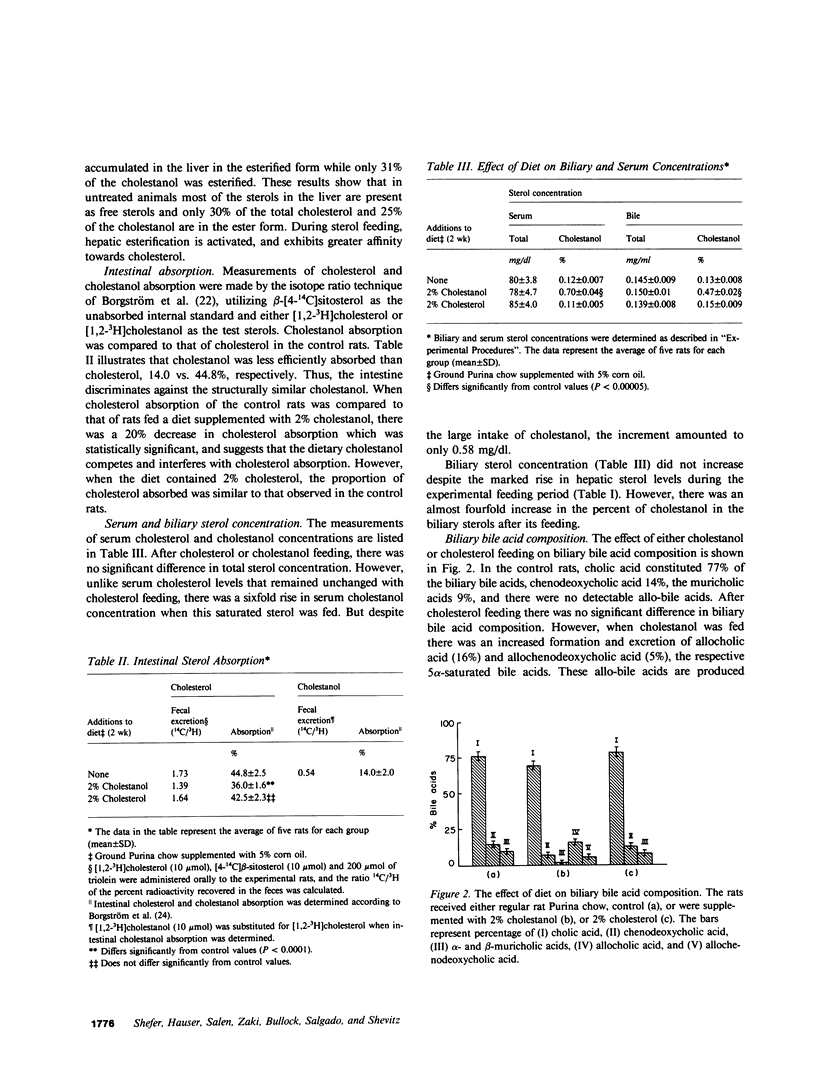
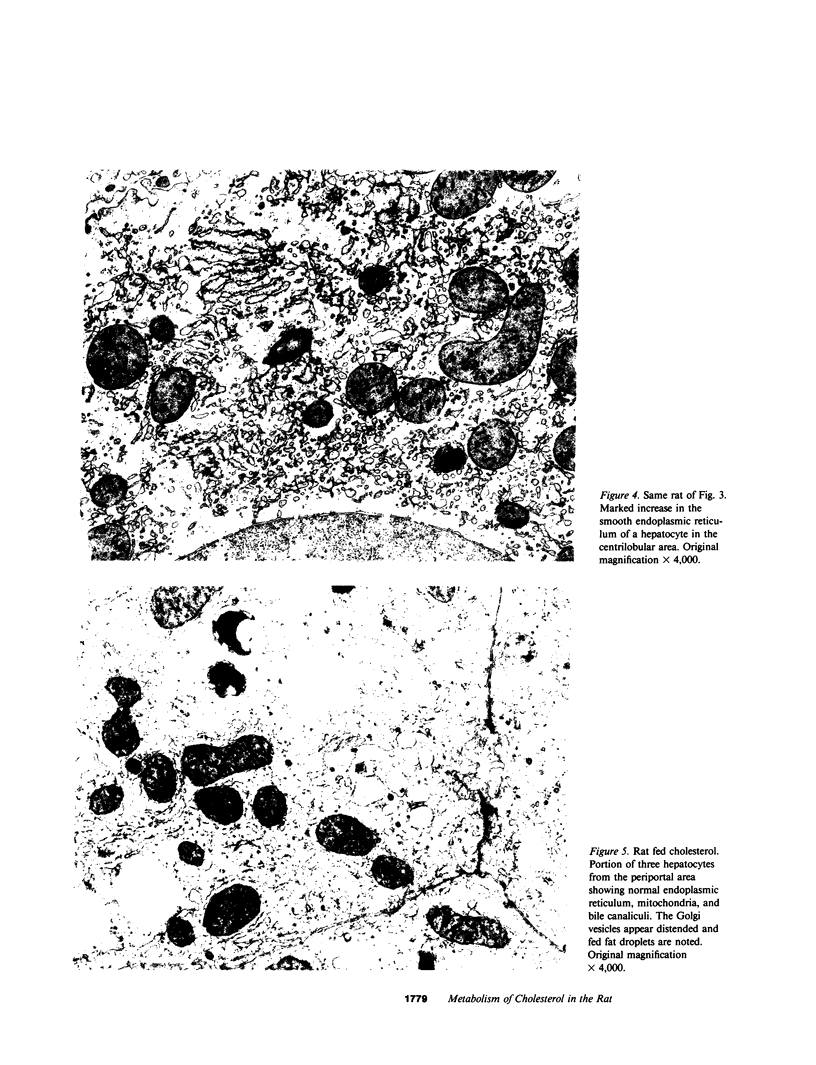
Large amounts of cholestanol, the 5 alpha-dihydro derivative of cholesterol are found in tissues of patients with the rare inherited sterol storage disease cerebrotendinous xanthomatosis. Although small amounts of cholestanol are present in virtually every tissue of normal man, little is known about its metabolism and effect on cholesterol and bile acid formation. The purpose of this study is to investigate the absorption and metabolism of cholestanol and its early effects on hepatic morphology and on the rate-limiting enzymes of cholesterol and bile acid biosynthesis. After 2 wk on a diet supplemented with 2% cholestanol, total liver sterol content increased by 48% (3.26 vs. 2.20 mg/g), and resulted in a significant rise in hepatic cholestanol concentration to 1.4 mg/g. However, cholestanol was less efficiently absorbed from the intestine than cholesterol and interfered with cholesterol absorption. Furthermore, hepatic hydroxymethylglutaryl-coenzyme A (HMG-CoA) reductase activity rose 2.6-fold (from 150.3 to 397.0 pmol/mg per min) during cholestanol feeding, and was associated with a marked proliferation of the smooth endoplasmic reticulum of the centrilobular areas. In addition, significant amounts of allocholic acid (16%) and allochenodeoxycholic acid (5%) were formed from cholestanol and excreted in the bile. These results show that cholestanol is absorbed from the intestine, interferes with cholesterol absorption, and is deposited in the liver. However, in contrast to cholesterol, cholestanol feeding was associated with a marked elevation of HMG-CoA reductase activity. Thus, despite structural similarity between cholesterol and its 5 alpha-saturated derivative, cholestanol does not exert feedback inhibition on hepatic cholesterol biosynthesis.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Björkhem I., Gustafsson J. On the conversion of cholestanol into allocholic acid in rat liver. Eur J Biochem. 1971 Jan;18(2):207–213. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1971.tb01232.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Borgström B. Quantitative aspects of the intestinal absorption and metabolism of cholesterol and beta-sitosterol in the rat. J Lipid Res. 1968 Jul;9(4):473–481. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Danielsson H. Relationship between diurnal variations in biosynthesis of cholesterol and bile acids. Steroids. 1972 Jul;20(1):63–72. doi: 10.1016/0039-128x(72)90118-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Souza N. J., Nes W. R. Improved separation of sterols by reversed-phase thin-layer chromatography. J Lipid Res. 1969 Mar;10(2):240–243. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GRUNDY S. M., AHRENS E. H., Jr, MIETTINEN T. A. QUANTITATIVE ISOLATION AND GAS--LIQUID CHROMATOGRAPHIC ANALYSIS OF TOTAL FECAL BILE ACIDS. J Lipid Res. 1965 Jul;6:397–410. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HSIA S. L., MATSCHINER J. T., MAHOWALD T. A., ELLIOTT W. H., DOISY E. A., Jr, THAYER S. A., DOISY E. A. Bile acids. V. Chemical studies on new bile acids from the rat and the hog. J Biol Chem. 1957 Apr;225(2):811–823. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HSLA S. L., MATSCHINER J. T., MAHOWALD T. A., ELLIOTT W. H., DOISY E. A., Jr, THAYER S. A., DOISY E. A. Bile acids. VI. The structure and synthesis of acid II. J Biol Chem. 1957 Jun;226(2):667–671. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LUFT J. H. Improvements in epoxy resin embedding methods. J Biophys Biochem Cytol. 1961 Feb;9:409–414. doi: 10.1083/jcb.9.2.409. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nervi F. O., Dietschy J. M. The mechanisms of and the interrelationship between bile acid and chylomicron-mediated regulation of hepatic cholesterol synthesis in the liver of the rat. J Clin Invest. 1978 Apr;61(4):895–909. doi: 10.1172/JCI109015. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nicolau G., Shefer S., Salen G., Mosbach E. H. Determination of hepatic 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl CoA reductase activity in man. J Lipid Res. 1974 Jan;15(1):94–98. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parmentier G. G., Janssen G. A., Eggermont E. A., Eyssen H. J. C27 bile acids in infants with coprostanic acidemia and occurrence of a 3 alpha,7 alpha,12 alpha-tridhydroxy-5 beta-C29 dicarboxylic bile acid as a major component in their serum. Eur J Biochem. 1979 Dec;102(1):173–183. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1979.tb06278.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- REYNOLDS E. S. The use of lead citrate at high pH as an electron-opaque stain in electron microscopy. J Cell Biol. 1963 Apr;17:208–212. doi: 10.1083/jcb.17.1.208. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SHEFER S., MILCH S., MOSBACH E. H. BIOSYNTHESIS OF 5-ALPHA-CHOLESTAN-3-BETA-OL IN THE RABBIT AND GUINEA PIG. J Biol Chem. 1964 Jun;239:1731–1736. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salen G., Grundy S. M. The metabolism of cholestanol, cholesterol, and bile acids in cerebrotendinous xanthomatosis. J Clin Invest. 1973 Nov;52(11):2822–2835. doi: 10.1172/JCI107478. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmitz F. J., McDonald F. J. Determination of hepatic cholesterol 7alpha-hydroxylase activity in man. J Lipid Res. 1974 Mar;15(2):146–151. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shapiro D. J., Rodwell V. W. Regulation of hepatic 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl coenzyme A reductase and cholesterol synthesis. J Biol Chem. 1971 May 25;246(10):3210–3216. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shefer S., Cheng F. W., Hauser S., Batta A. K., Salen G. Regulation of bile acid synthesis. Measurement of cholesterol 7 alpha-hydroxylase activity in rat liver microsomal preparations in the absence of endogenous cholesterol. J Lipid Res. 1981 Mar;22(3):532–536. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shefer S., Hauser S., Lapar V., Mosbach E. H. Regulatory effects of sterols and bile acids on hepatic 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl CoA reductase and cholesterol 7alpha-hydroxylase in the rat. J Lipid Res. 1973 Sep;14(5):573–580. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shefer S., Hauser S., Mosbach E. H. 7-alpha-hydroxylation of cholestanol by rat liver microsomes. J Lipid Res. 1968 May;9(3):328–333. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shefer S., Salen G., Hauser S., Dayal B., Batta A. K. Metabolism of iso-bile acids in the rat. J Biol Chem. 1982 Feb 10;257(3):1401–1406. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shefer S., Zaki F. G., Salen G. Early morphologic and enzymatic changes in livers of rats treated with chenodeoxycholic and ursodeoxycholic acids. Hepatology. 1983 Mar-Apr;3(2):201–208. doi: 10.1002/hep.1840030212. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tint G. S., Dayal B., Batta A. K., Shefer S., Cheng F. W., Salen G., Mosbach E. H. Gas-liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry of trimethylsilyl ethers of bile alcohols. J Lipid Res. 1978 Nov;19(8):956–966. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WERBIN H., CHAIKOFF I. L., IMADA M. R. 5alpha Cholestan-3beta-ol: its distribution in tissues and its synthesis from cholesterol in the guinea pig. J Biol Chem. 1962 Jul;237:2072–2077. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ziller S. A., Jr, Doisy E. A., Jr, Elliott W. H. Bile acids. XXV. Allochenodeoxycholic acid, a metabolite of 5 alpha-cholestan-3 beta-ol in the hyperthyroid rat. J Biol Chem. 1968 Oct 25;243(20):5280–5288. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]